1972–73 South Pacific cyclone season
| 1972–73 South Pacific cyclone season | |
|---|---|
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | October 19, 1972 |
| Last system dissipated | April 6, 1973 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Bebe |
| • Maximum winds | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 945 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total disturbances | 8 |
| Tropical cyclones | 8 |
| Severe tropical cyclones | 2 |
| Total fatalities | 24 |
| Total damage | $20 million ( USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 1972–73 South Pacific cyclone season ran year-round from July 1 to June 30. Tropical cyclone activity in the Southern Hemisphere reaches its peak from mid-February to early March.
Seasonal summary
Systems
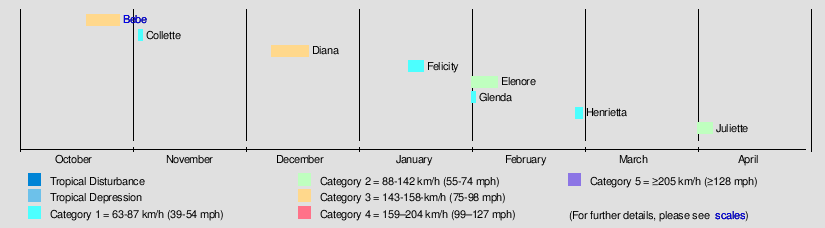
Severe Tropical Cyclone Bebe
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 19 – October 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min); 945 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Cyclone Bebe was a pre-season storm that impacted the Gilbert, Ellice, and Fiji island groups.[1] First spotted on October 20, the system intensified and grew in size through October 22. Its course began along a south-southwest trajectory before recurving near the 14th parallel south, which resulted in a south-southeast motion through the western portion of the Fiji island group.[1] It became the first cyclone to impact Fiji since 1952. On October 24, winds of 150 knots (280 km/h) or more were reported on Rotuma and Viti Levu. Cyclone Bebe passed through Funafuti on Saturday 21st and Sunday 22 October 1972. At about 4 p.m. on the 21st, sea water was bubbling through the coral on the airfield with the water reaching a height of about 4 –5 feet high. The Ellice Islands Colony's ship Moanaraoi was in the lagoon and survived, however 3 tuna boats were wrecked. Waves broke over the atoll. Five people died, two adults and a 3 month old child were swept away by waves, and two sailors from the tuna boats were drowned.[2] Cyclone Bebe knocked down 90% of the houses and trees. The storm surge created a wall of coral rubble along the ocean side of Funafuti and Funafala that was about ten to twelve miles long, and about ten to twenty feet thick at the bottom.[2] The cyclone submerged Funafuti and sources of drinking water were contaminated as a result of the system's storm surge and fresh water flooding. After passing by the archipelago, Bebe transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, with the remnants last noted on October 28.[1] A total of 28 people died and thousands were left homeless. Damages totaled $20 million (1972 USD).[3]
Tropical Cyclone Collette
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 2 – November 3 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
Collette existed from November 2 to November 3.
Severe Tropical Cyclone Diana
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 8 – December 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min); 965 hPa (mbar) |
Diana existed from December 6 to December 18.
Tropical Cyclone Felicity
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 14 – January 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
Felicity existed from January 14 to January 18.
Tropical Cyclone Elenore
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 31 – February 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
Elenore existed from January 31 to February 7.
Tropical Cyclone Glenda
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 31 – February 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
Glenda existed from January 31 to February 1.
Tropical Cyclone Henrietta
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 28 – March 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
Tropical Cyclone Juliette
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | April 2 – April 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
Juliette existed from April 2 to April 6.
Seasonal effects
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed | Pressure | ||||||
| Bebe | October 19 – 28 | Category 3 severe tropical cyclone | 155 km/h (100 mph) | 945 hPa (27.91 inHg) | Tuvalu, Fiji | |||
| Collette | November 2 – 3 | Category 1 tropical cyclone | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | ||||
| Diana | December 8 – 18 | Category 3 severe tropical cyclone | 130 km/h (80 mph) | 965 hPa (28.50 inHg) | ||||
| Felicity | January 14 – 18 | Category 1 tropical cyclone | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | ||||
| Elenore | January 31 – February 7 | Category 2 tropical cyclone | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | Fiji, Tonga | |||
| Glenda | January 31 – February 1 | Category 1 tropical cyclone | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | ||||
| Henrietta | February 28 – March 2 | Category 1 tropical cyclone | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | ||||
| Juliette | April 2 – 6 | Category 2 tropical cyclone | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | Fiji, Tonga | |||
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 8 systems | October 19 – April 6 | 155 km/h (100 mph) | 945 hPa (27.91 inHg) | |||||
See also
- Atlantic hurricane seasons: 1972, 1973
- Eastern Pacific hurricane seasons: 1972, 1973
- Western Pacific typhoon seasons: 1972, 1973
- North Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1972, 1973
References
- ^ a b c Bureau of Meteorology (1975) Tropical Cyclones in the Northern Australian Regions 1971-1972 Australian Government Publishing Service
- ^ a b Resture, Jane (5 October 2009). Hurricane Bebe 1972. Tuvalu and the Hurricanes: ‘The Hurricane in Funafuti, Tuvalu’ by Pasefika Falani (Pacific Frank).
- ^ Elwyn E. Wilson (January 1973). "October Hurricane Clobbers Fiji". Mariners Weather Log. 17 (1). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: 19–20.