Edmonton Metropolitan Transit Services Commission
 | |
| Founded | 2021 |
|---|---|
| Defunct | 2023 |
| Headquarters | 300, 106 Street Tower. 10055 106 Street, Edmonton, AB, T5J 2Y2. |
| Service area | Edmonton Metropolitan Region |
| Service type | Public Transit |
| Chief executive | Paul Jankowski |
| Website | https://emtsc.ca |
The Edmonton Metropolitan Transit Services Commission (EMTSC) was a proposed regional public transit service which was intended to encompass eight municipalities within the Edmonton Metropolitan Region of Alberta, Canada. The EMTSC was dissolved, after the City of Edmonton opted not to provide its share of the annual budget.[1]
History
The Edmonton Metropolitan Transit Services Commission (EMTSC) traces its roots to 2017, when the cities of Edmonton and St. Albert signed a Memorandum of Understanding to explore the creation of a regional transit services commission.[2] In February 2020, thirteen municipal councils voted to investigate the potential for a regional transit services commission (RTSC).[3] Nine of these municipalities, including Edmonton, St. Albert, Fort Saskatchewan, and Leduc, later submitted an application to the provincial government to establish the Edmonton Metropolitan Transit Services Commission.[2] The town of Morinville opted out soon after the application was submitted, chiefly due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[4]
The commission was given ministerial permission to operate on 28 January 2021.[5] The impetus for the commission's formation was the region's rapidly growing population, and the increasing interconnectivity of its member communities and their work forces.[6] Paul Jankowski, formerly the Commissioner of the Transportation Services Department for the Regional Municipality of York, began his tenure as the EMTSC's first CEO on 17 May 2021.[7] In November 2021, the board of directors voted to move the planned commencement of operations from late 2022 to early 2023.[8]
In December 2022, Edmonton's City Council voted against contributing $13 million toward the EMTSC annual budget.[1] In January 2023, the EMTSC board approved the implementation of a plan to permanently close the commission.[9]
Service Area
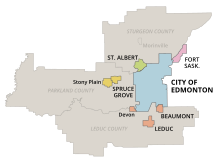
The EMTSC had a membership of six cities, two towns, and one Urban Service Area:[2]
- City of Beaumont (Beaumont Transit)
- City of Edmonton (ETS)
- City of Fort Saskatchewan (Fort Sask Transit)
- City of Leduc (Leduc Transit)
- City of Spruce Grove (Spruce Grove Transit)
- City of St. Albert (StAT)
- Town of Devon (Devon Transit)
- Town of Stony Plain (Spruce Grove Transit)
- Sherwood Park Urban Service Area (Strathcona County Transit)
Four regional municipalities were "non-voting, non-paying, advising stakeholders" which were not members of the commission:[4]
Operations
A board of elected representatives from each member community was conducting the initial setup of the commission, and working with the commission's inaugural CEO to develop its operational and planning capabilities.[10] The EMTSC would have begun service in Spring/Summer 2023.[11] Edmonton's local transit services and LRT network would not initially be transferred to the commission due to their size and operational costs; this was planned to be reconsidered in 2026.[6] Member communities were expected to save approximately $2.2 million on transit costs annually.[12] Communities would continue to plan and pay for their local transit routes, while the commission would determine how those routes were to be serviced.[6]
Launch plan
The commission was in phase three of its launch plan before the board voted to dissolve the commission.[1]
Phase one
Phase one, pre-implementation, was in effect from the time that the interim board was formed until the commission was given ministerial permission to operate.[6] During this time, the interim board focused on gaining provincial approval of the commission, drafting transition assessments and recommendations, and recruiting a CEO.[12]
Phase two
Phase two, also known as "formation and set-up," was when the commission established its initial workforce, infrastructure, policies and procedures.[6] Phase two lasted for the entirety of 2021 and into 2022, and included goals such as the creation of the commission's strategic and business plans, establishing lease agreements for transit-related facilities, and finalizing the regional service design.[6][8]
Phase three
"Preparation for service deployment" occurred in phase three, which was expected to be in effect for the first half of 2023.[1] This is when the commission would on board the remaining resources needed for it to roll out regional transit services in spring or summer 2023.[6] Key objectives of this phase included the development of a brand and marketing identity, transitioning all municipal transit services to EMTSC control by summer 2023 (with the exception of local ETS services), and planning fleet deployments.[6][8]
Phase four
Phase four, which would have started in spring or summer 2023, would mark the beginning of transit service delivery by the EMTSC.[6] It would occur in phases until the end of 2023.[6] During this phase, the EMTSC would focus on maintaining customer service and communications, analyzing the successes and failures of the rollout as it progressed, and recruiting more staff as the commission expanded its services.[6][8]
Phase five
The final phase of the commission's launch would begin by the end of 2023, with a focus on improving its services in preparation for its absorption of ETS local services.[6] During this time, the commission would focus on surveying riders, identifying service improvements such as the standardization of vehicle features (e.g. drivers' shields, Wi-Fi enabled buses, etc.), and revising local transit routes to meet specific guidelines.[6] This phase will last until 2026, when the commission aimed to adopt ETS local bus services and become the sole deliverer of bus transit services within its member communities.[6]
Fares
Fare levels would be determined by the commission's board of governors, and the service would allow fare payments with Arc cards.[6][13]
See also
- Arc card
- Edmonton Transit Service
- Edmonton Metropolitan Region
- Fort Sask Transit
- Leduc Transit
- St Albert Transit
References
- ^ a b c d Boothby, Lauren (December 15, 2022). "Edmonton's regional transit plan is dead". Edmonton Journal. Retrieved February 17, 2022.
- ^ a b c "Regional Transit Services Commission reaches major milestone with application to the Province / City of St. Albert". City of St. Albert. Archived from the original on 2021-01-21. Retrieved 2021-01-22.
- ^ "Edmonton city council votes to formally join push for new regional transit services commission". Global News. Retrieved 2021-01-22.
- ^ a b "Morinville drops public transit pilot project". StAlbertToday.ca. Retrieved 2021-01-28.
- ^ "Approval Received to Legally Form a Regional Transit Services Commission / City of St. Albert". City of St. Albert. Retrieved 2021-01-28.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Ernst & Young LLP (January 22, 2020). "Accelerating Transit in the Edmonton Metropolitan Region: Building a Regional Transit Services Commission" (PDF). City of Edmonton. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-06-19. Retrieved January 22, 2021.
- ^ "Regional Transit Commission appoints first CEO". fortsaskatchewanrecord. Retrieved 2021-05-06.
- ^ a b c d "Annual Organization Board Meeting". Edmonton Metropolitan Transit Services Commission. Archived from the original on 2021-11-25. Retrieved 2021-11-25.
- ^ "EMTSC Board approves wind-down plan". Edmonton Metropolitan Transit Services Commission. January 19, 2023. Retrieved 2023-02-17.
- ^ "Regional Transit Commission appoints first CEO". fortsaskatchewanrecord. Retrieved 2021-04-24.
- ^ "Regular Board Meeting". Edmonton Metropolitan Transit Services Commission. Retrieved 2021-06-18.
- ^ a b Ernst & Young LLP (June 1, 2020). "Accelerating Transit in the Edmonton Metropolitan Region: Building a Regional Transit Services Commission Addendum" (PDF). City of Edmonton. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-11-06. Retrieved January 22, 2021.
- ^ City of Edmonton (March 14, 2022), "March 14, 2022, City Council", YouTube, retrieved March 17, 2022
