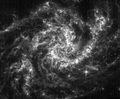
NGC 2283
| NGC 2283 | |
|---|---|
 The barred spiral galaxy NGC 2283 | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Canis Major |
| Right ascension | 06h 45m 52.7853s[1] |
| Declination | −18° 12′ 37.319″[1] |
| Redshift | 0.002805[1] |
| Heliocentric radial velocity | 841 ± 3 km/s[1] |
| Distance | 47.8 ± 3.4 Mly (14.66 ± 1.04 Mpc)[1] |
| Group or cluster | RR 140 |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.5[1] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SB(s)cd[1] |
| Size | ~56,500 ly (17.31 kpc) (estimated)[1] |
| Apparent size (V) | 3.6′ × 2.7′[1] |
| Other designations | |
| IRAS 06436-1809, 2MASS J06455276-1812374, MCG -03-18-002, PGC 19562, ESO 557- G 013, RR 140b[1] | |
NGC 2283 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation of Canis Major. Its velocity with respect to the cosmic microwave background is 994 ± 11 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 14.66 ± 1.04 Mpc (∼48 million light-years).[1] It was discovered by German-British astronomer William Herschel on 6 February 1785.[2]
NGC 2283 forms a physical pair with galaxy IC 2171, collectively named RR 140, with an optical separation of 1593″ between them.[3]
SIMBAD lists NGC 2283 as an active galaxy nucleus candidate.[4]
One supernova has been observed in NGC 2283: SN 2023axu (type II, mag 15.64) was discovered by the Distance Less Than 40 Mpc Survey (DLT40) on 28 January 2023.[5]
Image gallery
- Hubble Space Telescope image of NGC 2283.
- James Webb Space Telescope image of NGC 2283.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Results for object NGC 2283". NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database. NASA and Caltech. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ Seligman, Courtney. "New General Catalogue Objects: NGC 2283". Celestial Atlas. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
- ^ Reduzzi, L; Rampazzo, R. (1995). "Candidates for a southern extension of the Karachentsev catalogue of isolated pairs of galaxies". Astrophysical Letters and Communications. 30: 1–229. Bibcode:1995ApL&C..30....1R.
- ^ "NGC 2283". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
- ^ "SN 2023axu". Transient Name Server. IAU. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
External links
 Media related to NGC 2283 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to NGC 2283 at Wikimedia Commons- NGC 2283 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images