Ukrainian hryvnia
| українська гривня (Ukrainian) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| ISO 4217 | |||||
| Code | UAH (numeric: 980) | ||||
| Subunit | 0.01 | ||||
| Unit | |||||
| Plural | hryvni (nom. pl.), hryven (gen. pl.) | ||||
| Symbol | ₴ or грн | ||||
| Denominations | |||||
| Subunit | |||||
| 1⁄100 | kopiyka (копійка) | ||||
| Plural | |||||
| kopiyka (копійка) | kopiyky (nom. pl.), kopiyok (gen. pl.) | ||||
| Banknotes | |||||
| Freq. used | ₴20, ₴50, ₴100, ₴200, ₴500, ₴1,000 | ||||
| Rarely used | ₴1, ₴2, ₴5, ₴10 | ||||
| Coins | |||||
| Freq. used | ₴1, ₴2, ₴5, ₴10 | ||||
| Rarely used | 10, 50 kopiyok | ||||
| Demographics | |||||
| User(s) | |||||
| Issuance | |||||
| Central bank | National Bank of Ukraine | ||||
| Website | https://bank.gov.ua/en/ | ||||
| Printer | National Bank of Ukraine | ||||
| Mint | National Bank of Ukraine | ||||
| Valuation | |||||
| Inflation | 9.52% (2021 y-o-y)[1][failed verification] | ||||
| Source | NBU, 2019, May[2][failed verification] | ||||
| Method | CPI | ||||
The hryvnia (/(hə)ˈrɪvniə/ (hə-)RIV-nee-ə; Ukrainian: гривня [ˈɦrɪu̯nʲɐ] , abbr. грн hrn; sign: ₴; code: UAH) has been the national currency of Ukraine since 2 September 1996. The hryvnia is divided into 100 kopiyok. It is named after a measure of weight used in Kievan Rus'.[3]
Name
Etymology
The currency of Kievan Rus' in the 11th century was the grivna. The word is thought to derive from the Slavic griva; which compares with the Ukrainian, Russian, Bulgarian, and Serbo-Croatian word грива (griva, meaning "mane"). It might have indicated something valuable to be worn around the neck, that was usually made of silver or gold, and may be related to the Bulgarian and Serbian term grivna (гривна, "bracelet").
Following Ukraine's declared secession from Russia in 1917, the Ukrainian People's Republic named its currency hryvnia after the grivna of Kievan Rus'; these were designed by Heorhiy Narbut.
The word was used to describe silver or gold ingots of a certain weight.[citation needed]
Plural forms
The nominative plural of hryvnia is hryvni (Ukrainian: гривні), while the genitive plural is hryven’ (Ukrainian: гривень). In Ukrainian, the nominative plural form is used for numbers ending with 2, 3, or 4, as in dvi hryvni (дві гривні, "2 hryvni"), and the genitive plural is used for numbers ending with 5 to 9 and 0, for example sto hryven’ (сто гривень, "100 hryven’"); for numbers ending with 1 the nominative singular form is used, for example dvadtsiat’ odna hryvnia (двадцять одна гривня, "21 hryvnia").
An exception for this rule is numbers ending in 11, 12, 13 and 14 for which the genitive plural is also used, for example, dvanadciat’ hryven’ (дванадцять гривень, "12 hryven’"). The singular for the subdivision is копійка (kopiyka), the nominative plural is копійки (kopiyky) and the genitive is копійок (kopiyok).[citation needed]
Currency sign
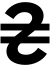
The hryvnia sign is a cursive Ukrainian letter He (г), with a double horizontal stroke (₴), symbolizing stability, similar to that used in other currency symbols such as the yen and Chinese yuan (¥, a symbol the currencies share), euro (€), and Indian rupee (₹). The sign was encoded as U+20B4 in Unicode 4.1 and released in 2005.[4] It is now supported by most systems. In Ukraine, if the hryvnia sign is unavailable, the Cyrillic abbreviation "грн" is used (which can be transliterated as "hrn").[citation needed]
History


On 22 December 1917, the Central Rada established Ukraine's state bank. The karbovanets became first currency of the Ukrainian People's Republic. On 5 January 1918, the first official 100 karbovanets banknote was issued, signed by Mykhailo Kryvetskyi, the first director of the state bank.
On 1 March 1918, the Central Council introduced a new currency, the hryvnia, consisting of 100 shahs and equaled to 1/2 of the previously issued karbovanets banknote.
In April 1918, Hetman Pavlo Skoropadsky reintroduced the karbovanets as the main currency of Ukraine. It consisted of 200 shahs, and denominations of 10, 25, 50, 100, 250 and 1,000 karbovanets were issued.
During the Nazi occupation of Ukraine in World War II, the German occupying government (Reichskommissariat Ukraine) issued banknotes denominated in karbovanets (karbowanez in German).
The third version of the karbovanets replaced rubles at par in 1992. The karbovanets was subject to hyperinflation in the early 1990s following the dissolution of the Soviet Union.[citation needed] The karbovanets was replaced by the hryvnia in September 1996, at a rate of 1 hryvnia to 100,000 karbovanets.[5]
The introduction of the hryvnia was done in a covert fashion.[6] It was introduced according to the Presidential Decree of 26 August 1996, published three days later. During the transition period, 2–16 September, both hryvnias and karbovanets could be used, but change could only be given in hryvnias. All bank accounts were converted to hryvnias automatically. During the transition period, 97% of karbovanets were taken out of circulation, with 56% being removed in the first five days of the currency reform.[6] After 16 September 1996, any remaining karbovanets in circulation could be exchanged for hryvnias in banks.[citation needed]
The hryvnia was introduced when the chairman of the National Bank of Ukraine was Viktor Yushchenko, but the new banknotes bore the signature of the previous chairman, Vadym Hetman. The first notes had been printed in 1992 by the Canadian Bank Note Company, but it was decided to delay their circulation until the hyperinflation in Ukraine had been brought under control.[citation needed]
On 18 March 2014, following the Russian annexation of Crimea, the interim administration of the Republic of Crimea announced that the hryvnia was to be dropped as the region's currency the following month.[7] It was replaced by the Russian ruble on 21 March 2014;[8] the hryvnia was allowed to be used for cash payments until 1 June.[8] Because of a lack of low-denomination Russian rubles in those raions of the Donbas under the control of the pro-Russian separatist states of Donetsk and Luhansk, the hryvnia remained the predominant currency until 2022.[9]
Coinage
Coins were first struck for the new currency in 1992, but were not introduced until September 1996. Initially, coins valued between 1 and 50 kopiyky were issued. In March 1997, ₴1 coins were added. Since 2004, commemorative ₴1 coins have been struck.
In October 2012, the National Bank of Ukraine announced that it was examining the possibility of withdrawing the 1 and 2 kopiyky coins from circulation,[10] as they had become too expensive to produce. After 2013, 1 and 2 kopiyky coins were not produced, but remained in circulation until 1 October 2019.[11] On 26 October 2012, the National Bank of Ukraine announced it was considering the introduction of a ₴2 coin.[12] Officially, as of 1 July 2016, 12.4 billion coins, with a face value of ₴1.4 billion were in circulation.[13] On 1 October 2019, 1, 2 and 5 kopiyky coins ceased to be legal tender. They can be still changed at banks.[14]
| Coins of the Ukrainian Hryvnia (1992–present)[15] | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image | Value | Technical parameters | Description | Date of | ||||||||
| Obverse | Reverse | Diameter | Mass | Composition | Edge | Obverse | Reverse | minting | issue | withdrawal | ||

|

|
1 kopiyka | 16 mm | 1.5 g | Stainless steel | Plain | Value, Ornaments |
Ukrainian Trident | 1992–2016 | 2 September 1996 | Not issued since 1 July 2018.[16] 1, 2, and 5-kopiyka coins withdrew from general circulation on 1 October 2019.[11] | |

|

|
2 kopiyky | 17.30 mm | 0.64 g (1992~1996) 1.8 g (2001–) |
aluminium (1992–1996), stainless steel (2001–) |
1992–2014 | ||||||

|

|
5 kopiyok | 24 mm | 4.3 g | stainless steel | Reeded | 1992–2015 | |||||

|

|
10 kopiyok | 16.3 mm | 1.7 g | brass (1992–1996), aluminium bronze (2001–) |
Reeded | Value, Ornaments |
Ukrainian Trident | 1992~present | 2 September 1996 | Current | |

|

|
25 kopiyok | 20.8 mm | 2.9 g | Reeded and plain sectors | 1992–2016 | Not issued since 1 July 2018.[16] 25-kopiyka coin ceased to be legal tender in Ukraine and gone out of circulation, effective 1 October 2020.[17][18] | |||||

|

|
50 kopiyok | 23 mm | 4.2 g | 1992~present | Current | ||||||

|

|
1 hryvnia | 26 mm | 7.1 g (1995,1996) 6.9 g (2001–) |
brass (1995, 1996), aluminium bronze (2001–) |
Inscription: "ОДНА ГРИВНЯ", minted year | 1995~2013 | 12 March 1997 | Current, but new design introduced in 2018 | |||

|

|
1 hryvnia | 26 mm | 6.8 g (2004–2016) | Aluminium bronze (2004–2016) | Plain with incuse lettering ("ОДНА · ГРИВНЯ · Date of issue") | Inscription: Coat of arms of Ukraine; УКРАЇНА 1 ГРИВНЯ; date of issue inside a decorative wreath | Half length figure of Volodymyr the Great holding a model church and staff with legend above | 2004–2016 | 2004 | ||
| 1 hryvnia | 18.9 mm | 3.3 g | Nickel-plated steel | Reeded | Coat of Arms of Ukraine, Value, Ornaments |
Volodymyr the Great | 2018[16] | Current | ||||

|

|
2 hryvni | 20.2 mm | 4.0 g | Yaroslav the Wise | |||||||

|

|
5 hryven | 22.1 mm | 5.2 g | Segmented (Plain and Reeded edges) | Bohdan Khmelnytsky | 2019 | |||||

|

|
10 hryven | 23.5 mm | 6.4 g | Nickel plated zinc alloy | Reeded | Ivan Mazepa | 2020[16] | ||||
| These images are to scale at 2.5 pixels per millimetre. For table standards, see the coin specification table. | ||||||||||||
Banknotes
In 1996, the first series of hryvnia banknotes was introduced into circulation by the National Bank of Ukraine. They were dated 1992 and were in denominations of 1, 2, 5, 10 and 20 hryvnias. The design of the banknotes was developed by Ukrainian artists Vasyl Lopata and Borys Maksymov.[19][20] The one hryvnia banknotes were printed by the Canadian Bank Note Company in 1992. The two, five and ten hryvnia banknotes were printed two years later. The banknotes were stored in Canada until they were put into circulation.[19]
Banknotes of the first series in denominations of 50 and 100 hryvnias also existed but were not introduced because these nominals were not needed in the economic crisis of the mid-1990s.
Also in 1996, the 1, 50, and 100 hryvnia notes of the second series were introduced, with 1 hryvnia dated 1994. The banknotes were designed and printed by Britain's De La Rue.[21] Since the opening of the Mint of the National Bank of Ukraine in cooperation with De La Rue in March 1994, all banknotes have been printed in Ukraine.[21]
Later, higher denominations were added. The 200 hryvnia notes of the second series were introduced in 2001, followed by the 500 hryvnia notes of the third series in 2006, and 1000 hryvnia notes of fourth series in 2019.
The 100 hryvnia denomination is quite common due to its moderately high value. Also common is the 200 and 500 hryvnia, as most Ukrainian ATMs dispense currency in these denominations.
In 2016, the NBU paper factory started producing banknote paper using flax instead of cotton.[22]
In 2019, the National Bank of Ukraine introduced a 1,000 hryvnia banknote and was issued into circulation on 25 October 2019.[23] The introduction of the new banknote was in response to the National Bank of Ukraine's efforts of streamlining the number of coins and banknotes already in circulation. The 1, 2, 5 and 10 hryvnia banknotes will continue to be legal tender alongside its equivalent coins in general circulation, while being withdrawn from circulation from repeated use in commerce.
In 2019, the National Bank of Ukraine introduced a revised 50 hryvnia banknote into circulation on 20 December 2019 and issued a revised 200 hryvnia banknote on 25 February 2020, thereby completing the family of notes which began with the issuance of the 100 hryvnia banknote in 2015.
Current series
| Denomination [1] and dimensions |
Image | Main colour | Description | Date of issue | Withdrawal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obverse | Reverse | Watermark | Obverse | Reverse | ||||
| ₴1 118 × 63 mm |
Yellow-blue | Volodymyr the Great of Kiev (c. 958–1015), Prince of Novgorod and Grand Prince of Kiev Ruler of Kievan Rus' in (980–1015) |
Volodymyr I's Fortress Wall in Kiev | 22 May 2006 | 1 October 2020 | |||
| ₴2 118 × 63 mm |
Terracotta | Yaroslav the Wise (c. 978 – 1054), Prince of Novgorod and Grand Prince of Kiev Ruler of Kievan Rus' in (1019–1054) |
Saint Sophia Cathedral, Kyiv | 24 September 2004 | ||||
| ₴5 118 × 63 mm |
Blue | Bohdan Khmelnytsky (c. 1595–1657), Hetman of Ukraine | A church in the village of Subotiv | 14 June 2004 | ||||
| ₴10 124 × 66 mm |
Crimson | Ivan Mazepa (1639–1709), Hetman of Ukraine | The Holy Dormition Cathedral of the Kyiv Pechersk Lavra | 1 November 2004 | ||||
| ₴20 130 × 69 mm |
Green | Ivan Franko (1856–1916), writer and politician | Lviv Theatre of Opera and Ballet | 25 September 2018 | Current | |||
| ₴50 136 × 72 mm |

|

|
Violet | Mykhailo Hrushevskyi (1866–1934), historian and politician. | The Tsentralna Rada building ("House of the Teacher" in Kyiv) | 20 December 2019 | ||
| ₴100 142 × 75 mm |

|

|
Olive | Taras Shevchenko (1814–1861), poet and artist | Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv | 9 March 2015 | ||
| ₴200 148 × 75 mm |

|

|
Pink | Lesya Ukrainka (1871–1913), poet and writer | Entrance Tower of Lutsk Castle | 25 February 2020 | ||
| ₴500 154 × 75 mm |

|

|
Brown | Hryhorii Skovoroda (1722–1794), philosopher and poet | National University of Kyiv-Mohyla Academy | 11 April 2016 | ||
| ₴1,000 160 × 75 mm |

|

|
Blue | Volodymyr Vernadskyi (1863–1945), historian, philosopher, naturalist and scientist | National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine | 25 October 2019 | ||
| These images are to scale at 0.7 pixel per millimetre. For table standards, see the banknote specification table. | ||||||||
Exchange rates
Official NBU exchange rate at moment of introduction was UAH 1.76 per 1 US dollar.[24]
Following the Asian financial crisis in 1998, the currency was devalued to UAH 5.6 = USD 1.00 in February 2000. Later, the exchange rate remained relatively stable at around 5.4 hryvnias for 1 US dollar and was fixed to 5.05 hryvnias for 1 US dollar from 21 April 2005 until 21 May 2008. In mid-October 2008 rapid devaluation began, in the course of a global financial crisis that hit Ukraine hard, with the hryvnia dropping 38.4% from UAH 4.85 for 1 US dollar on 23 September 2008 to UAH 7.88 for 1 US dollar on 19 December 2008.[25] After a period of instability, a new peg of 8 hryvnias per US dollar was established, remaining for several years. In 2012, the peg was changed to a managed float (much like that of the Chinese yuan) as the euro and other European countries' currencies weakened against the dollar due to the European debt crisis, and the value in mid-2012 was about ₴8.14 per dollar.[citation needed]
As from 7 February 2014, following political instability in Ukraine, the National Bank of Ukraine changed the hryvnia into a fluctuating/floating currency in an attempt to meet IMF requirements and to try to enforce a stable price for the currency in the Forex market.[26] In 2014 and 2015, the hryvnia lost about 70% of its value against the U.S. dollar, with the currency reaching a record low of ₴33 per dollar in February 2015.[27]
On 31 July 2019, the hryvnia to U.S. dollar exchange rate in the interbank foreign exchange market strengthened to ₴24.98 — the highest level in 3 years.[28]
Following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the official exchange rate of hryvnia was fixed at ₴29.25 per U.S. dollar and ₴33.17 per euro. On 21 July 2022, it was devalued to ₴36.5686 per US dollar,[29] to bring it into alignment with the black market.[30]
The international mid-market exchange rate fluctuates, but values the hryvnia slightly lower than the official rate.[31]
| Year | USD | EUR | RUB | CHF | BTC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 5.3345 | 4.9415 | 3.2246 | ||
| 2001 | 5.4125 | 4.4860 | 3.1871 | ||
| 2002 | 5.3304 | 5.0023 | 3.4288 | ||
| 2003 | 5.3318 | 6.1980 | 3.9614 | ||
| 2004 | 5.3072 | 6.9395 | 0.1986 | 4.2818 | |
| 2005 | 5.2799 | 6.1312 | 0.1805 | 4.1275 | |
| 2006 | 5.0500 | 6.3620 | 0.1843 | 4.0278 | |
| 2007 | 5.0500 | 7.0010 | 0.1943 | 4.2116 | |
| 2008 | 6.8777 | 8.9879 | 0.2433 | 4.8609 | |
| 2009 | 7.7038 | 11.2046 | 0.2619 | 7.1950 | 0.0000 |
| 2010 | 7.9356 | 10.5329 | 0.2610 | 7.6261 | 3.2992 |
| 2011 | 7.9930 | 11.0921 | 0.2720 | 9.0141 | 105.3409 |
| 2012 | 7.9880 | 10.2706 | 0.2570 | 8.5208 | 38.6018 |
| 2013 | 7.9930 | 10.6122 | 0.2510 | 8.6233 | 1,573.15 |
| 2014 | 12.2967 | 15.7159 | 0.3110 | 12.9501 | 5,428.19 |
| 2015 | 21.5751 | 24.2287 | 0.3620 | 22.6973 | 7,956.56 |
| 2016 | 25.2860 | 28.2919 | 0.3830 | 25.9546 | 13,427.58 |
| 2017 | 27.1194 | 30.0042 | 0.4560 | 26.9990 | 115,302.94 |
| 2018 | 27.4550 | 32.1429 | 0.4360 | 27.8305 | 219,979.42 |
| 2019 | 24.4558 | 28.9518 | 0.3990 | 26.0025 | 189,893.73 |
| 2020 | 25.4555 | 30.7900 | 0.3740 | 28.7600 | 313,830.20 |
| 2021 | 27.7235 | 32.3100 | 0.3700 | 29.8600 | 1,304,733.15 |
| 2022 | 34.5886 | 35.9210 | 0.4476 | 35.5610 | 815,943.77 |
| 2023 | 36.4136 | 38.3263 | 0.4054 | 40.1478 | 1,052,340.81 |
| 2024 | 38.3109 | 41.5476 | 0.4189 | 43.6031 | 1,818,454.39 |
| Current UAH exchange rates | |
|---|---|
| From Google Finance: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD |
| From Yahoo! Finance: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD |
| From XE.com: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD |
| From OANDA: | AUD CAD CHF CNY EUR GBP HKD JPY USD |
See also
References
- ^ "Ukrania Hryvnia". Archived from the original on 8 March 2017.
- ^ "Archived". Archived from the original on 2016-05-06. Retrieved 2016-06-01.
- ^ Langer, Lawrence N. (2002). "Grivna". Historical Dictionary of Medieval Russia. Scarecrow Press. pp. 56–57. ISBN 9780810866188. Archived from the original on 2020-01-17. Retrieved 2022-03-02.
- ^ * Michael Everson's "Proposal to encode the HYRVNIA SIGN and CEDI SIGN in the UCS" (PDF). 23 April 2004. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 October 2020. Retrieved 23 April 2004.
- ^ "National Bank of Ukraine". Bank.gov.ua. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- ^ a b "Volodymyr Matvienko. Autograph on Hryvnia" (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on December 31, 2008.
- ^ "Ukrainian hryvnia to be dropped in April: Crimean gov't official". CCTV News America. 18 March 2014. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 18 March 2014.
- ^ a b Crimea enters the rouble zone Archived 2014-11-29 at the Wayback Machine, ITAR-TASS (1 June 2014)
- ^ ""In theory, it is possible to pay with Ukrainian hryvnias, Russian rubles, US dollars, and euros in the DPR and the LPR. However, only the two former currencies are in common use. Their exchange rate has been fixed by the governments, and is 1:2 (one hryvnia is the equivalent of two rubles). However, there is a shortage of low denomination rubles, so the Ukrainian hryvnia is still the most popular means of payment."". Osw.waw.pl. 17 June 2015. Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ "НБУ в ближайшие месяцы рассмотрит вопрос о целесообразности использования 1-2-копеечных монет". Rbc.ua. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ a b "NBU Streamlines Hryvnia Banknote and Coin Denominations". National Bank of Ukraine. 25 June 2019. Archived from the original on 22 October 2020. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- ^ НБУ рассмотрит вопрос введения в обращение 2-гривневой монеты [RBK will consider the issuance of 2-hryvnia coin] (in Russian). RBK Ukraina. 26 October 2012. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014.
- ^ "Cash_Circulation". October 28, 2019. Archived from the original on 2019-10-28.
- ^ "Монетами 1, 2 та 5 копійок не можна розраховуватися з 1 жовтня 2019 року". Національний банк України. Archived from the original on 2021-04-16. Retrieved 2021-04-16.
- ^ "Розмінні й обігові монети". Bank.gov.ua. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ a b c d "Національний банк презентував нові обігові монети". Bank.gov.ua. Archived from the original on 2018-08-30. Retrieved 2018-04-07.
- ^ "25-Kopiyka Coins and Old Series Hryvnia Banknotes to Cease Being Legal Ten-der from 1 October 2020". National Bank of Ukraine. 2 Sep 2020. Archived from the original on 21 October 2020. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- ^ "NBU to Withdraw 25.Kopiyka Coins and Hryvnia Banknotes 01 Designed before 2003 from Circulation, Effective 1 October 2020". National Bank of Ukraine. 30 Sep 2020. Archived from the original on 13 October 2020. Retrieved 19 October 2020.
- ^ a b Как появилась гривна [How hryvnia was born] (in Russian). Podrobnosti. 4 September 2006. Archived from the original on 13 March 2014.
- ^ "The man who designed Hryvnia". Zerkalo Nedeli (in Russian). Archived from the original on April 23, 2008.
- ^ a b "Hryvnia-Immigrant". Zerkalo Nedeli (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 2010-12-29.
- ^ "NBU Starts Printing Money from Flax – Незалежний АУДИТОР". N-auditor.com.ua. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- ^ Brand new 1,000-hryvnia banknote put into circulation on Oct 25 Archived 2019-10-25 at the Wayback Machine, UNIAN (25 October 2019)
- ^ "Результати пошуку". Bank.gov.ua. Archived from the original on 22 December 2012. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- ^ National Bank of Ukraine Archived 2008-12-18 at the Wayback Machine, historical exchange rates
- ^ "7 лютого 2014 року Національний банк України вводить в обіг пам'ятну монету "Визволення Нікополя від фашистських загарбників"" [7 February 2014 the National Bank of Ukraine will issue commemorative coins "Nikopol Liberation from the Nazis"]. 7 February 2014. Archived from the original on 21 February 2014.
- ^ Ukraine teeters a few steps from chaos Archived 2019-05-19 at the Wayback Machine, BBC News (5 February 2016)
- ^ US dollar in Ukraine costs less than Hr 25 for the first time in 3 years Archived 2021-11-09 at the Wayback Machine Kyiv Post, July 31, 2019
- ^ Ukraine Devalues Hryvnia to Adjust to War-Time Economic Reality bloomberg.com, July 21, 2022
- ^ Culverwell, Dominic (21 July 2022). "Ukraine's central bank devalues hryvnia rate to 36.5686 to the dollar". bne IntelliNews. Berlin.
- ^ "Best USD to UAH Exchange Rates Compared Live". Money transfer. Current mid-market rate, updated frequently.
Bibliography
- Krause, Chester L.; Clifford Mishler (1991). Standard Catalog of World Coins: 1801–1991 (18th ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0873411501.
- Cuhaj, George S. (editor) (2006). Standard Catalog of World Paper Money: Modern Issues 1961-Present (12th ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0-89689-356-1.
{{cite book}}:|author1=has generic name (help)
External links
- The history of the hryvnia from the National Bank of Ukraine
- National Bank of Ukraine announcement of Hryvnia Sign (in Ukrainian)
- Proposed symbols for hryvnia during design competition (in Ukrainian)
- Images of hryvnia notes introduced in 1997
- The first Ukrainian Money (1917–1922) from the Odesa Numismatics Museum
- Ukraine monetary reform. Numismatics (in Russian)
- List of coins of Ukraine (Numista)
| Preceded by: Various |
Currency of Kievan Rus' 11th century – 15th century |
Succeeded by: Various |
| Preceded by: Ukrainian karbovanets |
Currency of Ukrainian People's Republic 1 March 1918 – April 1918 |
Succeeded by: Ukrainian karbovanets Reason: coup d'état (on 29 April 1918) |
| Preceded by: Ukrainian karbovanets Reason: coup d'état (on 14 December 1918) |
Currency of Ukrainian People's Republic December 1918 – November 1920 |
Succeeded by: Soviet karbovanets Reason: Soviet reintegration |
| Preceded by: Ukrainian karbovanets Reason: inflation (on 2 September 1996) Ratio: 1 hryvnia = 100,000 karbovanets |
Currency of Ukraine 2 September 1996 – |
Succeeded by: Current |





