Isotopes of boron
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight Ar°(B) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
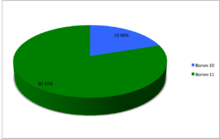
Boron (5B) naturally occurs as isotopes 10
B
and 11
B
, the latter of which makes up about 80% of natural boron. There are 13 radioisotopes that have been discovered, with mass numbers from 7 to 21, all with short half-lives, the longest being that of 8
B
, with a half-life of only 771.9(9) ms and 12
B
with a half-life of 20.20(2) ms. All other isotopes have half-lives shorter than 17.35 ms. Those isotopes with mass below 10 decay into helium (via short-lived isotopes of beryllium for 7
B
and 9
B
) while those with mass above 11 mostly become carbon.
List of isotopes
| Nuclide [n 1] |
Z | N | Isotopic mass (Da)[3] [n 2][n 3] |
Half-life[4] [resonance width] |
Decay mode[4] [n 4] |
Daughter isotope [n 5] |
Spin and parity[4] [n 6][n 7] |
Natural abundance (mole fraction) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excitation energy | Normal proportion[4] | Range of variation | |||||||||||||||||
| 6 B ?[n 8] |
5 | 1 | 6.050800(2150) | p-unstable | 2p? | 4 Li ? |
2−# | ||||||||||||
| 7 B |
5 | 2 | 7.029712(27) | 570(14) ys [801(20) keV] |
p | 6 Be [n 9] |
(3/2−) | ||||||||||||
| 8 B [n 10][n 11] |
5 | 3 | 8.0246073(11) | 771.9(9) ms | β+α | 4 He |
2+ | ||||||||||||
| 8m B |
10624(8) keV | 0+ | |||||||||||||||||
| 9 B |
5 | 4 | 9.0133296(10) | 800(300) zs | p | 8 Be [n 12] |
3/2− | ||||||||||||
| 10 B [n 13] |
5 | 5 | 10.012936862(16) | Stable | 3+ | [0.189, 0.204][5] | |||||||||||||
| 11 B |
5 | 6 | 11.009305167(13) | Stable | 3/2− | [0.796, 0.811][5] | |||||||||||||
| 11m B |
12560(9) keV | 1/2+, (3/2+) | |||||||||||||||||
| 12 B |
5 | 7 | 12.0143526(14) | 20.20(2) ms | β− (99.40(2)%) | 12 C |
1+ | ||||||||||||
| β−α (0.60(2)%) | 8 Be [n 14] | ||||||||||||||||||
| 13 B |
5 | 8 | 13.0177800(11) | 17.16(18) ms | β− (99.734(36)%) | 13 C |
3/2− | ||||||||||||
| β−n (0.266(36)%) | 12 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 14 B |
5 | 9 | 14.025404(23) | 12.36(29) ms | β− (93.96(23)%) | 14 C |
2− | ||||||||||||
| β−n (6.04(23)%) | 13 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| β−2n ?[n 15] | 12 C ? | ||||||||||||||||||
| 14m B |
17065(29) keV | 4.15(1.90) zs | IT ?[n 15] | 0+ | |||||||||||||||
| 15 B |
5 | 10 | 15.031087(23) | 10.18(35) ms | β−n (98.7(1.0)%) | 14 C |
3/2− | ||||||||||||
| β− (< 1.3%) | 15 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| β−2n (< 1.5%) | 13 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 16 B |
5 | 11 | 16.039841(26) | > 4.6 zs | n ?[n 15] | 15 B ? |
0− | ||||||||||||
| 17 B [n 16] |
5 | 12 | 17.04693(22) | 5.08(5) ms | β−n (63(1)%) | 16 C |
(3/2−) | ||||||||||||
| β− (21.1(2.4)%) | 17 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| β−2n (12(2)%) | 15 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| β−3n (3.5(7)%) | 14 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| β−4n (0.4(3)%) | 13 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 18 B |
5 | 13 | 18.05560(22) | < 26 ns | n | 17 B |
(2−) | ||||||||||||
| 19 B [n 16] |
5 | 14 | 19.06417(56) | 2.92(13) ms | β−n (71(9)%) | 18 C |
(3/2−) | ||||||||||||
| β−2n (17(5)%) | 17 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| β−3n (< 9.1%) | 16 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| β− (> 2.9%) | 19 C | ||||||||||||||||||
| 20 B [6] |
5 | 15 | 20.07451(59) | > 912.4 ys | n | 19 B |
(1−, 2−) | ||||||||||||
| 21 B [6] |
5 | 16 | 21.08415(60) | > 760 ys | 2n | 19 B |
(3/2−) | ||||||||||||
| This table header & footer: | |||||||||||||||||||
- ^ mB – Excited nuclear isomer.
- ^ ( ) – Uncertainty (1σ) is given in concise form in parentheses after the corresponding last digits.
- ^ # – Atomic mass marked #: value and uncertainty derived not from purely experimental data, but at least partly from trends from the Mass Surface (TMS).
- ^
Modes of decay:
n: Neutron emission p: Proton emission - ^ Bold symbol as daughter – Daughter product is stable.
- ^ ( ) spin value – Indicates spin with weak assignment arguments.
- ^ # – Values marked # are not purely derived from experimental data, but at least partly from trends of neighboring nuclides (TNN).
- ^ This isotope has not yet been observed; given data is inferred or estimated from periodic trends.
- ^ Subsequently decays by double proton emission to 4
He
for a net reaction of 7
B
→ 4
He
+ 3 1
H
- ^ Has 1 halo proton
- ^ Intermediate product of a branch of proton-proton chain in stellar nucleosynthesis as part of the process converting hydrogen to helium
- ^ Immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of 9
B
→ 2 4
He
+ 1
H
- ^ One of the few stable odd-odd nuclei
- ^ Immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of 12
B
→ 3 4
He
+ e− - ^ a b c Decay mode shown is energetically allowed, but has not been experimentally observed to occur in this nuclide.
- ^ a b Has 2 halo neutrons
Boron-8
Boron-8 is an isotope of boron that undergoes β+ decay to beryllium-8 with a half-life of 771.9(9) ms. It is the strongest candidate for a halo nucleus with a loosely-bound proton, in contrast to neutron halo nuclei such as lithium-11.[7]
Although neutrinos from boron-8 beta decays within the Sun make up only about 80 ppm of the total solar neutrino flux, they have a higher energy centered around 10 MeV,[8] and are an important background to dark matter direct detection experiments.[9] They are the first component of the neutrino floor that dark matter direct detection experiments are expected to eventually encounter.
Applications
Boron-10
Boron-10 is used in boron neutron capture therapy as an experimental treatment of some brain cancers.
References
- ^ "Standard Atomic Weights: Boron". CIAAW. 2009.
- ^ Prohaska, Thomas; Irrgeher, Johanna; Benefield, Jacqueline; Böhlke, John K.; Chesson, Lesley A.; Coplen, Tyler B.; Ding, Tiping; Dunn, Philip J. H.; Gröning, Manfred; Holden, Norman E.; Meijer, Harro A. J. (2022-05-04). "Standard atomic weights of the elements 2021 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. doi:10.1515/pac-2019-0603. ISSN 1365-3075.
- ^ Wang, Meng; Huang, W.J.; Kondev, F.G.; Audi, G.; Naimi, S. (2021). "The AME 2020 atomic mass evaluation (II). Tables, graphs and references*". Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030003. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddaf.
- ^ a b c d Kondev, F. G.; Wang, M.; Huang, W. J.; Naimi, S.; Audi, G. (2021). "The NUBASE2020 evaluation of nuclear properties" (PDF). Chinese Physics C. 45 (3): 030001. doi:10.1088/1674-1137/abddae.
- ^ a b "Atomic Weight of Boron". CIAAW.
- ^ a b Leblond, S.; et al. (2018). "First observation of 20B and 21B". Physical Review Letters. 121 (26): 262502–1–262502–6. arXiv:1901.00455. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.262502. PMID 30636115. S2CID 58602601.
- ^ Maaß, Bernhard; Müller, Peter; Nörtershäuser, Wilfried; Clark, Jason; Gorges, Christian; Kaufmann, Simon; König, Kristian; Krämer, Jörg; Levand, Anthony; Orford, Rodney; Sánchez, Rodolfo; Savard, Guy; Sommer, Felix (November 2017). "Towards laser spectroscopy of the proton-halo candidate boron-8". Hyperfine Interactions. 238 (1): 25. Bibcode:2017HyInt.238...25M. doi:10.1007/s10751-017-1399-5. S2CID 254551036.
- ^ Bellerive, A. (2004). "Review of solar neutrino experiments". International Journal of Modern Physics A. 19 (8): 1167–1179. arXiv:hep-ex/0312045. Bibcode:2004IJMPA..19.1167B. doi:10.1142/S0217751X04019093. S2CID 16980300.
- ^ Cerdeno, David G.; Fairbairn, Malcolm; Jubb, Thomas; Machado, Pedro; Vincent, Aaron C.; Boehm, Celine (2016). "Physics from solar neutrinos in dark matter direct detection experiments". JHEP. 2016 (5): 118. arXiv:1604.01025. Bibcode:2016JHEP...05..118C. doi:10.1007/JHEP05(2016)118. S2CID 55112052.
