Sophorose
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
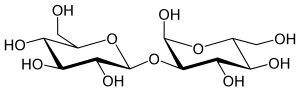
| IUPAC name 2-O-β-D-Glucopyranosyl-α-D-glucopyranose | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyoxane-3,4,5-triol (alpha-Sophorose) | |
| Other names 2-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-alpha-D-glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.072 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22O11 | |
| Molar mass | 342.30 g/mol |
| Density | 1.768 g/mL |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Sophorose is a disaccharide, a dimer of glucose. It differs from other glucose dimers such as maltose in having an unusual β-1,2 bond. It was isolated in 1938 from pods of Sophora japonica.[1] It is a component of sophorolipids.[2] It is a product of the caramelization of glucose. [3]
References
- ^ J.B. Harborne (1963). "Flavonoid sophorosides". Experientia. 19: 7–8. doi:10.1007/BF02135323. PMID 13952724. S2CID 37926298.
- ^ Ribeiro, Isabel; Castro, Matilde; Ribeiro, Maria (2013). "Sophorolipids". Applications of Microbial Engineering. pp. 367–407. doi:10.1201/b15250-15. ISBN 978-1-4665-8577-5.
- ^ Sugisawa, Hirqshi; Edo, Hiroshi (1966). "The Thermal Degradation of Sugars I. Thermal Polymerization of Glucose". Journal of Food Science. 31 (4): 561. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.1966.tb01905.x.
