Insect wing
Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to fly. They are found on the second and third thoracic segments (the mesothorax and metathorax), and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane (extreme examples include the dragonflies and lacewings). The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family or even genus level in many orders of insects.
Physically, some insects move their flight muscles directly, others indirectly. In insects with direct flight, the wing muscles directly attach to the wing base, so that a small downward movement of the wing base lifts the wing itself upward. Those insects with indirect flight have muscles that attach to and deform the thorax, causing the wings to move as well.
The wings are present in only one sex (often the male) in some groups such as velvet ants and Strepsiptera, or are selectively lost in "workers" of social insects such as ants and termites. Rarely, the female is winged but the male not, as in fig wasps. In some cases, wings are produced only at particular times in the life cycle, such as in the dispersal phase of aphids. Wing structure and colouration often vary with morphs, such as in the aphids, migratory phases of locusts and polymorphic butterflies. At rest, the wings may be held flat, or folded a number of times along specific patterns; most typically, it is the hindwings which are folded, but in a few groups such as the vespid wasps, it is the forewings.
The evolutionary origin of the insect wing is debated. During the 19th century, the question of insect wing evolution originally rested on two main positions. One position postulated insect wings evolved from pre-existing structures, while the second proposed insect wings were entirely novel formations.[1][2] The “novel” hypothesis suggested that insect wings did not form from pre-existing ancestral appendages but rather as outgrowths from the insect body wall.[3]
Long since, research on insect wing origins has built on the “pre-existing structures” position that was originally proposed in the 19th century.[2] Recent literature has pointed to several ancestral structures as being important to the origin of insect wings. Among these include: gills, respiratory appendages of legs, and lateral (paranotal) and posterolateral projections of the thorax to name a few.[4]
According to more current literature, possible candidates include gill-like structures, the paranotal lobe, and the crustacean tergal plate. The latter is based on recent insect genetic research which indicates that insects are pan-crustacean arthropods with a direct crustacean ancestor and shared genetic mechanisms of limb development.[3][5][6][7][8]
Other theories of the origin of insect wings are the paranotal lobe theory, the gill theory and the dual theory of insect wing evolution. These theories postulate that wings either developed from paranotal lobes, extensions of the thoracic terga;[5] that they are modifications of movable abdominal gills as found on aquatic naiads of mayflies;[5] or that insect wings arose from the fusion of pre-existing endite and exite structures each with pre-existing articulation and tracheation.[9][10]
Morphology

Internal
Each of the wings consists of a thin membrane supported by a system of veins. The membrane is formed by two layers of integument closely apposed, while the veins are formed where the two layers remain separate; sometimes the lower cuticle is thicker and more heavily sclerotized under a vein. Within each of the major veins there is a nerve and a trachea, and, since the cavities of the veins are connected with the hemocoel, hemolymph can flow into the wings.[11]
As the wing develops, the dorsal and ventral integumental layers become closely apposed over most of their area forming the wing membrane. The remaining areas form channels, the future veins, in which the nerves and tracheae may occur. The cuticle surrounding the veins becomes thickened and more heavily sclerotized to provide strength and rigidity to the wing. Two types of hair may occur on the wings: microtrichia, which are small and irregularly scattered, and macrotrichia, which are larger, socketed, and may be restricted to veins. The scales of Lepidoptera and Trichoptera are highly modified macrotrichia.[12]
Venation

In some very small insects, the venation may be greatly reduced. In chalcidoid wasps, for instance, only the subcosta and part of the radius are present. Conversely, an increase in venation may occur by the branching of existing veins to produce accessory veins or by the development of additional, intercalary veins between the original ones, as in the wings of Orthoptera (grasshoppers and crickets). Large numbers of cross-veins are present in some insects, and they may form a reticulum as in the wings of Odonata (dragonflies and damselflies) and at the base of the forewings of Tettigonioidea and Acridoidea (katydids and grasshoppers respectively).[11]
The archedictyon is the name given to a hypothetical scheme of wing venation proposed for the very first winged insect. It is based on a combination of speculation and fossil data. Since all winged insects are believed to have evolved from a common ancestor, the archedictyon represents the "template" that has been modified (and streamlined) by natural selection for 200 million years. According to current dogma, the archedictyon contained 6–8 longitudinal veins. These veins (and their branches) are named according to a system devised by John Comstock and George Needham—the Comstock–Needham system:[13]
- Costa (C) – the leading edge of the wing
- Subcosta (Sc) – second longitudinal vein (behind the costa), typically unbranched
- Radius (R) – third longitudinal vein, one to five branches reach the wing margin
- Media (M) – fourth longitudinal vein, one to four branches reach the wing margin
- Cubitus (Cu) – fifth longitudinal vein, one to three branches reach the wing margin
- Anal veins (A1, A2, A3) – unbranched veins behind the cubitus
The costa (C) is the leading marginal vein on most insects. Sometimes, there is a small vein above the costa called the precosta, although in almost all extant insects,[14]: 41–42 the precosta is fused with the costa. The costa rarely ever branches because it is at the leading edge, which is associated at its base with the humeral plate. The trachea of the costal vein is perhaps a branch of the subcostal trachea. Located after the costa is the third vein, the subcosta, which branches into two separate veins: the anterior and posterior. The base of the subcosta is associated with the distal end of the neck of the first axillary (see section below). The fourth vein is the radius (R), which is branched into five separate veins. The radius is generally the strongest vein of the wing. Toward the middle of the wing, it forks into a first undivided branch (R1) and a second branch, called the radial sector (Ra), which subdivides dichotomously into four distal branches (R2, R3, R4, R5). Basally, the radius is flexibly united with the anterior end of the second axillary (2Ax).[15]
The fifth vein of the wing is the media. In the archetype pattern (A), the media forks into two main branches: a media anterior (MA), which divides into two distal branches (MA1, MA2), and a median sector, or media posterior (MP), which has four terminal branches (M1, M2, M3, M4). In most modern insects the media anterior has been lost, and the usual "media" is the four-branched media posterior with the common basal stem. In the Ephemerida, according to present interpretations of the wing venation, both branches of the media are retained, while in Odonata the persisting media is the primitive anterior branch. The stem of the media is often united with the radius, but when it occurs as a distinct vein its base is associated with the distal median plate (m') or is continuously sclerotized with the latter. The cubitus, the sixth vein of the wing, is primarily two-branched. The primary forking of the takes place near the base of the wing, forming the two principal branches (Cu1, Cu2). The anterior branch may break up into a number of secondary branches, but commonly it forks into two distal branches. The second branch of the cubitus (Cu2) in Hymenoptera, Trichoptera, and Lepidoptera was mistaken by Comstock and Needham for the first anal. Proximally the main stem of the cubitus is associated with the distal median plate (m') of the wing base.[15]
Postcubitus (Pcu) is the first anal of the Comstock–Needham system. The postcubitus, however, has the status of an independent wing vein and should be recognized as such.[citation needed] In nymphal wings, its trachea arises between the cubital trachea and the group of vannal tracheae. In the mature wings of more generalized insect the Postcubitus is always associated proximally with the cubitus and is never intimately connected with the flexor sclerite (3Ax) of the wing base. In Neuroptera, Mecoptera, and Trichoptera the postcubitus may be more closely associated with the vannal veins, but its base is always free from the latter. The postcubitus is usually unbranched; it is primitively two branched. The vannal veins (lV to nV) are the anal veins that are immediately associated with the third axillary, and which are directly affected by the movement of this sclerite that brings about the flexion of the wings. In number the vannal veins vary. from 1 to 12, according to the expansion of the vannal area of the wing. The vannal tracheae usually arise from a common tracheal stem in nymphal insects, and the veins are regarded as branches of a single anal vein. Distally the vannal veins are either simple or branched. Jugal Veins (J) of the jugal lobe of the wing is often occupied by a network of irregular veins, or it may be entirely membranous; but sometimes it contains one or two distinct small veins, the first jugal vein, or vena arcuata, and the second jugal vein, or vena cardinalis (2J).[15]
- C-Sc cross-veins – run between the costa and subcosta
- R cross-veins – run between adjacent branches of the radius
- R-M cross-veins – run between the radius and media
- M-Cu cross-veins – run between the media and cubitus
All the veins of the wing are subject to secondary forking and to union by cross-veins. In some orders of insects the cross-veins are so numerous that the whole venational pattern becomes a close network of branching veins and cross-veins. Ordinarily, however, there is a definite number of cross-veins having specific locations. The more constant cross-veins are the humeral cross-vein (h) between costa and subcosta, the radial cross-vein (r) between R and the first fork of Rs, the sectorial cross-vein (s) between the two forks of R8, the median cross-vein (m–m) between M2 and M3, and the mediocubital cross-vein (m-cu) between media and cubitus.[15]
The veins of insect wings are characterized by a convex-concave placement, such as those seen in mayflies (i.e., concave is "down" and convex is "up") which alternate regularly and by its triadic type of branching; whenever a vein forks there is always an interpolated vein of the opposite position between the two branches. A concave vein will fork into two concave veins (with the interpolated vein being convex) and the regular alteration of the veins is preserved.[16] The veins of the wing appear to fall into an undulating pattern according to whether they have a tendency to fold up or down when the wing is relaxed. The basal shafts of the veins are convex, but each vein forks distally into an anterior convex branch and a posterior concave branch. Thus the costa and subcosta are regarded as convex and concave branches of a primary first vein, Rs is the concave branch of the radius, posterior media the concave branch of the media, Cu1 and Cu2 are respectively convex and concave, while the primitive Postcubitus and the first vannal have each an anterior convex branch and a posterior concave branch. The convex or concave nature of the veins has been used as evidence in determining the identities of the persisting distal branches of the veins of modern insects, but it has not been demonstrated to be consistent for all wings.[11][15]
Fields
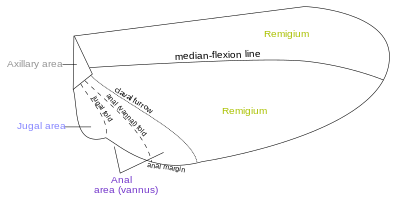
Wing areas are delimited and subdivided by fold-lines along which the wing can fold, and flexion-lines along which the wing can flex during flight. The fundamental distinction between the flexion-lines and the fold-lines is often blurred, as fold-lines may permit some flexibility or vice versa. Two constants that are found in nearly all insect wings are the claval (a flexion-line) and jugal folds (or fold line); forming variable and unsatisfactory boundaries. Wing foldings can be very complicated, with transverse folding occurring in the hindwings of Dermaptera and Coleoptera, and in some insects the anal area can be folded like a fan.[14] There are about four different fields found on the insect wings:
- Remigium
- Anal area (vannus)
- Jugal area
- Axillary area
- Alula
Most veins and crossveins occur in the anterior area of the remigium, which is responsible for most of the flight, powered by the thoracic muscles. The posterior portion of the remigium is sometimes called the clavus; the two other posterior fields are the anal and jugal ares.[14] When the vannal fold has the usual position anterior to the group of anal veins, the remigium contains the costal, subcostal, radial, medial, cubital, and postcubital veins. In the flexed wing the remigiumturns posteriorly on the flexible basal connection of the radius with the second axillary, and the base of the mediocubital field is folded medially on the axillary region along the plica basalis (bf) between the median plates (m, m') of the wing base.[15]
The vannus is bordered by the vannal fold, which typically occurs between the postcubitus and the first vannal vein. In Orthoptera it usually has this position. In the forewing of Blattidae, however, the only fold in this part of the wing lies immediately before the postcubitus. In Plecoptera the vannal fold is posterior to the postcubitus, but proximally it crosses the base of the first vannal vein. In the cicada the vannal fold lies immediately behind the first vannal vein (lV). These small variations in the actual position of the vannal fold, however, do not affect the unity of action of the vannal veins, controlled by the flexor sclerite (3Ax), in the flexion of the wing. In the hindwings of most Orthoptera a secondary vena dividens forms a rib in the vannal fold. The vannus is usually triangular in shape, and its veins typically spread out from the third axillary like the ribs of a fan. Some of the vannal veins may be branched, and secondary veins may alternate with the primary veins. The vannal region is usually best developed in the hindwing, in which it may be enlarged to form a sustaining surface, as in Plecoptera and Orthoptera. The great fanlike expansions of the hindwings of Acrididae are clearly the vannal regions, since their veins are all supported on the third axillary sclerites on the wing bases, though Martynov (1925) ascribes most of the fan areas in Acrididae to the jugal regions of the wings. The true jugum of the acridid wing is represented only by the small membrane (Ju) mesad of the last vannal vein. The jugum is more highly developed in some other Polyneoptera, as in the Mantidae. In most of the higher insects with narrow wings the vannus becomes reduced, and the vannal fold is lost, but even in such cases the flexed wing may bend along a line between the postcubitus and the first vannal vein.[15]
The Jugal Region, or Neala, is a region of the wing that is usually a small membranous area proximal to the base of the vannus strengthened by a few small, irregular veinlike thickenings; but when well developed it is a distinct section of the wing and may contain one or two jugal veins. When the jugal area of the forewing is developed as a free lobe, it projects beneath the humeral angle of the hindwing and thus serves to yoke the two wings together. In the Jugatae group of Lepidoptera it bears a long finger-like lobe. The jugal region was termed the neala ("new wing") because it is evidently a secondary and recently developed part of the wing.[15]
The axillary region is region containing the axillary sclerites has in general the form of a scalene triangle. The base of the triangle (a-b) is the hinge of the wing with the body; the apex (c) is the distal end of the third axillary sclerite; the longer side is anterior to the apex. The point d on the anterior side of the triangle marks the articulation of the radial vein with the second axillary sclerite. The line between d and c is the plica basalis (bf), or fold of the wing at the base of the mediocubital field.[15] The termen is the outer margin of the wing, between apex and hind or anal angle.[17][18]
At the posterior angle of the wing base in some Diptera there is a pair of membranous lobes (squamae, or calypteres) known as the alula. The alula is well developed in the house fly. The outer squama (c) arises from the wing base behind the third axillary sclerite (3Ax) and evidently represents the jugal lobe of other insects (A, D); the larger inner squama (d) arises from the posterior scutellar margin of the tergum of the wing-bearing segment and forms a protective, hoodlike canopy over the haltere. In the flexed wing the outer squama of the alula is turned upside down above the inner squama, the latter not being affected by the movement of the wing. In many Diptera a deep incision of the anal area of the wing membrane behind the single vannal vein sets off a proximal alar lobe distal to the outer squama of the alula.[15]
Joints

The various movements of the wings, especially in insects that flex the wings horizontally over the back when at rest, demand a more complicated articular structure at the wing base than a mere hinge of the wing with the body. Each wing is attached to the body by a membranous basal area, but the articular membrane contains a number of small articular sclerites, collectively known as the pteralia. The pteralia include an anterior humeral plate at the base of the costal vein, a group of axillaries (Ax) associated with the subcostal, radial, and vannal veins, and two less definite median plates (m, m') at the base of the mediocubital area. The axillaries are specifically developed only in the wing-flexing insects, where they constitute the flexor mechanism of the wing operated by the flexor muscle arising on the pleuron. Characteristic of the wing base is also a small lobe on the anterior margin of the articular area proximal to the humeral plate, which, in the forewing of some insects, is developed into a large, flat, scale-like flap, the tegula, overlapping the base of the wing. Posteriorly the articular membrane often forms an ample lobe between the wing and the body, and its margin is generally thickened and corrugated, giving the appearance of a ligament, the so-called axillary cord, continuous mesally with the posterior marginal scutellar fold of the tergal plate bearing the wing.[15]
The articular sclerites, or pteralia, of the wing base of the wing-flexing insects and their relations to the body and the wing veins, shown diagrammatically, are as follows:
- Humeral plates
- First Axillary
- Second Axillary
- Third Axillary
- Fourth Axillary
- Median plates (m, m')
The humeral plate is usually a small sclerite on the anterior margin of the wing base, movable and articulated with the base of the costal vein. Odonata have their humeral plate greatly enlarged,[15] with two muscles arising from the episternum inserted into the Humeral plates and two from the edge of the epimeron inserted into the axillary plate.[11]
The first axillary sclerite (lAx) is the anterior hinge plate of the wing base. Its anterior part is supported on the anterior notal wing process of the tergum (ANP); its posterior part articulates with the tergal margin. The anterior end of the sclerite is generally produced as a slender arm, the apex of which (e) is always associated with the base of the subcostal vein (Sc), though it is not united with the latter. The body of the sclerite articulates laterally with the second axillary. The second axillary sclerite (2Ax) is more variable in form than the first axillary, but its mechanical relations are no less definite. It is obliquely hinged to the outer margin of the body of the first axillary, and the radial vein (R) is always flexibly attached to its anterior end (d). The second axillary presents both a dorsal and a ventral sclerotization in the wing base; its ventral surface rests upon the fulcral wing process of the pleuron. The second axillary, therefore, is the pivotal sclerite of the wing base, and it specifically manipulates the radial vein.[15]
The third axillary sclerite (3Ax) lies in the posterior part of the articular region of the wing. Its form is highly variable and often irregular, but the third axillary is the sclerite on which is inserted the flexor muscle of the wing (D). Mesally it articulates anteriorly (f) with the posterior end of the second axillary, and posteriorly (b) with the posterior wing process of the tergum (PNP), or with a small fourth axillary when the latter is present. Distally the third axillary is prolonged in a process which is always associated with the bases of the group of veins in the anal region of the wing here termed the vannal veins (V). The third axillary, therefore, is usually the posterior hinge plate of the wing base and is the active sclerite of the flexor mechanism, which directly manipulates the vannal veins. The contraction of the flexor muscle (D) revolves the third axillary on its mesal articulations (b, f) and thereby lifts its distal arm; this movement produces the flexion of the wing. The Fourth Axillary sclerite is not a constant element of the wing base. When present it is usually a small plate intervening between the third axillary and the posterior notal wing process and is probably a detached piece of the latter.[15]
The median plates (m, m') are also sclerites that are not so definitely differentiated as specific plates as are the three principal axillaries, but nevertheless they are important elements of the flexor apparatus. They lie in the median area of the wing base distal to the second and third axillaries and are separated from each other by an oblique line (bf) which forms a prominent convex fold during flexion of the wing. The proximal plate (m) is usually attached to the distal arm of the third axillary and perhaps should be regarded as a part of the latter. The distal plate (m') is less constantly present as a distinct sclerite and may be represented by a general sclerotization of the base of the mediocubital field of the wing. When the veins of this region are distinct at their bases, they are associated with the outer median plate.[15]
Muscles

The muscles that control flight in insects can take up to 10% to 30% of the total body mass. The muscles that control flight vary with the two types of flight found in insects: indirect and direct. Insects that use first, indirect, have the muscles attach to the tergum instead of the wings, as the name suggests. As the muscles contract, the thoracic box becomes distorted, transferring the energy to the wing. There are two "bundles" of muscles, those that span parallel to the tergum, the dorsolongitudinals, and those that are attached to the tegum and extend to the sternum, the dorsoventrals.[19] In direct muscle, the connection is directly from the pleuron (thoracic wall) to individual sclerites located at the base of the wing. The subalar and basilar muscles have ligament attachments to the subalar and basilar sclerites. Here resilin, a highly elastic material, forms the ligaments connecting flight muscles to the wing apparatus.
In more derived orders of insects, such as Diptera (flies) and Hymenoptera (wasp), the indirect muscles occupy the greatest volume of the pterothorax and function as the primary source of power for the wingstroke. Contraction of the dorsolongitudinal muscles causes the severe arching of the notum which depresses the wing while contraction of the dorsoventral muscles causes opposite motion of notum. The most primitive extant flying insects, Ephemeroptera (mayflies) and Odonata (dragonflies), use direct muscles that are responsible for developing the needed power for the up and down strokes.[19][20]
Insect wing muscle is a strictly aerobic tissue. Per unit protein it consumes fuel and oxygen at rates taking place in a very concentrated and highly organized tissue so that the steady-state rates per unit volume represent an absolute record in biology. The fuel and oxygen rich blood is carried to the muscles through diffusion occurring in large amounts, in order to maintain the high level of energy used during flight. Many wing muscles are large and may be as large as 10 mm in length and 2 mm in width. Moreover, in some Diptera the fibres are of giant dimensions. For instance, in the very active Rutilia, the cross-section is 1800 μm long and more than 500 μm wide. The transport of fuel and oxygen from the surroundings to the sites of consumption and the reverse transport of carbon dioxide therefore represent a challenge to the biologist both in relation to transport in the liquid phase and in the intricate system of air tubes, i.e. in the tracheal system.[21]
Sensors
Several types of sensory neurons are found on insect wings: gustatory bristles,[22] mechanosensory bristles,[23] campaniform sensilla,[24] and chordotonal organs.[25] These sensors provide the nervous system with both external and internal proprioceptive feedback necessary for effective flight[26] and grooming.[27]
Coupling, folding, and other features
In many insect species, the forewing and hindwing can be coupled together, which improves the aerodynamic efficiency of flight by joining the forewing and hindwing into one bigger wing. The most common coupling mechanism (e.g., Hymenoptera and Trichoptera) is a row of small hooks on the forward margin of the hindwing, or "hamuli", which lock onto the forewing, keeping them held together (hamulate coupling). In some other insect species (e.g., Mecoptera, Lepidoptera, and some Trichoptera) the jugal lobe of the forewing covers a portion of the hindwing (jugal coupling), or the margins of the forewing and hindwing overlap broadly (amplexiform coupling), or the hindwing bristles, or frenulum, hook under the retaining structure or retinaculum on the forewing.[14]: 43
When at rest, the wings are held over the back in most insects, which may involve longitudinal folding of the wing membrane and sometimes also transverse folding. Folding may sometimes occur along the flexion lines. Though fold lines may be transverse, as in the hindwings of beetles and earwigs, they are normally radial to the base of the wing, allowing adjacent sections of a wing to be folded over or under each other. The commonest fold line is the jugal fold, situated just behind the third anal vein,[12] although, most Neoptera have a jugal fold just behind vein 3A on the forewings. It is sometimes also present on the hindwings. Where the anal area of the hindwing is large, as in Orthoptera and Blattodea, the whole of this part may be folded under the anterior part of the wing along a vannal fold a little posterior to the claval furrow. In addition, in Orthoptera and Blattodea, the anal area is folded like a fan along the veins, the anal veins being convex, at the crests of the folds, and the accessory veins concave. Whereas the claval furrow and jugal fold are probably homologous in different species, the vannal fold varies in position in different taxa. Folding is produced by a muscle arising on the pleuron and inserted into the third axillary sclerite in such a way that, when it contracts, the sclerite pivots about its points of articulation with the posterior notal process and the second axillary sclerite.[11]
As a result, the distal arm of the third axillary sclerite rotates upwards and inwards, so that finally its position is completely reversed. The anal veins are articulated with this sclerite in such a way that when it moves they are carried with it and become flexed over the back of the insect. Activity of the same muscle in flight affects the power output of the wing and so it is also important in flight control. In orthopteroid insects, the elasticity of the cuticle causes the vannal area of the wing to fold along the veins. Consequently, energy is expended in unfolding this region when the wings are moved to the flight position. In general, wing extension probably results from the contraction of muscles attached to the basilar sclerite or, in some insects, to the subalar sclerite.[11]
Flight

Flight mechanisms
Two groups of relatively large insects, the Ephemeroptera (mayflies) and the Odonata (dragonflies and damselflies) have the flight muscles attached directly to their wings; the wings can beat no faster than the rate at which nerves can send impulses to command the muscles to beat.[28] All other living winged insects fly using a different mechanism, involving indirect flight muscles which cause the thorax to vibrate; the wings can beat faster than the rate at which the muscles receive nerve impulses. This mechanism evolved once, and is the defining feature (synapomorphy) for the infraclass Neoptera.[28]
Aerodynamics
There are two basic aerodynamic models of insect flight. Most insects use a method that creates a spiralling leading edge vortex.[29][30] Some very small insects use the fling and clap or Weis-Fogh mechanism in which the wings clap together above the insect's body and then fling apart. As they fling open, the air gets sucked in and creates a vortex over each wing. This bound vortex then moves across the wing and, in the clap, acts as the starting vortex for the other wing. Circulation and lift are increased, at the price of wear and tear on the wings.[29][30]
Many insects can hover by beating their wings rapidly, requiring sideways stabilization as well as lift.[31]
A few insects use gliding flight, without the use of thrust.
Evolution
Sometime in the Carboniferous Period, some 350 million years ago, when there were only two major land masses, insects began flying. How and why insect wings developed, however, is not well understood, largely due to the scarcity of appropriate fossils from the period of their development in the Lower Carboniferous. Three main theories on the origins of insect flight are that wings developed from paranotal lobes, extensions of the thoracic terga; that they are modifications of movable abdominal gills as found on aquatic naiads of mayflies; or that they developed from thoracic protrusions used as radiators.[32]
Fossils

Fossils from the Devonian (400 million years ago) are all wingless, but by the Carboniferous (320 million years ago), more than 10 different genera of insects had fully functional wings. There is little preservation of transitional forms between the two periods. The earliest winged insects are from this time period (Pterygota), including the Blattoptera, Caloneurodea, primitive stem-group Ephemeropterans, Orthoptera and Palaeodictyopteroidea. Very early Blattopterans (during the Carboniferous) had a very large discoid pronotum and coriaceous forewings with a distinct CuP vein (an unbranched wing vein, lying near the claval fold and reaching the wing posterior margin).[33]: 399 Even though the oldest possible insect fossil is the Devonian Rhyniognatha hirsti, estimated at 396–407 million years old, it possessed dicondylic mandibles, a feature associated with winged insects,[34] although it is later considered as possible myriapod.[35]
During the Permian, the dragonflies (Odonata) were the dominant aerial predator and probably dominated terrestrial insect predation as well. True Odonata appeared in the Permian[36][37] and all are amphibious. Their prototypes are the oldest winged fossils,[38] go back to the Devonian, and are different from other wings in every way.[39] Their prototypes may have had the beginnings of many modern attributes even by late Carboniferous and it is possible that they even captured small vertebrates, for some species had a wing span of 71 cm.[37] The earliest beetle-like species during the Permian had pointed, leather like forewings with cells and pits. Hemiptera, or true bugs had appeared in the form of Arctiniscytina and Paraknightia having forewings with unusual venation, possibly diverging from Blattoptera.[33]: 186
A single large wing from a species of Diptera in the Triassic (10 mm instead of usual 2–6 mm) was found in Australia (Mt. Crosby).This family Tilliardipteridae, despite the numerous 'tipuloid' features, should be included in Psychodomorpha sensu Hennig on account of loss of the convex distal 1A reaching wing margin and formation of the anal loop.[40]
Hypotheses

A Hypothetical wingless ancestor
B Paranotal theory:
Hypothetical insect with wings from the back (Notum)
C Hypothetical insect with wings from the Pleurum
D Epicoxal theory
Hypothetical insect with wings from annex of the legs
1 Notum (back)
2 Pleurum
3 Exite (outer attachments of the legs)
- Paranotal hypothesis: This hypothesis suggests that the insect's wings developed from paranotal lobes, a preadaptation found in insect fossils that is believed to have assisted stabilization while hopping or falling. In favor of this hypothesis is the tendency of most insects, when startled while climbing on branches, to escape by dropping to the ground. Such lobes would have served as parachutes and enable the insect to land more softly. The theory suggests that these lobes gradually grew larger and in a later stage developed a joint with the thorax. Even later would appear the muscles to move these crude wings. This model implies a progressive increase in the effectiveness of the wings, starting with parachuting, then gliding and finally active flight. Still, lack of substantial fossil evidence of the development of the wing joints and muscles poses a major difficulty to the theory, as does the seemingly spontaneous development of articulation and venation.[32]
- Epicoxal hypothesis: This theory, first proposed in 1870 by Carl Gegenbaur, suggested that a possible origin for insect wings might have been the movable abdominal gills found in many aquatic insects, such as on naiads of mayflies.[41] According to this theory these tracheal gills, which started their way as exits of the respiratory system and over time were modified into locomotive purposes, eventually developed into wings. The tracheal gills are equipped with little winglets that perpetually vibrate and have their own tiny straight muscles.[32]
- Endite-exite hypothesis: This hypothesis stems from the adaptation of endites and exites, appendages on the respective inner and outer aspects of the primitive arthropod limb. It was advanced by Trueman[42] based on a study by Goldschmidt in 1945 on Drosophila melanogaster, in which a pod variation displayed a mutation transforming normal wings to what was interpreted as a triple-jointed leg arrangement with some additional appendages but lacking the tarsus, where the wing's costal surface normally would be. This mutation was reinterpreted as strong evidence for a dorsal exite and endite fusion, rather than a leg, with the appendages fitting in much better with this hypothesis. The innervation, articulation and musculature required for the evolution of wings are already present in podomeres.[32]
- Paranota plus leg gene recruitment hypothesis (also known as the dual origin hypothesis): The fossil larvae of Coxoplectoptera provided important new clues to the disputed question of the evolutionary origin of insect wings. Before the larvae fossil discovery the paranotal-hypothesis and the leg-exite-hypothesis have been considered as incompatible alternative explanations, which have both been supported by a set of evidences from the fossil record, comparative morphology, developmental biology and genetics. The expression of leg genes in the ontogeny of the insect wing has been universally considered as conclusive evidence in favour of the leg-exite-hypothesis, which proposes that insect wings are derived from mobile leg appendages (exites). However, the larvae of Coxoplectoptera show that the abdominal gills of mayflies and their ancestors, which are generally considered as corresponding structures to insect wings, articulated within the dorsal tergite plates. This cannot be seen in modern mayfly larvae, because their abdominal tergites and sternites are fused to rings, without any traces left even in embryonic development. If larval gills and wings are corresponding ("serial homologous") structures and thus share the same evolutionary origin, the new results from Coxoplectoptera demonstrate that also wings are of tergal origin, as proposed by the classical paranotal-hypothesis. Staniczek, Bechly & Godunko (2011)[32][43] therefore suggested a new hypothesis that could reconcile the apparently conflicting evidence from paleontology and developmental genetics: wings first originated as stiff outgrowths of tergal plates (paranota), and only later in evolution became mobile, articulated appendages through secondary recruiting of leg genes.[32] More recent fossil analysis of Paleozoic nymph wing pads provides additional support for the fusion of the paranota elements and arthopodan leg genes.[44]
Suggestions have been made that wings may have evolved initially for sailing on the surface of water as seen in some stoneflies.[45] An alternative idea is that it derives from directed aerial gliding descent—a preflight phenomena found in some apterygote, a wingless sister taxa to the winged insects.[46] The earliest fliers were similar to dragonflies with two sets of wings, direct flight muscles, and no ability to fold their wings over their abdomens. Most insects today, which evolved from those first fliers, have simplified to either one pair of wings or two pairs functioning as a single pair and using a system of indirect flight muscles.[32]
Natural selection has played an enormous role in refining the wings, control and sensory systems, and anything else that affects aerodynamics or kinematics. One noteworthy trait is wing twist. Most insect wings are twisted, as are helicopter blades, with a higher angle of attack at the base. The twist generally is between 10 and 20 degrees. In addition to this twist, the wing surfaces are not necessarily flat or featureless; most larger insects have wing membranes distorted and angled between the veins in such a way that the cross-section of the wings approximates an airfoil. Thus, the wing's basic shape already is capable of generating a small amount of lift at zero angle of attack. Most insects control their wings by adjusting tilt, stiffness, and flapping frequency of the wings with tiny muscles in the thorax (below). Some insects evolved other wing features that are not advantageous for flight, but play a role in something else, such as mating or protection.[32]
| Evolution of the ways the wings at rest to the body to create | ||
| wings do not fold back (recent Archaeoptera) |
spread laterally (large bubbles) | |
| over the back against one another (damselflies, mayflies) | ||
| Folding (Neoptera) | ||
| wings not foldable (e.g., stoneflies) | ||
| Folding | fan-fold (e.g., front wings of wasps) | |
| Cross fold (such as the rear wing of the beetle) | ||
| Subjects folding (such as the rear wing of the earwigs) | ||
Some insects, occupying the biological niches that they do, need to be incredibly maneuverable. They must find their food in tight spaces and be capable of escaping larger predators – or they may themselves be predators, and need to capture prey. Their maneuverability, from an aerodynamic viewpoint, is provided by high lift and thrust forces. Typical insect fliers can attain lift forces up to three times their weight and horizontal thrust forces up to five times their weight. There are two substantially different insect flight mechanisms, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages – just because odonates have a more primitive flight mechanism does not mean they are less able fliers; they are, in certain ways, more agile than anything that has evolved afterward.[32]
Morphogenesis
While the development of wings in insects is clearly defined in those who are members of Endopterygota, which undergo complete metamorphosis; in these species, the wing develops while in the pupal stage of the insects life cycle. However, insects that undergo incomplete metamorphosis do not have a pupal stage, therefore they must have a different wing morphogenesis. Insects such as those that are hemimetabolic have wings that start out as buds, which are found underneath the exoskeleton, and do not become exposed until the last instar of the nymph.[47]
The first indication of the wing buds is of a thickening of the hypodermis, which can be observed in insect species as early the embryo, and in the earliest stages of the life cycle. During the development of morphological features while in the embryo, or embryogenesis, a cluster of cells grow underneath the ectoderm which later in development, after the lateral ectoderm has grown dorsally to form wind imaginal disc. An example of wing bud development in the larvae, can be seen in those of White butterflies (Pieris). In the second instar the histoblast become more prominent, which now form a pocket-like structure. As of the third and fourth instars, the histoblast become more elongated. This greatly extended and evaginated, or protruding, part is what becomes the wing. By the close of the last instar, or fifth, the wing is pushed out of the wing-pocket, although continues to lie under the old larval cuticle while in its prepupal stage. It is not until the butterfly is in its pupal stage that the wing-bud becomes exposed, and shortly after eclosion, the wing begins to expand and form its definitive shape.[47]
The development of tracheation of the wings begin before the wing histoblast form, as it is important to note that they develop near a large trachea. During the fourth instar, cells from the epithelium of this trachea become greatly enlarged extend into the cavity of the wing bud, with each cell having developed a closely coiled tracheole. Each trachcole is of unicellular origin, and is at first intracellular in position; while tracheae are of multicellular origin and the lumen of each is intercellular in position. The development of tracheoles, each coiled within a single cell of the epithelium of a trachea, and the subsequent opening of communication between the tracheoles and the lumen of the trachea, and the uncoiling and stretching out of the tracheoles, so that they reach all parts of the wing.[47]
In the earlier stages of its development, the wing-bud is not provided with special organs of respiration such as tracheation, as it resembles in this respect the other portions of the hypodermis of which it is still a part. The histoblast is developed near a large trachea, a cross-section of which is shown in, which represents sections of these parts of the first, second, third and fourth instars respectively. At the same time the tracheoles uncoil, and extend in bundles in the forming vein-cavities of the wing-bud. At the molt that marks the beginning of the pupal stadium stage, they become functional. At the same time, the larval tracheoles degenerate; their function having been replaced by the wing tracheae.[47]
Nomenclature
Most of the nomenclature of insect orders is based on the Ancient Greek word for wing, πτερόν (pteron), as the suffix -ptera.
| Scientific Name | linguistic root | Translation of the Scientific name | English Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anisoptera | ἀνισο- (aniso-) | Unequal wings | Dragonfly |
| Aptera | ἀ- (a-), not | Wingless | Apterygotans, now obsolete |
| Apterygota | πτερύγιον (pterygion small wing)[citation needed] ἀ- (a-), not |
Wingless | Apterygotans |
| Coleoptera | Κολεός (koleos, sheath) | Hardened wings | Beetles |
| Dermaptera | Δέρμα (derma, skin, leather) | Leather wings | Earwigs |
| Diaphanopterodea | Διαφανής (diaphanes, transparent or translucent) | With transparent wings | diaphanopteroideans |
| Dictyoptera | Δίκτυον (diktyon, network) | Wings with netted venation | Cockroaches, mantises and termites |
| Diptera | Δύο- (dyo-, two) | Two wings | Flies |
| Embioptera | ἐν- (en, inside; βίος bios, life) | Interior living winged insects | Webspinners |
| Endopterygota | ἐντός (entos, inside; πτερύγιον, small wing) | Inside wings | Holometabolous insects |
| Ephemeroptera | ἐφήμερος (ephemeros about one day long) | Short lived winged insects | Mayflies |
| Exopterygota | ἔξω (exo, external) | External wings | Insects that undergo incomplete metamorphosis (and thus have externally visible wing buds as nymphs) |
| Hemiptera | ἡμι- (hemi-, half) | Halfwinged insects | Hemiptera (true bugs, leafhoppers, aphids, etc.) |
| Heteroptera | ἑτερο- (hetero-, different) | Different winged | True bugs |
| Homoptera | ὅμο- (homo-, similar) | Same winged | now obsolete |
| Hymenoptera | ὑμένιον (hymenion, membrane) | Insects with wings of thin membranes | bees, wasps, ants, etc. |
| Isoptera | ἶσον (ison, equal) | Same winged | Termites |
| Lepidoptera | Λεπίς (lepis, scale) | Scaled wings | Butterflies & Moths |
| Lonchopteridae | Λόγχη (lonche, lance) | Lance wings | Lance flies |
| Mecoptera | μῆκος (mekos, length) | Long wings | Snake flies, etc. |
| Megaloptera | Μεγαλο- (megalo-, large) | Large wings | Dobsonflies, fishflies |
| Neuroptera | νεῦρον (neuron, vein) | Veined wing | Lacewings, owlflies, antlions, etc. |
| Neoptera | νέος (neos, new, young) | New wings | Includes all currently living orders of flying insects except mayflies and dragonflies |
| Oligoneoptera | ὀλίγον- (oligon-, few) νέος (neos or new) |
New with little veins | Division of the Neoptera |
| Orthoptera | ὀρθο (ortho-, straight) | Straight wings | Grasshoppers, katydids, and crickets |
| Palaeodictyoptera | Παλαιός (palaios-, old) δίκτυον (diktyon meaning network) |
Old veined wings | Primitive palaeozoic paleopterous insects |
| Palaeoptera | Παλαιός (Palaios, old) | Old wings | Mayflies, dragonflies, and several fossil orders |
| Paraneoptera | Παρα- (Para-) νέος (neos, new) |
Part of Neoptera, mostly with piercing mouthparts | True bugs, lice, barklice, thrips |
| Phthiraptera | Φθείρ (phtheir, lice) ἀ, a-, not |
Lice without wings | Animal lice |
| Plecoptera | Πλέκειν (plekein, fold) | Folded wings | Stoneflies |
| Polyneoptera | Πολύς (polys, many νέοςneosnew) |
Many veined wings | Neoptera with hemimetabolous development |
| Psocoptera | Ψώχω (psocho, to rub) | Rubbing wings | Barklice, booklice |
| Pterygota | Πτερύγιον (pterygion, wing) | Winged insects | In class, unlike Apterygota, including winged and wingless secondary systems |
| Raphidioptera | ῥαφίς (rhaphis, needle) | Needle wings | Snakeflies |
| Siphonaptera | Σίφων (siphon, tube) ἀ- or without |
Wingless siphon | Fleas |
| Strepsiptera | Στρέψις (strepsis, to turn around) | Rotating or twisted wings | twisted-winged parasites |
| Thysanoptera | Θύσανοι (thysanoi, fringes) | Fringe winged | Thrips |
| Trichoptera | Τρίχωμα (trichoma, hair) | Haired wings | Caddisflies |
| Zoraptera | Ζωρός (zōros meaning strong) | Strong wings | Zorapterans |
| Zygoptera | ζεῦγος (zeugos meaning pair) | Paired wings | Damselflies |
Adaptations
Variation
Insect wings are fundamental in identifying and classifying species as there is no other set of structures in studying insects more significant. Each order and insect family has distinctive wing shapes and features. In many cases, even species may be distinguished from each other by differences of color and pattern. For example, just by position one can identify species, albeit to a much lesser extent. Though most insects fold their wings when at rest, dragonflies and some damselflies rest with their wings spread out horizontally, while groups such as the caddisflies, stoneflies, alderflies, and lacewings hold their wings sloped roof-like over their backs. A few moths wrap their wings around their bodies, while many flies and most butterflies close their wings together straight upward over the back.[48]
Many times the shape of the wings correlates with the type of insect flight. The best-flying insects tend to have long, slender wings. In many species of Sphingidae (sphinx moths), the forewings are large and sharply pointed, forming with the small hindwings a triangle that is suggestive of the wings of fast, modern airplanes. Another, possibly more important correlation, is that of the size and power of the muscles to the speed and power of flight. In the powerfully flying insects, the wings are most adapted for the stresses and aerodynamics of flight. The veins are thicker, stronger, and closer together toward the front edge (or "leading edge") and thinner yet flexible toward the rear edge (or "trailing edge"). This makes the insect wing an excellently constructed airfoil, capable of exerting both propulsion and lift while minimizing drag.[48]
Variation of the wing beat may also occur, not just amongst different species, but even among individuals at different times. In general, the frequency is dependent upon the ratio between the power of the wing muscles and the resistance of the load. Large-winged, light-bodied butterflies may have a wing beat frequency of 4–20 per second whereas small-winged, heavy-bodied flies and bees beat their wings more than 100 times a second and mosquitoes can beat up to 988–1046 times a second. The same goes for flight; though it is generally difficult to estimate the speed of insects in flight, most insects can probably fly faster in nature than they do in controlled experiments.[48]
Coleoptera
In species of Coleoptera (beetles), the only functional wings are the hindwings. The hindwings are longer than the elytra, folded longitudinally and transversely under the elytra. The wing is rotated forwards on its base into flight position. This action spread the wing and unfolded longitudinally and transversely. There is the spring mechanism in the wing structure, sometimes with the help of abdomen movement, to keep the wing in folded position. The beetle wing venation is reduced and modified due to the folding structure, which include:[49]
- Costa (C), Subcosta posterior (ScP) – at the leading wing marginal, fused for most of the length.
- Radius anterior (RA) – divided into two branches beyond the middle of the wing.
- Radius posterior (RP) – basal connection is lost.
- Media posterior (MP) – branches, long and strong vein.
- Cubitus anterior (CuA)
- Anal veins (AA, AP) – veins behind the cubitus, separated by anal fold.
In most species of beetles, the front pair of wings are modified and sclerotised (hardened) to form elytra and they protect the delicate hindwings which are folded beneath.[33] The elytra are connected to the pterathorax; being called as such because it is where the wings are connected (pteron meaning "wing" in Greek). The elytra are not used for flight, but tend to cover the hind part of the body and protect the second pair of wings (alae). The elytra must be raised in order to move the hind flight wings. A beetle's flight wings are crossed with veins and are folded after landing, often along these veins, and are stored below the elytra. In some beetles, the ability to fly has been lost. These include some ground beetles (family Carabidae) and some "true weevils" (family Curculionidae), but also some desert and cave-dwelling species of other families. Many of these species have the two elytra fused together, forming a solid shield over the abdomen. In a few families, both the ability to fly and the elytra have been lost, with the best known example being the glow-worms of the family Phengodidae, in which the females are larviform throughout their lives.[13][33]
Lepidoptera

The two pairs of wings are found on the middle and third segment, or mesothorax and metathorax respectively. In the more recent genera, the wings of the second segment are much more pronounced, however some more primitive forms have similarly sized wings of both segments. The wings are covered in scales arranged like shingles, forming the extraordinary variety seen in color. The mesothorax is evolved to have more powerful muscles to propel moth or butterfly through the air, with the wing of said segment having a stronger vein structure.[33]: 560 The largest superfamily, Noctuidae, has the wings modified to act as tympanal or hearing organs[50] Modifications in the wing's venation include:[49]
- Costa (C) – not found in Butterflies.
- Subcosta (Sc) + Radius 1 (Sc+R1) – at the leading wing marginal, fused or very close for most of the length, in hindwing fused and well developed in the humeral area, subcosta never branches in butterfly.
- Radius (R2-R5) – radius divides into branches beyond the middle of the wing up to five branches in Papilionidae. On forewing, the last R is stalked in all butterflies except Hesperiidae is separated.
- Radius sector (Rs) – in hindwing.
- Media (M1-M3) – the basal section has been lost.
- Cubitus anterior (CuA1-CuA2) – CuP section has been lost.
- Anal veins (A, 1A+2A, 3A) – either one vein A, or two veins 1A+2A, 3A.
- Humeral vein – The hindwing of most butterflies has the humeral vein, except Lycaenidae There is the enlargement of the humeral area of the hindwing which is overlapped with the forewing. The humeral vein strengthened the hindwing overlapped area so that the two wings coupling better.
The wings, head parts of thorax and abdomen of Lepidoptera are covered with minute scales, from which feature the order 'Lepidoptera' derives its names, the word "lepteron" in Ancient Greek meaning 'scale'. Most scales are lamellar, or blade-like and attached with a pedicel, while other forms may be hair-like or specialized as secondary sexual characteristics.[51] The lumen or surface of the lamella, has a complex structure. It gives color either due to the pigmentary colors contained within or due to its three-dimensional structure.[52] Scales provide a number of functions, which include insulation, thermoregulation, aiding gliding flight, amongst others, the most important of which is the large diversity of vivid or indistinct patterns they provide which help the organism protect itself by camouflage, mimicry, and to seek mates.[51]
Odonata
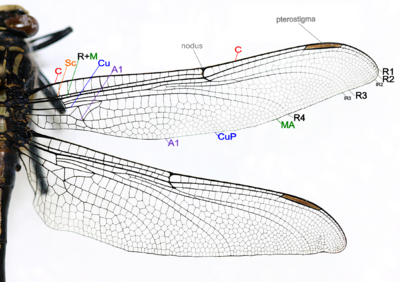
Species of Odonata (Damselflies and dragonflies) both have two pairs of wings which are about equal in size and shape and are clear in color. There are five, if the R+M is counted as 1, main vein stems on dragonfly and damselfly wings, and wing veins are fused at their bases and the wings cannot be folded over the body at rest, which also include:[49]
- Costa (C) – at the leading edge of the wing, strong and marginal, extends to the apex of the wing.
- Subcosta (Sc) – second longitudinal vein, it is unbranched, joins C at nodus.
- Radius and Media (R+M) – third and fourth longitudinal vein, the strongest vein on the wing, with branches, R1-R4, reach the wing margin, the media anterior (MA) are also reach the wing margin. IR2 and IR3 are intercalary veins behind R2 and R3 respectively.
- Cubitus (Cu) – fifth longitudinal vein, cubitus posterior (CuP) is unbranched and reach the wing margin.
- Anal veins (A1) – unbranched veins behind the cubitus.
- A nodus is formed where the second main vein meets the leading edge of the wing. The black pterostigma is carried near the wing tip.
The main veins and the crossveins form the wing venation pattern. The venation patterns are different in different species. There may be very numerous crossveins or rather few. The Australian Flatwing Damselfly's wings are one of the few veins patterns. The venation pattern is useful for species identification.[49] Almost all Anisoptera settle with the wings held out sideways or slightly downward, however most Zygoptera settle with the wings held together, dorsal surfaces apposed. The thorax of Zygoptera is so oblique that when held in this way the wings fit neatly along the top of the abdomen. They do not appear to be held straight up as in butterflies or mayflies. In a few zygopteran families the wings are held horizontally at rest, and in one anisopteran genus (e.g. Cordulephya, Corduliidae) the wings are held in the typical damselfly resting position. Adult species possess two pairs of equal or subequal wings. There appear to be only five main vein stems. A nodus is formed where the second main vein (subcosta) meets the leading edge of the wing. In most families a conspicuous pterostigma is carried near the wing tip. Identification as Odonata can be based on the venation. The only likely confusion is with some lacewings (order Neuroptera) which have many crossveins in the wings. Until the early years of the 20th century Odonata were often regarded as being related to lacewings and were given the ordinal name Paraneuroptera, but any resemblance between these two orders is entirely superficial. In Anisoptera the hindwing is broader than the forewing and in both wings a crossvein divides the discoidal cell into a Triangle and Supertriangle.[53]
Orthoptera

Species of Orthoptera (grasshoppers and crickets) have forewings that are tough opaque tegmina, narrow which are normally covering the hindwings and abdomen at rest. The hindwings are board membranous and folded in fan-like manner, which include the following venation:[49]
- Costa (C) – at the leading marginal of the forewing and hindwing, unbranched.
- Subcosta (Sc) – second longitudinal vein, unbranched.
- Radius (R) – third longitudinal vein, branched to Rs in forewing and hindwing.
- Media anterior (MA) – fourth longitudinal vein, branched in basal part as Media posterior (MP).
- Cubitus (Cu) – fifth longitudinal vein, on forewing and hindwing dividing near the wing base into branched CuA, and unbranched CuP.
- Anal veins (A) – veins behind the cubitus, unbranched, two in forewing, many in hindwing.
Phasmatodea
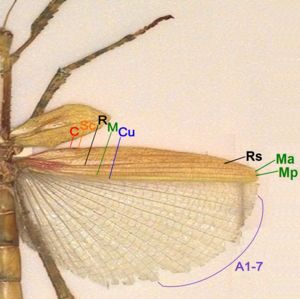
- Costa (C) – at the leading marginal of the hindwing, unbranched, absent in forewing.
- Subcosta (Sc) – second longitudinal vein, unbranched.
- Radius (R) – third longitudinal vein, branched to Rs in hindwing, unbranched in forewing.
- Media anterior (MA) – fourth longitudinal vein, branched in basal part as Media posterior (MP).
- Cubitus (Cu) – fifth longitudinal vein, unbranched.
- Anal veins (A) – veins behind the cubitus, unbranched, two in forewing, many in hindwing 1A-7A in one group and the rest in another group.
Stick insect have forewings that are tough, opaque tegmina, short and covering only the base part of the hindwings at rest. Hindwings from costa to Cubitus are tough and opaque like the forewings. The large anal area are membranous and folded in fan-like manner. There are no or very few branching in stick insect wing veins.[49]
Dermaptera
Other orders such as the Dermaptera (earwigs), Orthoptera (grasshoppers, crickets), Mantodea (praying mantis) and Blattodea (cockroaches) have rigid leathery forewings that are not flapped while flying, sometimes called tegmen (pl. tegmina), elytron (pl. elytra), or pseudoelytron.[13]
Hemiptera
In Hemiptera (true bugs), the forewings may be hardened, though to a lesser extent than in the beetles. For example, the anterior part of the front wings of stink bugs is hardened, while the posterior part is membranous. They are called hemelytron (pl. hemelytra). They are only found in the suborder Heteroptera; the wings of the Homoptera, such as the cicada, are typically entirely membranous. Both forewings and hindwings of Cicada are membranous. Most species are glass-like although some are opaque. Cicadas are not good fliers and most fly only a few seconds. When flying, forewing and hindwing are hooked together by a grooved coupling along the hindwing costa and forewing margin. Most species have a basic venation as shown in the following picture.[49]
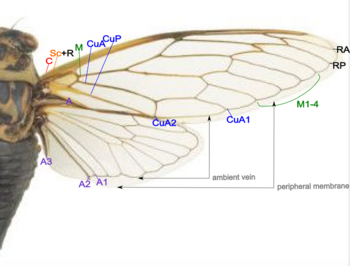
- Costa (C) – at the leading wing marginal, in forewing extends to the node and lies close to Sc+R.
- Subcosta + Radius (Sc+R) – in forewing Sc and R fused together to the node. Radial sector (Rs) arises near the node and unbranches.
- Radius anterior (RA)
- Radius posterior (RP)
- Media (M) – branches to M1 to M4.
- Cubitus anterior (CuA) – branches to CuA1 and CuA2.
- Cubitus posterior (CuP) – unbranches.
- Anal veins (A) – veins behind the cubitus, 1A and 2A fused in the forewing, CuP and 2A are folded.
Also notice there are the ambient veins and peripheral membranes on the margin of both wings.
Diptera
In the Diptera (true flies), there is only one pair of functional wings, with the posterior pair of wings are reduced to halteres, which help the fly to sense its orientation and movement, as well as to improve balance by acting similar to gyroscopes. In Calyptratae, the very hindmost portion of the wings are modified into somewhat thickened flaps called calypters which cover the halteres.[49]

- Costa (C) – not found in Diptera.
- Subcosta (Sc) – became the leading wing vein, unbranched.
- Radius (R) – branched to R1-R5.
- Media (M) – branched to M1-M4.
- Cubitus anterior(CuA)- unbranched, CuP is reduced in Diptera. Some species CuA and 1A are separated, some species meets when reaching the wing margin, some species fused.
- Anal veins (A) – only two anal veins 1A and 2A are present, 2A is not distinctive in some species.
- Discal Cell (dc) – well defined in most species.
Blattodea
Species of Blattodea (cockroaches) have a forewing, are also known as tegmen, that is more or less sclerotized. It is used in flight as well as a form of protection of the membranous hindwings. The veins of hindwing are about the same as front wing but with large anal lobe folded at rest between CuP and 1A. The anal lobe usually folded in a fan-like manner.[49]

- Costa (C) – at the leading edge of the wing.
- Subcosta (Sc) – second longitudinal vein, it is relatively short.
- Radius (R) – third longitudinal vein, with many pectinate branches.
- Media (M) – fourth longitudinal vein, reach the wing margin.
- Cubitus anterior (CuA) – fifth longitudinal vein, with dichotomous branches occupy large part of tegmen.
- Cubitus posterior (CuP) – is unbranched, curved and reach the wing margin.
- Anal veins (A) – veins behind the cubitus.
Hymenoptera
| An example of Longitudinal folding in wasps (Vespidae) | |

|
The main fold line of the forewing seen halfway up as a bright horizontal line. The wing part that is behind this line is turned back down. The narrow strip at the front edge of the wing is in front of the first strong wire folded forward and down. |

|
So in rest position, the outer lining forms the tough outer edge of the wing, which protects the sides of the abdomen as a shock absorber. The rear wing is covered largely by the forewing. |
Hymenoptera adults, including sawflies, wasps, bees, and non-worker ants, all have two pairs of membranous wings.[49]
- Costa (C) – not found in Hymenoptera.
- Subcosta (Sc) – unbranched.
- Radius (R) – branched to R1-R5.
- Media (M) – M is unbranched, in forewing M is fused with Rs for part of its length.
- Cubitus (CuA) – unbranched, CuP is absent in Hymenoptera.
- Anal veins (A) – only two anal veins 1A and 2A are present, 2A is not distinctive in some species.
- Wing-coupling – Row of hooks on the leading edge of hindwing engage the hind margin of the forewing, strongly couple the wings in flight.
- Line of wing folding – Some species, including Vespidae, the forewing are longitudinally folded along the 'line of wing folding' at rest.
- Pterostigma – is present for some species.
The forward margin of the hindwing bears a number of hooked bristles, or "hamuli", which lock onto the forewing, keeping them held together. The smaller species may have only two or three hamuli on each side, but the largest wasps may have a considerable number, keeping the wings gripped together especially tightly. Hymenopteran wings have relatively few veins compared with many other insects, especially in the smaller species.[13]
Other families
Termites are relatively poor fliers and are readily blown downwind in wind speeds of less than 2 km/h, shedding their wings soon after landing at an acceptable site, where they mate and attempt to form a nest in damp timber or earth.[54] Wings of most termites have three heavy veins along the basal part of the front edge of the forewing and the crossveins near the wing tip are angled, making trapezoidal cells. Although subterranean termite wings have just two major veins along the front edge of the forewing and the cross veins towards the wingtip are perpendicular to these veins, making square and rectangular cells.[55]
Species of Thysanoptera (thrips), Ptiliidae and other flying microinsects have slender front and hindwings with long fringes of hair, called fringed wings, also referred to as ptiloptery.[56] While species of Trichoptera (caddisfly) have hairy wings with the front and hindwings clothed with setae.[13]
Male Strepsiptera also have halteres that evolved from the forewings instead of the hindwings. This means that only their hindwings are functional at flying, as opposed to Diptera which have functional forewings and halteres for hindwings. Also the hindwings in males of Coccidae are reduced to halteres (or are absent).[57]
See also
- Appendage
- Comstock-Needham system
- Wing
- Insect inspired robots: RoboBee, DelFly
Notes
- ^ Crampton, G. (1916). "The Phylogenetic Origin and the Nature of the Wings of Insects According to the Paranotal Theory". Journal of the New York Entomological Society. 24 (1): 1–39. JSTOR 25003692.
- ^ a b Ross, Andrew (2017). "Insect Evolution: The Origin of Wings". Current Biology. 27 (3): R113–R115. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2016.12.014. PMID 28171756 – via Web of Science.
- ^ a b Averof, Michalis, and S. M. Cohen. (1997). "Evolutionary origin of insect wings from ancestral gills". Nature. 385 (6617): 627–630. Bibcode:1997Natur.385..627A. doi:10.1038/385627a0. PMID 9024659. S2CID 4257270 – via Web of Science.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Grodnitsky, Dmitry, L. (1999). Form and Function of Insect Wings: The Evolution of Biological Structures. pp. 82–83.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Alexander, David, E. (2015). On the Wing: Insects, Pterosaurs, Birds, Bats and the Evolution of Animal Flight. Oxford University Press. pp. 74–101.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Haug, Joachim, C. Haug., and R. J. Garwood. (2016). "Evolution of insect wings and development – new details from Palaeozoic nymphs". Biological Reviews. 91 (1): 53–69. doi:10.1111/brv.12159. PMID 25400084. S2CID 21031689.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Almudi, Isabel; Vizueta, Joel; Wyatt, Christopher D. R.; de Mendoza, Alex; Marlétaz, Ferdinand; Firbas, Panos N.; Feuda, Roberto; Masiero, Giulio; Medina, Patricia; Alcaina-Caro, Ana; Cruz, Fernando (2020). "Genomic adaptations to aquatic and aerial life in mayflies and the origin of insect wings". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 2631. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.2631A. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16284-8. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7250882. PMID 32457347.
- ^ Bruce, Heather, N.H. Patel. (2020). "Knockout of crustacean leg patterning genes suggests that insect wings and body walls evolved from ancient leg segments". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 4 (12): 1703–1712. Bibcode:2020NatEE...4.1703B. doi:10.1038/s41559-020-01349-0. PMID 33262517. S2CID 227253368.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Clark-Hatchel, Courtney (2013). "Insights into insect wing origin provided by functional analysis of vestigial in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (42): 16951–16956. Bibcode:2013PNAS..11016951C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1304332110. PMC 3801059. PMID 24085843.
- ^ Prokop, Jakub, Pecharová, M., Nel, A., Hörnschemeyer, T., Krzemińska, E., Krzemiński, W., & Engel, M (2017). "Paleozoic Nymphal Wing Pads Support Dual Model of Insect Wing Origins". Current Biology. 27 (2): 263–269. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2016.11.021. PMID 28089512.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d e f Chapman, R.F. (1998). The Insects: Structure and function (4th ed.). Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-57048-4.
- ^ a b Gilliott, Cedric (August 1995). Entomology (2 ed.). Springer-Verlag New York, LLC. ISBN 0-306-44967-6.
- ^ a b c d e Meyer, John R. (5 January 2007). "External Anatomy: WINGS". Department of Entomology, North Carolina State University. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-21.
- ^ a b c d Gullan, P. J.; Cranston, P. S. (2004). The insects: an outline of entomology. UK: Blackwell Publishing. p. 42. ISBN 1-4051-1113-5.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Snodgrass, R. E. (December 1993). Principles of Insect Morphology. Cornell Univ Press. ISBN 0-8014-8125-2.
- ^ Spieth, HT (1932). "A New Method of Studying the Wing Veins of the Mayflies and Some Results Therefrom (Ephemerida)" (PDF). Entomological News. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-30.
- ^ "EXPLANATION OF TERMS USED IN ENTOMOLOGY". www.gutenberg.org. Retrieved 2024-01-08.
- ^ "Definition of TERMEN". www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 2024-01-08.
- ^ a b Knospe, Carl R. (Fall 1998). "Insect Flight Mechanisms: Anatomy and Kinematics" (PDF). Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, University of Virginia.
- ^ Weis-Fogh, T (July 1963). "Diffusion In Insect Wing Muscle, The Most Active Tissue Known". J Exp Biol. 41 (2): 229–256. doi:10.1242/jeb.41.2.229. PMID 14187297.
- ^ Tiegs, O. W. (February 1954). "The Flight Muscles of Insects-Their Anatomy and Histology; with Some Observations on the Structure of Striated Muscle in General". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 238 (656): 221–348. Bibcode:1955RSPTB.238..221T. doi:10.1098/rstb.1955.0001. JSTOR 3739600.
- ^ He, Zhe; Luo, Yichen; Shang, Xueying; Sun, Jennifer S.; Carlson, John R. (21 May 2019). "Chemosensory sensilla of the Drosophila wing express a candidate ionotropic pheromone receptor". PLOS Biology. 17 (5): e2006619. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.2006619.
- ^ Valmalette, J.C., Raad, H., Qiu, N., Ohara, S., Capovilla, M. and Robichon, A., 2015. Nano-architecture of gustatory chemosensory bristles and trachea in Drosophila wings. Scientific reports, 5(1), pp.1-11.
- ^ Dinges, G.F., Chockley, A.S., Bockemühl, T., Ito, K., Blanke, A. and Büschges, A., 2021. Location and arrangement of campaniform sensilla in Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 529(4), pp.905-925.
- ^ Field, L.H. and Matheson, T., 1998. Chordotonal organs of insects. In Advances in insect physiology (Vol. 27, pp. 1-228). Academic Press.
- ^ Wolf, H., 1993. The locust tegula: significance for flight rhythm generation, wing movement control and aerodynamic force production. Journal of Experimental Biology, 182(1), pp.229-253.
- ^ Zhang, N. and Simpson, J.H., 2022. A pair of commissural command neurons induces Drosophila wing grooming. Iscience, 25(2), p.103792.
- ^ a b Chapman, A. D. (2006). Numbers of living species in Australia and the World. Canberra: Australian Biological Resources Study. pp. 60pp. ISBN 978-0-642-56850-2. Archived from the original on 2009-05-19. Retrieved 2012-06-18.
- ^ a b Wang, Z. Jane (2005). "Dissecting Insect Flight" (PDF). Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics. 37 (1). Annual Reviews: 183–210. Bibcode:2005AnRFM..37..183W. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.36.050802.121940.
- ^ a b Sane, Sanjay P. (2003). "The aerodynamics of insect flight" (PDF). The Journal of Experimental Biology. 206 (23): 4191–4208. doi:10.1242/jeb.00663. PMID 14581590. S2CID 17453426.
- ^ Davidovits, Paul (2008). Physics in Biology and Medicine. Academic Press. pp. 78–79. ISBN 978-0-12-369411-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Grimaldi, David; Engel, Michael S. (2005). Evolution of the Insects. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ a b c d e Powell, Jerry A. (2009). "Coleoptera". In Resh, Vincent H.; Cardé, Ring T. (eds.). Encyclopedia of Insects (2 (illustrated) ed.). Academic Press. p. 1132. ISBN 978-0-12-374144-8.
- ^ Michael S. Engel; David A. Grimaldi (2004). "New light shed on the oldest insect". Nature. 427 (6975): 627–630. Bibcode:2004Natur.427..627E. doi:10.1038/nature02291. PMID 14961119. S2CID 4431205.
- ^ Haug, Carolin; Haug, Joachim T. (2017-05-30). "The presumed oldest flying insect: more likely a myriapod?". PeerJ. 5: e3402. doi:10.7717/peerj.3402. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 5452959. PMID 28584727.
- ^ Grzimek HC Bernhard (1975) Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia Vol 22 Insects. Van Nostrand Reinhold Co. NY.
- ^ a b Riek EF Kukalova-Peck J (1984). "A new interpretation of dragonfly wing venation based on early Upper Carboniferous fossils from Argentina (Insecta: Odonatoida and basic character states in Pterygote wings.)". Can. J. Zool. 62 (6): 1150–1160. doi:10.1139/z84-166.
- ^ Wakeling JM Ellington CP (1997). "Dragonfly flight III lift and power requirements". Journal of Experimental Biology. 200 (Pt 3): 583–600 (589). doi:10.1242/jeb.200.3.583. PMID 9318294.
- ^ Matsuda R (1970). "Morphology and evolution of the insect thorax". Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 102 (76): 1–431. doi:10.4039/entm10276fv.
- ^ V. A. Blagoderov; E. D. Lukashevich; M. B. Mostovski (2002). "Order Diptera Linné, 1758. The true flies". In A. P. Rasnitsyn; D. L. J. Quicke (eds.). History of Insects. Kluwer Academic Publishers. ISBN 1-4020-0026-X.
- ^ Gegenbaur, Carl (1870). Grundzüge der vergleichenden Anatomie. W. Engelmann.
- ^ Trueman JWH (1990), Comment: evolution of insect wings: a limb exite plus endite model Canadian Journal of Zoology
- ^ Staniczek, A.H.; Bechly, G. & Godunko, R.J. (2011). "Coxoplectoptera, a new fossil order of Palaeoptera (Arthropoda: Insecta), with comments on the phylogeny of the stem group of mayflies (Ephemeroptera)" (PDF). Insect Systematics & Evolution. 42 (2): 101–138. doi:10.1163/187631211X578406. S2CID 4986911. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-03.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Prokop, Jakub; Pecharová, Martina; Nel, André; Hörnschemeyer, Thomas; Krzemińska, Ewa; Krzemiński, Wiesław; Engel, Michael S. (January 2017). "Paleozoic Nymphal Wing Pads Support Dual Model of Insect Wing Origins". Current Biology. 27 (2): 263–269. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2016.11.021. PMID 28089512.
- ^ Adrian L. R. Thomas; R. Åke Norberg (1996). "Skimming the surface — the origin of flight in insects?". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 11 (5): 187–188. doi:10.1016/0169-5347(96)30022-0. PMID 21237803.
- ^ Yanoviak SP, Kaspari M, Dudley R (2009). "Gliding hexapods and the origins of insect aerial behaviour". Biology Letters. 5 (4): 510–2. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2009.0029. PMC 2781901. PMID 19324632.
- ^ a b c d H. Comstock, Henry (1918). The Wings of Insects. Ithaca, NY: The Comstack Publishing Company. p. 114.
- ^ a b c "Insect Wings in General". Aerodynamics of Insects. Cislunar Aerospace. 1997. Retrieved March 28, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Chew, Peter (May 9, 2009). "Insect Wings". Brisbane Insects and Spiders. Retrieved 2011-03-21.
- ^ Scoble, MJ. (1992). The Lepidoptera: Form, function, and diversity. Oxford Univ. Press. ISBN 978-1-4020-6242-1.
- ^ a b Scoble (1995). Section Scales, (pp 63 – 66).
- ^ Vukusic, P. (2006). "Structural color in Lepidoptera" (PDF). Current Biology. 16 (16): R621–3. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.07.040. PMID 16920604. S2CID 52828850. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ^ Trueman, John W. H.; Richard J. Rowe (16 October 2009). "Odonata. Dragonflies and damselflies". Tolweb.org. Retrieved 2011-03-21.
- ^ Abe T., Bignell D.E; Higashi M (2000). Termites: evolution, sociality, symbioses, ecology, ecolab. Kluwer academic publishers. ISBN 0-7923-6361-2.
- ^ "Termite". Texas AgriLife Extension Service. Archived from the original on 2011-04-13.
- ^ Polilov, Alexey A.; Reshetnikova, Natalia I.; Petrov, Pyotr N.; Farisenkov, Sergey E. (January 2019). "Wing morphology in featherwing beetles (Coleoptera: Ptiliidae): Features associated with miniaturization and functional scaling analysis". Arthropod Structure & Development. Special Issue: Miniaturization in Panarthropoda. 48: 56–70. Bibcode:2019ArtSD..48...56P. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2019.01.003.
- ^ Camacho, Ernesto Robayo; Chong, Juang-Horng (2015). "General Biology and Current Management Approaches of Soft Scale Pests (Hemiptera: Coccidae)" (PDF). Journal of Integrated Pest Management. 6 (1): 17. doi:10.1093/jipm/pmv016. ISSN 2155-7470. PMC 4725186. PMID 26823990.
References
- Triplehorn, Charles A.; Johnson Norman F. (2005). Borror and DeLong's introduction to the study of insects (7th ed.). Thomson Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0-03-096835-6.
External links
- Brisbane University course on insect wings
- North-Carolina State University course on insect wings
- Insect wing drawings