Jersey City, New Jersey: Difference between revisions
→External links: rm link, per external links guidelines |
|||
| Line 332: | Line 332: | ||
*[http://www.jclist.com/ Jersey City List] |
*[http://www.jclist.com/ Jersey City List] |
||
*[http://www.wearenew.com/ NEW Contemporary Guide to Jersey City] |
*[http://www.wearenew.com/ NEW Contemporary Guide to Jersey City] |
||
*[http://andrewprokos.com/photos/new-york/skylines/ Views of Lower Manhattan from Jersey City, NJ] |
|||
*[http://www.jerseycityonline.com/jerseycity/municipal_government.htm Jersity City Online - Questions about City Government] |
*[http://www.jerseycityonline.com/jerseycity/municipal_government.htm Jersity City Online - Questions about City Government] |
||
*[http://www.gentrify.us/jerseycity.html Jersey City Gentrification - Article, photos, interactive map and other resources] |
*[http://www.gentrify.us/jerseycity.html Jersey City Gentrification - Article, photos, interactive map and other resources] |
||
Revision as of 14:58, 9 July 2007
Jersey City, New Jersey | |
|---|---|
 | |
Flag of Jersey City, New Jersey Flag | |
 Location of Jersey City within New Jersey. | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New Jersey |
| County | Hudson |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Jerramiah T. Healy |
| • Business Administrator | Brian P. O'Reilly |
| Population (2005)[1] | |
• Total | 239,614 |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| Website | www.cityofjerseycity.com |
Jersey City is a city in Hudson County, New Jersey, United States. As of the United States 2000 Census, the population of Jersey City was 240,055, making it New Jersey's second-largest city, trailing Newark. It is the county seat of Hudson County.Template:GR
Jersey City lies on the west bank of the Hudson River across from Lower Manhattan in New York City, and is part of the New York metropolitan area. A commercial and industrial center, it is a port of entry and a manufacturing center. With 11 miles (17.7 km) of waterfront and significant rail connections, Jersey City is an important transportation terminus and distribution center. It has railroad shops, oil refineries, warehouses, and plants that manufacture a diverse assortment of products, including chemicals, petroleum, electronics, textiles, and cosmetics. Jersey City has benefited from its location near the island of Manhattan, as many of its companies are extensions of businesses headquartered there. Recent developments have included increased housing and shopping areas; some parts of the city, however, remain run-down after years of commercial inactivity.
Jersey City is one of the most ethnically and culturally diverse cities in the country, with an almost equal mix of non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic blacks, Asians, and Latinos. Of all cities in the United States, it has one of the largest Arab and Muslim populations and proportions, one of the largest Asian proportions, and one of the largest proportions of various Latino and Hispanic ethnicities outside the Southwest. It also has higher fractions of Jews, Italians, Cubans, Filipinos, Polish, Indians, and Irish than most cities in the nation.
History
The Lenape and New Netherland

The land comprising what is now Jersey City was wilderness inhabited by the Lenape, a collection of tribes (later called Delaware Indian). In 1609, Henry Hudson, seeking an alternate route to East Asia, anchored his small vessel The Half Moon at Sandy Hook, Harsimus and Weehawken Cove, and elsewhere along what was later named the North River. After spending nine days surveying the area and meeting its inhabitants, he returned to The Netherlands. The Dutch organized the United New Netherlands Company to manage this new territory and in June 1623, The New Netherlands became a Dutch province, with headquarters in New Amsterdam. Michael Reyniersz Pauw, Lord of Achtienhoven, a burgermeester of Amsterdam and a director of the West India Company, received a land grant as patroon on the condition that he would establish a settlement of not fewer than fifty persons within four years. He chose the west bank of the Hudson River and purchased the land from the Lenape. This grant is dated November 22, 1630 and is the earliest known conveyance for what are now Hoboken and Jersey City. Pauw, however was an absentee landlord who neglected to populate the area and was obliged to sell his holdings back to the Company in 1633.[2] That year, a house was built at Communipaw, an area adjacent to present-day Liberty State Park. for Jan Evertsen Bout, superintendent of the colony, which had been named Pavonia (the Latinized form of Pauw's name).[3] Shortly after, another house was built at Harsimus Cove (near the present-day corner of Fourth Street and Marín Boulevard) and became the home of Cornelius Van Vorst, who had succeeded Bout as superintendent, and whose family would become influential in the development of the city. Relations with the Lenape deteriorated, in part because of the colonialist's mismanagement and misundertanding of the indigenous people, and led to series of raids and reprisals and the virtual destruction of the settlement the west bank. During Kieft's War, approximately eighty Lenapes were killed by the Dutch in a massacre at Pavonia on the night of February 25, 1643.[4].

Scattered communities of farmsteads characterized the Dutch settlements at Pavonia, Communipaw, Harsimus, Paulus Hook, Hoebuck, Awiehaken, and other lands "behind Kil van Kull". The first village (located inside a palisaded garrison) established on what is now Bergen Square in 1660. Bergen Township, and is considered to be the oldest town in what would become the state of New Jersey. [2].
Early America
During the American Revolutionary War the area was in the hands of the British who controlled New York, until Paulus Hook was captured by Major Light Horse Harry Lee on August 19, 1779. After the war Alexander Hamilton and other prominent New Yorkers and New Jerseyeans attempted to develop the area that would become historic dowtown Jersey City and laid out the city squares and streets that still characterize the neighborhood, giving them names also seen in Lower Manhattan or after war heros (Grove, Varick, Mercer, Wayne, Monmouth, and Montgomery among them) The oldest surviving house in Jersey City is the stone Van Vorst house of 1742.
Underground Railroad
During the 19th century, Jersey City played an integral role in the Underground Railroad. Four routes through New Jersey converged in Jersey City.[5]
Incorporation and merger
The City of Jersey was incorporated by an Act of the New Jersey Legislature on January 28, 1820, from portions of North Bergen Township, while the area was still a part of Bergen County. The city was reincorporated on January 23, 1829, and again on February 22, 1838, at which time it became completely independent of North Bergen and was given its present name. On February 22, 1840, it became part of the newly-created Hudson County.[6]
As Jersey City grew, several neighboring communities were annexed: Van Vorst Township (March 18, 1851), Bergen City and Hudson City (both on May 2, 1870), and Greenville Township (February 4, 1873).[6] These annexations have resulted in the current boundaries of Jersey City.
Jersey City was a dock and manufacturing town for much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Much like New York City, Jersey City has always been a landing pad for new immigrants to the United States. In its heyday before World War II, German, Irish, and Italian immigrants found work at Colgate, Chloro, or Dixon Ticonderoga. However, the largest employers at the time were the railroads, whose national networks dead-ended on the Hudson River. The most significant railroad for Jersey City was the Pennsylvania Railroad Company whose eastern terminus was in the Downtown area until 1911, when the company built the first tunnel under the river to Penn Station, New York. Before that time, Pennsy rail passengers transferred in Jersey City to ferries headed to Manhattan or to trolleys that fanned out through Hudson County and beyond. The last streetcar was decommissioned in 1949 and today there are three passenger rail systems passing through or serving Jersey City. Several New Jersey Transit heavy rail lines pass through Jersey City en route to nearby Hoboken Terminal. There are four underground Port Authority Trans Hudson (PATH) train stations in Jersey City, which serve as a subway system for Jersey City and link the city by rail to the cities of Newark New Jersey and Manhattan. There is also a newly constructed multi-billion Hudson Bergen Light Rail (HBLR) which is a modern electric trolley system that provides a north-south mass transit connection between Jersey City and other Hudson County communities.
Black Tom explosion
The Black Tom explosion occurred on July 30, 1916 as an act of sabotage on American ammunition supplies by German agents to prevent the materials from being used by the Allies in World War I.
Frank Hague
From 1917 to 1947, Jersey City was ruled by Mayor Frank Hague. The Jersey City History Web Site states that "His name is synonymous with the early twentieth century urban American blend of political favoritism and social welfare known as bossism." "Hanky-Panky," as he was known then, ruled the city with an iron fist while, at the same time, molding governors, United States senators, and judges to his whims. Boss Hague was known to be loud and vulgar, and would often dismiss his enemies as "reds" or "commies." Citizens of Jersey City dared not speak out against him for fear of being harassed by Hague's police or being ostracized or publicly embarrassed in some way. Remarkably, Hague lived like a millionaire, despite having an average annual salary of $8,000. He was able to maintain a fourteen-room duplex apartment in Jersey City, a suite at the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel in Manhattan, and a palatial summer home in Deal, New Jersey, and he traveled to Europe yearly in the royal suites of the best liners.

The city developed a reputation for corruption, even after Hague left office. By the 1970s, it was caught up in a wave of urban decline that saw many of its wealthy residents fleeing to the suburbs, and led to an influx of working class citizens scarred by rising crime, civil unrest, political corruption, and economic hardship. From 1950 to 1980, Jersey City lost 75,000 residents, and from 1975 to 1982, it lost 5,000 jobs, or 9% of its workforce.[7] The city experienced a surge of violent crime during this period. New immigrants sought refuge in Jersey City because of its low housing costs, despite the decline in many of its neighborhoods due to decay, abandonment, or neglect.
Renaissance
Many formerly abandoned buildings are being renovated, and the light rail line from North Bergen through Hoboken extends through eastern Jersey City, with branches to the western reaches of the city and south to Bayonne. As the waterfront continues to grow, Jersey City's downtown neighborhoods are experiencing rapid gentrification as professionals working in Manhattan are beginning to move in. Many of Jersey City's neighborhoods, including the downtown area, Jersey City Heights, and West Bergen, have an impressive stock of historic houses in the Victorian style.
Also, many financial corporations including Goldman Sachs, Chase Manhattan Bank, Lehman Brothers, Merrill Lynch, and the investment firm Charles Schwab have relocated from New York City to Jersey City or expanded their offices in Jersey City since the September 11, 2001 attacks.
The Jersey City skyline is developing as Jersey City gains popularity. The skyline recently gained five new buildings with heights over 100 m. This group includes a 238 m high-rise at 30 Hudson Street. Completed in 2004, it is the one of the 200 tallest buildings in the world.[8]
Government
Local government
Jersey City is currently governed under the Faulkner Act (Mayor-Council) system of municipal government.
The current Mayor of Jersey City is Jerramiah Healy. The current Business Administrator of Jersey City is Brian P. O'Reilly.
Members of the City Council are:[9]
- Mariano Vega, Jr., Council President
- Willie Flood, Councilwoman-at-Large
- Peter Brennan, Councilman-at-Large
- Michael Sottolano, Ward A - Greenville, Councilman
- Mary Spinello, Ward B - Westside, Councilwoman
- Steve Lipski, Ward C - Journal Square, Councilman
- William Gaughan, Ward D - Heights, Councilman
- Steven Fulop, Ward E - Downtown, Councilman
- Viola Richardson, Ward F - Bergen, Councilwoman
Jersey City Municipal Court gets a fairly heavy load of criminal cases along with some traffic violations. Mayor Healy is a member of the Mayors Against Illegal Guns Coalition[10], a bi-partisan group with a stated goal of "making the public safer by getting illegal guns off the streets." The Coalition is co-chaired by by Boston Mayor Thomas Menino and New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg.
Federal, state and county representation
Jersey City is in the Ninth, Tenth and Thirteenth Congressional Districts and is part of New Jersey's 31st, 32nd and 33rd Legislative Districts.[11]
For the 119th United States Congress, New Jersey's 9th congressional district is represented by Nellie Pou (D, North Haledon)[12] For the 119th United States Congress, New Jersey's 10th congressional district is represented by LaMonica McIver (D, Newark).[13] New Jersey's 13th congressional district is represented by Albio Sires (D, West New York). New Jersey is represented in the United States Senate by Democrats Cory Booker (Newark, term ends 2027) and Andy Kim (Moorestown, term ends 2031).[14]
For the 2024-2025 session, the 31st legislative district of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Angela V. McKnight (D, Jersey City) and in the General Assembly by Barbara McCann Stamato (D, Jersey City) and William Sampson (D, Bayonne).[15] For the 2024-2025 session, the 32nd legislative district of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Raj Mukherji (D, Jersey City) and in the General Assembly by John Allen (D, Hoboken) and Jessica Ramirez (D, Jersey City).[16] For the 2024–2025 session, the 33rd legislative district of the New Jersey Legislature is represented in the State Senate by Brian P. Stack (D, Union City) and in the General Assembly by Julio Marenco (D, North Bergen) and Gabe Rodriguez (D, West New York).[17] Template:NJ Governor
Hudson County is governed by the directly elected Hudson County Executive and by a Board of County Commissioners, which serves as the county's legislative body. As of 2025, Hudson County's Hudson County Executive is Craig Guy (D, Jersey City), whose term of office expires December 31, 2027.[18] Hudson County's Commissioners are Kenneth Kopacz (D, District 1 - Bayonne and parts of Jersey City; 2026, Bayonne),[19][20] William O'Dea (D, District 2 - Western Jersey City; 2026, Jersey City),[21][22] Vice Chair Jerry Walker (D, District 3 - South Eastern Jersey City[23][24] Yraida Aponte-Lipski (D, District 4 - North Eastern Jersey City; 2026, Jersey City),[25][26] Chair Anthony L. Romano Jr. (D, District 5 - Hoboken and parts of Jersey City; 2026, Hoboken),[27][28] Fanny J. Cedeño (D, District 6 - Union City; 2026, Union City),[29][30] Caridad Rodriguez (D, District 7 - Weehawken, West New York, and Gutenberg; 2026, West New York),[31][32] Robert Bascelice (D, District 8 - West New York, North Bergen, Secaucus; 2026, North Bergen)[33][34] and Albert J. Cifelli (D, District 9 - Secaucus, Kearny, East Newark, Harrison; 2026, Harrison)[35][36][37][38][39]
Hudson County's constitutional officers are County Clerk E. Junior Maldonado (D, Jersey City, 2027),[40][41] Register Jeffrey Dublin (D, Jersey City, 2026)[42][43][44] Sheriff Frank X. Schillari (D, Jersey City, 2025)[45][46] and Surrogate Tilo E. Rivas (D, Jersey City, 2029)[47][48][49]
Education
Colleges and universities
Jersey City is home to the New Jersey City University (NJCU) and Saint Peter's College, both of which are located in the city's West Side district. It is also home to Hudson County Community College, which is located in Journal Square. The University of Phoenix has a small location at Newport, and Rutgers University offers MBA classes at Harborside Center.
Public schools
The Jersey City Public Schools serve students in kindergarten through twelfth grade. JCPS is an Abbott District.
Dr. Ronald E. McNair Academic High School, the most recently founded public school in Jersey City, was the top-ranked public high school in New Jersey out of 316 schools statewide, in New Jersey Monthly magazine's September 2006 cover story on the state's Top Public High Schools[50] and was selected as 15th best high school in the United States in Newsweek magazine's national 2005 survey.[51] In contrast, William L. Dickinson High School, located near Jersey City's downtown area, is the oldest high school in the city. It is also one of the largest schools in Hudson County, in terms of student population. Opened in 1906 as the Jersey City High School, it is one of the oldest sites in Jersey City. It is a three-story Beaux-Arts structure located on a hilltop facing the Hudson River. Other public high schools in Jersey City are James J. Ferris High School, the Hudson County Schools of Technology (which also has campuses in North Bergen and Secaucus), Liberty High School, Lincoln High School and Henry Snyder High School.
Private schools
Hudson Catholic Regional High School, a regional high school established in 1964 for young men of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Newark, serves around 550 young men and is run by the De La Salle Christian Brothers. St. Peter's Preparatory High School is a private high school founded in 1872 by the Society of Jesus. It is the only Jesuit high school in New Jersey.
Other private high schools in Jersey City include the Academy of St. Aloysius, Kenmare High School for Women, St. Anthony High School two-time national champions in Boys High School Basketball, Saint Aloysius High School, Saint Dominic Academy and St. Mary High School.
There are many choices for grade school, including Resurrection School and the OLC School. Catholic schools serve every area of the City and a number of other charter and private schools are also available. Genesis Educational Center [3] is a private Christian school located in historic downtown Jersey City (ages newborn through 8th grade).
Neighborhoods

Jersey City consists of Six Districts or Wards; Greenville, West Side, Journal Square, The Heights, Downtown, and Bergen/Lafayette. Each of these Districts is comprised of smaller neighborhoods, for example the Paulus Hook Neighborhood of the Downtown District and the Western Slope Neighborhood of The Heights District. Jersey City is a city of neighborhoods, each with a different aesthetic and architectural style, to some degree.
Downtown Jersey City includes the Waterfront (including Newport, Paulus Hook, and Exchange Place), Hamilton Park, Grove Street, Harsimus Cove, Van Vorst Park, and Liberty State Park. Jersey City Heights (or, simply, "The Heights") includes the Western Slope and the Central Avenue Shopping area. Journal Square, site of the Jersey Journal and PATH Transportation Center, West Side features West Bergen/Lincoln Park and Hudson Mall, Bergen/Lafayette where Communipaw Avenue connects the West Side with Liberty State Park, Greenville featuring Port Liberte and residential neighborhoods.
Downtown Jersey City
Downtown Jersey City is the area from the Hudson River westward to the Newark Bay Extension of the New Jersey Turnpike (Interstate 78) and the New Jersey Palisades; it is also bounded by Hoboken to the north and Liberty State Park to the south.
Newport and Exchange Place are redeveloped waterfront areas comprised mostly of residential towers, hotels and office buildings. Newport is a planned mixed-use community, built on the old Erie Lackawanna Railway yards, made up of residential rental towers, condominiums, office buildings, a marina, schools, restaurants, hotels, Newport Centre Mall, a waterfront walkway, transportation facilities, and on-site parking for more than 15,000 vehicles. Newport had a hand in the renaissance of Jersey City although, before ground was broken, much of the downtown area had already begun a steady climb (much like Hoboken). Some critics have derided the Newport development for its isolation because it is cut off from the rest of the city by the Newport Centre Mall and other big box retail.
Exchange Place, the first part of Jersey City to redevelop, was built on the grounds of the old Jersey City Penn Station, ferry and shipping terminals. It is now a bustling business and financial district.
To the west lay three brownstone neighborhoods with "historic" protected districts — Hamilton Park, Van Vorst Park, and Harsimus Cove — separated from the waterfront by a legacy of older infrastructure, big-box development, and old warehouses still awaiting re-use.
Paulus Hook is another neighborhood with a historic designated zone. It borders Exchange Place and Liberty State Park on the waterfront, and blends older brownstone-lined streets with newer luxury developments. The Essex Street stop on the Hudson-Bergen Light Rail cuts through the southern portion of the neighborhood. The area has become increasingly active with development to the east and the construction of the light rail; many of its streets are lined with shops, and restaurants with outdoor seating.

The Jersey City Medical Center operated in the 20th century on Baldwin Avenue south of Journal Square. Now JCMC is located on Grand Street downtown.
Journal Square
Once the commercial heart of Jersey City, Journal Square has become rather derelict in recent years, but is in the process of rehabilitation, in part because of the efforts of the Journal Square Restoration Corporation (JSRC) and the Jersey City Economic Development Corporation (JCEDC). Here, Kennedy Boulevard and Bergen Avenue, main thoroughfares in the city, are at their widest, lined on both sides by brick houses and medium-density apartment complexes. The Stanley Theater, currently a Jehovah's Witness meeting hall, and Loew's Jersey Theater on Kennedy Boulevard are among the city's most noted landmarks, and are two of the best preserved movie palaces in the Tri-State area. Directly across Kennedy Boulevard from the Loews is the Journal Square Transportation Center (JSTC), which houses the Journal Square PATH station and the city's largest bus terminal. The Journal Square PATH station serves as a hub between Newark, Newark Airport, and the World Trade Center PATH Station in New York City, approximately 10 minutes ride from Journal Square. Buses from the JSTC connect Jersey City to communities throughout Hudson County, as well as to the Port Authority Bus Terminal in Midtown Manhattan. Saint Peter's College is located about 10 blocks south of Journal Square. To the north of the square on Newark Avenue lies India Square, one of the larger and livelier Indian neighborhoods in New Jersey.
West Side
Jersey City's West Side is very ethnically diverse. Many ethnic grocery shops (Filipino, Indian, West Indian) line West Side Avenue. West Side runs from Broadway near U.S. Route 1/9 Truck along Route 440 to the Bayonne city line. This neighborhood is served by the Hudson-Bergen Light Rail at Claremont Avenue. West Side also features Hudson Mall, Jersey City Incinerator Authority, Lincoln County Park and Society Hill running along Route 440 and U.S. 1/9 Truck. In this district, at the old Roosevelt Stadium, Jackie Robinson broke the color barrier in Minor League Baseball before his Major League Baseball debut.
Greenville
Greenville (also known as "The Hill") is primarily residential--once the home of Frank Sinatra, with a principal commercial corridor surrounding Danforth Avenue. The neighborhood is adjacent to Greenville Yards, a former Conrail rail yard now being used as a distribution center. Jersey City includes the Port Liberté development, a high-end gated residential community on the Hudson River waterfront, as being part of Greenville, although Jersey City residents typically consider Port Liberté to be distinct from Greenville as they are separated by the New Jersey Turnpike extension (Interstate 78) and represent vastly different socioeconomic backgrounds.
The Greenville section runs from about 10 blocks south of Communipaw Avenue to the Bayonne city line. It includes some of the most depressed areas in the city, but is slowly being revitalized, particularly along the light rail line. The crime rate is higher here than in any other part of Jersey City and many streets are lined with abandoned homes, but municipal aid over the past few years has helped in rebuilding many of them and in bringing life back to many of Greenville's neglected streets. With the gentrification of the downtown area, many of the city's working-class tenants have moved into this area.
The Heights
Jersey City Heights (aka "The Heights") is a neighborhood atop the New Jersey Palisades overlooking Hoboken to its east and the Hudson River. It is comprised mostly of two- and three-family houses, and remains traditionally middle-class. The primary commercial strip is Central Avenue, with residential districts flanking it on both sides. Six blocks to the east, and parallel to it, are Palisade and Ogden Avenues, both of which offer breathtaking views of the Manhattan skyline from Riverside Park. The Hudson-Bergen Light Rail station at Congress Street and Ninth Street connect this area of the Heights directly to the Hoboken PATH train and regional New Jersey Transit train lines. Many stately Victorian and Edwardian homes contribute to the attractiveness of the Heights, particularly along Summit Avenue and Sherman Place as well as areas to the east of Central Avenue. Pershing Field is a park near the center of this district, offering green space, a running track, several baseball fields, basketball and tennis courts, an olympic size swimming pool and an ice skating rink. Adjacent to Pershing Field Park is an abandoned reservoir which constitutes one of the largest patches of green space in Jersey City Heights. The future of the reservoir has been hotly contested as business interests, city government, and environmentalist groups have each proposed a different use for the land. Recently, the Mayor of Jersey City has announced that the city has decided to move forward with plans to develop the reservoir into a nature preserve which will be open to the public.
Bergen/Lafayette
Bergen/Lafayette, formerly Bergen City, New Jersey, lies between Greenville on the south and Journal Square on the north. It also borders with West Side and Liberty State Park. Communipaw Avenue and Bergen Avenue (approaching Journal Square) both have many small shops.
Geography
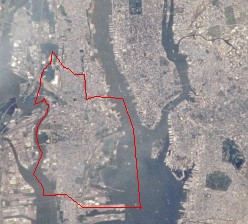
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 54.7 km² (21.1 mi²). 38.6 km² (14.9 mi²) of it is land and 16.1 km² (6.2 mi²) of it is water. It has the smallest land area of the 100 largest cities in America. The total area is 29.37% water. Jersey City is bordered to the east by the Hudson River, to the north by Union City and Hoboken, to the west by Kearny and Newark, and to the south by Bayonne.
Given its proximity to Manhattan, Jersey City and Hudson County are sometimes referred to as New York City's sixth borough.[52]
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1840 | 3,072 | — | |
| 1850 | 6,856 | 123.2% | |
| 1860 | 29,226 | 326.3% | |
| 1870 | 82,546 | 182.4% | |
| 1880 | 120,722 | 46.2% | |
| 1890 | 163,003 | 35.0% | |
| 1900 | 206,433 | 26.6% | |
| 1910 | 267,779 | 29.7% | |
| 1920 | 298,103 | 11.3% | |
| 1930 | 316,715 | 6.2% | |
| 1940 | 301,173 | −4.9% | |
| 1950 | 299,017 | −0.7% | |
| 1960 | 276,101 | −7.7% | |
| 1970 | 260,350 | −5.7% | |
| 1980 | 223,532 | −14.1% | |
| 1990 | 228,537 | 2.2% | |
| 2000 | 240,055 | 5.0% | |
| 2005 (est.) | 239,614 | [1] | |
| historical data sources:[53][54][55] | |||
As of the censusTemplate:GR of 2000, there were 240,055 people, 88,632 households, and 55,660 families residing in the city. The United States Census Bureau has estimated the 2004 population at 239,079. The population density was 6195.2/km² (16,045.6/mi²). There were 93,648 housing units at an average density of 2,423.4/km² (6,278.3/mi²). The racial makeup of the city was 34.01% White, 28.32% African American, 0.45% Native American, 16.20% Asian, 0.08% Pacific Islander, 15.11% from other races, and 5.84% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 28.31% of the population. Relations between ethnic groups in this heavily-mixed population are not always amicable, as evidenced by incidents such as the infamous Dotbusters gang attacks of 1987 against residents of South Asian descent, and, more recently, the March 2007 defacing of a local sports field with Nazi slogans and racial slurs.
Of all households, 31.1% have children under the age of 18 living there, 36.4% were married couples living together, 20.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 37.2% were non-families. 29.2% of all households were made up of individuals and 8.2% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.67 and the average family size was 3.37.
The age distribution is spread out with 24.7% under the age of 18, 10.7% from 18 to 24, 35.1% from 25 to 44, 19.7% from 45 to 64, and 9.8% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 32 years. For every 100 females there were 95.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 92.6 males.
The median income of its households is $37,862, and the median income of its families is $41,639. Males had a median income of $35,119 versus $30,494 for females. The per capita income for the city was $19,410. About 16.4% of families and 18.6% of the population were below the poverty line, including 27.0% of those under age 18 and 17.5% of those age 65 or over.
Transportation
Of all Jersey City commuters, 8.17% walk to work, and 40.26% take public transit. This is the second highest percentage of public transit riders of any city with a population of 100,000+ in the United States, behind only New York City and ahead of Washington, D.C.
Rail
- Hudson-Bergen Light Rail: Thirteen stations in Jersey City along two branches. Southbound from Pavonia/Newport through downtown to Liberty State Park with one spur to Bayonne and one spur to West Side Avenue. Northbound to Hoboken Terminal, and along Hoboken's western perimeter at 2nd Street and 9th/Congress Streets (with elevator service to the Heights) to the Weehawken waterfront, and Bergenline and Tonnelle Avenues.
- PATH: 24-hour subway service with four stations in Jersey City: Exchange Place, Pavonia-Newport, Grove Street, and Journal Square to Hoboken Terminal (HOB), midtown Manhattan (33rd) (along 6th Ave to Herald Square/Pennsylvania Station), World Trade Center (WTC), and Newark Penn Station (NWK).
- Hoboken Terminal-New Jersey Transit Hoboken Division: Main Line (to Suffern, and in partnership with MTA/Metro-North, express service to Port Jervis), Bergen County Line, and Pascack Valley Line (limited AM inbound and PM outbound service), all via Secaucus Junction (where transfer is possible to Northeast Corridor Line); Montclair-Boonton Line and Morris and Essex Lines (both via Newark Broad Street Station); North Jersey Coast Line (limited service as Waterfront Connection via Newark Penn Station to Long Branch and Bay Head); Raritan Valley Line (limited service via Newark Penn Station);
Water
- NY Waterway operates ferries between Newport, Harborside, Colgate, Liberty Harbor, Port Liberté and the World Financial Center and Pier 11 lower Manhattan and 39th Street in midtown Manhattan, where free transfer is available to a variety of "loop" buses.
- Circle Line provides service between Liberty State Park and Ellis and Liberty Island
Surface
The Journal Square Transportation Center, Exchange Place, and Hoboken Terminal (just over the city line's northeast corner) are major origination/destination points for buses. Service is available to numerous points within Jersey City, Hudson County, and some suburban areas as well as to Newark on the 1, 2, 22, 43, 64, 68, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 88, 125, 305, 319, 981 routes, and to the Port Authority Bus Terminal in Midtown Manhattan via the 125 and 126 routes.[56]
Air
- Newark Liberty Airport (EWR), is the second international airport serving the New York City metropolitan area, and directly connected to Jersey City via PATH train.
- LaGuardia Airport (LGA) is in Flushing, Queens
- John F. Kennedy Airport (JFK)on Jamaica Bay in Queens
- Teterboro Airport, in the Hackensack Meadowlands, serves private and corporate planes
Road
- Holland Tunnel: in downtown Jersey City with eastern terminus at Canal Street, Manhattan
- Highways include the New Jersey Turnpike, Interstate 78, U.S. Routes 1 and 9, and New Jersey Routes 139 and 440.
Street alignments
A majority of the streets in Jersey City are named streets, with Downtown the only district with numbered streets - in an East-West alignment.
- The numbered streets go from 1 to 18 and cover only half of Downtown. Some numbered streets are discontinuous, being interrupted at various points by buildings. Second Street is the only numbered street in the city that runs from the Palisades to the edge of the Hudson River without obstruction.
- Many streets are named for Jersey City families who owned land in the city. Examples; Van Vorst Street (the Van Vorst Family) and Monmouth Street (the Monmouth Family).
- Many avenues are named after cities or other locations, whether in or out of New Jersey. Examples; Newark Avenue, Communipaw Avenue, New York Avenue, and Palisades Avenue.
- All boulevards are named after famous people in history and cross city lines. These include Luis Muñoz Marín Boulevard (named for Luis Muñoz Marín, the first elected Governor of Puerto Rico), which crosses the Hoboken city line, and John F. Kennedy Boulevard - County Route 501.
- Most drives are named after people in city and world history and are wholly contained within a district. Examples; Martin Luther King Drive in Bergen/Lafeyette, Christopher Columbus Drive in Downtown, and Audrey Zapp Drive in Liberty State Park.
- Jersey City has small residential streets called Parkways. They feature a street island, and are commonly found in the Greenville District. Examples; Stegman Parkway, and Wegman Parkway.
- There are several "roads" in Jersey City including Old Bergen Road, Caven Point Road, Secaucus Road and Paterson Plank Road.
- The names of many residential streets in Jersey City change along their route. One notable continuity change is Grove Street. It is named Grove Street between the Hoboken border and Boyle Plaza, Manila Avenue between 12th Street and 1st Street, then Grove Street again between 1st Street and Grand Street.
Community
- Ellis Island is inside Jersey City's borders, and is managed jointly by the states of New Jersey and New York. About 10 years ago the State of New York went to the Supreme Court to sue the State of New Jersey over the ownership of this real estate, but New York lost, and the US Government weighed in on New Jersey's side.[57]
- The Katyń Memorial by well-known Polish American artist Andrzej Pityński on Exchange Place is the first memorial of its kind to be raised on American soil to honor the dead of the Katyń Forest Massacre
- The Colgate Clock, promoted by Colgate-Palmolive as the largest in the world, sits in Jersey City and faces Lower New York Bay and Lower Manhattan (it is clearly visible from Battery Park in lower Manhattan). The clock, which is 50 feet in diameter with a minute hand weighing 2,200 pounds, was erected in 1924 to replace a smaller one.
- Jersey City residents have nicknamed Jersey City "Chilltown."[58]
- The tallest building in New Jersey is Jersey City's Goldman Sachs Tower, which was completed in 2004. Other notable buildings in Jersey City include 101 Hudson Street, the Newport Tower, and the Exchange Place Centre.
- In 1916, German agents set off a series of explosions in present-day Liberty State Park in what came to be known as the Black Tom Explosion.
- Part of the 1993 Saturday Night Live spin-off movie Coneheads was filmed in Jersey City.
- Much of the 1999 movie Ghost Dog: The Way of the Samurai was filmed in Jersey City.
- The movie City Hall, starring Al Pacino and John Cusack is partly set in the Tunnel Diner, next to the Holland Tunnel
- In The Ren and Stimpy Show episode Black Hole/Stimpy's Invention, Ren and Stimpy tried to escape the Black Hole by riding an Intergalactic Bus to Jersey City, but did not have the money to pay the fare.
- On The History Channel's 10 Days that Unexpectedly Changed America episode, When America was Rocked, an old newspaper article of a city-wide ban of Rock and Roll in Jersey City was shown and archival film footage of the Mayor explaining his reasoning of the ban was also shown.
- The animated series Megas XLR takes place primarily in Jersey City.
- The bar scenes in the movie CopLand, were filmed in the Paulus Hook Pub (no longer in existence) on Grand Street, owned by life-long Jersey City resident and civil servant Roy Zevoteck. It featured Sylvester Stallone, Debbie Harry, Ray Liotta, Harvey Keitel, Robert Patrick, Michael Rapaport and Frank Vincent.
- One of the scenes in the movie 8 Mile is shot behind Indian Square, along the PATH train's route to Newark.
- The Last Days of Disco was filmed in the lobby of the Loew's Jersey City Theatre in Journal Square.
- Z-100 WHTZ 100.3 The top rated New York City radio station broadcasts from the Merrill Lynch Building (101 Hudson Street) in Jersey City.
Sister cities
Jersey City has some sister cities, as designated by Sister Cities International, Inc. (SCI):
See also
- Hudson River Waterfront Walkway
- Hackensack RiverWalk
- List of Mayors of Jersey City, New Jersey
- List of people from Jersey City, New Jersey
- Jersey City Reporter
- Gateway Region
- Gold Coast, New Jersey
- Bergen Township,
References
- ^ a b Census data for Jersey City city, United States Census Bureau. Accessed March 1, 2007.
- ^ Jersey City Past and Present: Pavonia, New Jersey City University. Accessed May 10, 2006.
- ^ A Virtual Tour of New Netherland, New Netherland Institute. Accessed May 10, 2006.
- ^ Ellis, Edward Robb (1966). The Epic of New York City. Old Town Books. pp. p. 38.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ "Jersey City's Underground Railroad history," Jersey City Magazine, Spring & Summer 2005.
- ^ a b "The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606-1968", John P. Snyder, Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. p. 146-147.
- ^ A City Whose Time Has Come Again, The New York Times, April 30, 2000.
- ^ Worlds Tallest Skyscrapers, Emporis. Accessed March 11, 2007.
- ^ Municipal Council Information, City of Jersey City. Accessed August 3, 2006.
- ^ "Mayors Against Illegal Guns: Coalition Members".
- ^ 2006 New Jersey Citizen's Guide to Government, New Jersey League of Women Voters, p. 59. Accessed August 30, 2006.
- ^ Fox, Joey. [1], New Jersey Globe, January 3, 2024. Accessed January 4, 2023.
- ^ "McIver sworn in to fill late New Jersey Rep. Payne's seat". The Hill. September 23, 2024.
- ^ States in the Senate: New Jersey, United States Senate. Accessed January 23, 2025. "Cory A. Booker (D) Hometown: Newark; Andy Kim (D) Hometown: Moorestown"
- ^ Legislative Roster for District 31, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 20, 2024.
- ^ Legislative Roster for District 32, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 20, 2024.
- ^ Legislative Roster for District 33, New Jersey Legislature. Accessed January 20, 2024.
- ^ About the County Executive, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 1 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Kenneth Kopacz District 1, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 2 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ William O’Dea District 2, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 3 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Jerry Walker District 3, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 4 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Yraida Aponte-Lipski District 4, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 5 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Anthony L. Romano Jr. District 5, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 6 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Fanny J. Cedeño District 6, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 7 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Caridad Rodriguez District 7, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 8 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Robert P. Baselice District 8, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ District 9 Hudson County Board of County Commissioners Series Boundaries Adopted 2022, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Albert J. Cifelli District 9, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ County Commissioners, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ County Officials, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ 2024 County Data Sheet, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Biography, Hudson County Clerk. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Members List: Clerks, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Register Dublin's Bio, Hudson County Register of Deeds and Mortgages. Accessed October 13, 2024.
- ^ About Us, Hudson County Register of Deeds & Mortgages. Accessed January 31, 2025. "The Hudson County Register is elected by the people of Hudson County for a five-year term. The Office of the Register is responsible for the recording of all formal written documents which affect real property throughout the 12 municipalities that make up the County."
- ^ Members List: Registers, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Home, Hudson County Sheriff. Accessed January 31, 2025
- ^ Members List: Sheriffs, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Hudson County Surrogate, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Members List: Surrogates, Constitutional Officers Association of New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025.
- ^ Directory, Hudson County, New Jersey. Accessed January 31, 2025
- ^ Top Public High Schools in New Jersey, New Jersey Monthly, September 2006
- ^ Top 1000 High Schools in The United States, Newsweek August 5, 2005.
- ^ Holusha, John. " Commercial Property / The Jersey Riverfront; On the Hudson's West Bank, Optimistic Developers", The New York Times, October 11, 1998. Accessed May 25, 2007. 'That simply is out of the question in midtown, he said, adding that some formerly fringe areas in Midtown South that had previously been available were filled up as well. Given that the buildings on the New Jersey waterfront are new and equipped with the latest technology and just a few stops on the PATH trains from Manhattan, they become an attractive alternative. It's the sixth borough, he said.
- ^ "New Jersey Resident Population by Municipality: 1930 - 1990". Retrieved 2007-03-03.
- ^ Campbell Gibson (June 1998). "Population of the 100 Largest Cities and Other Urban Places in The United States: 1790 TO 1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2007-03-06.
- ^ Wm. C. Hunt, Chief Statistician for Population. "Fourteenth Census of The United States: 1920; Population: New Jersey; Number of inhabitants, by counties and minor civil divisions" (ZIP). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2007-03-21.
- ^ Hudson County Bus/rail Connections, New Jersey Transit. Accessed July 3, 2007.
- ^ States fight over New York landmark, BBC News, January 12, 1998.
- ^ "Why do people call Jersey City 'Chilltown?': Residents shed light on origin of rap nickname", Jersey City Reporter, April 10, 2005.
External links
- City of Jersey City
- Jersey City Board of Education
- School Performance Reports for the Jersey City Public Schools, New Jersey Department of Education
- National Center for Education Statistics data for the Jersey City Public Schools
- Jersey City Economic Development Corporation
- Jersey City Neighborhoods
- Jersey City Museum
- Jersey City Reservoir Preservation Alliance
- Jersey City: Past and Present
- Jersey City Landmarks Conservancy
- History of Jersey City
- Jersey City History
- Lincoln Park Neighborhood
- Jersey City Magazine
- Jersey City Portal
- Jersey City Tourism Web site - DestinationJerseyCity.com
- Jersey City Vibe
- Jersey City List
- NEW Contemporary Guide to Jersey City
- Jersity City Online - Questions about City Government
- Jersey City Gentrification - Article, photos, interactive map and other resources
- Jersey City Municipal Court
- Interactive neighborhood map of Jersey City from the BusyTonight America's Neighborhoods project


