September 1941 lunar eclipse
| Partial eclipse | |||||||||||||
 The Moon's hourly motion shown right to left | |||||||||||||
| Date | September 5, 1941 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.9747 | ||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 0.0511 | ||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 117 (48 of 72) | ||||||||||||
| Partiality | 53 minutes, 21 seconds | ||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 279 minutes, 17 seconds | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
A partial lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Friday, September 5, 1941,[1] with an umbral magnitude of 0.0511. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A partial lunar eclipse occurs when one part of the Moon is in the Earth's umbra, while the other part is in the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 5.9 days before apogee (on September 11, 1941, at 14:15 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.[2]
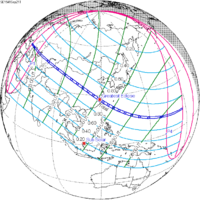
Visibility
The eclipse was completely visible over much of Asia, Australia, and Antarctica, seen rising over Africa and Europe and setting over northeast Asia and the central Pacific Ocean.[3]
 
|
Eclipse details
Shown below is a table displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. It describes various parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[4]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Penumbral Magnitude | 1.08839 |
| Umbral Magnitude | 0.05110 |
| Gamma | 0.97469 |
| Sun Right Ascension | 10h56m24.2s |
| Sun Declination | +06°46'29.9" |
| Sun Semi-Diameter | 15'52.1" |
| Sun Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 08.7" |
| Moon Right Ascension | 22h55m20.3s |
| Moon Declination | -05°54'07.9" |
| Moon Semi-Diameter | 15'17.9" |
| Moon Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 0°56'08.6" |
| ΔT | 25.2 s |
Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
| September 5 Descending node (full moon) |
September 21 Ascending node (new moon) |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Partial lunar eclipse Lunar Saros 117 |
Total solar eclipse Solar Saros 143 |
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 1941
- A partial lunar eclipse on March 13.
- An annular solar eclipse on March 27.
- A partial lunar eclipse on September 5.
- A total solar eclipse on September 21.
Metonic
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of November 18, 1937
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of June 25, 1945
Tzolkinex
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of July 26, 1934
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of October 18, 1948
Half-Saros
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of August 31, 1932
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of September 12, 1950
Tritos
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of October 7, 1930
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of August 5, 1952
Lunar Saros 117
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of August 26, 1923
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of September 17, 1959
Inex
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of September 26, 1912
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of August 17, 1970
Triad
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of November 4, 1854
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of July 6, 2028
Lunar eclipses of 1940–1944
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of lunar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[5]
The penumbral lunar eclipses on April 22, 1940 and October 16, 1940 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set, and the penumbral lunar eclipses on July 6, 1944 and December 29, 1944 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1940 to 1944 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart | |
| 102 | 1940 Mar 23
|
Penumbral
|
107 | |||
| 112 | 1941 Mar 13
|
Partial
|
117 | 1941 Sep 05
|
Partial
| |
| 122 | 1942 Mar 03
|
Total
|
127 | 1942 Aug 26
|
Total
| |
| 132 | 1943 Feb 20
|
Partial
|
137 | 1943 Aug 15
|
Partial
| |
| 142 | 1944 Feb 09
|
Penumbral
|
147 | 1944 Aug 04
|
Penumbral
| |
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[6] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 124.
| August 31, 1932 | September 12, 1950 |
|---|---|

|

|
See also
References
- ^ "September 5–6, 1941 Partial Lunar Eclipse". timeanddate. Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ^ "Moon Distances for London, United Kingdom, England". timeanddate. Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ^ "Partial Lunar Eclipse of 1941 Sep 05" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ^ "Partial Lunar Eclipse of 1941 Sep 05". EclipseWise.com. Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- Saros series 117
- 1941 Sep 05 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC



