Tramways in Adelaide
| Tramways in Adelaide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 In December 2009, one of Adelaide's 1929-vintage "Glenelg" or "Bay" trams, no. 367, was at the Glengowrie depot with two newcomers: Flexity Classic no. 104 and Alstom Citadis no. 203. No. 367 was one of the last two trams of its type to run in Adelaide, in February 2015. Many were dispersed to museums around Australia – especially South Australia's Tramway Museum, St Kilda – and overseas. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Adelaide, South Australia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Adelaide tramways network served much of the inner suburbs and several outer suburbs of Adelaide, Australia, from 1878 until soon after World War II, when it started to decline. The sole Glenelg light rail line, which was the only route to survive the closures, did however remain in operation. After falling into a state of disrepair and neglect, in the 2000s the line underwent major civil engineering upgrades and, progressively, 5.5 kilometres (3.4 miles) of route extensions; and received a new tram fleet.[1]
about trams in Adelaide
The article you are reading is an overview article about tramways in South Australia's capital city. Other articles are:
- Tram types in Adelaide (1878–)
- The horse trams era (1878–1914)
- Glenelg ("South Terrace") line (1873–)
- Municipal Tramways Trust (1907–1975); includes the electric street network (1909–1958)
- W.G.T. Goodman, General Manager MTT (1907–1950)
- State Transport Authority (1975–1994)
- TransAdelaide (1994–2010), branded as Adelaide Metro from 2000
- Tramways revival in Adelaide (2005–)
- Department for Infrastructure and Transport (2010–)
- Trolleybuses in Adelaide (1937–1963).
A related article is Tramway Museum, St Kilda. The museum's collection, much of it operational, includes almost every type of tram that ran in Adelaide in the 20th century.
History
Synopsis
Adelaide's first, horse-drawn tramway was opened in 1878. A succession of services followed until in 1907 the South Australian Government established the Municipal Tramways Trust (MTT), which bought out their private-sector owners. A year later the MTT operated its first electric tram and before long the entire network was powered by electricity.
The early use of trams was for recreation as well as daily travel, by entire families and tourists. Until the 1950s, trams were used for family outings to the extent that the MTT constructed gardens in the suburb of Kensington Gardens, extending the Kensington line to attract customers. By 1945 the MTT was collecting fares for 95 million trips annually – 295 trips per head of population.
After the Great Depression, maintenance of the tramway system deteriorated no new trams were purchased. Competition from private buses, the MTT's own bus fleet and much-increased private car ownership all took patrons from the tram network. By the 1950s, the network was losing money and being replaced by a fleet of petrol-driven buses and trolleybuses powered by double overhead electric wires. All street tramways were closed in 1958 and subsequently dismantled except for the Glenelg tramline, which comprised a 9.2 kilometres (5.7 miles) exclusive right-of-way and 800 metres (870 yards) of street trackage – in the Adelaide central business district and Glenelg shopping precinct – at each end.[2]: 6–7 of ch. 1.22
In a tramway renaissance starting in 2005, the Glenelg line was upgaded and extended to Adelaide railway station in 2007 and to Adelaide Entertainment Centre in 2010. The upgrade included the first new tram purchases in more than 50 years. Flexity Classic and Citadis 302 trams now run on the line. Patronage has quadrupled (with the exception of the Covid pandemic years) since 2015.
Horse tramways

In early 1855, less than twenty years after the colony was founded, South Australia's first horse tram began operating between Goolwa and Port Elliot on the Fleurieu Peninsula.[3] Just over twenty years later Adelaide became the first city in Australia to introduce horse trams, and eventually the last to discard them for more modern public transport.[4] Although two trials of street level trains were run, the state of Adelaide's streets, with mud in winter and dust in summer, led to the decision that they would not be reliable.[5]
Sir Edwin Smith and William Buik, both prominent in Kensington and Norwood Corporation then Adelaide City Council (and both later mayors of Adelaide), spent some time inspecting European tramways during the 1870s. They were impressed with horse tram systems and, on returning to Adelaide, they promoted the concept leading to a prospectus being issued for the Adelaide and Suburban Tramway Co (A&ST). Private commercial interests lobbied government for legislative support, over Adelaide council's objections related to licensing and control. As a result, the Government of South Australia passed an 1876 private act, authorising construction of Adelaide's first horse tram network.[6]: 23 It was scheduled for completion within two years, with 10.8 miles (17.4 km) of lines from Adelaide's city-centre to the suburbs of Kensington and North Adelaide.[7] Completed in May 1878,[8] services began in June from Adelaide to Kensington Park with trams imported from John Stephenson Co of New York, United States.[9]
Until 1907, all horse tram operations were by private companies, with the government passing legislation authorising line construction. Growth of the network and rolling stock was driven largely by commercial considerations. On the opening day, the newly founded A&ST began with six trams, expanding to 90 trams and 650 horses by 1907 with its own tram manufacturing facility at Kensington.[10]
A Private act, passed in September 1881, allowed the construction of more private horse tramways and additional acts were passed authorising more line construction and services by more companies.[4] Most of the companies operated double-decker tram, although some were single level cabs with many built by John Stephenson Co, Duncan & Fraser of Adelaide, and from 1897 by the A&ST at Kensington.[10] The trams ran at an average speed of 5 miles per hour (8 km/h), usually two horses pulling each tram from a pool of four to ten.[11]
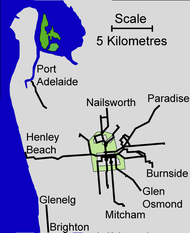

Various companies expanded the network from its initial line to Kensington, with eleven companies operating within six years, three more having already failed before constructing tracks.[12] The Adelaide to North Adelaide line opened in December 1878, a separate one from Port Adelaide to Albert Park in 1879, Adelaide to Mitcham and Hindmarsh in 1881, Walkerville 1882, Burnside, Prospect, Nailsworth and Enfield in 1883, and Maylands in 1892.[13] Various streets were widened especially for the tram lines including Brougham Place, North Adelaide by 10 feet (3 m) and Prospect Road to a total width of 60 feet (18 m).[14][15]
All but one line was built in 1435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) with the exception from Port Adelaide to Albert Park, built to 1600 mm (5 ft 3 in) to accommodate steam locomotives; some of the line was raised on embankments to avoid swampy ground and flooding.[16] There were 119 kilometres (74 mi) of tramlines with 1062 horses and 162 cars by 1901[17] and isolated lines from Port Adelaide to Albert Park and Glenelg to Brighton, as well as a network joining many suburbs to Adelaide's CBD by 1907.
The network had termini in Henley Beach, Hindmarsh, Prospect, Nailsworth, Paradise, Magill, Burnside, Glen Osmond, Mitcham, Clarence Park, Hyde Park and Walkerville.[18] To accommodate the specific needs of horses, most streets were left unsealed. The horses' urine needed an unsealed surface for absorption and their hooves a soft surface for good traction.[11]
Electrification

Adelaide's first experiment with electric powered trams was a demonstration run on the Adelaide and Hindmarsh Tramway company's line. A battery powered tram fitted with Julien's Patent Electric Traction[19][20] ran in 1889 to Henley Beach. The trial was unsuccessful due to the batteries poor capacity, and the promoters' deaths in a level crossing accident shortly after precluded further experiments.[21]
As with horse trams, commercial interests pursued government support for the introduction of electric tramways. The most influential was the "Snow scheme", promoted by Francis H. Snow largely on behalf of two London companies, British Westinghouse and Callender's Cable Construction. The scheme involved the purchase of major horse tramways, merging into an electric tramway company with twenty-one years of exclusive running rights. Legislation was passed in 1901, a referendum held in 1902, but the required funds had been spent and the scheme collapsed. Adelaide's council proposed their own scheme backed by different companies, but failed to raise the required capital, and J. H. Packard promoted various plans of his own devising that also never eventuated.[6]: 31–33 [22]
By 1901, Adelaide's horse trams were seen by the public as a blot on the city's image. With a population of 162,000 the slow speed of the trams, and the lines subsequent low traffic capacity, made them inadequate for public transport needs. The unsealed roads the horses required became quagmires in winter and sources of dust in summer. The 10 pounds of manure each horse left behind daily, was also not well regarded.[11] Under these various pressures the government negotiated to purchase the horse tramway companies. A 28 March 1906 newspaper notice announced that the government had purchased all of the city tramways for £280,000.[17] Bill No.913, passed 22 December 1906, created the Municipal Tramways Trust (MTT) with the authority to build new and purchase existing tramways.[23]

Not all tramway companies were purchased, as the Glenelg to Marino company continued operating separately until its failure in 1914.[24] The government purchased the properties, plant and equipment of existing tramways but did not purchase the companies themselves.[23] The equipment included 162 trams, 22 other vehicles and 1,056 horses. By 1909 at the launch of Adelaide's electric tram services there remained 163 horse trams and 650 horses under the control of the MTT.[25]
Due to the time required to electrify the network, the MTT continued to run horse trams until 1914. The cost of purchasing the tramways was funded by treasury bills[23] and the act capped total construction costs at £12,000 per mile of track.[26] £457,000 was let in contracts to March 1908 for construction of the tramways, trams, strengthening the Adelaide bridge over the River Torrens and associated works.[27] The official ceremony starting track construction was in May 1908, with tracks originally laid on Jarrah sleepers.[28]
On 30 November 1908, there were two trial runs from the MTT's depot on Hackney Road to the nearby Adelaide Botanic Garden and back, the evening trial carrying the Premier and Governor.[28] At the official opening ceremony on 9 March 1909, Electric Tram 1 was driven by Anne Price, wife of Premier Thomas Price, from the Hackney depot to Kensington and back, assisted by the MTT's chief engineer.[29]
At the 1909 opening, 35 miles (56 kilometres) of track had been completed with electricity supplied by the Electric Lighting and Supply Co.[30] The electric tram system ran on 600 Volts DC supplied at first from two converter stations,[31] No.1 converter station on East Terrace with 2,500 kW of AC to DC capacity and No.2 station at Thebarton with a capacity of 900 kW.[32] To cope with variable loads on the system, very large storage lead–acid batteries were installed, the initial one at East Terrace comprising 293 cells and a 50 ton tank of sulphuric acid.[33]
The Glenelg line was, from 1873, a 5 ft 3 in (1,600 mm) steam railway that ran at street level into Victoria Square.[34] Originally privately owned it was taken over by the South Australian Railways then transferred to the MTT in 1927. The line was closed to be rebuilt to 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge, electrified at 600 Volts DC and converted to tramway operation, reopening in late 1929.
The Port Adelaide line, which until that time had still used horse trams, began to be converted to electric operation in 1914 and opened on 3 April 1917.[25] A line from Magill to Morialta opened in 1915 for weekend tourist traffic, with only a single return service on weekdays. The line ran in the valley of 4th creek, a tributary of the River Torrens, across farmland and along unmade and ungazetted roads.[35]
On 18 September 1918, a tram line opened from Sturt Street, via West Terrace and then Anzac Highway (then Bay Road[36]) to Keswick. It was used to transport soldiers returned from World War I to the military hospital there.[37] Known as the West City Line, ran down West Terrace and Goodwood Road turned west into Park Terrace (now Greenhill Road) before turning in to Bay Road, and terminating at the entry to the Keswick Barracks. In 1925, a small loop branch line was added, to service the Wayville Showgrounds. After redevelopment of Anzac Highway in the 1930s, the tram line was eventually truncated at the new Keswick Road Bridge in March 1939, at a stop known as Wayville West. This line was closed in December 1957.[38]
The MTT

The MTT was established in 1906 as a tax-exempt body with eight members, mostly by appointed local councils but with some government appointees.[39] They established a 9 acres (3.6 ha) tram depot site near the corner of Hackney Road and Botanic Road with a depot building, twenty-four incoming tracks and a large administration office.[40] William Goodman was appointed as its first engineer, later general manager and remained as general manager until his 1950 retirement.[41]
To cater for family outings the MTT constructed gardens in the current suburb of Kensington Gardens, extending the Kensington line to attract customers.[42] By 1945 the MTT was collecting fares for 95 million trips annually, representing 295 trips per head of population (350,000).[43]
Former electric tram types
From 1908 to 1909, 100 electric trams were manufactured by Duncan & Fraser of Adelaide[42] at a cost of approximately £100 each.[44] Up to its last tram purchase in 1953, the MTT commissioned over 300 electric trams, some of which remained in service for over 75 years. The first of 11 Bombardier Flexity Classic trams were introduced in January 2006, followed by the first of six Alstom Citadis trams in December 2009. A further three Citadis trams entered service in 2018.[45][46]
Trolleybuses
During the Great Depression the MTT needed to expand services but finances prevented laying new tracks. A decision was made to trial trolleybuses, and a converted petrol bus began running experimentally on the Payneham and Paradise lines in 1932. A permanent trolleybus system opened in 1937, and trolleybuses continued running until July 1963.[47]
Mid-century decline and closure

From 1915 onwards the MTT had to compete against unregulated private buses, often preceding the trams on the same route to steal fares, which the MTT countered by opening their own motor bus routes from 1925.[48] The South Australian government began regulating buses within the state in 1927, although some private operators argued that Section 92 of the Constitution of Australia, which deals with interstate matters, exempted them from following the regulation. By notionally marking each ticket as a fare from the pickup point to Murrayville, Victoria (but allowing passengers to board or alight sooner) companies avoided having to abide by the regulation for some time.[49] The case was considered by the High Court, during the course of which Justice Isaac Isaacs offered a temporary compromise agreed to by both parties, but it appears that a final judgment was never delivered.[50] Eventually, most of the affected bus operators sold their buses to the MTT or other operators who followed the routes described.[49] Up until the end of World War I, most Adelaideans were dependent on public transport for daily journeys. The introduction of private automobiles decreased passenger numbers until petrol rationing during World War II led to a resurgence in patronage; patronage remained higher than before the war, until rationing was discontinued in 1951.[51]
From the start of the Great Depression until the closure of the network only one lot of trams was purchased by the MTT. Due to shortages there was minimal maintenance of the network during World War II and post-war shortages prevented the purchase of new trams.[52] In 1951–1952 the MTT lost £313,320 and made the decision to convert the Erindale, Burnside and Linden Park lines to electric trolleybuses. The last trams on these lines ran on 24 May 1952 with the lines lifted from 18 April 1953. A 1953 royal commission was held to inquire into the financial affairs of the MTT resulting in a completely reconstituted board.[53] Late the same year, with driver safety concerns about the conflict with increasing traffic on the road, the Glen Osmond line was temporarily converted to motor buses. The line was never converted back to trams and much comment was made about the continuing maintenance of unused overhead lines.[54]
The final first generation "streetcar" journey was made by Type F1 car no. 269 with a load of more than 200 passengers starting from the City to Cheltenham at 11.40 pm on Saturday 22 November 1958. A crowd of more than 2000, many in their night attire, was at the terminus to farewell it. The tram departed for the City at 12.35 am, leading a long line of noisily tooting motorists, arriving in Victoria Square at 1.35 am and entering the City depot in Angas Street at 1.40.[2]: 48 of ch. 1.33
Only the Glenelg line remained.[55] Except for the Glenelg line's Type H cars, the trams were sold or scrapped. Some were used as shacks, playrooms or preserved by museums. The Tramway Museum, St Kilda, a half-hour's drive north of the city centre, has at least one example of each 20th century tram.[44]
Renewal and expansion
A 1.2-kilometre (0.75 mi) extension of the line from the Victoria Square terminus was announced in April 2005, which would see trams continue along King William Street and west along North Terrace through Adelaide railway station and the western city campus of the University of South Australia. An additional two Flexity Classic trams were ordered to cater for the expanded services. Construction commenced in 2007 and a new Victoria Square stop, relocated from the centre of the square to the west, was opened in August 2007. Testing of the extension began in September 2007 before it was officially opened on 14 October 2007 with shuttle services along the new extension until the release of the new timetable on 15 October when normal through services commenced.[56] A free City Shuttle service between South Terrace and City West also began on 15 October to complement the main Glenelg to City West service.[57] Further extensions at that time were the subject of public debate; Tourism Minister Jane Lomax-Smith expressed support for the line to be extended to North Adelaide and Prospect although the Transport Minister stated that this was not a practical option,[58] with his preferred option the creation of a fare free city loop.[59]

In the 2008 state budget, the government announced that it would extend the tram line further. The first extension, completed in early 2010, was from the existing North Terrace terminus to the Adelaide Entertainment Centre in the inner north-west suburb of Hindmarsh, with a park and ride service set up on Port Road.[60] Following the expected electrification of the Outer Harbor and Grange railway lines, new tram-trains were proposed to run to West Lakes, Port Adelaide and Semaphore by 2018.[61] However, these plans were later scrapped in the 2012 state budget.[62]
In 2017, another stage of expansion was announced, adding a four-way tram junction at the intersection of North Terrace, King William Street and King William Road. One further stop would be provided north of that junction, adjacent to the Adelaide Festival Centre, and three to the east of it near the South Australian Museum, University of Adelaide and East End at the new eastern terminus in front of the old Royal Adelaide Hospital. The project was expected to cost $80 million with the contract awarded to a joint venture of Downer Rail and York Civil. Preliminary works began in July 2017 with major works commencing in October. York Civil went broke the next year.[63][64][65] The extensions opened on 13 October 2018, seven months behind schedule,[66] with the stop at the end of the eastward line known as Botanic Gardens owing to its proximity to Adelaide Botanic Garden.[67]
In July 2019, the government announced the provision of tram services would be contracted out, along with other transport services in Adelaide.[68] In July 2020, Torrens Connect commenced operating Adelaide's trams under an eight-year contract.[69][70][71]
Adelaide City Council has stated that it plans a tram extension to North Adelaide by 2036, anticipating a doubling of its present population.[72]
Routes
| Line | Terminus A | Terminus B | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLNELG | Glenelg | Royal Adelaide Hospital | In peak times, services continue through beyond the Royal Adelaide Hospital along the Botanic Gardens line to the Entertainment Centre. Services operate at 5–10 minute frequencies during day hours and up to every 20 minutes in later hours. |
| BTANIC | Entertainment Centre | Botanic Gardens | The line saw a large patronage increase during peak periods in late 2019–2020 seeing the higher capacity Citadis trams primarily allocated to the line in peak periods. |
| FESTVL | Glenelg | Festival Plaza | Services operate on Weekends and Public holidays, along with Adelaide Oval special event days due to the city terminus' proximity to the venue. The terminus often holds many trams during these events. |
| ADLOOP | South Terrace | South Terrace | A 'loop' service operates inline with the Adelaide Fringe Festival to accommodate for a large patronage increase. It runs from the South Terrace to Festival Plaza, then Botanic Gardens and returns to South Terrace. It utilises the two left hand turns on the eastern side of the union junction near the Adelaide Railway Station. |
Cancelled extension proposals
Throughout the 21st century, there have been a number of proposals to expand the tram network both within and beyond the city centre.
In 2016, the Weatherill Government released a report detailing a proposal under the name "AdeLINK" that listed five routes that would radiate from a new CityLINK city centre loop: an eastern EastLINK route to Magill; a collection of north western PortLINK routes; a northern ProspectLINK route to Kilburn; a southern UnleyLINK route to either Mitcham or Daw Park; and a western WestLINK route to Adelaide Airport.[73] The PortLINK proposal, that would replace the Outer Harbor railway line with light rail, is reminiscent of a previous extension proposal to West Lakes, Port Adelaide and Semaphore that was announced in the 2008 South Australian Budget but later abandoned in the 2012 budget.[74][62]
Following the 2018 state election, the incoming Marshall Government abandoned the previous AdeLINK proposal, announcing that they would instead develop the network within the city centre only, announcing a vision of four routes: Glenelg to North Adelaide via the existing Glenelg line; Entertainment Centre to Central Market through the eastern half of the city; a loop service operating from Glenelg along the existing Glenelg line and through the eastern half of the city; and the existing South Terrace to Royal Adelaide Hospital "City Shuttle" service.[75][76] The proposed city loop service from Glenelg would require the King William Street-North Terrace intersection to be reconstructed with a right-hand turn from King William Street to the eastern side of North Terrace, which the Liberals had announced during its campaign. This would have required the junction relaid in December 2017 to be dug up and replaced.[77] The right-hand turn project was cancelled in November 2018 due to rising costs and engineering challenges.[78]
Rolling stock
Flexity Classic (100 Series)

15 Bombardier Flexity Classic trams operate on all three main routes on the Adelaide network
A contract for nine Bombardier Flexity Classic trams was awarded to Bombardier in September 2004.[79] The first three arrived at Outer Harbor in November 2005. One (no. 103) had been damaged in transit; a replacement was built and no. 103 became a source of spare parts.[80] Following a period of commissioning and staff training, both entered service in January 2006.[80] The remainder were landed at Port Melbourne, moving to Adelaide by road. The last of the original nine arrived in Adelaide in September 2006.[81]
A further two were added to the order in 2005 following the decision to extend the line along King William Street.[82][83] Both arrived in the first half of 2007, 111 being diverted to Yarra Trams' Preston Workshops and completing over 400 kilometres of trial running on the Melbourne network.[84] The replacement 103 arrived in June 2007.[85] Another four were ordered in June 2008 as part of the Adelaide Entertainment Centre extension, entering service in 2011/12.[86][87] Numbered 101–115, all were built by Bombardier in Bautzen, Germany.
Citadis 302 (200 Series)

9 Alstom Citadis 302 trams operate on all three main routes on the Adelaide network. They are more prominently used on the Botanic Gardens line during busy and peak periods due to their higher capacity.
In May 2009 the State Government purchased six Citadis 302 five-car trams for $36 million. Manufactured by Alstom in La Rochelle, France, they had been ordered for the Metro Ligero system in Madrid, Spain, but became surplus following the line they were ordered for being scaled back.[88][89] Most had not been used.[90]
The trams were delivered in two separate batches of three being landed in Melbourne in September and November 2009 for modifications at Preston Workshops before being moved by road to Adelaide.[91][92] In December 2017 a further three arrived.[93][94]
H Type (300 Series)
Until January 2006, 1929-vintage H Type trams provided almost all services on the Glenelg line. They were built for the opening of the Glenelg line when it was converted to standard gauge and electrified, and they also operated on some street lines. This type had many of the characteristics of North American interurban cars of the same period.[95] Thirty were built by local manufacturer A Pengelly & Co; road numbers were 351 to 380.
Twenty-one remained in service in 2005.[96] Five were refurbished in 2000 following the arrival of the Flexity Classics; the remainder were disposed of.[97] By 2012, three were in store at Mitsubishi Motors Australia's Clovelly Park plant.[98] The remaining two – numbers 351 and 352 (previously 367) – were refurbished by Bluebird Rail Operations, one briefly operating weekend services in August 2013.[99][100] The only other recorded use of the pair was in February 2015 when they operated a charter.[101] To make room for new Alstom Citadis trams at the Glengowrie depot, in December 2017 both were moved to the Department of Planning, Transport & Infrastructure's Walkley Heights facility.[102] These trams have since been donated to The Tramway Museum, St. Kilda. Tram 361 was on display at Wigley Reserve, Glenelg, for many years, then moved to "Mist on Bridgewater", a business in the Adelaide Hills, in April 2023, joining Tram 376, which they acquired from Glossop High School in late 2022.[103]
Patronage
Detailed information is in the Patronage section of Tramways revival in Adelaide.
The route extensions that opened from 2007, although only 5.4 km (3.4 mi) long, mainly served parts of Adelaide city with high vehicular and pedestrian traffic, and thus reduced inner-city traffic congestion. Free tram travel introduced in this area and in the Glenelg shopping precinct during financial year 2014–15 almost quadrupled patronage, from 2.29 million to 8.88 million.[104][105] (Increased reliability of the new trams, with more than 96 per cent on-time running, was also cited in 2017 as a factor in increased patronage.)[106] Increases during the next four years totalled 570,000 until the COVID-19 pandemic severely affected patronage from mid-March 2020.[107]
See also
- Transport in Adelaide
- Transport in South Australia
- Henwood v Municipal Tramways Trust
- Railways in Adelaide
- List of public transport routes in Adelaide
- Trams in Australia
- Horse trams in Adelaide (1878–1914)
- Department for Infrastructure and Transport, branded as Adelaide Metro (2010–)
- Dry Creek explosives tramway
References
- ^ Tramway Museum St Kilda
- ^ a b Wilson, Tom; Radcliffe, John; Steele, Christopher (2021). Adelaide's public transport – the first 180 years. PDF book. Adelaide, South Australia: Wakefield Press. ISBN 9781743058855.
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 6
- ^ a b The Critic (1909), p. 8
- ^ Kingsborough L.S. (1965), p. 2
- ^ a b Radcliffe, John C.; Steele, Christopher I.M. (1974). Adelaide road passenger transport, 1836–1958. Adelaide: Libraries Board of South Australia. ISBN 0724300457.
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 7
- ^ Lewis H. (1985), p. 139
- ^ Hickey A. (2004), p. 16
- ^ a b Steele C. (1981), p. 11
- ^ a b c Steele C. (1986), p. 5
- ^ Kingsborough, L.S. (1965), p. 8
- ^ Horse tram line opening dates from Steel C. (1981), p. 10, The Critic (1909), pp. 9–11, Nagel P. (1971), p. 50 and Lewis H. (1985), p. 139
- ^ Nagel P. (1971), p. 50
- ^ Lamshed M. (1972), p. 30
- ^ Kingsborough L.S. (1965), p. 17
- ^ a b The Critic (1909), p. 14
- ^ 1945 map of the 1907 Horse tramways, Published by the MTT and created by L.S. Kingsborough and C.J.M. Steele. Kingsborough L.S. (1965), p. 85
- ^ "julien".
- ^ "julien".
- ^ Australian Electric Transport Museum (1974), p. 24
- ^ The critic (1909), p. 13
- ^ a b c The Critic (1909), p. 15
- ^ Kingsborough, L. S. (1965), pp. 43–44
- ^ a b State Transport Authority (1978)
- ^ The Critic (1909), pp. 17–18
- ^ The Critic (1909), pp. 19–21
- ^ a b The Critic (1909), p. 21
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 37
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 23
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 32
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 34
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 35
- ^ State Transport Authority (1979), p. 9
- ^ Steele C. (1986), p. 43
- ^ "Claret Ash (Fraxinus oxycarpa 'Raywood')". National Trust. 24 May 2018. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ "Keswick Hospital: The Diggers Hospital". State Library of South Australia. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ "The Western Lines". Tramway Museum, St Kilda. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ The Critic (1909), pp.15,17–18
- ^ The Critic (1909), p. 27
- ^ McCarthy, G. J. (22 June 2005). "Goodman, William George Toop (1872–1961)". The University of Melbourne eScholarship Research Centre. Retrieved 23 April 2007.
- ^ a b Steele C. (1981), p. 15
- ^ Steele C. (1981), p. 37
- ^ a b Oldland, Jenny (16 January 2007). "Tram 104 departs Foul Bay". Yorke Peninsula Country Times. Retrieved 6 February 2007. [dead link]
- ^ SA mid-year budget review: $20 million for more Adelaide trams and a new spur line ABC News 15 December 2016
- ^ Here & There Trolley Wire issue 352 February 2018 page 19
- ^ The Tramway Museum, St Kilda (S.A.) (Undated), information brochure on tram fleets
- ^ Steele C. (1981), p. 23
- ^ a b Steele C. (1981), p. 32
- ^ "Murrayville" Buses, The Observer, 14 July 1928.
- ^ Steele C. (1986), pp.23,43
- ^ Steele C. (1981), p. 42
- ^ Steele C. (1981), p. 43
- ^ Steele C. (1981), p. 45
- ^ Steele C. (1981), p. 47
- ^ Official opening for tram extension ABC News 14 October 2007
- ^ Adelaide's Tramway Extension Opens Trolley Wire issue 311 November 2007 pages 3–8
- ^ Bildstien, Craig (23 January 2007). "Minister 'mortified' by ruling on trams". Adelaide Now. News Limited. Retrieved 11 February 2007.
- ^ "Free tram network 'to drive city's future". The Advertiser. News Limited. 19 February 2007. p. 2.
- ^ "Park 'n' Ride Users – 7 days". Adelaide Entertainment Centre. Retrieved 5 December 2013.
- ^ "2008 State Budget". South Australian Department of Treasury and Finance. 5 June 2008. Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ a b "Port, Semaphore tramline derailed in State Budget". The Advertiser/AdelaideNow. 8 May 2009. Retrieved 7 October 2014.
- ^ Kemp, Miles (21 July 2017). "New tram stops and extra funding to ease traffic problems announced for North Terrace extension". The Advertiser. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- ^ North Terrace services detoured for tram line extension works Adelaide Metro
- ^ "Major construction set to begin on $80 million City Tram Extension Project". Department of Planning, Transport and Infrastructure. 18 September 2017. Archived from the original on 4 October 2017. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- ^ Boisvert, Eugene (13 October 2018). "Surprise start for Adelaide's long-delayed tram extension". ABC News. Retrieved 14 October 2018.
- ^ "New tram services now operating". Adelaide Metro. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ^ SA government to privatise operation of Adelaide Metro trains and trams ABC News 1 July 2019
- ^ Adelaide Bus and Public Transport Contracts Announced Australasian Bus & Coach 10 March 2020
- ^ Welcome to a new era for public transport in South Australia Department of Planning, Transport & Infrastructure 20 March 2020
- ^ UGL and John Holland to operate Adelaide trams Metro Report International 12 March 2020
- ^ Back to the future: derailed tram extension resurrected for 2036

subscription: the source is only accessible via a paid subscription ("paywall"). - ^ "AdeLINK Multi-Criteria Analysis Summary Report" (PDF). Department of Transport, Planning and Infrastructure. 2016. pp. 10–19.
- ^ "2008 State Budget". South Australian Department of Treasury and Finance. 5 June 2008. Archived from the original on 5 June 2008. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ "People Focused Public Transport" (PDF). Liberal Party of Australia (South Australian Division). Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ^ Siebert, Bension (9 March 2018). "Libs won't rebuild Adelaide's suburban tram network". InDaily. Retrieved 6 April 2018.
- ^ MacLennan, Leah (8 March 2018). "Liberal Party promises to add right-hand turn to Adelaide tram line". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- ^ "SA Liberals can't get Adelaide tram to go right". ABC News. 18 November 2018. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- ^ "Metros" Railway Gazette International December 2004 page 820
- ^ a b Adelaide's New Trams Trolley Wire issue 304 February 2006 pages 16, 17
- ^ Adelaide news Trolley Wire issue 307 November 2006 page 26
- ^ Cabinet, Subjects for Consideration, 8 August 2004 Department of the Premier & Cabinet
- ^ City West to Glenelg Service Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine Tramway Museum, St Kilda
- ^ Adelaide – another Flexity enters service Trolley Wire" issue 309 May 2007 page 16
- ^ Adelaide: last Flexity arrives Trolley Wire" issue 310 August 2007
- ^ Additional trams Trolley Wire issue 314 August 2008 page 15
- ^ Entertainment Centre, Hindmarsh to Glenelg Service Archived 24 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine Tramway Museum, St Kilda
- ^ Castello, Renato (24 May 2009). "European trams to bolster our City-Glenelg fleet". The Adelaide Advertiser. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- ^ Fenton, Andrew (7 June 2009). "Six new trams for Adelaide-ex-Madrid". The Adelaide Advertiser. Retrieved 27 May 2014.
- ^ Six new trams for Adelaide Trolley Wire issue 318 August 2009 page 21
- ^ New European trams a massive boost to Adelaide network Rail Express 24 June 2009
- ^ "Photos of Madrid tram at Preston". Trams Down Under archive. 10 September 2009."Another Madrid Citadis". Trams Down Under archive. 11 November 2009."Madrid tram to Adelaide". Trams Down Under archive. 11 November 2009.
- ^ Job lot as new trams heading to SA The Independent Weekly 18 October 2017
- ^ More Spanish trams arrive Catch Point issue 243 January 2018 page 18
- ^ Due, John F. (c. 1955). "Sir Adam Beck and the Hydro Radial proposals" (PDF). Internet Archive. Upper Canada Railway Society. p. 10. Retrieved 3 November 2021.
- ^ Trams TransAdelaide
- ^ Glenelg Tram Refurbishment Project Trolley Wire issue 285 May 2001 pages 16–19
- ^ Adelaide tram news Trolley Wire issue 328 February 2012 page 16
- ^ H-Class tram to return to the Glenelg to Adelaide tramline Adelaide Advertiser 27 July 2013
- ^ H type trams won’t be brought back into service despite successful trial The Australian 15 February 2014
- ^ Here & There Trolley Wire issue 341 May 2015 page 22
- ^ Here & There Trolley Wire issue 352 February 2018 page 19
- ^ "A new home for Tram 361".
- ^ "DPTI Annual Report 2014-15 – Transport Acts". Department of Planning, Transport and Infrastructure. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ "DPTI Annual Report 2013-14" (PDF). Department of Planning, Transport and Infrastructure. p. 88. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ "Old trams with outdated technology being considered for Adelaide, Opposition says". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 19 February 2017. Retrieved 7 January 2018.
- ^ "DPTI Annual Report 2018-19 – Adelaide Metro patronage 2018–19" (PDF). Department of Planning, Transport and Infrastructure. Retrieved 4 December 2019.
- Australian Electric Transport Museum (1974). Australian electric transport museum, St Kilda, South Australia.
- Hickey, Alan, ed. (2004). Postcards: On the Road Again. Wakefield Press. ISBN 1-86254-597-9.
- Kingsborough, L.S. (1965). The horse tramways of Adelaide and its suburbs, 1875–1907. Adelaide: Libraries board of South Australia.
- Lamshed, Max (1972). Prospect 1872–1972, a portrait of a city. Adelaide: The corporation of the city of Prospect. ISBN 0-9599015-0-7.
- Lewis, H. John (1985). Enfield and the northern villages. The corporation of the city of Enfield. ISBN 0-85864-090-2.
- Metropolitan tramways trust (1974). The Adelaide tramways, pocket guide. A catalogue of rolling stock 1909–1974. Adelaide: Metropolitan tramways trust.
- Municipal Tramways Trust (1975). 1907–1974 Development of street transport in Adelaide, Official history of the municipal tramways trust. Adelaide: Municipal Tramways Trust.
- Nagel, Paula (1971). North Adelaide 1937–1901. Adelaide: Austaprint. ISBN 0-85872-104-X.
- Radcliffe, John C.; Steele, Christopher I.M. (1974). Adelaide road passenger transport, 1836–1958. Adelaide: Libraries Board of South Australia. ISBN 0724300457.
- State Transport Authority (1979). Adelaide railways. Adelaide: State Transport Authority.
- State Transport Authority (1978). Transit in Adelaide: the story of the development of street public transportation in Adelaide from horse trams to the present bus and tram system. Adelaide: State Transport Authority. ISBN 0-7243-5299-6.
- Steele, Christopher (1981). The Burnside lines. Sydney: Australian Electric Traction Association. ISBN 0-909459-08-8.
- Steele, Christopher (1986). The tramways and buses of Adelaide's north-east suburbs. Norwood, South Australia: Australian Electric Traction Association. ISBN 1-86252-089-5.
- Taylor, Edna (2003). The history and development of St Kilda South Australia. Salisbury, South Australia: Lions Club of Salisbury. ISBN 0-646-42219-7.
- The Critic (1909). The tramways of Adelaide, past, present, and future: a complete illustrated and historical souvenir of the Adelaide tramways from the inception of the horse trams to the inauguration of the present magnificent electric trolley car system. Adelaide: The Critic.
- Wilson, Tom; Radcliffe, John; Steele, Christopher (2021). Adelaide's public transport – the first 180 years. PDF book. Adelaide, South Australia: Wakefield Press. ISBN 9781743058855.
Further reading
- Eardley, Gifford (June 1961). "The Adelaide and Hindmarsh-Henley Beach Tramway Company". Australian Railway Historical Society Bulletin.
- Eardley, Gifford (May 1974). "The Adelaide, Unley and Mitcham Tramway Company". Australian Railway Historical Society Bulletin.
- Churchman, Geoffrey B. (1995). Railway Electrification in Australia and New Zealand. Sydney & Wellington: IPL Books. pp. 158–160. ISBN 0-908876-79-3.
External links
- The Tramway Museum, St Kilda
- "The Eastern Lines". Tramway Museum, St Kilda.
- Adelaide's Tram History
- Adelaide H No 373
- Bendigo Tramway Museum
- Adelaide's H class has arrived. (Sydney Tramway Museum)
- Bill's Glenelg tram page with Flexity coverage
- Curious Adelaide: Why was Adelaide's tram network ripped up in the 1950s?, Candice Prosser, ABC, 1 December 2017.
