Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta: Difference between revisions
m →External links: WP:CHECKWIKI error fixes - Replaced endash with hyphen in sortkey per WP:MCSTJR using AWB (9100) |
Andrew Lancaster (talk | contribs) →History: add history |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
[[File:North Holland 1st-10th Century.jpg|thumb|400px|none|Historical evolution of the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt area from the Roman Period to the Middle Ages]] |
[[File:North Holland 1st-10th Century.jpg|thumb|400px|none|Historical evolution of the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt area from the Roman Period to the Middle Ages]] |
||
[[Pliny the Elder]]'s ''[[Natural History (Pliny)|Natural History]]'' gives a list of tribes living in the "Gaulish islands" within the delta region between different mouths of the Rhine. First he mentions the large island of the [[Batavians]] and the [[Cananefates]], and then he gives the list of other peoples who he says are stretched out along 100 [[Roman miles]], between the mouths ''[[Helinium|Helinius]]'' and ''[[Flevum|Flevus]]''.<ref>[http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.02.0137%3Abook%3D4%3Achapter%3D29 Plin. Nat. 4.29]</ref> The Helinius (or Helinium) is understood to be the main mouth of the [[Meuse]], where the main water of the southern branch of the Rhine, the [[Waal (river)|Waal]] (Latin Vacalis) also discharged. ''Flevus'' (or ''Flevum'') was a Roman fortification on the Ocean, north of the Rhine, mentioned by Tacitus, and equated today with [[Velsen]].<ref>[http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Tac.%20Ann.%204.72&lang=original Tac. Ann. 4.72]</ref> Although the details are no longer clear there was apparently a northerly outlet of the Rhine here, north of the main [[Old Rhine]].<ref>''Germania'' By Cornelius Tacitus, [http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.02.0078%3Abook%3D4%3Achapter%3D72 4.72]</ref> But the term Flevo was also have used by Pomponius Mela to refer to the fresh water lakes which were in the area of the modern [[Zuiderzee]], which Mela specifically says that the Rhine fed into. So the Rhine mouth mentioned by Pliny might have been a discharge into a lake, or perhaps water running to Flevum on the coast may have run via the lakes to the coast, perhaps first through an ancient version of the [[Vecht (Utrecht)|Vecht]], or the [[Ijssel]].<ref>{{citation|url=http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0064:entry=flevo-lacus-geo&highlight=flevo|title=Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography| year=1854|first=William |last=Smith}}</ref> |
|||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
Revision as of 07:53, 6 July 2013
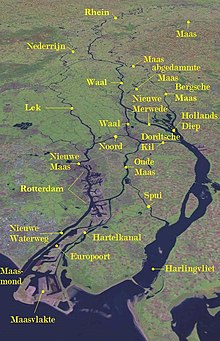
The Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta or Helinium is a river delta in the Netherlands and Belgium formed by the confluence of the Rhine, the Meuse and the Scheldt rivers. The result is a multitude of islands, branches and branch names that may at first sight look bewildering, especially as a waterway that appears to be one continuous stream may change names as many as seven times, e.g. Rhine → Bijlands Kanaal → Pannerdens Kanaal → Nederrijn → Lek → Nieuwe Maas → Het Scheur → Nieuwe Waterweg (→ North Sea). Since the Rhine contributes most of the water, the shorter term Rhine Delta is commonly used. However, this name is also used for the river delta where the Rhine flows into Lake Constance, so it is clearer to call the larger one Rhine-Meuse delta, or even Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt Delta, as the Scheldt ends in the same delta.
The economic importance of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta is enormous, since the three rivers are important navigable waterways. The delta is the entrance from the North Sea to the vast German and Central European hinterland (and to a lesser extent France). Major ports in the delta are Rotterdam, Antwerp (Belgium), Vlissingen, Amsterdam (through the Amsterdam–Rhine Canal), and Ghent (through the Ghent–Terneuzen Canal). The land areas in the Delta are protected from flooding by the Delta Works.
Geography

The shape of the Rhine delta is determined by two bifurcations: first, at Millingen aan de Rijn, the Rhine splits into Waal and Nederrijn, and second near Arnhem, the IJssel branches off from the Nederrijn. This creates three main flows, two of which change names rather often. The largest and southern main branch begins as Waal and continues as Boven Merwede ("Upper Merwede"), Beneden Merwede ("Lower Merwede"), Noord River ("North River"), Nieuwe Maas ("New Meuse"), Het Scheur ("the Rip") and Nieuwe Waterweg ("New Waterway"). The middle flow begins as Nederrijn, then changes into Lek, then joins the Noord, thereby forming Nieuwe Maas. The northern flow keeps the name IJssel until it flows into Lake IJsselmeer. Three more flows carry significant amounts of water: the Nieuwe Merwede ("New Merwede"), which branches off from the southern branch where it changes from Boven to Beneden Merwede; the Oude Maas ("Old Meuse"), which branches off from the southern branch where it changes from Benede Merwede into Noord, and Dordtsche Kil, which branches off from Oude Maas.
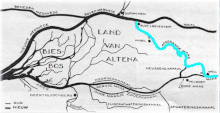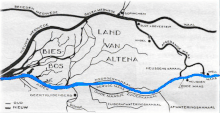
Before the St. Elizabeth's flood (1421) the Meuse flowed just south of today's line Merwede-Oude Maas to the North Sea and formed an archipelago-like estuary with Waal and Lek. This system of numerous bays, estuary-like extended rivers, many islands and constant changes of the coastline, is hard to imagine today. From 1421 to 1904, the Meuse and Waal merged further upstream at Gorinchem to form Merwede. For flood protection reasons, the Meuse was separated from the Waal through a lock and diverted into a new outlet called "Bergse Maas", then Amer and then flows into the former bay Hollands Diep.
The northwestern part of the estuary (around Hook of Holland), is still called Maasmond ("Meuse Mouth"), ignoring the fact that it now carries only water from the Rhine. This might explain the confusing naming of the various branches.
The hydrography of the current delta is characterized by the delta's main arms, disconnected arms (Hollandse IJssel, Linge, Vecht, etc.) and smaller rivers and streams. Many rivers have been closed ("dammed") and now serve as drainage channels for the numerous polders. The construction of Delta Works changed the Delta in the second half of the 20th Century fundamentally. Currently Rhine water runs into the sea, or into former marine bays now separated from the sea, in five places, namely at the mouths of the Nieuwe Merwede, Nieuwe Waterway (Nieuwe Maas), Dordtse Kil, Spui and IJssel.
The Rhine-Meuse Delta is a tidal delta, shaped not only by the sedimentation of the rivers, but also by tidal currents. This meant that high tide formed a serious risk because strong tidal currents could tear huge areas of land into the sea. Before the construction of the Delta Works, tidal influence was palpable up to Nijmegen, and even today, after the regulatory action of the Delta Works, the tide acts far inland. At the Waal, for example, the most landward tidal influence can be detected between Brakel and Zaltbommel.
History

Pliny the Elder's Natural History gives a list of tribes living in the "Gaulish islands" within the delta region between different mouths of the Rhine. First he mentions the large island of the Batavians and the Cananefates, and then he gives the list of other peoples who he says are stretched out along 100 Roman miles, between the mouths Helinius and Flevus.[1] The Helinius (or Helinium) is understood to be the main mouth of the Meuse, where the main water of the southern branch of the Rhine, the Waal (Latin Vacalis) also discharged. Flevus (or Flevum) was a Roman fortification on the Ocean, north of the Rhine, mentioned by Tacitus, and equated today with Velsen.[2] Although the details are no longer clear there was apparently a northerly outlet of the Rhine here, north of the main Old Rhine.[3] But the term Flevo was also have used by Pomponius Mela to refer to the fresh water lakes which were in the area of the modern Zuiderzee, which Mela specifically says that the Rhine fed into. So the Rhine mouth mentioned by Pliny might have been a discharge into a lake, or perhaps water running to Flevum on the coast may have run via the lakes to the coast, perhaps first through an ancient version of the Vecht, or the Ijssel.[4]
External links
51°43′50″N 4°42′57″E / 51.730431°N 4.715881°E
- ^ Plin. Nat. 4.29
- ^ Tac. Ann. 4.72
- ^ Germania By Cornelius Tacitus, 4.72
- ^ Smith, William (1854), Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography
