General Confederation of the Kingdom of Poland
Kingdom of Poland | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1812–1813 | |||||||||||||
Seal: | |||||||||||||
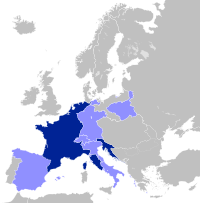
 The territories of the General Confederation of the Kingdom of Poland, including the Duchy of Warsaw, and the Lithuanian Provisional Governing Commission, at their territorial peak in 1812. | |||||||||||||
| Capital | Warsaw | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Polish, French, German, Lithuanian, Belarusian | ||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Polish | ||||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||||
• 1812-1813 | Frederick Augustus I | ||||||||||||
| Marshal of the General Council | |||||||||||||
• 1812–1813 | Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski | ||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||
• Declared | 28 June 1812 | ||||||||||||
• Dissolved | 30 April 1813 | ||||||||||||
| Currency | Złoty | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Today part of | Lithuania, Belarus, Poland | ||||||||||||
The General Confederation of the Kingdom of Poland (28 June 1812 – 30 April 1813, Polish Konfederacja Generalna Królestwa Polskiego) was a governing body of the Duchy of Warsaw created by Napoleon Bonaparte and the Polish political elite on the onset of Napoleon's campaign against Russia, which was proclaimed as "the second Polish war". It took the form of a confederated sejm (parliament). Officially assembled on the 28th of June, 1812,[1] it oversaw the formal transformation of the Duchy of Warsaw into the "Kingdom of Poland".
The newly renamed state laid claim to the territory annexed by the Russian Empire during the partitions, the so called "seized lands" or "seized country" (Polish Ziemie zabrane), which were formally retaken in July of 1812. After the defeat of Napoleon in 1813 and the Russian occupation of the Duchy, the Confederation's accomplishments were rendered null in practice.
Origin
Napoleon came forward with the plan to create the Confederation in Poznań, on the 31st of May of the same year. He had consulted the issue with Tadeusz Matuszewicz, the treasury minister. In bringing the plans to life, the king of Saxony and duke of Warsaw, Frederick August I, put out a decree on the 26th of May, in which he ceded his powers to the Council of Ministers (Polish Rada Ministrów Księstwa Warszawskiego), retaining only the right to appointing and calling off ministers and influence over the law. Reinstating the Kingdom of Poland was intended to strengthen the alliance in the war against Russia. And by doing so, the Grande Armée figured as a liberating force, when entering the territories that had been lost to Russia.
Government

Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski was appointed marshal of the Confederation. Executive power was granted to a body called "General Council of the Confederation" (Polish Rada Generalna Konfederacji, Generalność).[2] Members included: Bishop Jan Klemens Gołaszewski, Kajetan Koźmian, Aleksander Linowski, Antoni Ostrowski, Bishop Karol Skórkowski, Fryderyk Skórzewski, Franciszek Wężyk, Stanisław Kostka Zamoyski, Marcin Badeni, Joachim Owidzki, Franciszek Łubieński.[2] The official act of formation of the council was added to "The Crown Metric" (Latin Metrica Regni Poloniae, Polish Metryka Koronna), the register of Polish state documents, acts and letters from as far back as the 1400s, thereby drawing continuity between the Confederation and the partitioned kingdom.
Tenure
The Confederation effectively sought to bring back the political system of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, including its coat of arms and colours, white-crimson. (The latter had been last used by the Bar Confederation.) Its formation was met with great enthusiasm throughout the nation and many hastily assembled local parliaments unanimously agreed to join the confederation.
On the 11th of July, Napoleon received a delegation from the General Council led by Józef Wybicki. The delegation implored the emperor to fully restore the Kingdom of Poland, but was unsuccessful. (Napoleon was allied with the Austrian Empire, one of Poland's partitioners, and thus could not commit to returning any of the annexed territory.)[3]
After the 14th of July, the Confederation formally took administrative control of the Russo-Lithuanian territories taken by the Napoleonic forces. A special commission was formed for the purpose.
In the face of the occupation of Poland by Russian forces, starting with the 30th of April 1813, the Confederation ceased its activities.
References
- ^ Jędruch, Jacek (1998). Constitutions, Elections, and Legislatures of Poland, 1493-1993: A Guide to Their History. EJJ Books. pp. 206–207. ISBN 978-0-7818-0637-4.
- ^ a b ""Królestwo Polskie Przywrócone", Gazeta Warszawska. 1812, nr 52" ['The Warsaw Gazette']. Gazeta Warszawska (in Polish). Vol. 52. Tadeusz Włodek. 1812.
- ^ "Odpowiedź Napoleona deputowanym Konfederacji Generalnej Królestwa Polskiego z 11 VII 1812 r." ['Napoleon's Answer to the Deputies of the General Confederacy of the Kingdom of Poland'] (in Polish). Archived from the original on 2017-10-13.
Bibliography
- Diariusz Sejmowy z roku 1812, "Teki Archiwalne", t. 21, 1989, pp. 146–152
- A. Rembowski, Konfederacja Generalna i pospolite ruszenie w roku 1812, "Biblioteka Warszawska", t. 1, 1896, z. 3, pp. 478–514, t. 2, 1896, z. 1, pp. 67–86
- Marian Kukiel, Wojna 1812 roku, Kraków 1937