Aquaspirillum
| Aquaspirillum | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Pseudomonadota |
| Class: | Betaproteobacteria |
| Order: | Neisseriales |
| Family: | Neisseriaceae |
| Genus: | Aquaspirillum Hylemon, 1973 |
| Species | |
|
see text | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Microvirgula Paturaeu, 1998 | |
Aquaspirillum /ˌakwəspəˈrɪləm/ is a genus of helical aerobic bacteria in the family Neisseriaceae that lives in freshwater.
Taxonomy
In 1832, the genus Spirillum was created and encompassed an array of helical bacteria. In 1957, the large genus was reviewed and narrowed to include 19 species based on morphology and a few other physiological characteristics. The genus Aquaspirillum was not created until 1973, when another review of Spirillum led to the division of the genus into Aquaspirillum, Oceanospirillum, and Spirillum.[1]
Etymology
The genus' name is a combination of several words. Aqua comes from Latin, meaning water; speîra comes from Greek, meaning a spiral; spirillum come from Neo-Latin, meaning a small spiral. Put together, the genus' name means "small water spiral".[2]
Species
The new genus comprised the following 13 species when it was created:
- Aquaspirillum anulus
- Aquaspirillum aquaticum
- Aquaspirillum arcticum
- Aquaspirillum delicatum
- Aquaspirillum dispar
- Aquaspirillum giesbergeri
- Aquaspirillum gracile
- Aquaspirillum itersonii
- Aquaspirillum metamorphum
- fr: Aquaspirillum polymorphum
- Aquaspirillum putridiconchylium
- Aquaspirillum serpens (type species)[2]
- Aquaspirillum sinuosum
The following five species were added to Aquaspirillum in the years after its creation:[3]
- Aquaspirillum autotrophicum
- Aquaspirillum bengal
- Aquaspirillum fasciculus
- Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum
- Aquaspirillum psychrophilum
Phylogenetic Analysis
A phylogenetic analysis of the genus showed data that suggested all but three species of Aquaspirillum should be moved into their own respective genera as Aquaspirillum is phylogenetically heterogeneous.[4] However, no new genera for the misclassified species have been proposed, so they technically remain in Aquaspirillum.[5]
Description
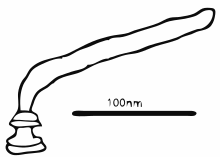
All Aquaspirillum species are rigid helical cells with the exception of A. delicatum and A. fasciculus. The cells measure 0.2–1.5 mcm in diameter. They all have a polar membrane underneath their cytoplasmic membrane, and generally have two tufts of flagella, on each pole. However, they may instead have one single flagellum at each pole instead of either of these tufts.[1][6]
Growth Requirements
Most species of Aquaspirillum are aerobic, but some exist in areas with microaerophilic activity, performing certain amounts of nitrogen fixation. The aerobic species respire using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor, but the some species, including the microaerophilic ones, can also grow anaerobically using nitrate.[1] Most species experience optimal growth in a medium which is 30–32 °C.[7]
References
- ^ a b c Pot, Bruno; Gillis, Monique; De Ley, Jozef (2006). "The Genus Aquaspirillum". The Prokaryotes: 710–722. doi:10.1007/0-387-30745-1_30. ISBN 978-0-387-25495-1 – via Springer Link.
- ^ a b "Genus: Aquaspirillum". LPSN - List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature. Retrieved 2021-05-07.
- ^ Terasaki, Yasuke (1 April 1979). "Transfer of Five Species and Two Subspecies of Spirillum to Other Genera (Aquaspirillum and Oceanospirillum), with Emended Descriptions of the Species and Subspecies". International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. 29 (2): 130–144. doi:10.1099/00207713-29-2-130.
- ^ Ding, L; Yokota, A (2002). "Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aquaspirillum based on 16S rRNA gene sequences". FEMS Microbiol Lett. 212 (2): 165–9. doi:10.1016/s0378-1097(02)00747-4. PMID 12113929.
- ^ Pot, B. and Gillis, M. 2015. Aquaspirillum. Bergey's Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. 1–39.
- ^ "Aquaspirillum". web2.uwindsor.ca. Archived from the original on 26 February 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2021.
- ^ Hylelmon, P.B., J.S. Wells, N.R.Krieg and H.W. Jannasch (1973) The genus Spirillum: a taxonomic study
