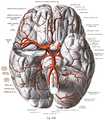
Basilar artery
| Basilar artery | |
|---|---|
 The basilar artery lies at the front of the brainstem in the midline and is formed from the union of the two vertebral arteries. | |
 Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain (inferior view). The basilar artery terminates by splitting into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Vertebral arteries |
| Branches | Pontine arteries anterior inferior cerebellar (AICA) Paramedian arteries superior cerebellar arteries terminal posterior cerebral arteries |
| Supplies | Pons, and superior and inferior aspects of the cerebellum |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria basilaris |
| MeSH | D001488 |
| TA98 | A12.2.07.081 |
| TA2 | 4548 |
| FMA | 50542 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The basilar artery (U.K.: /ˈbæz.ɪ.lə/;[1][2] U.S.: /ˈbæs.ə.lər/[3]) is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.
The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are known as the vertebral basilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part of the circle of Willis and joins with blood supplied to the anterior part of the circle of Willis from the internal carotid arteries.[4][5][6]
Structure
The diameter of the basilar artery range from 1.5 to 6.6 mm.[7]
Origin
The basilar artery arises from the union of the two vertebral arteries at the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons between the abducens nerves (CN VI).[8]
Course
It ascends along the basilar sulcus of the ventral pons. It divides at the junction of the midbrain and pons into the posterior cerebral arteries.[citation needed]
Branches
Its branches from caudal to rostral include:[citation needed]
- anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- labyrinthine artery (<15% of people, usually branches from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery)
- pontine arteries
- superior cerebellar artery
Clinical relevance
A basilar artery stroke classically leads to locked-in syndrome.[9][10]
Additional images
- The internal carotid and vertebral arteries (Right side view)
- Basilar artery
- The arteries of the base of the brain. Basilar artery labeled below center. The temporal pole of the cerebrum and the cerebellar hemisphere have been removed on the right side. Inferior aspect (viewed from below).
References
- ^ "BASILAR | meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary". dictionary.cambridge.org.
- ^ "basilar - WordReference.com Dictionary of English". www.wordreference.com.
- ^ "Definition of basilar | Dictionary.com". www.dictionary.com. Retrieved 14 April 2023.
- ^ Jones, Jeremy. "Basilar artery | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia.
- ^ Purves, Dale (2012). Neuroscience (5th ed.). Sunderland, Mass. pp. 737–738. ISBN 9780878936953.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Carpenter, Malcolm B. (1985). Core text of neuroanatomy (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. pp. 406–410. ISBN 0683014552.
- ^ Pico F, Labreuche J, Gourfinkel-An I, Amarenco P (September 2006). "Basilar artery diameter and 5-year mortality in patients with stroke". Stroke. 37 (9): 2342–7. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000236058.57880.03. PMID 16888278. S2CID 5862145.
- ^ Byrne, James (2012). "Chapter 2. Cranial arterial anatomy". Tutorials in endovascular neurosurgery and interventional neuroradiology. Berlin: Springer. pp. 37–38. ISBN 9783642191541.
- ^ Belash, V. O.; Mokhov, D. E.; Tregubova, E. S. (2018). "[The use of the osteopathic correction for the combined treatment and rehabilitation of the patients presenting with the vertebral artery syndrome]". Voprosy Kurortologii, Fizioterapii, I Lechebnoi Fizicheskoi Kultury. 95 (6): 34–43. doi:10.17116/kurort20189506134. ISSN 0042-8787. PMID 30499484.
- ^ Efendić, Alma; Isaković, Eldar; Delić, Jasmin; Mehinović, Anel; Hrustić, Asmir (August 2014). "Vascular geometry of vertebrobasilar tree with and without aneurysm". Medicinski Glasnik. 11 (2): 252–257. ISSN 1840-2445. PMID 25082236.
External links
- Basilar Artery at neuroangio.org
- Anatomy photo:28:09-0204 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Cranial Fossae: Arteries, Inferior Surface of the Brain"
- Blood supply at neuropat.dote.hu
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 1 January 2014.
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-3". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 1 January 2014.