Kipchak languages: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
m Fixed typo Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit App select source |
No edit summary Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
| |
| |
||
* '''[[Dobrujan Tatar dialect|Dobrujan Tatar]]''' |
* '''[[Dobrujan Tatar dialect|Dobrujan Tatar]]''' |
||
* {{extinct}} |
* {{extinct}} |
||
* '''[[Kazakh language|Kazakh]]''' |
* '''[[Kazakh language|Kazakh]]''' |
||
* '''[[Karakalpak language|Karakalpak]]''' |
* '''[[Karakalpak language|Karakalpak]]''' |
||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
** '''[[Teleut language|Teleut]]'''<ref name="Nevskaya">{{cite web |url=https://lingsib.iea.ras.ru/en/languages/teleut.shtml |author=Nevskaya, I. A. |title=The Teleut Language |work=Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia |publisher=[[UNESCO]] |access-date=2021-07-16}}</ref> |
** '''[[Teleut language|Teleut]]'''<ref name="Nevskaya">{{cite web |url=https://lingsib.iea.ras.ru/en/languages/teleut.shtml |author=Nevskaya, I. A. |title=The Teleut Language |work=Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia |publisher=[[UNESCO]] |access-date=2021-07-16}}</ref> |
||
* '''[[Kyrgyz language|Kyrgyz]]''' |
* '''[[Kyrgyz language|Kyrgyz]]''' |
||
* † Fergana Kipchak |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
Revision as of 17:09, 14 September 2024
| Kipchak | |
|---|---|
| Northwestern Turkic | |
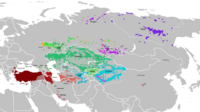
| Geographic distribution | Central Asia, Russia, Northern Caucasus, Balkans, Anatolia, Ukraine, China |
| Ethnicity | Kipchaks |
| Linguistic classification | Turkic
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | kipc1239 |
The Kipchak languages (also known as the Kypchak, Qypchaq, Qypshaq or the Northwestern Turkic languages) are a sub-branch of the Turkic language family spoken by approximately 30 million people in much of Central Asia and Eastern Europe, spanning from Ukraine to China. Some of the most widely spoken languages in this group are Kazakh, Kyrgyz, and Tatar.
Linguistic features
The Kipchak languages share a number of features that have led linguists to classify them together. Some of these features are shared with other Common Turkic languages; others are unique to the Kipchak family.
Shared features
- Change of Proto-Turkic *d to /j/ (e.g. *hadaq > ajaq "foot")
- Loss of initial *h (preserved only in Khalaj), see above example
Unique features
Family-specific
- Extensive labial vowel harmony (e.g. olor vs. olar "them") [citation needed]
- Frequent fortition (in the form of assibilation) of initial */j/ (e.g. *jetti > ʒetti "seven")
- Diphthongs from syllable-final */ɡ/ and */b/ (e.g. *taɡ > taw "mountain", *sub > suw "water")
Language-specific
- In both Tatar and Bashkir, the original mid and high vowels are swapped in position by vowel raising and lowering:
| Old Turkic | Tatar (for example) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mid → high | |||
| *e | /e/ | i | /i/ |
| *o | /o/ | u | /u/ |
| *ö | /ø/ | ü | /y/ |
| High → Mid | |||
| *i | /i/ | e | /e/ |
| *ı | /ɯ/ | î | /ɤ/ |
| *u | /u/ | o | /o/ |
| *ü | /y/ | ö | /ø/ |
Classification
The Kipchak languages may be broken down into four groups based on geography and shared features (languages in bold are still spoken today):
| Proto-Turkic | Common Turkic | Kipchak | Kipchak–Bulgar (Uralian, Uralo-Caspian) | ||
| Kipchak–Cuman (Ponto-Caspian) |
| ||||
| Kipchak–Nogai (Aralo-Caspian) | |||||
| Kyrgyz–Kipchak (Kyrgyz) |
| ||||
See also
Notes
- ^ Except for the Southern "dialect", which is classified among the Western Oghuz languages despite its dialect status.[2]
References
- ^ Encyclopedia of Bashkortostan.
- ^ Yazyki mira Языки мира [Languages of the World]. Vol. 2. Indirk: Институт языкознания (Российская академия наук). 1997. pp. 19–20.
- ^ Махмутова Л. Т. Опыт исследования тюркских диалектов: мишарский диалект татарского языка. — М.: Наука, 1978
- ^ Some dialects are close to Kirghiz (Johanson 1998)
- ^ Nevskaya, I. A. "The Teleut Language". Endangered Languages of Indigenous Peoples of Siberia. UNESCO. Retrieved 2021-07-16.
Bibliography
- Johanson, Lars; Csató, Éva Ágnes (1998). The Turkic Languages. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-08200-5.
- Menges, Karl H. (1995). The Turkic Languages and Peoples (2nd ed.). Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz. ISBN 3-447-03533-1.