List of Olympic Games boycotts
| Olympic Games |
|---|
 |
| Main topics |
| Games |
| Regional games |
| Defunct games |
The Olympic Games is a major international multi-sport event.
South Africa were not invited to the 1964 Games, while its invitation to the 1968 Games was withdrawn after several other African countries threatened to boycott the Games due to apartheid. South Africa would not be permitted to return to the Olympics until 1992.
Rhodesia was also prevented from entering the 1972 Summer Olympics when its invitation was withdrawn by the International Olympic Committee following protests by other African countries.
Possibly the most famous Olympic boycotts occurred in 1980 and 1984, due to the Soviet invasion in Afghanistan. Iran and Albania are the only countries that boycotted both the 1980 and 1984 Olympics. Albania is also the only country that boycotted the 1976, 1980 and 1984 Olympics.
In 2021, several nations announced a diplomatic boycott of the 2022 Winter Olympics to protest against Chinese mistreatment of the Uyghur population, thus prohibiting many government officials from attending the games in an official capacity, while still permitting athletes to compete.[1] Later, India joined the boycott over China's decision to choose Qi Fabao, a regimental commander in the People's Liberation Army, as a torchbearer for the event.[2][3]
List of full boycotts of an Olympic Games or full non-attendance
List of non-attendance of government officials or diplomatic boycotts of the Olympic Games
The following is the list of countries that did not send official delegations to the Games, but permitted their athletes to participate.
| Games | Year | Host Country | Host City | Boycotting countries | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List | Map | ||||
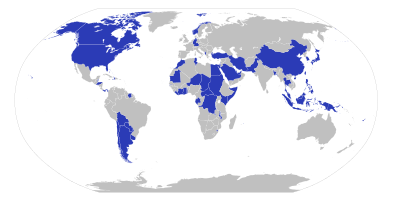
| XXXII Olympic Summer Olympics | 2020 | Tokyo |
|
 | |
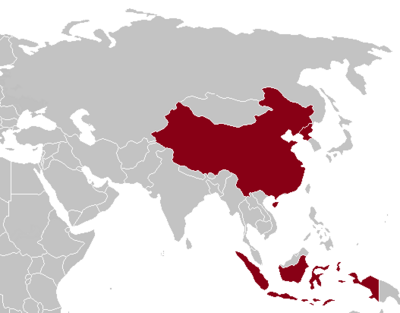
| XXIV Olympic Winter Games | 2022 | Beijing | 
| ||
Other
During the 2014 Winter Paralympics in Russia, the United States and United Kingdom diplomatically boycotted the event, and the entire Ukrainian delegation except for their flagbearer boycotted the opening ceremony due to Russia's annexation of Crimea and the violation of the Olympic Truce.
References
- ^ "2022 Beijing Winter Olympics: Australia joins US diplomatic boycott". BBC News. 2021-12-08. Retrieved 2021-12-08.
- ^ "India announces diplomatic boycott of Beijing Winter Olympics". The Hindu. 2022-02-03. Retrieved 2022-02-03.
- ^ "India launches last-minute diplomatic boycott of Beijing Olympics over Chinese soldier". 4 February 2022.
- ^ "Tokyo Olympics: North Korea to skip Games over Covid-19 fears". BBC News. 2021-04-06. Retrieved 2022-07-17.
- ^ "Lithuania confirms diplomatic boycott of Beijing 2022 Winter Olympics". ANI News. 3 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ Allie Malloy and Kate Sullivan. "White House announces US diplomatic boycott of 2022 Winter Olympics in Beijing". CNN. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "Australia joins diplomatic boycott of Beijing Winter Olympics". ABC News. 7 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "UK 'effectively' plans a diplomatic boycott of Beijing Winter Olympics, joining the United States, Australia and Lithuania". chicagotribune.com. 8 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ Tasker, John Paul (8 December 2021). "Trudeau announces diplomatic boycott of Beijing Olympics". CBC/Radio-Canada. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "Kosovo boycotts Beijing Winter Olympics". Alsat News. 8 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ "Which Countries Are Boycotting China's Winter Olympics? Full List". Newsweek. 8 December 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2021.
- ^ "Estonian government officials in no mood to attend Beijing Olympics". Baltic News Network. 18 January 2022. Archived from the original on 29 January 2022. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- ^ "Taiwan to boycott Beijing Winter Olympics: source". taipeitimes.com. 26 January 2022. Retrieved 26 January 2022.
- ^ "Denmark to join diplomatic boycott of Beijing Olympics over human rights". Reuters. 14 January 2022. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ IndiaToday, Geeta Mohan 3rd Feb'22. "Indian diplomats to boycott Beijing Winter Olympics after China makes Galwan PLA soldier torchbearer". IndiaToday. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)