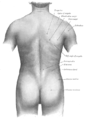
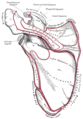
Teres major muscle
| Teres major muscle | |
|---|---|
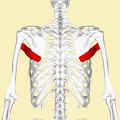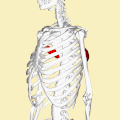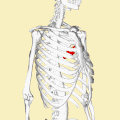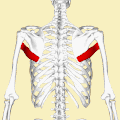
 Posterior view showing the relations between teres major muscle (in red) and the other muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column. | |
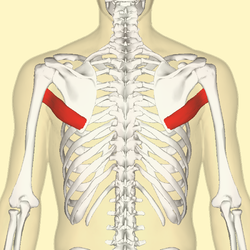 Teres major muscle (in red) seen from back (posterior to anterior perspective). | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Posterior aspect of the inferior angle of the scapula |
| Insertion | Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus |
| Artery | Subscapular and circumflex scapular arteries |
| Nerve | Lower subscapular nerve (segmental levels C5 and C6) |
| Actions | Adduct the humerus, internal rotation (medial rotation) of the humerus, extend the humerus from flexed position |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus teres major |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.011 |
| TA2 | 2462 |
| FMA | 32549 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
The teres major muscle (from Latin teres, meaning "rounded") is positioned above the latissimus dorsi muscle and assists in the extension and medial rotation of the humerus. This muscle is commonly confused as a rotator cuff muscle, but it is not, because it does not attach to the capsule of the shoulder joint, unlike the teres minor muscle, for example.
Structure
The teres major muscle originates on the dorsal surface of the inferior angle and the lower part of the lateral border of the scapula.
The fibers of teres major insert into the medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus of the humerus.[1]
Relations
The tendon, at its insertion, lies behind that of the latissimus dorsi, from which it is separated by a bursa, the two tendons being, however, united along their lower borders for a short distance. The fibers of these two muscles run parallel to each other, and both muscles insert at the crest of the lesser tubercle of the humerus (also described as the medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus).
Together with teres minor muscle, teres major muscle forms the axillary space, through which several important arteries and veins pass.[2][3]
Innervation
Teres major is supplied primarily by the lower subscapular nerve[4] and additionally by the thoracodorsal nerve (middle subscapular nerve). These are distal to the upper subscapular nerve. These three nerves branch off the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. The nerves that innervate teres major consist of fibers from spinal nerves C5-C8.[4]
Function
The teres major is a medial rotator and adductor of the humerus and assists the latissimus dorsi in drawing the previously raised humerus downwards and backwards (extension, but not hyperextension). It also helps stabilise the humeral head in the glenoid cavity.
Injury
Isolated teres major injuries are rare. They are almost exclusively encountered in professional and high-level recreational athletes— baseball pitchers in particular. These injuries can be debilitating, requiring lengthy rehabilitation periods and missed seasons of athletics. No clear indications for surgical treatment exist. Outcomes have been generally good after both nonoperative and operative treatment.[5]
Additional images
- Position of teres major muscle (shown in red). Animation.
- Muscles on the dorsum of the scapula, and the Triceps brachii muscle:
#3 latissimus dorsi muscle
#5 teres major muscle
#6 teres minor muscle
#7 supraspinatus muscle
#8 infraspinatus muscle
#13 long head of triceps brachii muscle - Surface anatomy of the back. (Label for Teres major at upper right.)
- Left humerus. Anterior view.
- Teres major muscle
- Left scapula. Posterior surface.
- Teres major muscle
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 442 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 442 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Grosclaude, M.; Najihi, N.; Lädermann, A.; Menetrey, J.; Ziltener, J.-L. (February 2012). "Teres major muscle tear in two professional ice hockey players: cases study and literature review". Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Surgery & Research. 98 (1): 122–125. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2011.09.014. ISSN 1877-0568. PMID 22197182.
- ^ Bouche, P. (January 1, 2013), Said, Gérard; Krarup, Christian (eds.), "Chapter 19 - Compression and entrapment neuropathies", Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Peripheral Nerve Disorders, 115, Elsevier: 311–366, doi:10.1016/b978-0-444-52902-2.00019-9, ISBN 9780444529022, PMID 23931789, retrieved November 2, 2020
- ^ Pindrik, Jonathan; Dorsi, Michael; Belzberg, Allan (January 1, 2015), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 9 - Surgical Exposures for Nerves of the Upper Limbs", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 131–138, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-802653-3.00058-0, ISBN 978-0-12-802653-3, retrieved November 2, 2020
- ^ a b Bertorini, Tulio E. (January 1, 2008), Bertorini, Tulio E. (ed.), "1 - Neuromuscular Anatomy and Function", Neuromuscular Case Studies, Philadelphia: Butterworth-Heinemann, pp. 1–25, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7506-7332-7.50005-2, ISBN 978-0-7506-7332-7, retrieved November 2, 2020
- ^ Donohue, Benjamin; Lubitz, Marc (December 20, 2016). "Sports Injuries to the Latissimus Dorsi and Teres Major". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 45 (10): 2428–2435. doi:10.1177/0363546516676062. PMID 28125914. S2CID 3872258.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 03:03-06 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- PTCentral