1976–77 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season
| 1976–77 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season | |
|---|---|
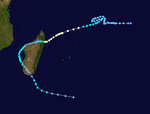
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | 3 October 1976 |
| Last system dissipated | 2 March 1977 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Jack-Io |
| • Maximum winds | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 935 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 9 |
| Total storms | 8 |
| Tropical cyclones | 3 |
| Intense tropical cyclones | 1 |
| Total fatalities | 301 |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
The 1976–77 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was a below-average cyclone season. The season officially ran from November 1, 1976, to April 30, 1977.
Systems

Moderate Tropical Storm Agathe
| Moderate tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 3 – October 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 995 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Storm Brigitta
| Severe tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 16 – December 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
This system formed west of Diego Garcia on November 15. For the next eleven days, Brigitta meandered southward as a tropical depression. After assuming a westward course, Brigitta strengthened into a tropical storm on November 26. The system reached its peak intensity as it passed by the northern tip of Madagascar. The system moved through the Comoros Islands, and then turned southward into Mozambique.[1]
Cyclone Clarence
| Tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 1 (Entered basin after January 5) – January 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min); 960 hPa (mbar) |
On January 8, Clarence passed near St. Brandon, producing high waves that destroyed four boats and several homes. Wind gusts on the island reached 169 km/h (105 mph). For several days moved in a counterclockwise track around the Mascarene Islands, producing high waves and beneficial rainfall on Réunion.[2]
Moderate Tropical Storm Domitile
| Moderate tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 18 – January 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Storm Emilie
| Severe tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 28 – February 5 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
Cyclone Emilie struck the east coast of Mozambique and northeastern South Africa in February 1977. Heavy flooding in the Limpopo Valley killed at least 300 people.[3][4]
Tropical Cyclone Fifi
| Tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 29 – February 10 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min); 985 hPa (mbar) |
Cyclone Fifi passed west of Réunion on February 6, bringing four days' of rainfall that reached 656 mm (25.8 in). Flooding damaged crops and roads, and one person died while attempting to cross an inundated road.[5][6]
Tropical Depression Gilda
| Tropical depression (MFR) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 4 (Entered basin) – February 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
Severe Tropical Storm Hervea
| Severe tropical storm (MFR) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 10 – March 3 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min); 970 hPa (mbar) |
The storm passed just south of Agaléga, dropping 147 mm (5.8 in) of rainfall.[7]
Intense Tropical Cyclone Jack–Io
| Intense tropical cyclone (MFR) | |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 20 (Entered basin) – March 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min); ≤935 hPa (mbar) |
See also
- Atlantic hurricane seasons: 1976, 1977
- Eastern Pacific hurricane seasons: 1976, 1977
- Western Pacific typhoon seasons: 1976, 1977
- North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1976, 1977
References
- ^ Dick DeAngelis (March 1977). "Hurricane Alley". Mariners Weather Log. 21 (2). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 92.
- ^ Hurricane Clarence, 1-16 January. National Climatic Data Center (Report). Global tropical/extratropical cyclone climatic atlas. 1996. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ Shugart, H. H.; Macko, S. A.; Lesolle, P.; Szuba, T. A.; Mukelabai, M. M.; Dowty, P.; Swap, R. J. (2004). "The SAFARI 2000 - Kalahari Transect Wet Season Campaign of year 2000". Global Change Biology. 10 (3): 273–280. Bibcode:2004GCBio..10..273S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2004.00732.x. S2CID 85391768.
- ^ Grobler, Roger R. (2003). A framework for modelling losses arising from natural catastrophes in South Africa (MCom thesis). University of Pretoria. hdl:2263/23749. Retrieved 2022-11-17.
- ^ Hurricane Fifi, 25 January-10 February. National Climatic Data Center (Report). Global tropical/extratropical cyclone climatic atlas. 1996. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ "Le "club des 500 mm"" (in French). Meteo-France. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ Hurricane Hervea, 10 February-3 March. National Climatic Data Center (Report). Global tropical/extratropical cyclone climatic atlas. 1996. Retrieved February 7, 2019.