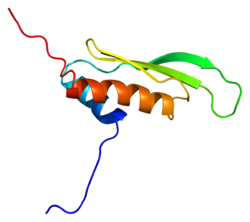
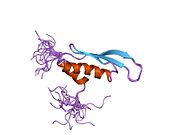
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
Protein kinase, interferon-inducible double stranded RNA dependent activator , also known as interferon-inducible double stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activator A or P rotein ACT ivator of the interferon-induced protein kinasePACT ) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRKRA gene .[ 5] [ 6] [ 7] protein kinase R .[ 6] [ 8] [ 9]
References
^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000180228 – Ensembl , May 2017^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000002731 – Ensembl , May 2017^ "Human PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ "Entrez Gene: PRKRA protein kinase, interferon-inducible double stranded RNA dependent activator" .^ a b Patel RC, Sen GC (August 1998). "PACT, a protein activator of the interferon-induced protein kinase, PKR" . EMBO J . 17 (15): 4379– 90. doi :10.1093/emboj/17.15.4379 . PMC 1170771 PMID 9687506 . ^ Ito T, Yang M, May WS (May 1999). "RAX, a cellular activator for double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase during stress signaling" . J. Biol. Chem . 274 (22): 15427– 32. doi :10.1074/jbc.274.22.15427 PMID 10336432 . ^ Huang X, Hutchins B, Patel RC (August 2002). "The C-terminal, third conserved motif of the protein activator PACT plays an essential role in the activation of double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR)" . Biochem. J . 366 (Pt 1): 175– 86. doi :10.1042/BJ20020204 . PMC 1222748 PMID 11985496 . ^ Camargos S, Scholz S, Simón-Sánchez J, Paisán-Ruiz C, Lewis P, Hernandez D, Ding J, Gibbs JR, Cookson MR, Bras J, Guerreiro R, Oliveira CR, Lees A, Hardy J, Cardoso F, Singleton AB (March 2008). "DYT16, a novel young-onset dystonia-parkinsonism disorder: identification of a segregating mutation in the stress-response protein PRKRA". Lancet Neurology . 7 (3): 207– 215. doi :10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70022-X . PMID 18243799 . S2CID 206157913 .
Further reading
Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene . 138 (1– 2): 171– 4. doi :10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8 . PMID 8125298 . Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene . 200 (1– 2): 149– 56. doi :10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3 . PMID 9373149 . Peters GA, Hartmann R, Qin J, et al. (2001). "Modular structure of PACT: distinct domains for binding and activating PKR" . Mol Cell Biol . 21 (6): 1908– 20. doi :10.1128/MCB.21.6.1908-1920.2001 . PMC 86773 PMID 11238927 . Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, et al. (2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs" . Genome Res . 11 (3): 422– 35. doi :10.1101/gr.GR1547R . PMC 311072 PMID 11230166 . Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing" . EMBO Rep . 1 (3): 287– 92. doi :10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058 . PMC 1083732 PMID 11256614 . Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R (2001). "TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway". Nat. Immunol . 2 (9): 835– 41. doi :10.1038/ni0901-835 . PMID 11526399 . S2CID 7296195 . Huang X, Hutchins B, Patel RC (2002). "The C-terminal, third conserved motif of the protein activator PACT plays an essential role in the activation of double-stranded-RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR)" . Biochem. J . 366 (Pt 1): 175– 86. doi :10.1042/BJ20020204 . PMC 1222748 PMID 11985496 . Peters GA, Khoo D, Mohr I, Sen GC (2002). "Inhibition of PACT-mediated activation of PKR by the herpes simplex virus type 1 Us11 protein" . J. Virol . 76 (21): 11054– 64. doi :10.1128/JVI.76.21.11054-11064.2002 . PMC 136652 PMID 12368348 . Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences" . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A . 99 (26): 16899– 903. Bibcode :2002PNAS...9916899M . doi :10.1073/pnas.242603899 PMC 139241 PMID 12477932 . Yang M, Ito T, May WS (2003). "A novel role for RAX, the cellular activator of PKR, in synergistically stimulating SV40 large T antigen-dependent gene expression" . J. Biol. Chem . 278 (40): 38325– 32. doi :10.1074/jbc.M303420200 PMID 12874289 . Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs" . Nat. Genet . 36 (1): 40– 5. doi :10.1038/ng1285 PMID 14702039 . Bennett RL, Blalock WL, May WS (2004). "Serine 18 phosphorylation of RAX, the PKR activator, is required for PKR activation and consequent translation inhibition" . J. Biol. Chem . 279 (41): 42687– 93. doi :10.1074/jbc.M403321200 PMID 15299031 . Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)" . Genome Res . 14 (10B): 2121– 7. doi :10.1101/gr.2596504 . PMC 528928 PMID 15489334 . Hillier LW, Graves TA, Fulton RS, et al. (2005). "Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4" . Nature . 434 (7034): 724– 31. Bibcode :2005Natur.434..724H . doi :10.1038/nature03466 PMID 15815621 . Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, et al. (2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell . 122 (6): 957– 68. doi :10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029 . hdl :11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0 PMID 16169070 . S2CID 8235923 . Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature . 437 (7062): 1173– 8. Bibcode :2005Natur.437.1173R . doi :10.1038/nature04209 . PMID 16189514 . S2CID 4427026 . Peters GA, Li S, Sen GC (2006). "Phosphorylation of specific serine residues in the PKR-activation domain of PACT is essential for its ability to mediate apoptosis" . J Biol Chem . 281 (46): 35129– 36. doi :10.1074/jbc.M607714200 PMID 16982605 . Rowe TM, Rizzi M, Hirose K, Peters GA, et al. (2006). "A role of the double-stranded RNA-binding protein PACT in mouse ear development and hearing" . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . 103 (15): 5823– 8. Bibcode :2006PNAS..103.5823R . doi :10.1073/pnas.0601287103 PMC 1458657 PMID 16571658 . Li S, Peters GA, Ding K, et al. (2006). "Molecular basis for PKR activation by PACT or dsRNA" . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . 103 (26): 10005– 10. Bibcode :2006PNAS..10310005L . doi :10.1073/pnas.0602317103 PMC 1502496 PMID 16785445 . Lee Y, Hur I, Park SY, et al. (2006). "The role of PACT in the RNA silencing pathway" . EMBO J . 25 (3): 522– 32. doi :10.1038/sj.emboj.7600942 . PMC 1383527 PMID 16424907 . Bennett RL, Blalock WL, Abtahi DM, et al. (2006). "RAX, the PKR activator, sensitizes cells to inflammatory cytokines, serum withdrawal, chemotherapy, and viral infection" . Blood . 108 (3): 821– 9. doi :10.1182/blood-2005-11-006817 . PMC 1617065 PMID 16861340 .