Umkomasia
| Umkomasia Temporal range: | |
|---|---|

| |
| Umkomasia macleanii ovulate structure, Late Triassic, Molteno Formation, Umkomaas, South Africa. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Order: | †Corystospermales |
| Family: | †Corystospermaceae |
| Genus: | †Umkomasia Thomas 1933 |
| Species | |
| |
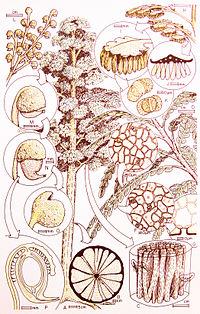
Umkomasia is a genus of seed bearing organs produced by corystosperm seed ferns, first based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa.[3] He recognized on the basis of cuticular similarities that the same plant produced pollen organs Pteruchus and the leaves Dicroidium. Various other corystosperm seed bearing organs from the Jurassic and Cretaceous have been assigned to this genus, but recently have been given distinct genera, with Umkomasia being restricted to the Triassic.[4]
Description
Umkomasia has helmet like cupules around ovules born in complex large branching structures.
Whole plant associations
- Umkomasia feistmantelii from the Early Triassic of Australia may have been produced by the same plant as Pteruchus barrealensis (pollen organs) and Dicroidium zuberi (leaves)[5]
- Umkomasia macleanii from the Late Triassic of South Africa may have been produced by the same plant as Pteruchus africanus (pollen organs) and Dicroidium odontopteroides (leaves)[3][6]
Reassigned species
- U. franconica Lower Jurassic, Germany, reassigned to the genus Kirchmuellia
- U. asiatica Triassic, China reassigned to the genus Stenorachis
- U. mongolica Lower Cretaceous, Mongolia, moved to the genus Doylea.
See also
References
- ^ Gongle Shi; Andrew B. Leslie; Patrick S. Herendeen; Fabiany Herrera; Niiden Ichinnorov; Masamichi Takahashi; Patrick Knopf & Peter R. Crane (2016). "Early Cretaceous Umkomasia from Mongolia: implications for homology of corystosperm cupules". New Phytologist. 210 (4): 1418–1429. doi:10.1111/nph.13871. PMID 26840646.
- ^ However, Rothwell & Stockey (2016) transferred this species to the genus Doylea. See: Gar W. Rothwell; Ruth A. Stockey (2016). "Phylogenetic diversification of Early Cretaceous seed plants: The compound seed cone of Doylea tetrahedrasperma". American Journal of Botany. 103 (5): 923–937. doi:10.3732/ajb.1600030. PMID 27208360.
- ^ a b Thomas, H.H. (1933). "On some pteridospermous plants from the Mesozoic rocks of South Africa". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 222 (483–493): 193–265. doi:10.1098/rstb.1932.0016.
- ^ Anderson, Heidi M.; Barbacka, Maria K.; Bamford, Marion K.; Holmes, W. B. Keith; Anderson, John M. (2019-01-02). "Umkomasia (megasporophyll): part 1 of a reassessment of Gondwana Triassic plant genera and a reclassification of some previously attributed". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 43 (1): 43–70. doi:10.1080/03115518.2018.1554748. ISSN 0311-5518. S2CID 134483119.
- ^ Retallack G.J. (1977). "Reconstructing Triassic vegetation of southeastern Australia: a new approach to the biostratigraphy of Gondwanaland". Alcheringa. 1: 247–265. doi:10.1080/03115517708527763.
- ^ Retallack, G.J. & Dilcher, D.L. (1988). "Reconstructions of selected seed ferns". Missouri Botanical Garden Annals. 75 (3): 1010–1057. doi:10.2307/2399379. JSTOR 2399379.
External links
- "Fossilworks: Lepidopteris". paleodb.org. Retrieved 2016-03-18.
