Mesa J mine
| Location | |
|---|---|
| Location | Shire of Ashburton, Pilbara |
| State | Western Australia |
| Country | Australia |
| Coordinates | 21°45′00″S 116°14′32″E / 21.750059°S 116.242203°E |
| Production | |
| Products | Iron ore |
| Production | 7 million tonnes/annum |
| History | |
| Opened | 1994 |
| Owner | |
| Company | Rio Tinto Iron Ore (53%)Mitsui & Co. (33%)Nippon Steel (10.5%)Sumitomo Metal Industries (3.5%) |
| Year of acquisition | Rio Tinto: 2000 |
 | |
The Mesa J mine is an iron ore mine located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia, 16 kilometres south-west of Pannawonica.[1]
The mine is owned by Robe River Iron Associates (53% Rio Tinto) and operated by Rio Tinto Iron Ore and is one of twelve iron ore mines the company operates in the Pilbara.[2][3] In 2009, the combined Pilbara operations produced 202 million tonnes of iron ore, a 15 percent increase from 2008.[4] The Pilbara operations accounted for almost 13 percent of the world's 2009 iron ore production of 1.59 billion tonnes.[5][6]
The Hamersley Range, where the mine is located, contains 80 percent of all identified iron ore reserves in Australia and is one of the world's major iron ore provinces.[7]
Overview
Rio Tinto's iron ore operations in the Pilbara began in 1966.[2] The mine itself began operations in 1994. The mine has an annual production capacity of 7 million tonnes of iron ore, sourced from open-pit operations. The ore is processed on site before being loaded onto rail.[8] At the height of production, the mine produced 35 million tonnes of iron ore annually.[9]
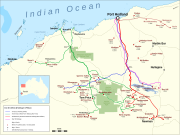
Ore from the mine is then transported to the coast through the Hamersley & Robe River railway, where it is loaded onto ships.[10] Ore from Mesa J, like from the West Angelas, is taken to Cape Lambert by rail to be exported as fines. The fines have a maximum size of 9.5 mm.[11]
The mine's workforce is predominantly a Residential mine with workers taking residence in Pannawonica, and around 20% of the workforce on a fly-in fly-out roster.[8]
The mine is located near the Mesa A mine.[2] The new Mesa A mine is scheduled to replace the Mesa J mine which is nearing the end of its life span. The combined investment of Rio Tinto in the new Mesa A and Brockman 4 mines is A$2.4 billion.[12]
Robe River Iron Associates
Robe River Iron, owner of the mine, is jointly owned by the following companies:[1]
- Rio Tinto Group - 53% - operator
- Mitsui and Co. (Australia) Ltd - 33%
- Nippon Steel Australia Pty Ltd - 10.5%
- Sumitomo Metal Australia Pty Ltd - 3.5%
Robe River Iron operates the West Angelas, Mesa A and Mesa J mines.[12] Rio Tinto acquired its share of 53% in late 2000, when it took over mining company North Limited.[13]
References
- ^ a b MINEDEX website: Deepdale Mesa J search result Archived 2008-09-11 at the Wayback Machine accessed: 6 November 2010
- ^ a b c Pilbara Archived 2013-10-21 at the Wayback Machine Rio Tinto Iron Ore website, accessed: 6 November 2010
- ^ Mining Archived 2010-06-12 at the Wayback Machine Rio Tinto Iron Ore website, accessed: 6 November 2010
- ^ Preparing for the future Archived 2011-07-15 at the Wayback Machine Rio Tinto presentation, published: 23 March 2010, accessed: 7 November 2010
- ^ Global iron-ore production falls 6,2% in 2009 - Unctad report miningweekly.com, published: 30 July 2010, accessed: 7 November 2010
- ^ Production of iron ore fell in 2009, but shipments continued to increase, report says[permanent dead link] UNCTAD website, published: 30 July 2010, accessed: 7 November 2010
- ^ Iron fact sheet - Australian Resources and Deposits Archived 2011-02-18 at the Wayback Machine Geoscience Australia website, accessed: 7 November 2010
- ^ a b Mesa J mine Archived 2010-06-14 at the Wayback Machine Rio Tinto Iron Ore website, accessed: 6 November 2010
- ^ Rio's Pilbara railway extension begins operating Archived 2012-06-03 at the Wayback Machine perthnow.com.au, published: 22 February 2010, accessed: 8 November 2010
- ^ Rail Archived 2013-07-01 at the Wayback Machine Rio Tinto Iron Ore website, accessed: 6 November 2010
- ^ Iron fact sheet - Mining Archived 2011-02-18 at the Wayback Machine Geoscience Australia website, accessed: 7 November 2010
- ^ a b Western Australian Mineral and Petroleum Statistic Digest 2008-09 Department of Mines and Petroleum website, accessed: 8 November 2010
- ^ The Australian Mines Handbook - 2003-04 edition, editor: Ross Louthean, publisher: Louthean Media Pty Ltd, page: 243