Molvizarin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
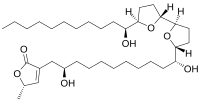
| IUPAC name (2S)-4-[(2R,11R)-2,11-Dihydroxy-11-[(2R,5R)-5-[(2R,5R)-5-[(1S)-1-hydroxyundecyl]oxolan-2-yl]oxolan-2-yl]undecyl]-2-methyl-2H-furan-5-one[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C35H62O7 | |
| Molar mass | 594.874 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Molvizarin is a cytotoxic acetogenin derivate with the molecular formula C35H62O7 which has been isolated from the bark of the plant Annona cherimolia.[2][1][3][4][5] Molvizarin has in vitro activity against tumor cells.[6]
References
- ^ a b "Molvizarin". Pubchem.ncbi.NLM.nih.gov.
- ^ Kintzios, Spiridon E.; Barberaki, Maria G. (15 January 2004). Plants that Fight Cancer. CRC Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-1-4200-2371-8.
- ^ Cortes, Diego; Myint, Saw H.; Hocquemiller, Reynald (September 1991). "Molvizarin and motrilin: Two novel cytotoxic bis-tetrahydro-furanic γ-lactone acetogenins from Annona cherimolia". Tetrahedron. 47 (38): 8195–8202. doi:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)91014-2.
- ^ Xu, Jun-Ping (25 November 2016). Cancer Inhibitors from Chinese Natural Medicines. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-315-34923-7.
- ^ Issues in Materials and Manufacturing Research: 2011 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. 9 January 2012. p. 5103. ISBN 978-1-4649-6331-5.
- ^ Nakanishi, Yuka; Chang, Fang-Rong; Liaw, Chih-Chuang; Wu, Yang-Chang; Bastow, Kenneth F.; Lee, Kuo-Hsiung (1 July 2003). "Acetogenins as Selective Inhibitors of the Human Ovarian 1A9 Tumor Cell Line". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 46 (15): 3185–3188. doi:10.1021/jm020548b. PMID 12852747.
