Laurel Hollow, New York
Laurel Hollow, New York Lauralton, New York | |
|---|---|
| Incorporated Village of Laurel Hollow | |
 The Charles Davenport Residence in Laurel Hollow, part of the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. | |
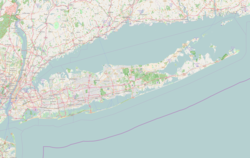
 Location in Nassau County and the state of New York. | |
| Coordinates: 40°51′25″N 73°28′37″W / 40.85694°N 73.47694°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Nassau |
| Town | Oyster Bay |
| Incorporated | 1926 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Dan DeVita[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 3.16 sq mi (8.19 km2) |
| • Land | 2.96 sq mi (7.66 km2) |
| • Water | 0.20 sq mi (0.53 km2) |
| Elevation | 240 ft (73 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 1,940 |
| • Density | 655.85/sq mi (253.25/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP codes | 11771, 11791, 11724, 11797 |
| Area codes | 516, 363 |
| FIPS code | 36-41487 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0955090 |
| Website | www |
Laurel Hollow is a village in the Town of Oyster Bay in Nassau County, on the North Shore of Long Island, in New York, United States. The population was 1,952 at the 2010 census.[3] According to Bloomberg BusinessWeek, Laurel Hollow was the eighth wealthiest town in America.[4]
History
The settlement began circa 1653 with purchase of land from the local natives.[5] The village was incorporated in 1926 as "Lauralton," but the name was changed to "Laurel Hollow" in 1935 to avoid postal confusion with Laurelton in Queens.[5] Today, Laurel Hollow is served by post offices in the hamlets of Syosset, Oyster Bay, Woodbury and Cold Spring Harbor.
The globally renowned Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory is located in the village.
Geography
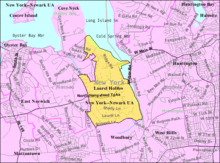
According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of 3.1 square miles (8.0 km2), of which 2.9 square miles (7.5 km2) is land and 0.2 square miles (0.52 km2), or 5.18%, is water.[6]
The village is situated in Nassau County and creates a portion of Nassau's eastern border with Suffolk County. Hilly terrain predominates in the area, and the forests are mostly deciduous trees with a low canopy of laurel bushes that provide a low evergreen canopy. New York State Route 25A passes through Laurel Hollow east-west.
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1930 | 161 | — | |
| 1940 | 110 | −31.7% | |
| 1950 | 169 | 53.6% | |
| 1960 | 834 | 393.5% | |
| 1970 | 1,401 | 68.0% | |
| 1980 | 1,527 | 9.0% | |
| 1990 | 1,748 | 14.5% | |
| 2000 | 1,930 | 10.4% | |
| 2010 | 1,952 | 1.1% | |
| 2020 | 1,940 | −0.6% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[7] | |||
As of the census[8] of 2000, there were 1,930 people, 598 households, and 528 families residing in the village. The population density was 660.0 inhabitants per square mile (254.8/km2). There were 621 housing units at an average density of 212.4 per square mile (82.0/km2). The racial makeup of the village was 91.30% White, 0.88% African American, 6.84% Asian, 0.21% from other races, and 0.78% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.97% of the population.
There were 598 households, out of which 44.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 81.8% were married couples living together, 5.4% had a female householder with no husband present, and 11.7% were non-families. 10.4% of all households were made up of individuals, and 4.5% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.20 and the average family size was 3.37.
In the village, the population was spread out, with 30.4% under the age of 18, 4.4% from 18 to 24, 21.7% from 25 to 44, 30.0% from 45 to 64, and 13.5% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 41 years. For every 100 females, there were 88.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 87.0 males.
The median income for a household in the village was in excess of $200,000, as is the median income for a family. Males had a median income of over $100,000 versus $60,000 for females. The per capita income for the village was $83,366. About 0.7% of families and 1.9% of the population were below the poverty line, including 1.0% of those under age 18 and 7.3% of those age 65 or over.
Education
Laurel Hollow is primarily served by the Cold Spring Harbor Central School District in Cold Spring Harbor (which is predominantly in Suffolk County), although a small portion of the village is served by the Oyster Bay-East Norwich Central School District.[9]
Landmarks
- Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, a non-profit institute that conducts biomedical research, trains scientists, and organizes scientific conferences.
- Cold Spring Harbor Fish Hatchery and Aquarium.
- Laurel Hollow Beach, on the west coast of Cold Spring Harbor's inner harbor.
Notable people
- Jay Gould, leading American railroad developer and speculator. His success at business made him the ninth richest U.S. citizen in history. Built Cedar Knolls for his grandson Frank Gould.[10]
- John Lennon, member of The Beatles, owned Cannon Hill, an estate with wife Yoko Ono in Laurel Hollow at the time of his death.[11]
- Lindsay Lohan, actress and TV personality, spent her early childhood years in Laurel Hollow.[12]
- Doug Morris, current Chairman of 12Tone Music Group. He previously served as Chairman and CEO of the Universal Music Group from 1995 to 2011, and Chairman and CEO of Sony Music Entertainment from 2011 to 2017. Founder (and former Chairman) of VEVO.[13]
- Louis Comfort Tiffany, the artist and decorative designer whose glass vases, lamps and windows depict scenes inspired by the view from Laurelton Hall, his estate in Laurel Hollow, and three of whose stained glass windows are housed in St. John's Episcopal Church in Cold Spring Harbor.
- James D. Watson, one of the first scientists to understand the double-helix structure of DNA and former chancellor of Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
- Ned Lamont, Governor of Connecticut (2019–present), spent some of his childhood years in Laurel Hollow.
References
- ^ [1], Village of Laurel Hollow:Homepage. Accessed September 24, 2017.
- ^ "ArcGIS REST Services Directory". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 20, 2022.
- ^ "Race, Hispanic or Latino, Age, and Housing Occupancy: 2010 Census Redistricting Data (Public Law 94-171) Summary File (QT-PL), Laurel Hollow village, New York". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 4, 2011.
- ^ "The Wealthiest Towns in America". BusinessWeek. Archived from the original on March 21, 2009. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ a b Winsche, Richard (October 1, 1999). The History of Nassau County Community Place-Names. Interlaken, New York: Empire State Books. ISBN 978-1557871541.
- ^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- ^ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ "Long Island Index: Interactive Map". www.longislandindexmaps.org. Retrieved August 29, 2021.
- ^ "'Cedar Knolls'".
- ^ "ColdSpringHarbor.com » Cold Spring Harbor Notable People, Lindsay Lohan, James Watson, John Lennon". coldspringharbor.com. Archived from the original on November 11, 2010.
- ^ "Lindsay Lohan's former LI home on market for $1.295M".
- ^ "Whitepages".