Golden Gate of the Ecliptic

The Golden Gate of the Ecliptic is an asterism in the constellation Taurus that has been known for several thousand years. The asterism is formed of the two eye-catching open star clusters, the Pleiades and the Hyades that form the posts of a virtual gate on either side of the ecliptic line.
Since all planets as well as the Moon and the Sun always move very closely along the virtual circle of the ecliptic, all these seven orbiting bodies regularly pass through the Golden Gate of the Ecliptic. Since the Moon is the closest of these heavenly bodies to the Earth and it is inclined at a high enough angle to the ecliptic, on some occasions, the Moon can cover the stars of the open star clusters or even pass outside the Gate.[1]
- Golden Gate of the Ecliptic
- From lower left to upper right: Sirius (Canis majoris), constellation Orion, constellation Taurus with open star cluster Hyades, planet Mars exactly in the Golden Gate of the Ecliptic, open star cluster Pleiades.
History
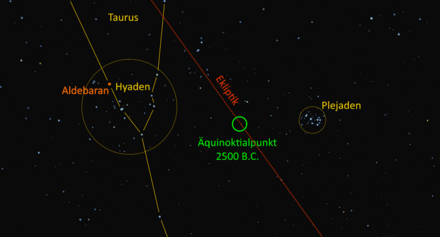
From 4000 to 1500 BC the equinox was within the constellation Taurus, and therefore great importance was attached to this constellation.[2] The 4500 year old sky tablet of the neolithic Tal-Qadi Temple in Malta is thought to display the Golden Gate of the Ecliptic.[3]
Sources
- Michael A. Rappenglück: Palaeolithic Timekeepers Looking at the Golden Gate of the Ecliptic; The Lunar Cycle and the Pleiades in the Cave of La-Tête-du-lion (Ardèche, France) — 21,000 BP, in: Barbieri C., Rampazzi F. (editors): Earth-Moon Relationships, Springer, Dordrecht
External links
- The Golden Gate of the Ecliptic. In Wikibook: The Tal-Qadi Sky Tablet
References
- ^ Tor! 1:0 für die Venus, astronomie-heute.de, 19 April 2020, retrieved 30 August 2020
- ^ Was Sie schon immer über Sterne wissen wollten - Der Sternenhimmel im Winter 2009, sternschnuppenschenken, 5 Februar 2009, retrieved 30 August 2020
- ^ Peter Kurzmann: Die neolithische Sternkarte von Tal-Qadi auf Malta, Archäologie online, 25 July 2014, retrieved 30 August 2020

