NBQX
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
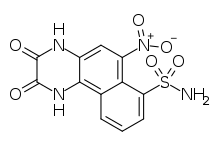
| Preferred IUPAC name 6-Nitro-2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.984 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8N4O6S | |
| Molar mass | 336.281 |
| Appearance | brown/red powder |
| Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
NBQX (2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzo[f]quinoxaline) is an antagonist of the AMPA receptor.
NBQX blocks AMPA receptors in micromolar concentrations (~10–20 μM) and also blocks kainate receptors. In experiments, it is used to counter glutamate excitotoxicity.[1] NBQX was found to have anticonvulsant activity in rodent seizure models.[2]
As the disodium salt, NBQX is soluble in water at high concentrations (at least up to 100 mM).
See also
- CNQX
- DNQX
- Fanapanel (MPQX)
- Quinoxalinedione
References
- ^ Pitt, D.; Werner, P.; Raine, C. S. (2000). "Glutamate excitotoxicity in a model of multiple sclerosis". Nat Med. 6 (1): 67–70.
- ^ Yamaguchi, S.; Donevan, S.D.; Rogawski, M.A. (1993). Anticonvulsant activity of AMPA/kainate antagonists: comparison of GYKI 52466 and NBOX in maximal electroshock and chemoconvulsant seizure models. Epilepsy Res. 15:179–184.
