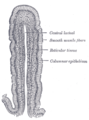
Simple columnar epithelium
| simple columnar epithelium | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | epithelium simplex columnare |
| TH | H2.00.02.0.02020 |
| FMA | 45567 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
| This article is part of a series on |
| Epithelia |
|---|
| Squamous epithelial cell |
| Columnar epithelial cell |
| Cuboidal epithelial cell |
| Specialised epithelia |
|
| Other |
Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple columnar epithelium lines most organs of the digestive tract including the stomach, and intestines. Simple columnar epithelium also lines the uterus.
Structure
Simple columnar epithelium is further divided into two categories: ciliated and non-ciliated (glandular). The ciliated part of the simple columnar epithelium has tiny hairs which help move mucus and other substances up the respiratory tract.
The shape of the simple columnar epithelium cells are tall and narrow giving a column like appearance. the apical surfaces of the tissue face the lumen of organs while the basal side faces the basement membrane.[1] The nuclei are located closer along the basal side of the cell.[1]
Absorptive columnar epithelium is characterized as having a striated border on its apical side, this border is made up of non-motile microvilli allowing for increase surface area for absorption.[1] These are known as non-ciliated columnar epithelium. Non-ciliated simple columnar epithelium is made up of glandular goblet cells which secrete mucin to form mucus.[1] The rest of the cell is made up of cytoplasm with membrane bound secretory granules which secrete the mucin, and are found towards the apical surface of the cell.[1]
Ciliated
Ciliated columnar epithelium has many cilia which moves mucus and other substances via mucociliary clearance in the respiratory tract.
It is present in the lining of the fallopian tubes, where currents generated by the cilia propel the egg cell toward the uterus.
Ciliated columnar epithelium forms the neuroepithelium of the ependyma that lines the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord. These cilia move the cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF).
Non-ciliated
These are found in the lining sections of the gastrointestinal tract (inner lining of oesophagus, stomach, etc.) and may be brush bordered.
- Vertical section of a villus from the dog's small intestine. X 80. (Simple columnar epithelium labelled at right, third from the top.)
- Transverse section of a villus, from the human intestine. X 350.
a. Basement membrane, here somewhat shrunken away from the epithelium.
b. Lacteal.
c. Columnar epithelium.
d. Its striated border.
e. Goblet cells.
f. Leucocytes in epithelium.
f’. Leucocytes below epithelium.
g. Blood vessels.
h. Muscle cells cut across.