Tropical Storm Aere (2016)
 Severe Tropical Storm Aere near peak intensity on October 7 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | October 4, 2016 |
| Remnant low | October 10, and re-generated on October 13 |
| Dissipated | October 14, 2016 |
| Severe tropical storm | |
| 10-minute sustained (JMA) | |
| Highest winds | 110 km/h (70 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 975 hPa (mbar); 28.79 inHg |
| Tropical storm | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/JTWC) | |
| Highest winds | 100 km/h (65 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 985 hPa (mbar); 29.09 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 37 total |
| Damage | $209 million (2016 USD) |
| Areas affected | Philippines, Taiwan, South China, Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 2016 Pacific typhoon season | |
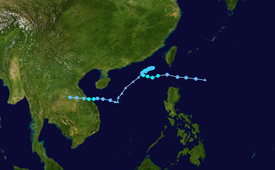
Severe Tropical Storm Aere, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Julian, was a long-lived tropical cyclone that struck Central Vietnam in October 2016. The nineteenth named storm of the annual typhoon season, Aere formed on October 4, 2016 as a tropical depression to the east of Luzon, Philippines shortly after the JMA had started tracking Songda. On the next day, the system had become a tropical storm and it moved into South China Sea. During October 7, it intensified into a severe tropical storm and reached peak intensity with 10-minute winds of 110 km/h (70 mph). Shortly thereafter, due to remaining in almost the same area for hours, Aere began to weaken to a tropical storm, and on October 10, it weakened to a tropical depression, before weakening to a low-pressure area late on October 11. On October 13, Aere re-generated into a tropical depression and it made landfall in Huế, Vietnam late that day. The system moved towards Laos and Thailand before it fully dissipated on October 14.
Aere affected parts of Southeast Asia in October 2016, but its impact was most severe in Vietnam. Heavy flooding triggered by the remnants of Aere from October 13 to October 17, 2016 in North-Central Vietnam caused severe damage. A total of 7 people were killed and total damage reached US$209 million. The remnants of Aere also caused heavy rains in northeast Thailand.
Meteorological history
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
At the start of October 2016, a broad area of atmospheric convection persisted, to the east-southeast of Anderson Air Force Base on Guam.[1] The system was located within a favourable environment for further development, with low vertical wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures.[1] Over the next couple of days the system moved north-westwards and started to consolidate, as it developed a low level circulation centre. It was subsequently classified as a tropical depression during October 4, by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), while it was located about 1,000 km (620 mi) to the northeast of Manila in the Philippines,[2] to the east to the Babuyan Group of Islands.[3][4] Later that day, PAGASA had named the system Julian.[5] The JTWC started issuing advisories on the system while it moved westward during October 5, with the designation of 22W.[6] Despite Julian having a disorganised structure while crossing the Luzon Strait, the system was located in an area of light to moderate wind shear and very warm sea surface temperatures.[7] After satellite imagery had depicted a significant increase of convection, all agencies upgraded Julian to a tropical storm, with the JMA naming it as Aere.[8][9][10][11] Hours later, when Aere had emerged to the extreme northern part of the South China Sea, Aere reached peak intensity with 10-minute winds of 110 km/h (70 mph), just shy of typhoon strength, after it remained nearly stationary between two subtropical ridges.[12][13] Shortly thereafter, due to remaining in almost the same area for hours, Aere began to weaken and the JMA downgraded it to a tropical storm.[14][15] By October 10, Aere's LLCC became exposed due to southwesterly wind shear and both the JMA and JTWC issued their final advisory three hours later.[16][17] The JMA tracked its remnants as it moved southwestward until it weakened to a low-pressure area late on October 11.[18]
Later, the low-pressure area moved southwestward on October 12,[19] until the well-marked low pressure area of Aere re-generated into a tropical depression early on October 13.[20][21] The JMA started to tracked the tropical depression[22] and the JTWC re-issued advisories too.[23] Now moving westward, Aere had flaring convection with weak banding and was located in an area of high SSTs and low wind shear.[24] Although the system had failed to re-organize into a weak tropical storm, the JTWC issued its final advisory and shortly thereafter it made landfall several kilometers north of Da Nang, Vietnam.[25] The remnants of Aere was tracked by the JMA as a weak tropical depression on October 14.[26] It moved towards Laos and Thailand[27] until it fully dissipated later that day.[26]
Prepations and impact
Vietnam

Aere was known in Vietnam as Cơn bão số 6 (the 6th storm in 2016).[28] After Aere re-generated into a tropical depression on October 13, it made landfall in Huế, Central Vietnam, peaked gust at category 9 (Beaufort scale).[29] It caused very heavy rainfall in North–Central Vietnam,[29][30] with accumulations of about 300–900 mm (1–3 ft) recorded in coastal provinces,[31] peaked heavy rainfall at 747 mm (29.4 in) in Đồng Hới, the record since 1955.[32] Heavy rains from the remnants of Aere and the northeast monsoon caused flooding in North–Central Vietnam from October 13 to October 17, . A total of 37 people were killed, mostly in Quảng Bình with 22 people.[33][34] Total damage estimated for transport works were at 130 billion ₫(US$5.83 million).[35] In Quảng Bình Province, 93 thousand houses, two thousand crops and 600 hectares of annual food-fields were destroyed.[34][36] In Hà Tĩnh, 3,200 hectares of agricultural land were destroyed and a total of 175 thousand cattle and poultry were dead; total damages reached at ₫994 billion (US$44.6 million). In Nghệ An, more than 8,200 houses and 9.700ha rice and vegetables fields were flooded, total damages estimated at ₫468 billion (US$21 million).[37] Total damages from the flooding reached ₫4.6 trillion (US$209 million).[33] Some say that North–Central Vietnam had its worst flooding since 2010.[32]
Other areas

During October 6, the Stand By Signal No.1 was hoisted for the Chinese territories of Hong Kong by the Hong Kong Observatory.[38] When Aere moved westward to South China Sea on October 6[39] and became almost stationary on October 8,[12] it brought heavy rains in Guangdong and Southeast China.[40] On October 13, when Aere were re-generated over the east coast of Vietnam, the Thai Meteorological Department issued widespread rain forecast for east side of provinces.[41] The remnants of Aere moved into Laos and Thailand on October 14. It caused heavy rains in the east side of northeastern provinces of Thailand from October 14 to October 16.[27]
Aftermath
On October 18, the Vietnam Red Cross allocated relief assistance of goods, total cost at ₫1.97 billion (US$88,300) for 4 provinces in flooded areas.[42] On October 20, The National Assembly of Vietnam and President of Vietnam supported relief assistance for north–central flooded provinces.[43][44]
See also
- Weather of 2016
- Tropical cyclones in 2016
- Typhoon Cimaron (2006)
- Tropical Depression 18W (2013)
- Typhoon Krosa (2013)
- Tropical Storm Vamco (2015)
- October 2017 Vietnam tropical depression
- Tropical Storm Son-Tinh (2018)
References
- ^ a b "Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans October 2, 2016 06z". United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 2, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Tropical Storm Aere" (RSMC Tropical Cyclone Best Track). Japan Meteorological Agency. November 22, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ "WebCite query result". webcitation.org. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "WebCite query result". webcitation.org. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #1: Tropical Depression "JULIAN"". PAGASA. October 4, 2016. Archived from the original on October 6, 2016.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 22W (Twenty-two) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 5, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 22W (Twenty-two) Warning Nr 02". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 5, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 05". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 6, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "TS 1619 AERE (1619) UPGRADED FROM TD". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 5, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 07". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 7, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "STS 1619 AERE (1619) UPGRADED FROM TS". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 7, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ a b "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 09". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 7, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "STS 1619 AERE (1619)". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 7, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Trm iopical Storm 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 11". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 8, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "TS 1619 AERE (1619) DOWNGRADED FROM STS". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 8, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 019". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 10, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "TD DOWNGRADED FROM TS 1619 AERE (1619)". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 10, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "WebCite query result". webcitation.org. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Archived copy". tgftp.nws.noaa.gov. Archived from the original on 26 November 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Xuất hiện áp thấp nhiệt đới trên Biển Đông". 13 October 2016. Archived from the original on 27 November 2016. Retrieved 26 November 2016.
- ^ "WebCite query result". webcitation.org. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Marine Weather Warning for GMDSS Metarea XI 2016-10-13T00:00:00Z « WIS Portal – GISC Tokyo". www.wis-jma.go.jp. Archived from the original on 26 November 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 20". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 13, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 21". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 13, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 22W (Aere) Warning Nr 022". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 13, 2016. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024.
- ^ a b "WebCite query result". webcitation.org. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ a b "Thai Meteorological Department - Waring". Archived from the original on November 13, 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Bão số 6 - AERE giật cấp 13 quần thảo biển Đông". vietnamnet.vn. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ a b "áp thấp nhiệt đới đã đi vào đất liền tỉnh Thừa Thiên Huế". vov.vn. 14 October 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Mưa lũ miền Trung, nhà ngập tận nóc - Xã hội - Báo điện tử Tiền Phong". tienphong.vn. 15 October 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Vietnam Braces for Typhoon Sarika After Deadly Flooding". Wall Street Journal. October 15, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2016.
- ^ a b "Mưa ở Quảng Bình là 'kỷ lục chưa từng có' - VnExpress". vnexpress.net. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ a b 2016 VIETNAM REPORT
- ^ a b "35 người chết, 4 người mất tích do mưa lũ - VnExpress". vnexpress.net. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Đường bộ thiệt hại 130 tỷ đồng do mưa lũ". GIAO THÔNG PHÁT TRIỂN. October 17, 2016. Archived from the original on October 18, 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Quảng Bình thiệt hại quá nặng nề do mưa lũ". dantri.com.vn. 16 October 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Hà Tĩnh Nghệ An thiệt hại gần 1500 tỷ đồng do mưa lũ". vov.vn. 19 October 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Typhoon No 1 standby signal issued for Hong Kong - South China Morning Post". scmp.com. 6 October 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Bão Aere vào Biển Đông, gió giật cấp 10". 6 October 2016.
- ^ "Typhoon Aere to bring rainstorm to south China - Xinhua | English.news.cn". news.xinhuanet.com. Archived from the original on 2016-10-08.
- ^ "Thai Meteorological Department - Waring". www.tmd.go.th. Archived from the original on 24 November 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "Cả nước chung tay hỗ trợ miền Trung - VnExpress". vnexpress.net. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Văn phòng Chủ tịch nước quyên góp ủng hộ đồng bào miền Trung". vov.vn. 18 October 2016. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
- ^ "Báo Nhân Dân - Phiên bản tiếng Việt - Tiếp tục ủng hộ đồng bào miền trung". nhandan.com.vn. Retrieved November 13, 2016.
External links
- JMA General Information of Severe Tropical Storm Aere (1619) from Digital Typhoon
- JMA Best Track Data of Severe Tropical Storm Aere (1619) (in Japanese)
- 22W.AERE from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory