Color motion picture film: Difference between revisions
202.141.75.162 (talk) No edit summary |
VMS Mosaic (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
:''See also [[List of motion picture film stocks]]'' |
:''See also [[List of motion picture film stocks]]'' |
||
Motion picture film |
Motion picture film, primarily because of the rem-jet backing, requires different processing than standard [[C-41 process]] color film. The process necessary is [[Eastman Color Negative|Eastman Color Negative 2]] (ECN-2), which has an initial step using an alkaline bath to remove the backing layer. There are also minor differences in the remainder of the process. If motion picture negative is run through a standard C-41 color film developer bath, the rem-jet backing will partially dissolve and destroy the integrity of the developer and, potentially, ruin the film. |
||
There are two main companies manufacturing color film for motion picture use: [[Eastman Kodak]] and [[Fujifilm]]. |
There are two main companies manufacturing color film for motion picture use: [[Eastman Kodak]] and [[Fujifilm]]. |
||
Revision as of 02:56, 18 November 2009
Color motion picture film refers to motion pictures in color. The first motion pictures were made with silver halide-based photographic emulsion on a clear base. The resulting image was projected in a range of blacks to whites, depending on the luminous intensity of the original subject.
With color motion picture film, not only is the luminance of a subject recorded, but the color of the subject, too. Whether the color is photographed on separate pieces of film or within the same emulsion, all color photography is synthesized through various parts of the image recording discrete spectra of light.
The earliest motion picture stocks were orthochromatic and recorded cyan (blue and green) light, but not red light. Recording all three major wavelengths of light required making film stock panchromatic to some degree.
Tinting and hand coloring
Since orthochromatic film stock hindered color photography in its beginnings, the first films with color in them utilized aniline dyes in order to create artificial color. Hand-colored films began in 1895 with Thomas Edison's hand-painted Anabelle's Dance made for his Kinetoscope viewers.
Many of the early filmmakers from the first ten years of film also used this method to some degree. George Méliès offered hand-painted prints of his own films at an additional cost over the black and white versions, including the visual-effects pioneering A Trip to the Moon (1902). The film had various parts of the film painted frame-by-frame by twenty-one women in Montreuil[1] in a production-line method.[2]
The first commercially successful stencil color process was introduced in 1905 by Pathé Frères. Pathé Color (renamed Pathéchrome in 1929) became one of the most accurate and reliable stencil coloring systems. It incorporated an original print of a film with sections cut by pantograph in the appropriate areas for up to six colors[1] by a coloring machine with dye-soaked, velvet rollers.[3] After a stencil had been made for the whole film, it was placed into contact with the print to be colored and run at high speed (60 feet per minute) through the coloring (staining) machine. The process was repeated for each set of stencils corresponding to a different color. By 1910, Pathé had over 400 women employed as stencilers in their Vincennes factory. Pathéchrome continued production through the 1930s.[1]
A more common technique emerged in the early 1910s known as film tinting, a process in which either the emulsion or the film base is dyed, giving the image a uniform monochromatic color. This process was popular during the silent era, with specific colors employed for certain narrative effects (red for scenes with fire or firelight, blue for night, etc.).[2]
A complementary process, called toning, replaces the silver particles in the film with metallic salts or mordanted dyes. This creates a color effect in which the dark parts of the image are replaced with a color (e.g., blue and white rather than black and white). Tinting and toning were sometimes applied together.[2]
In the United States, St. Louis engraver Max Handschiegl and cinematographer Alvin Wyckoff created the Handschiegl Color Process, a stencil process first used in Joan the Woman (1917) directed by Cecil B. DeMille, and used in special effects sequences for films such as The Phantom of the Opera (1925). The process employed the principles of three-color lithography to tint films by machine.[1]
Eastman Kodak introduced its own system of pre-tinted black-and-white film stocks called Sonochrome in 1929. The Sonochrome line featured films tinted in seventeen different colors including Peachblow, Inferno, Candle Flame, Sunshine, Purple Haze, Firelight, Azure, Nocturne, Verdante, Aquagreen,[4] Caprice, Fleur de Lis, Rose Doree, and the neutral-density Argent, which kept the screen from becoming excessively bright when switching to a black-and-white scene.[1]
Tinting and toning continued to be used well into the sound era. In the '30s and '40s, some western films were processed in a sepia-toning solution to evoke the feeling of old photographs of the day. Tinting was used as late as 1951 for Samuel Newfield's The Lost Continent for the green lost-world sequences. Alfred Hitchcock used a form of hand-coloring for the orange-red gun-blast at the audience in Spellbound (1945).[1] Kodak's Sonochrome and similar pre-tinted stocks were still in production until the 1970s and were used commonly for custom theatrical trailers and snipes.
Physics of light and color
The principles on which color photography are based were first proposed by Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell in 1855 and presented at the Royal Society in London in 1861.[1] By that time, it was known that light comprises a spectrum of different wavelengths that are perceived as different colors as they are absorbed and reflected by natural objects. Maxwell discovered that all natural colors in this spectrum may be reproduced with additive combinations of three primary colors - red, green, and blue - which, when equally mixed together, produce white light.[1]
Between 1900 and 1935, dozens of natural color systems were introduced, although only a few were successful.[4]
Additive color
The first color systems that appeared in motion pictures were additive color systems. Additive color was practical because no special color stock was necessary. Black and white film could be processed and used in both filming and projection. The various additive systems entailed the use of color filters on both the movie camera and projector. Additive color adds lights of the primary colors in various proportions to the projected image. Because of the limited amount of space to record images on film, and later because the lack of a camera that could record more than two strips of film at once, most early motion-picture color systems consisted of two colors, often red and green or red and blue.[2]
Practical color in the motion picture business began with Kinemacolor, first introduced in 1906.[3] This was a two-color system created in England by Edward R. Turner and George Albert Smith, and promoted by film pioneer Charles Urban's The Charles Urban Trading Company in 1908. It was used for a series of films including the documentary With Our King and Queen Through India, depicting the Delhi Durbar (also known as The Durbar at Delhi, 1912) which was filmed in December 1911. The Kinemacolor process consisted of alternating frames of specially sensitized black-and-white film which were photographed at 32 frames per second through a rotating filter with alternating red and green areas. The film was then printed and projected through the same alternating red and green filter at the same speed. The sense of color was achieved through a combination of separate red and green alternating images and the viewer's persistence of vision.[2][5]
William Friese-Greene invented another additive color system called Biocolour, which was developed by his son Claude Friese-Greene after William's death in 1921. William sued George Albert Smith, alleging that the Kinemacolor process infringed on the patents for his Bioschemes, Ltd.; as a result, Smith's patent was revoked in 1914.[1] Both Kinemacolor and Biocolour had problems with "fringing" or "haloing" of the image, due to the separate red and green images not fully matching up.[1]
French inventor Louis Dufay developed Dufaycolor in 1931, which was a reversal film (producing a positive image on the camera original) that used a mosaic of tiny filter elements of the primary colors between the emulsion and base of the film.[3].
By the nature of the systems, additive color was not economical. Because of the filters used to project the films, more light was required than was typically projected onto the screen, resulting in an image that was dimmer than the average black and white image. The larger the screen, the dimmer the picture. For this, and other case-by-case reasons, additive processes for motion pictures grew out of favor about the time of the Second World War, though a variation of additive color systems are employed for all the color video and computer display systems of today.[2]
Subtractive color
The first successful Subtractive color system began with Kodak's Kodachrome system. Using duplitized film, red and green records were exposed. By bleaching away the silver and replacing it with color dye, a color image was obtained. Kodak's first narrative film with the process was a short subject entitled Concerning $1000 in 1916.
Kodachrome, however, did not find much use in the commercial market, and the first truly successful subtractive color process was William van Doren Kelley's Prizma,[6] an early color process that was first introduced at the American Museum of Natural History in New York City on 8 February 1917 with the short film Our Navy.[7] Prizma began in 1916 as an additive system similar to Kinemacolor. However, after 1917, Kelley reinvented the process as a subtractive one with several years of short films and travelogues, such as Everywhere With Prizma (1919) and Catalina Island (1920) before releasing features such as The Glorious Adventure (1922) and Venus of the South Seas (1924).[citation needed]
The invention of Prizma led to a series of similarly-printed color processes. This bipack color system used two strips of film running through the camera, one recording red, and one recording blue-green light. With the black and white negatives being printed onto duplitized film, the color images were then toned red and blue, effectively creating a subtractive color print.
Leon Forrest Douglass (1869-1940), a founder of Victor Records, developed a system he called Naturalcolor, and first showed a short test film made in the process on 15 May 1917 at his home in Mill Valley, California. The only feature film known to have been made in this process, Cupid Angling (1918) -- starring Ruth Roland and with cameo appearances by Mary Pickford and Douglas Fairbanks -- was filmed in the Lake Lagunitas area of Marin County, California.[8]
After experimenting with more advanced methods of additive systems (including a camera with two apertures (one with a red filter one with green) from 1915 to 1921, Dr. Herbert Kalmus, Dr. Daniel Comstock, and mechanic W. Burton Wescott (who left the company in 1921) developed the subtractive color system for Technicolor. This system used a beam splitter in a specially modified camera to send red and green light waves to separate black-and-white film negatives. From these negatives, two prints were made on film stock with half the normal base thickness, which were toned accordingly: one red, the other green.[3] Then they were cemented together, base-to-base, into a single strip of film. The first film using this process was Toll of the Sea (1922) starring Anna May Wong. Perhaps the most ambitious film made with this process was The Black Pirate (1926), starring and produced by Douglas Fairbanks and directed by Albert Parker. The system was refined through the incorporation of dye imbibition, which allowed for the transferring of dyes from both color matrices into a single print, thus avoiding the problems at attaching two prints back-to-back and allowing for multiple prints to be created from a single pair of matrices.[2]
Technicolor's system was extremely popular for a number of years, but it was a very expensive process: shooting cost three times that of black and white photography and printing costs were no cheaper. By 1932, general color photography had nearly been abandoned by major studios, until Technicolor developed a new advancement to record all three primary colors. Utilizing a special dichroic beam splitter equipped with two 45-degree prisms in the form of a cube, light from the lens was deflected by the prisms and split into two paths to expose each one of three black and white negatives (one each to record the densities for red, green, and blue).[9]
The three negatives were then printed to gelatin matrices, which also completely bleached the image, washing out the silver and leaving only the gelatin record of the image. A receiver print, consisting of a 50% density print of the black and white negative for the green record strip, and including the soundtrack, was struck and treated with dye mordants to aid in the imbibition process (this "black" layer was discontinued in the early 1940s). The matrices for each strip were coated with their complementary dye (yellow, cyan, or magenta), and then each successively brought into high-pressure contact with the receiver, which would imbibe and hold the dyes which collectively were able to render a wider spectrum of colors than the previous technologies.[10] The first animation film with the three-color (also called three-strip) system was Walt Disney's Flowers and Trees (1932), the first short live-action film was La Cucaracha (1934), and the first feature was Becky Sharp (1935).[3]
The real push for color films, and the nearly immediate changeover from black and white production to nearly all color films was pushed forward by the prevalence of television in the early 1950s. In 1947, only 12 percent of American films were made in color. By 1954, that number rose to over 50 percent.[1] The rise in color films was also aided by the breakup of Technicolor's near monopoly on the medium. In 1947, the United States Justice Department filed an antitrust suit against Technicolor for monopolization of color cinematography (even though rival processes such as Cinecolor and Trucolor were in general use). In 1950, a Federal court ordered Technicolor to allot a number of its three-strip cameras for use by independent studios and filmmakers. Although this certainly affected Technicolor, its real undoing was the invention of Eastmancolor that same year.[1]
Monopack color film

Modern color film is based on the subtractive color system, which filters colors from white light through dyed or color sensitive layers within a single strip of film. A subtractive color (cyan, magenta, yellow) is what remains when one of the additive primary colors (red, green, blue) has been removed from the spectrum. Eastman Kodak's monopack color film incorporated three separate layers of color sensitive emulsions into one strip of film. Kodachrome was the first commercially successful application of monopack multilayer film, introduced in 1935.[11]
Eastmancolor, introduced in 1950,[12] was Kodak's first economical, single-strip 35 mm negative-recording system incorporated into one strip of film. This rendered three-strip color photography relatively obsolete, even though, for the first few years, Technicolor's quality control in printing produced colors that were more precise than monopack film and the dye-transfer print would maintain its color much longer than an Eastman print, which would fade over time, mostly due to poor processing and improper storage.[4] The first commercial feature film to use Eastmancolor was the documentary Royal Journey, released in December 1951.[13] Hollywood studios waited until an improved version of Eastmancolor negative came out in 1952 before using it.
Technicolor continued to offer the dye-imbibition print process for projection prints until 1975, and even briefly revived it in 1998. As an archival format, Technicolor prints are one of the most stable color print processes yet created, and prints properly cared for are estimated to retain their color for centuries.[14] With the introduction of low-fade (LPP) films, properly stored (at 45 °F or 7 °C and 25 per cent relative humidity) monopack color film is expected to last, with no fading, a comparative amount of time. Kodachrome transparency film stored at 0oF (−18 °C) is predicted to last a similar length in time without noticeable picture degradation. Improperly stored monopack color film from before 1983 can incur a 30 per cent image loss in as little as 25 years.[15]
How modern color film works
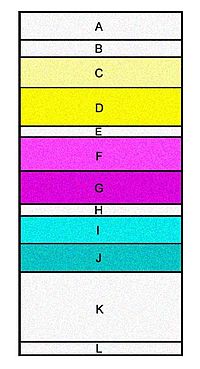
Modern color film is made up of many different layers all working together to create the color image. In color negative films there are three main color layers: the blue record, green record, and red record; each made up of two separate layers containing silver halide crystals and dye-couplers. A cross-sectional representation of a piece of developed color negative film is shown in the figure at right. Each layer of the film is so thin that the composite of all layers, in addition to the triacetate base and antihalation backing, is less than 0.0003" (8 µm) thick.[16]
The three color records are stacked as shown at right with a UV filter on top to keep the non-visible ultraviolet radiation from exposing the silver-halide crystals, which are naturally sensitive to UV light. Next are the fast and slow blue-sensitive layers, which, when developed, form the latent image. When the exposed silver-halide crystal is developed, it is coupled with a dye grain of its complementary color. This forms a dye "cloud" (like a drop of water on a paper towel) and is limited in its growth by development-inhibitor-releasing (DIR) couplers, which also serve to refine the sharpness of the processed image by limiting the size of the dye clouds. The dye clouds formed in the blue layer are actually yellow (the opposite or complementary color to blue).[17] There are two layers to each color; a "fast" and a "slow." The fast layer features larger grains that are more sensitive to light than the slow layer, which has finer grain and is less sensitive to light. Silver-halide crystals are naturally sensitive to blue light, so the blue layers are on the top of the film and they are followed immediately by a yellow filter, which stops any more blue light from passing through to the green and red layers and biasing those crystals with extra blue exposure. Next are the red-sensitive record (which forms cyan dyes when developed); and, at the bottom, the green-sensitive record, which forms magenta dyes when developed. Each color is separated by a gelatin layer which prevents silver development in one record from causing unwanted dye formation in another. The bottom of the whole stack (film base) is an anti-halation layer that prevents bright light from reflecting off the clear base of the film and passing back through the negative to double-expose the crystals and create halos of light around bright spots. In color film, this backing is rem-jet, which is a black-pigmented, non-gelatin layer on the back of the film base and is removed in the developing process.[16]
Eastman Kodak manufactures film in 54-inch (1,372 mm) wide rolls. These rolls are then slit into various sizes (65 mm, 35 mm, 16 mm) as needed.
Modern manufacturers of color film for motion picture use
- See also List of motion picture film stocks
Motion picture film, primarily because of the rem-jet backing, requires different processing than standard C-41 process color film. The process necessary is Eastman Color Negative 2 (ECN-2), which has an initial step using an alkaline bath to remove the backing layer. There are also minor differences in the remainder of the process. If motion picture negative is run through a standard C-41 color film developer bath, the rem-jet backing will partially dissolve and destroy the integrity of the developer and, potentially, ruin the film.
There are two main companies manufacturing color film for motion picture use: Eastman Kodak and Fujifilm.
Kodak color motion picture films
In the late 1980s, Kodak introduced the T-Grain emulsion, a technological advancement in the shape and make-up of silver halide grains in their films. T-Grain is a tabular silver halide grain that allows for greater overall surface area, resulting in greater light sensitivity with a relatively small grain and a more uniform shape which results in a less overall graininess to the film. This made for sharper and more sensitive films. The T-Grain technology was first employed in Kodak's EXR line of motion picture color negative stocks.[18] This was further refined in 1996 with the Vision line of emulsions, followed by Vision2 in the early 2000s and Vision3 in 2007.
Fuji color motion picture films
Fuji films also integrate tabular grains in their SUFG (Super Unified Fine Grain) films. In their case, the SUFG grain is not only tabular, it is hexagonal and consistent in shape throughout the emulsion layers. Like the T-grain, it has a larger surface area in a smaller grain (about one-third the size of traditional grain) for the same light sensitivity. In 2005, Fuji unveiled their Eterna 500T stock, the first in a new line of advanced emulsions, with Super Nano-structure Σ Grain Technology.
See also
- List of color film systems
- List of film formats
- List of motion picture film stocks
- Film stock
- Photographic film mainly about film for stills
- Film base
- Kinemacolor
- Prizma
- Multicolor
- Cinecolor
- Technicolor
- 35 mm film
- 135 film
- Color photography
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Cook, David A. (1990) (2nd ed). A History of Narrative Film W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-95553-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g Konigsberg, Ira (1987). The Complete Film Dictionary Meridan PAL books. ISBN 0-452-00980-4.
- ^ a b c d e Katz, Ephraim (1994) (2nd ed). The Film Encyclopedia HarperCollins Press. ISBN 0-06-273089-4
- ^ a b c Monaco, James (1981) (Revised ed) How to Read a Film Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-502806-6.
- ^ (1917) "Kinemacolor" How to Make and Operate Moving Pictures Funk & Wagnalls. Courtesy of Wide Screen Museum
- ^ Slide, Anthony. (1990) "Prizma Color" The American Film Industry: A Historical Dictionary Limelight p. 271. ISBN 0-87910-139-3
- ^ Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian. (1951) Colour Cinematography Chapman and Hall press.
- ^ Gracyk, Tim. Leon F. Douglass: Inventor and Victor's First Vice-President (Retrieved on 2007-03-26)
- ^ Slide, Anthony. (1990) "Technicolor" The American Film Industry: A Historical Dictionary Limelight pp. 338-340. ISBN 0-87910-139-3
- ^ Hart, Martin (2003). "The History of Technicolor" Widescreenmuseum.com. Retrieved 2006-07-07.
- ^ Exploring the Color Image (1996) Eastman Kodak Publication H-188.
- ^ Chronology of Motion Picture Films: 1940–1959, Kodak.
- ^ Chronology of Motion Picture Films: 1940–1959, Kodak.
- ^ Wilhelm, Henry with Brower, Carol (1993) The Permanence and Care of Color Photographs. Preservation Publishing Company. Chapter 10 "The Extraordinarily Stable Technicolor Dye Imbibition Motion Picture Color Print Process" pp. 345-366
- ^ Holben, Jay (June 1999). "Preserving Negatives for the Next Generation" American Cinematographer Magazine ASC Press. pp. 147-152.
- ^ a b Kodak Motion Picture Film (H1) (4th ed). Eastman Kodak Company. ISBN 0-87985-477-4
- ^ Holben, Jay. (April 2000). "Taking Stock" Part 1 of 2. American Cinematographer Magazine ASC Press. pp. 118-130
- ^ Probst, Christopher. (May 2000). "Taking Stock" Part 2 of 2 American Cinematographer Magazine ASC Press. pp. 110-120
Further reading
- John Waner, Hollywood's Conversion of All Production to Color, Tobey Publishing, 2000.
External links
- The American Widescreen Museum has a thorough treatise on early motion picture color processes.
- List of films in Prizma at IMDb
- "Animation in Natural Colours", Moving Pictures, 1912.
