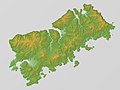
Shikotan
| Disputed island | |
|---|---|
 NASA picture of Shikotan Island | |
 | |
| Other names | Japanese: 色丹島 Russian: Шикотан |
| Geography | |
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 43°48′N 146°45′E / 43.800°N 146.750°E |
| Archipelago | Kuril Islands |
| Total islands | 1 |
| Area | 225 km2 (87 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 412 m (1352 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Shakotan |
| Administration | |
| Federal subject | Sakhalin Oblast |
| District | Yuzhno-Kurilsky |
| Claimed by | |
| Prefecture | Hokkaido |
| Subprefecture | Nemuro |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 2,100 |
Shikotan, also known as Shpanberg or Spanberg, is an island in the Kurils administered by the Russian Federation as part of Yuzhno-Kurilsky District of Sakhalin Oblast. It is claimed by Japan as the titular Shikotan District (色丹郡, Shikotan-gun), organized as part of Nemuro Subprefecture of Hokkaido Prefecture. The island's primary economic activities are fisheries and fishing, with the principal marine products being cod, crab, and kelp.
Names
The English name Shikotan transcribes both the Japanese name 色丹 and the Russian name Шикотан. The Japanese name derives from the Ainu Sikotan (シコタン or シコタヌ). The name combines the Ainu reflexive or embellishing prefix si- and the word kotan ("settlement, village"), used metonymically in Ainu for each of the islands of the Kurils.
The alternative Russian name Shpanberg (Шпанберг), sometimes anglicized as Spanberg, honors Martin Spanberg, one of Vitus Bering's lieutenants who led three voyages in 1738, 1739, and 1742 that first initiated Russian diplomatic relations with Japan and helped accelerate Russian control of the Kurils.
Geography
The total land area of Shikotan is 225 square kilometers (87 sq mi). The island is hilly, averaging 300 metres (984 ft) in elevation. The highest elevation is 412 metres (1,352 ft). The shores of the island are very indented and covered with oceanic meadows. The island is formed by the volcanic rock and sandstone of the Upper Cretaceous and Cenozoic periods. There are two extinct volcanoes on Shikotan: Mount Tomari and Mount Notoro. A number of tiny islets and rocks are scattered around the coast of Shikotan. Two larger islands lie off the south coast: Griega island; and Aivazovskogo island which lies in a bay near the western end of the southern coast.
Shikotan's vegetation consists mostly of Sakhalin fir, larch, deciduous trees, bamboo underbrush, and juniper brushwood.
There are two villages: Malokurilskoye, formerly Shikotan (色丹); and Krabozavodskoye, formerly Anama (穴澗)
History
Russia recognised Japanese sovereignty over the island in the 19th century under Shimoda Treaty. In 1885, Hanasaki District, to which the island belongs, was split off of Nemuro Province and incorporated into Chishima Province.[citation needed]
On 1 September 1945, during the final days of World War II, the island, which had a population of 1,038 at the time,[citation needed] was invaded by 600 Soviet troops during the Soviet invasion of the Kuril Islands.[1] It is one of the islands (along with the Habomai Islands) which the Soviet Union agreed in 1956 to transfer to Japan in the event of a peace treaty between the two countries, but such a peace treaty has never been concluded.[2] During the late 1950s and the 1960s, the Soviet Union fortified the island against a possible seaborne invasion by repurposing old tanks (mainly IS-2 and IS-3 heavy tanks) as coastal artillery, digging them into the ground to serve as fixed gun emplacements.[3]
On 6 November 1958, a magnitude 8.3 to 8.4 earthquake in the Pacific Ocean off Iturup in the Kuril Islands generated a tsunami with a height of up to 5 metres (16.4 ft) at Shikotan.[4] A magnitude 8.3 earthquake in the Pacific Ocean just off Shikotan and subsequent tsunami on 4 October 1994 caused major damage on the island's coastline. The tsunami had a run-up height of as much as 10 metres (33 ft) on Shikotan.[5]
In popular culture
The 2014 anime film Giovanni's Island is a fictionalized account of the fate of Japanese civilians living on Shikotan at the time of the 1945 Soviet occupation.
Gallery
- Relief Map
- Shikotan Island, 1990.
- Shikotan, 1980.
- Lighthouse, 1980.
- Landscape, 1980.

See also
References
- ^ "Japan's prime minister plans a steamy tête-à-tête with Russia's president". The Economist. 10 September 2016. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ "Russia PM visits disputed isle off Japan's Hokkaido". english.kyodonews.net. 27 July 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2023.
- ^ "Texts of Soviet–Japanese Statements; Peace Declaration Trade Protocol". The New York Times, page 2, October 20, 1956.
Moscow, October 19. (UP) – Following are the texts of a Soviet–Japanese peace declaration and of a trade protocol between the two countries, signed here today, in unofficial translation from the Russian
...The U.S.S.R. and Japan have agreed to continue, after the establishment of normal diplomatic relations between them, negotiations for the conclusion of a peace treaty. Hereby, the U.S.S.R., in response to the desires of Japan and taking into consideration the interest of the Japanese state, agrees to hand over to Japan the Habomai and the Shikotan Islands, provided that the actual changing over to Japan of these islands will be carried out after the conclusion of a peace treaty...
- ^ "Catalog of Tsunamis in Japan and Its Neighboring Countries". Tsunami Digital Library. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ "M 9.0 - 89 km ESE of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Russia". United States Geological Survey Earthquake Hazards Program. Retrieved 25 November 2024.