Ethylenetetracarboxylic acid
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Ethene-1,1,2,2-tetracarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4O8 | |
| Molar mass | 204.090 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
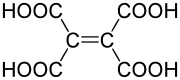
Ethylenetetracarboxylic acid is an organic compound with formula C
6H
4O
8, or (HO(OC)-)2C=C(-(CO)OH)2.
By removal of four protons, the acid yields the anion C
6O4−
8, ethylenetetracarboxylate, which is one of the oxocarbon anions (consisting solely of oxygen and carbon). By loss of 1 through 3 protons, it forms the anions C
6H
3O−
8, C
6H
2O2−
8, and C
6HO3−
8, called respectively trihydrogen-, dihydrogen-, and hydrogenethylenetetracarboxylate. The same names are used for the corresponding esters.
The acid can be obtained by hydrolysis of tetraethyl ethylenetetracarboxylate, which in turn can be obtained from diethyl dibromomalonate with sodium iodide.[1]
Ethylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride, a twofold acid anhydride of this compound, can be formed by direct dehydration at high temperature.[2]
References
- ^ B. I. Zapadinskii, B. I. Liogon'kii, and A. A. Berlin (1973), Syntheses of Tetracarboxylic Acids. Russian Chemical Reviews, volume 42 issue 11, page 939. Online version accessed on 2010-01-03.
- ^ John M. Patterson, Nabeel F. Haidar, Loren L. Braun and Walter T. Smith, Jr. (1981), The pyrolytic behavior of ethylenetetracarboxylic acid. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, Volume 2, Issue 4, Pages 331-337 doi:10.1016/0165-2370(81)80005-8
