Portal:Climate change
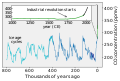
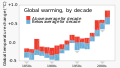
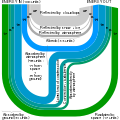
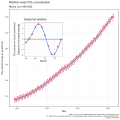
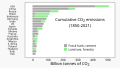
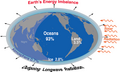
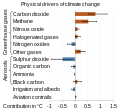
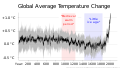
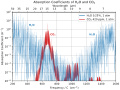
The Climate Change Portal Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth’s climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contributed to thawing permafrost, retreat of glaciers and sea ice decline. Higher temperatures are also causing more intense storms, droughts, and other weather extremes. Rapid environmental change in mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic is forcing many species to relocate or become extinct. Even if efforts to minimize future warming are successful, some effects will continue for centuries. These include ocean heating, ocean acidification and sea level rise. Climate change threatens people with increased flooding, extreme heat, increased food and water scarcity, more disease, and economic loss. Human migration and conflict can also be a result. The World Health Organization calls climate change one of the biggest threats to global health in the 21st century. Societies and ecosystems will experience more severe risks without action to limit warming. Adapting to climate change through efforts like flood control measures or drought-resistant crops partially reduces climate change risks, although some limits to adaptation have already been reached. Poorer communities are responsible for a small share of global emissions, yet have the least ability to adapt and are most vulnerable to climate change. Many climate change impacts have been observed in the first decades of the 21st century, with 2024 the warmest on record at +1.60 °C (2.88 °F) since regular tracking began in 1850. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as melting all of the Greenland ice sheet. Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2 °C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about 2.8 °C (5.0 °F) by the end of the century. Limiting warming to 1.5 °C would require halving emissions by 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Fossil fuel use can be phased out by conserving energy and switching to energy sources that do not produce significant carbon pollution. These energy sources include wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear power. Cleanly generated electricity can replace fossil fuels for powering transportation, heating buildings, and running industrial processes. Carbon can also be removed from the atmosphere, for instance by increasing forest cover and farming with methods that capture carbon in soil. (Full article...) Selected article – The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or come from an external source, such as its host star. In the case of Earth, the Sun emits shortwave radiation (sunlight) that passes through greenhouse gases to heat the Earth's surface. In response, the Earth's surface emits longwave radiation that is mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. The absorption of longwave radiation prevents it from reaching space, reducing the rate at which the Earth can cool off. Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's average surface temperature would be as cold as −18 °C (−0.4 °F). This is of course much less than the 20th century average of about 14 °C (57 °F). In addition to naturally present greenhouse gases, burning of fossil fuels has increased amounts of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere. As a result, global warming of about 1.2 °C (2.2 °F) has occurred since the Industrial Revolution, with the global average surface temperature increasing at a rate of 0.18 °C (0.32 °F) per decade since 1981. All objects with a temperature above absolute zero emit thermal radiation. The wavelengths of thermal radiation emitted by the Sun and Earth differ because their surface temperatures are different. The Sun has a surface temperature of 5,500 °C (9,900 °F), so it emits most of its energy as shortwave radiation in near-infrared and visible wavelengths (as sunlight). In contrast, Earth's surface has a much lower temperature, so it emits longwave radiation at mid- and far-infrared wavelengths. A gas is a greenhouse gas if it absorbs longwave radiation. Earth's atmosphere absorbs only 23% of incoming shortwave radiation, but absorbs 90% of the longwave radiation emitted by the surface, thus accumulating energy and warming the Earth's surface. (Full article...) Selected picture –Global vegetation – Food, fuel and shelter. Vegetation is one of the most important requirements for human populations around the world. Satellites monitor how "green" different parts of the planet are and how that greenness changes over time. These observations help scientists understand the influence of natural cycles, such as drought and pest outbreaks, on vegetation, as well as human influences, such as land-clearing and global warming. WikiProjectsIn the newsAdditional News
Selected biography –Adenike Oladosu (born 1994) is a Nigerian climate activist, and initiator of the school strike for climate in Nigeria. She has showcased her climate action at international conferences including the UN Climate Change Conference, World Economic Forum, and Elevate festival in Graz-Austria. In December 2019, Oladosu attended the COP25 gathering in Spain as a Nigerian youth diplomat where she gave a "moving address" about climate change in Africa and how it influences lives. (Full article...) General imagesThe following are images from various climate-related articles on Wikipedia. Did you know –Related portalsSelected panorama – Credit: U.S. Geological Survey – Northern Rocky Mountain Science Center (NOROCK) Authors: Myrna H. P. Hall and Daniel B. Fagre, 2003 Animation of Modeled Climate-Induced Glacier Change in Glacier National Park, 1850- 2100. The simulation reflects the predicted exponential rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations, a 2xCO2 "global warming" scenario, with a concurrent warming of 2-3 degrees centigrade (4-5 degrees Fahrenheit) by the year 2050. In addition it assumes that precipitation, primarily in the form of rain, will increase over the same time period about 10 percent (based on the research of Dr. Steven Running, University of Montana). Topics
CategoriesWeb resources
Things to do
WikimediaReferences
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|