Blacksmith lapwing
| Blacksmith lapwing | |
|---|---|

| |
| At Etosha National Park, Namibia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Charadriidae |
| Genus: | Vanellus |
| Species: | V. armatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Vanellus armatus (Burchell, 1822) | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Anitibyx armatus (Burchell, 1822) | |
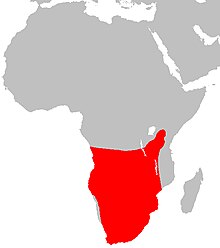
The blacksmith lapwing or blacksmith plover (Vanellus armatus) is a lapwing species that occurs commonly from Kenya through central Tanzania to southern and southwestern Africa. The vernacular name derives from the repeated metallic 'tink, tink, tink' alarm call, which suggests a blacksmith's hammer striking an anvil.
Description
Blacksmith lapwings are very boldly patterned in black, grey and white, possibly warning colours to predators. It is one of five lapwing species (two African, one Asian and two Neotropical) that share the characteristics of red eyes and a bold pied plumage, with a carpal (wing) spur adorning the wrist joint; a sharp black protrusion which they use to aggressively defend their young from potential threats, through persistent aerial dives typically targeting the head. The portions of the bird's body bare to plumage average a black coloration for the bill, and either a black or white-grey dappling on the legs. Females average larger and heavier but the sexes are generally alike.[2]
Habitat and numbers
The blacksmith lapwing occurs in association with wetlands of all sizes. Even very small damp areas caused by a spilling water trough can attract them. In South Africa they are most numerous in the mesic grassland region, less so in higher-rainfall grasslands. Like the crowned lapwing, this species may leave Zambia and Zimbabwe in years of high rainfall and return in dry years. It avoids mountains of any type.[3]
Blacksmith lapwings expanded their range in the 20th century into areas where dams were built and where intensive farming was practiced. Consequently, they are now numerous and established in the western Cape region of South Africa, where they were absent until the 1930s.[3] In this region they have also entered estuarine mud flats in winter where they aggressively displace other waders.[2] Although they are partially migratory, they do not seem to engage in large-scale, regular migrations.[3]
Ecology
During the breeding season, the species often reacts aggressively to other lapwings or African jacanas that may enter its wetland habitat. Nests are shallow depressions on bare ground or short grass, close to water, and tend to be spaced at least 400 m apart.[1] The blacksmith lapwing breeds in spring, but its choice of nesting site and timing may be opportunistic. The young separate gradually from their parents and do not return to natal areas afterwards.[3] This lapwing feeds on aquatic and terrestrial invertebrates.[2]
See also
References
- ^ a b BirdLife International (2016). "Vanellus armatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22693978A93432296. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22693978A93432296.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ a b c Hockey, P.A.R.; Dean, W.R.J.; Ryan, P.G. (2005). Roberts' Birds of Southern Africa (7th ed.). Trustees of J. Voelcker Bird Book Fund.
- ^ a b c d Ward, D.; Underhill, L.G.; Tree, A.J. "Blacksmith Plover". The atlas of southern African birds - Blacksmith Plover (PDF). Vol. 1: Non-passerines.
Gallery
- Nesting in a road in Kenya
- Adult, nest and egg in Tanzania
- Clutch near freshwater shoreline
- Clutch covered with plant debris in a garden
- Foraging at Lake Nakuru, Kenya
- In the Okavango Delta, Botswana
- At Etosha pan, Namibia
- In flight, showing wing spurs
Further reading
- Sinclair, I.; Ryan, P. (2003). Birds of Africa south of the Sahara.
- Marchant, J.; Prater, T.; Hayman, P. (1986). Shorebirds: An identification guide.









