Charlemagne-class battleship
 St Louis, April 1903 | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name | Charlemagne |
| Builders | Brest and Lorient shipyards |
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | Bouvet |
| Succeeded by | Iéna |
| Built | 1894–1899 |
| In service | 1897–1931 |
| In commission | 1897–1915 |
| Completed | 3 |
| Lost | 1 |
| Scrapped | 2 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Pre-dreadnought battleship |
| Displacement | 11,275 t (11,097 long tons) (deep load) |
| Length | 117.7 m (386 ft 2 in) |
| Beam | 20.3 m (66 ft 7 in) |
| Draught | 8.4 m (27 ft 7 in) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | 3 shafts, 3 triple-expansion steam engines |
| Speed | 18 knots (33 km/h; 21 mph) |
| Range | 4,200 miles (3,650 nmi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement | 727 |
| Armament |
|
| Armour |
|
The Charlemagne class consisted of three pre-dreadnought battleships built for the French Navy in the 1890s. The ships spent most of their careers assigned to the Mediterranean Squadron (Escadre de la Méditerranée). They had oddly eventful peacetime careers as they were involved in four accidental collisions among them, one of which sank a French submarine with all hands. Saint Louis was usually a fleet flagship during her career and Charlemagne twice participated in the occupation of the port of Mytilene on the island of Lesbos—then owned by the Ottoman Empire—once as part of a French expedition and another as part of an international squadron.
During World War I, they were initially used to escort Allied troop convoys in the Mediterranean. All three ships were ordered to the Dardanelles in November 1914 to guard against a sortie into the Mediterranean by the German battlecruiser SMS Goeben. Charlemagne and Gaulois joined British ships in bombarding Turkish fortifications in early 1915 while Saint Louis was briefly assigned to bombard Turkish positions in Palestine and the Sinai Peninsula. Gaulois was badly damaged by a Turkish shell during one of these bombardments and had to beach herself to avoid sinking. After repairs she returned to the Dardanelles and rejoined her sisters, providing fire support during the Gallipoli Campaign until the Allies evacuated their troops. Saint Louis and Charlemagne were transferred to the squadron assigned to prevent any interference by the Greeks with Allied operations on the Salonica front in 1916 and Gaulois was en route to join them when she was sunk by a German submarine later that year.
The two surviving ships were placed in reserve during 1917. Charlemagne was decommissioned later in 1917 and sold for scrap in 1923. Saint Louis briefly became a training ship in 1919–1920 and was then converted to serve as an accommodation hulk in 1920. She was not sold until 1933, although she had been listed for disposal in 1931.
Design and description

The Charlemagne-class battleships were 117.7 metres (386 ft 2 in) long overall and had a beam of 20.3 metres (66 ft 7 in). At deep load, they had a draught of 7.4 metres (24 ft 3 in) forward and 8.4 metres (27 ft 7 in) aft. They displaced 11,275 tonnes (11,097 long tons) at deep load.[1] Their crew generally consisted of 727 officers and enlisted men[2] as a private ship, or 41 officers and 744 men as a fleet flagship.[3]
The Charlemagne-class ships did not function well in a head sea. Stormy weather in the Bay of Biscay in 1900 caused the captain of Gaulois to complain that the ship's forward gun turret and casemates were flooded out and that the ship generated enormous sheets of spray when water came over the bow. Like most French capital ships of the period, they had pronounced tumblehome. Gaulois's captain also said that his ship was a steady gunnery platform and manoeuvred well in tight spaces but he criticized the armour layout as not high enough to prevent shells from penetrating above the main armour belt and detonating below the secondary armament positions.[4]
The ships used three 4-cylinder vertical triple-expansion steam engines, each engine driving a 4.3-metre (14 ft 1 in) propeller.[5] Rated at 14,500 metric horsepower (10,700 kW), they produced between 14,220–15,295 metric horsepower (10,459–11,249 kW) during their sea trials using steam generated by 20 Belleville water-tube boilers. The boilers had a maximum operating pressure of 17 kg/cm2 (1,667 kPa; 242 psi).[1] The ships reached top speeds of 18 to 18.5 knots (33.3 to 34.3 km/h; 20.7 to 21.3 mph) on their trials.[1][5] They carried a maximum of 1,050 tonnes (1,030 long tons) of coal which allowed them to steam for 4,200 miles (3,600 nmi) at a speed of 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph).[1]
Armament
The Charlemagnes carried their main armament of four 40-calibre Canon de 305 mm (12 in) Modèle 1893 guns in two twin-gun turrets, one each fore and aft.[5] These were the first twin 305 mm gun turrets to be used by the French Navy. They were rotated by electric motors, but the guns were hand-cranked to elevate and depress.[6] This ranged from -5° to +15°[5] and the guns were loaded at full depression. The turrets had a ready rack holding 10 shells before they needed to reload from the magazine.[7] The guns fired 349.4-kilogram (770 lb) armour-piercing projectiles at a muzzle velocity of 815 m/s (2,670 ft/s)[6] at a theoretical rate of one round every 1.3 minutes.[8] At maximum elevation, this provided a range of 12,900 metres (14,100 yd). The guns were provided with 45 shells each.[5]
The ships' secondary armament consisted of ten 45-calibre Canon de 138.6 mm (5.5 in) Modèle 1893 guns, eight of which were mounted in individual casemates and the remaining pair in shielded mounts on the forecastle deck amidships. The guns had an elevation range between -5°30" and +19°30".[5] They fired four 35-kilogram (77 lb) armour-piercing shells per minute at a muzzle velocity of 730 m/s (2,400 ft/s). This gave them a range of 11,000 metres (12,000 yd) at maximum elevation. The ships carried a total of 2316 rounds for these guns.[5][9]
They also carried eight 45-calibre Canon de 100 mm (3.9 in) Modèle 1893 guns in shielded mounts on the superstructure. These guns could elevate from -10° to +20°[5] and they fired a 16-kilogram (35 lb)[10] shell at a rate of five rounds per minute.[8] With a muzzle velocity of 710 m/s (2,300 ft/s),[10] they had a range of 10,000 metres (11,000 yd) at maximum elevation. A total of 2288 rounds, or 286 rounds per gun, was carried for them in each ship.[5] Their anti-torpedo boat defences consisted of twenty 40-calibre Canon de 47 mm (1.9 in) Modèle 1885 Hotchkiss guns, fitted in platforms on both masts, on the superstructure, and in casemates in the hull. These guns could depress to -21° and elevate to +24°[5] They fired 1.5-kilogram (3.3 lb) projectiles at a muzzle velocity of 650 m/s (2,100 ft/s)[11] at a rate of 12 rounds every minute. They had a maximum range of 4,000 metres (4,400 yd) and were provided with a total of 10,500 rounds.[5]
The Charlemagne class mounted four 450-millimetre (17.7 in) torpedo tubes, two on each broadside. Two of these were submerged, angled 20° from the ship's axis, and the other two were above the waterline. They were provided with a total of twelve Modèle 1892 torpedoes.[12] These torpedoes had a 75-kilogram (165 lb) warhead and a maximum range of 800 metres (870 yd) at a speed of 27.5 knots (50.9 km/h; 31.6 mph).[13] Beginning about 1906, the above-water torpedo tubes were removed from each ship.[1] As was common with ships of their generation, they were built with a plough-shaped ram.[14]
Armour
The Charlemagne-class ships carried a total of 820.7 tonnes (807.7 long tons)[5] of Harvey armour.[15] They had a complete waterline armour belt that was 3.26 metres (10 ft 8 in) high. The armour belt tapered from its maximum thickness of 400 mm (15.7 in) to a thickness of 110 mm (4.3 in) at its lower edge. The armoured deck was 55 mm (2.2 in) thick on the flat and was reinforced with an additional 35 mm (1.4 in) plate where it angled downwards to meet the armoured belt. The main turrets were protected by 320 mm (12.6 in) of armour and their roofs were 50 mm (2.0 in) thick. Their barbettes were 270 mm (10.6 in) thick. The outer walls of the casemates for the 138.6-millimetre (5.46 in) guns were 55 mm thick and they were protected by transverse bulkheads 150 mm (5.9 in) thick. The conning tower walls were 326 mm (12.8 in) thick and its roof consisted of 50 mm armour plates. Its communications tube was protected by armour plates 200 mm (7.9 in) thick.[5]
Ships
| Ship | Builder[1] | Laid down | Launched[1] | Commissioned[16] | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charlemagne | Arsenal de Brest | 2 August 1894[17] | 17 October 1895 | 12 September 1899 | Sold for scrap, 1923[17] |
| Saint Louis | Arsenal de Lorient | 25 March 1895[2] | 2 September 1896 | 1 September 1900 | Sold for scrap, 25 April 1933[2] |
| Gaulois | Arsenal de Brest | 6 January 1896[8] | 6 October 1896 | 15 January 1899 | Sunk by UB-47, 27 December 1916[18] |
Service history
Charlemagne, the first ship completed, was initially assigned to the Northern Squadron (Escadre du Nord), but all three ships were assigned to the Mediterranean Squadron during 1900. Saint Louis became the flagship of the squadron almost as soon as she reached Toulon and all three participated in a number of port visits and naval reviews. Shortly after her arrival in Toulon, Gaulois accidentally rammed the destroyer Hallebarde and later rammed the battleship Bouvet in 1903, none of the ships involved were seriously damaged. In 1901, Gaulois and Charlemagne participated in the occupation of Mytilene in an effort to force the Turkish Sultan, Abdul Hamid II, to enforce contracts made with French companies and to repay loans made by French banks.[19] Charlemagne was the French contribution to an international squadron that briefly occupied Mytilene in November–December 1905 for much the same purposes.[20] Together with the battleships Iéna and Bouvet, Gaulois aided survivors of the April 1906 eruption of Mount Vesuvius in Naples.[21]
All three ships were transferred to the Northern Squadron in 1909–1910 and Saint Louis was accidentally rammed by the destroyer Poignard during manoeuvers off Hyères in 1911. Repairs were combined with a major refit later in the year. She accidentally rammed and sank the submarine Vendémiaire on 8 June 1912 off the Casquets, killing all 24 of the submarine's crew.[3] Her sisters received their refits during 1912–1913.[22] All three ships were transferred back to the Mediterranean Fleet after their refits, although their exact assignments differed. Saint Louis became a divisional flagship and Charlemagne was assigned to the Training Division. The Navy intended to assign Gaulois to the Training Division in October 1914, but the war intervened.[3][23]
World War I
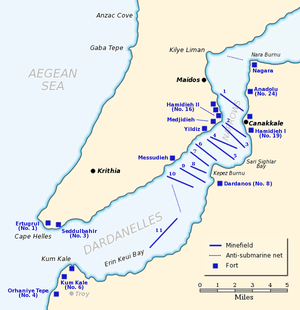
Together with the older French pre-dreadnoughts, the trio escorted Allied troop convoys through the Mediterranean for the first several months of the war. All three ships were ordered to Tenedos Island, not far from the Gallipoli Peninsula of Turkey, in November to guard against a sortie by the German battlecruiser Goeben. Gaulois became the temporary flagship of Rear Admiral (contre-amiral) Émile Guépratte upon her arrival until the return of the battleship Suffren in January 1915.[24] Saint Louis became the flagship of the newly formed Syrian Squadron (Escadre de Syrie) on 9 February. The squadron was intended to attack Turkish positions and lines of communication in Syria, Lebanon, Palestine and the Sinai Peninsula. Saint Louis participated in the bombardment of Gaza and El Arish in April before she was transferred back to the Dardanelles in May.[3]
During the bombardment of 19 February, Gaulois bombarded Turkish forts covering the mouth of the Dardanelles, although Charlemagne did not participate that day. During the day's action, the ship was hit twice, but was only lightly damaged. The two ships traded positions during the bombardment of 25 February, although Charlemagne was not damaged. On 2 March, the French squadron bombarded targets in the Gulf of Saros, at the base of the Gallipoli Peninsula. Five days later, the French squadron attempted to suppress the Turkish guns while British battleships bombarded the fortifications. Gaulois was hit by one shell during this attack that failed to detonate. Admiral Guépratte and his squadron returned to the Gulf of Saros on 11 March where they again bombarded Turkish fortifications.[25]
They returned to assist in the major attack on the fortifications planned for 18 March. British ships made the initial entry into the Dardanelles, but the French ships passed through them to engage the forts at closer range. Gaulois was hit twice during this bombardment, but only one shell did any significant damage. It hit just above the waterline on the starboard bow and pushed in the armour plates below the waterline and opened up a hole through which water flooded in. Little could be done to staunch the inflow and the ship's captain decided to head for the Rabbit Islands, north of Tenedos, where he could beach his ship for temporary repairs. Escorted by Charlemagne in case she foundered en route, Gaulois managed to reach the islands. After temporary repairs, the ship was refloated and sailed for Toulon, escorted by Suffren. They encountered heavy weather en route and emergency repairs had to be made in the Bay of Navarin. She made Toulon without further incident where the ship was refitted and extensively modified to improve her stability, returning to the Dardanelles in July.[26]
Charlemagne was less severely damaged and was repaired at Bizerte, returning to the Dardanelles in May. Saint Louis arrived that same month and both ships provided fire support for French troops ashore.[3] Charlemagne was transferred to Salonica in October 1915 where she joined the French squadron assigned to prevent any interference by the Greeks with Allied operations in Greece. Saint Louis departed for a refit in Lorient that same month and relieved Charlemagne at Salonica in May 1916 so the latter could be refitted in Bizerte.[3][27] Gaulois remained at the Dardanelles until August, covering the evacuation of Allied troops from Gallipoli at the end of 1915, when she started a refit at Brest.[28]
Saint Louis became flagship of the Eastern Naval Division (Division navale d'Orient) in October 1916 until she was transferred to Bizerte in February 1917. Charlemagne returned to Salonica in August 1916 and remained there until ordered to Toulon in August 1917.[29] Gaulois was en route to Salonica after the completion of her refit in December and was sunk on 27 December 1916 by the German U-boat UB-47. Four crewmen were killed, but the rest of the crew was rescued by her escorts.[30] Both of her sisters were placed in reserve upon their arrivals in Bizerte and Toulon. Charlemagne was disarmed on 1 November 1917, condemned on 21 June 1920[27] and later sold for scrap in 1923.[2] Saint Louis was transferred to Toulon in January 1919 and was disarmed and decommissioned the following month. She became a training ship for stokers and engineers that same month. The ship was condemned in June 1920, although she was converted into an accommodation hulk. Saint Louis listed for disposal in 1931, but was not sold until 1933.[3]
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f g Gille, p. 98
- ^ a b c d Silverstone, p. 111
- ^ a b c d e f g d'Ausson, p. 6
- ^ Caresse, p. 120
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Caresse, p. 117
- ^ a b Friedman, p. 211
- ^ Friedman, pp. 211–212
- ^ a b c Caresse, p. 116
- ^ Friedman, p. 224
- ^ a b Friedman, p. 227
- ^ Friedman, p. 228
- ^ Caresse, pp. 114, 116–117
- ^ Friedman, p. 345
- ^ Caresse, p. 114
- ^ Chesneau & Kolesnik, p. 117
- ^ Jordan & Caresse, p. 44
- ^ a b Silverstone, p. 92
- ^ Caresse, p. 134
- ^ Caresse, pp. 120–122
- ^ Gille, p. 96
- ^ Caresse, p. 124
- ^ Gille, pp. 97–98
- ^ Gille, p. 97; Caresse, pp. 126–127
- ^ Caresse, p. 128
- ^ Corbett, pp. 144, 148, 157–160, 172, 192–193, 206, 214, 218; Caresse, pp. 128–129; Gille, p. 97
- ^ Caresse, pp. 129–132
- ^ a b Gille, p. 97
- ^ Caresse, p. 132
- ^ Gille, pp. 97–99
- ^ Caresse, p. 133
Bibliography
- d'Ausson, Enseigne de Vaisseau de la Loge (1978). "French Battleship St. Louis". F. P. D. S. Newsletter. VI (1): 6–7. OCLC 41554533.
- Caresse, Philippe (2012). "The Battleship Gaulois". In Jordan, John (ed.). Warship 2012. London: Conway. ISBN 978-1-84486-156-9.
- Chesneau, Roger & Kolesnik, Eugene M., eds. (1979). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. Greenwich, UK: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-8317-0302-4.
- Corbett, Julian (1997). Naval Operations. History of the Great War: Based on Official Documents. Vol. II (reprint of the 1929 second ed.). London; Nashville, Tennessee: Imperial War Museum in association with the Battery Press. ISBN 1-870423-74-7.
- Friedman, Norman (2011). Naval Weapons of World War One: Guns, Torpedoes, Mines and ASW Weapons of All Nations; An Illustrated Directory. Barnsley: Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84832-100-7.
- Gille, Eric (1999). Cent ans de cuirassés français [A Century of French Battleships] (in French). Nantes: Marines édition. ISBN 2-909-675-50-5.
- Jordan, John & Caresse, Philippe (2017). French Battleships of World War One. Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-639-1.
- Silverstone, Paul H. (1984). Directory of the World's Capital Ships. New York: Hippocrene Books. ISBN 0-88254-979-0.
External links
- (in French) CUIRASSE Charlemagne
