Anthracycline

Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from Streptomyces peucetius bacterium.[2][3][4] These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, bladder cancer, and lung cancers. The first anthracycline discovered was daunorubicin (trade name Daunomycin), which is produced naturally by Streptomyces peucetius, a species of Actinomycetota. Clinically the most important anthracyclines are doxorubicin, daunorubicin, epirubicin and idarubicin.[5]
The anthracyclines are among the most effective anticancer treatments ever developed and are effective against more types of cancer than any other class of chemotherapeutic agents.[5][6][7] Their main adverse effect is cardiotoxicity, which considerably limits their usefulness. Use of anthracyclines has also been shown to be significantly associated with cycle 1 severe or febrile neutropenia.[8] Other adverse effects include vomiting.
The drugs act mainly by intercalating with DNA and interfering with DNA metabolism and RNA production. Cytotoxicity is primarily due to inhibition of topoisomerase II after the enzyme induces a break in DNA, preventing religation of the break and leading to cell death. The basic structure of anthracyclines is that of a tetracyclic molecule with an anthraquinone backbone connected to a sugar moiety by a glycosidic linkage. When taken up by a cell the four ring structure intercalates between DNA bases pairs while the sugar sits within the minor groove and interacts with adjacent base pairs.
History
Daunorubicin is a red pigmented drug which was discovered in the early 1960s. It was isolated from a strain of Streptomyces peucetius by A. Di Marco and coworkers, working for Farmitalia Research Laboratories in Italy who called it daunomycin.[9] About the same time Dubost and coworkers in France also discovered the compound and named it rubidomycin.[10] Daunorubicin was adopted as the international name.[5] Initially it was seen to have activity against murine tumours and then in clinical trials it was found to be active against leukaemia and lymphomas.
Doxorubicin was isolated from a mutated variant of S. peucetius (var. caesius). It differs from daunorubicin only by the addition of a hydroxyl group at the carbon 14 position. This modification greatly changes the activity of the drug making it highly effective against a wide range of solid tumours, leukaemia and lymphomas. It is the standard by which novel anthracyclines are judged.[11][12][13][14][15]
The first anthracyclines were so successful that thousands of analogues have been produced in attempts to find compounds with improved therapeutic applications. Only epirubicin and idarubicin have been adopted for worldwide use. Epirubicin has similar activity to doxorubicin, however has reduced cardiotoxic side effects.[16] Idarubicin is a fat soluble variant of daunorubicin and is orally bioavailable.[5][17]
Several groups of researchers focused on designing compounds that retained the polycyclic aromatic chromophore of the anthracyclines (favouring intercalation into DNA) and substituting the sugar residue with simple side chains. This led to the identification of the mitoxantrone which is classed as an anthracenedione compound and is used in the clinic for the management of various cancers.[18] Disaccharide analogues have been shown to retain anticancer activity, and are being further investigated with respect to their mechanism of action.[19]
Although it has been 50 years from the discovery of anthracyclines, and despite recent advances in the development of targeted therapies for cancers, around 32% of breast cancer patients, 57%-70% of elderly lymphoma patients and 50–60% of childhood cancer patients are treated with anthracyclines.[4] Some cancers benefit from neoadjuvant anthracycline-based regimes, and these include triple negative breast cancers that do not respond well to targeted therapies due to the lack of available receptors that can be targeted.[20] Compared to non-triple negative breast cancer patients, triple negative breast cancer patients have shown better response rate and higher pathological response rate with anthracycline use, an indicator used for predicting improved long-term outcomes.[20]
Clinical trials
Anthracyclines remain some of the most widely used chemotherapeutic agents but their potential is limited by its dose-limiting toxicities. Currently, there are many studies being conducted in the search for anthracyclines with better anti-tumour efficacy or with reduced side effects using different nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems.[21][22][23][24]
Mechanism of action

The anthracyclines have been widely studied for their interactions with cellular components and impact on cellular processes. This includes studies in cultured cells and in whole animal systems. A myriad of drug-cellular interactions have been documented in the scientific literature and these vary with respect to the properties of target cells, drug dose and drug intermediates produced. Since artefactual mechanisms of action can be observed,[26] the following mechanisms which occur at clinically relevant drug concentrations are the most important.
DNA Intercalation
Anthracyclines are readily taken up by cells and localised to the nucleus. The chromophore moiety of anthracyclines has intercalating function and inserts in between the adjacent base pair of DNA.[26] The intercalating function inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis in highly replicating cells, subsequently blocking the transcription and replication processes.[26]
Topoisomerase II poison
This is by far the most-accepted mechanism to explain the action of anthracyclines as topoisomerase-II mediated toxicity is evident at clinically relevant drug concentrations.[19][26] Topoisomerase-II is an enzyme that creates temporary double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) breaks and reseals them after managing torsion of DNA supercoils. Anthracyclines intercalated into DNA, form a stable anthracycline-DNA-topoisomerase II ternary complex thus "poisoning" the enzyme and impeding the religation of double-stranded DNA breaks.[27] This topoisomerase-II-mediated DNA damage subsequently promotes growth arrest and recruits DNA repair machinery. When the repair process fails, the lesions initiate programmed cell death.[6]
Reactive oxygen species
The quinone moiety of anthracyclines can undergo redox reactions to generate excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the presence of oxidoreductive enzymes such as cytochrome P450 reductase, NADH dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase. Converting quinone to semiquinone produces free radicals that actively react with oxygen to generate superoxides, hydroxyl radicals and peroxides.[28][29] In addition, the availability of cellular iron catalyses redox reactions and further generates ROS.[28][29] The excessive ROS that cannot be detoxified results in oxidative stress, DNA damage, and lipid peroxidation thereby triggering apoptosis.[28][29]
DNA adduct formation
Anthracyclines can also form adducts with DNA by a single covalent bond through an aminal linkage from the 3’-amino of daunosamine to the exocyclic amino of guanine.[30] The supply of extracellular formaldehyde using formaldehyde-releasing prodrugs can promote covalent DNA adduct formation. Such adducts have been shown to block GpC specific transcription factors and induce apoptotic responses.[30][31]
Clinical implications
Results from a recent meta-analysis provide evidence that breast cancer patients with either duplication of centromere 17 or aberrations in TOP2A, the gene coding for topoisomerase-IIα, benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy that incorporates anthracyclines.[32] This does not include subgroups of patients that harbour amplification of HER2. The observations from this study also allow patients to be identified where anthracyclines might be safely omitted from treatment strategies.[32]
Side effects
Anthracycline administration is often accompanied by adverse drug reactions that limit the use of anthracyclines in the clinics. Two major dose limiting toxicities of anthracyclines include myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity. Fortunately, the introduction of therapeutic cytokines allows management of myelosuppression.[29][21] Hence, cardiac injury remains as the major drawback of anthracycline-based anti-cancer agents. Cardiotoxicity in patients and mice can be mitigated by circulating hemopexin.[33]
Anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity is dose-dependent and cumulative, with the damage imposed to heart occurring upon the very first dose and then accumulating with each anthracycline cycle. There are four types of anthracycline-associated cardiotoxicity that have been described.
| Types of cardiotoxicity | Time to presentation | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Acute | During and immediately after drug administration | Vasodilation, hypotension, transient cardiac rhythm disturbances |
| Subchronic | 1–3 days post-drug administration | Pericarditis-myocarditis |
| Early chronic | Less than 1 year after completing anthracycline treatment | Dilated cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy (uncommon), left ventricular contractile dysfunction, congestive heart failure |
| Delayed/late onset chronic | More than 1 year after completing anthracycline treatment | Restrictive cardiomyopathy, dilated cardiomyopathy, congestive heart failure |
In the clinic, a maximum recommended cumulative dose is set for anthracyclines to prevent the development of congestive heart failure.[35] As an example, the incidence of congestive heart failure is 4.7%, 26% and 48% respectively when patients received doxorubicin at 400 mg/m2, 550 mg/m2 and 700 mg/m2.[4] Therefore, the lifetime cumulative doxorubicin exposure is limited to 400–450 mg/m2 in order to reduce congestive heart failure incidence to less than 5%, although variation in terms of tolerance to doxorubicin exists between individuals.[35] The risk factors that influence the extent of cardiac injury caused by anthracyclines include genetic variability, age (low or high age groups), previous treatments with cardiotoxic drugs and history of cardiac diseases.[29] Children are particularly at risk due to the anthracycline activity that can compromise the development of the immature heart.[35]
Cardiac injury that occurs in response to initial doses of anthracycline can be detected by a rise in troponin level immediately after administration.[35] Biopsy also allows early detection of cardiac injury by evaluating heart ultrastructure changes.[35] Receiving cumulative doses of anthracycline causes left ventricle dysfunction and with continued dosage reaches a certain threshold that can be clinically detected by non-invasive techniques such as 2D echocardiography and strain rate imaging. Advances in developing more sensitive imaging techniques and biomarkers allow early detection of cardiotoxicity and allow cardioprotective intervention to prevent anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity.[35]
The predominant susceptibility of the heart to anthracyclines is due in part to a preferential mitochondrial localisation of anthracyclines. This is attributed to high affinity interaction between anthracyclines and cardiolipin, a phospholipid present in the heart mitochondrial membrane, as heart tissue contains a relatively high number of mitochondria per cell.[29] Heart tissue also has an impaired defence against oxidative stress, displaying a low level of anti-oxidant enzymes such as catalase and superoxide dismutase for detoxifying anthracycline-mediated ROS.[29]
The mechanisms accounting for anthracycline-induced cardiac damage are complex and interrelated. It was first recognised to be related to the oxidative stress induced by anthracyclines.[29] A more recent explanation has emerged, in which anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity is due to anthracycline-topoisomerase IIb poisoning, leading to downstream oxidative stress.[36]
In order to reduce the impact of cardiac injury in response to anthracyclines, a few cardioprotective strategies have been explored. Liposomal formulations of anthracyclines (discussed below) have been developed and used to reduce cardiac damage.[37] Other novel anthracycline analogues such as epirubicin and idarubicin also provide options to reduce adverse cardiac events; these analogues have failed to show superior anti-cancer activity to the parent compounds.[6][35] An alternative drug administration method involving continuous infusion for 72 h as compared to bolus administration provides some protection and can be used when high cumulative doses are anticipated.[35]
When anthracyclines are given intravenously, it may result in accidental extravasation at injection sites. It is estimated that the extravasation incidence ranges from 0.1% to 6%.[38] Extravasation causes serious complications to surrounding tissues with the symptoms of tissue necrosis and skin ulceration.[38] Dexrazoxane is primarily used to treat anthracyclines post-extravasation by acting as a topoisomerase II inhibitor as well as a chelating agent to reduce oxidative stress caused by anthracyclines.[38] Dexrazoxane has also been used with success as a cardioprotective compound in combination with doxorubicin in metastatic breast cancer patients who have been treated with more than 300 mg/m2 doxorubicin, as well as in patients who are anticipated to have a beneficial effect from high cumulative doses of doxorubicin.[39][37]
There is no high quality evidence to confirm if cardioprotective treatments are effective.[40] Studies of the cardioprotective nature of dexrazoxane, provide evidence that it can prevent heart damage without interfering with the anti-tumour effects of anthracycline treatment. Patients given dexrazoxane with their anthracycline treatment had their risk of heart failure reduced compared to those treated with anthracyclines without dexrazoxane. There was no effect on survival though.
Radiolabelled doxorubicin has been utilised as a breast cancer lesion imaging agent in a pilot study. This radiochemical, 99mTc-doxorubicin, localised to mammary tumour lesions in female patients, and is a potential radiopharmaceutical for imaging of breast tumours.[41]
In some cases, anthracyclines may be ineffective due to the development of drug resistance. It can either be primary resistance (insensitive response to initial therapy) or acquired resistance (present after demonstrating complete or partial response to treatment).[42] Resistance to anthracyclines involves many factors, but it is often related to overexpression of the transmembrane drug efflux protein P-glycoprotein (P-gp) or multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1), which removes anthracyclines from cancer cells.[43][42] A large research effort has been focused in designing inhibitors against MRP1 to re-sensitise anthracycline resistant cells, but many such drugs have failed during clinical trials.[43]
Liposomal-based clinical formulations
Liposomes are spherical shape, phospholipid vesicles that can be formed with one or more lipid bilayers with phospholipids or cholesterols.[45] The ability of liposomes to encapsulate both hydrophobic and hydrophilic drug compounds allowed liposomes to be an efficient drug delivery systems (DDS) to deliver a range of drugs in these nano-carriers.[45]
Liposomal formulations of anthracyclines have been developed to maintain or even enhance the therapeutic efficacy of anthracyclines while reduce its limiting toxicities to healthy tissues, particularly cardiotoxicity. Currently, there are two liposomal formulations of doxorubicin available in the clinics.
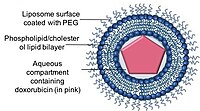
Doxil/Caelyx is the first FDA approved liposomal DDS, and was initially used to treat AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma in 1995 and is now being used for treating recurrent ovarian cancer, metastatic breast cancer with increased cardiac risk, and multiple myeloma.[46][21][47] Doxorubicin is encapsulated in a nano-carrier known as Stealth or sterically stabilised liposomes, consisting of unilamellar liposomes coated with hydrophilic polymer polyethylene glycol (PEG) that is covalently linked to liposome phospholipids.[48] The PEG coating serves as a barrier from opsonisation, rapid clearance while the drug is stably retained inside the nano-carriers via an ammonium sulphate chemical gradient.[37][49] A major advantage of using nano-carriers as a drug delivery system is the ability of the nano-carriers to utilise the leaky vasculature of tumours and their impaired lymphatic drainage via the EPR effect.[50]
The maximum plasma concentration of free doxorubicin after Doxil administration is substantially lower compared to conventional doxorubicin, providing an explanation for its low cardiotoxicity profile.[37] However, Doxil can cause Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (PPE, hand and foot syndrome) due to its accumulation in the skin. Doxil has lower maximum tolerable dose (MTD) at 50 mg/m2 every 4 weeks compared to free doxorubicin at 60 mg/m2 every 3 weeks.[37] Despite this, the maximum cumulative dose for Doxil is still higher compared to doxorubicin due to its cardioprotective characteristics.[48]
Myocet is another non-pegylated liposome encapsulated doxorubicin citrate complex approved for use in combination with cyclophosphamide in metastatic breast cancer patients as first line treatment in Europe and Canada. Doxorubicin is loaded into the liposomes just before administration to patients with a maximum single dose of 75 mg/m2 every 3 weeks.[48] Myocet has similar efficacy as conventional doxorubicin, while significantly reducing cardiac toxicity.[51][52][53]
| Doxil | Myocet | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition of liposomes | PEG-phospholipid
Phospholipid Cholesterol |
Phospholipid
Cholesterol |
[37][54] |
| Size | 80 nm – 100 nm | 150 nm - 250 nm | [55] |
| Drug loading method | Ammonium salt gradient | Citric acid gradient | [37][54] |
| Pharmacokinetics | Dose: Single dose at 10 mg/m2 - 20 mg/m2 Peak plasma concentration: 7.4 μM – 15.3 μM[a]
Elimination half life: 50.2 h – 54.5 h[b] |
Dose: Single dose at 60 mg/m2
Peak plasma concentration: 16 μM Elimination half life: 16.4 h[c] |
[37][56] |
| Clinical indication | AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, recurrent ovarian cancer and metastatic breast cancer | Metastatic breast cancer | [21] |
Adverse drug interactions
Drug interactions with anthracyclines can be complex and might be due to the effect, side effects, or metabolism of the anthracycline. Drugs which inhibit Cytochrome P450 or other oxidases may reduce clearance of anthracyclines, prolonging their circulating half-life which can increase cardiotoxicity and other side effects.[57] As they act as antibiotics anthracyclines can reduce the effectiveness of live culture treatments such as Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy for bladder cancer.[58] As they act as myelosuppressors anthracyclines can reduce the effectiveness of vaccines by inhibiting the immune system.[59]
Several interactions are of particular clinical importance. Though dexrazoxane can be used to mitigate cardiotoxicity or extravasation damage of anthracyclines it also may reduce their effectiveness and the recommendation is not to start dexrazoxane treatment upon initial anthracycline treatment.[60] Trastuzumab (a HER2 antibody used to treat breast cancer) may enhance the cardiotoxicity of anthracyclines[61][62] although the interaction can be minimised by implementing a time interval between anthracycline and trastuzumab administration.[63] Taxanes (except docetaxel) may decrease anthracycline metabolism, increasing serum concentrations of anthracyclines.[64] The recommendation is to treat with anthracyclines first if combination treatment with taxanes is required.[58]
See also
References
![]() This article was adapted from the following source under a CC BY 4.0 license (2019) (reviewer reports):
Alison Cheong; Sean McGrath; Suzanne Cutts (6 December 2018). "Anthracyclines" (PDF). WikiJournal of Medicine. 5 (1): 1. doi:10.15347/WJM/2018.001. ISSN 2002-4436. Wikidata Q60638523.
This article was adapted from the following source under a CC BY 4.0 license (2019) (reviewer reports):
Alison Cheong; Sean McGrath; Suzanne Cutts (6 December 2018). "Anthracyclines" (PDF). WikiJournal of Medicine. 5 (1): 1. doi:10.15347/WJM/2018.001. ISSN 2002-4436. Wikidata Q60638523.
- ^ Frederick CA, Williams LD, Ughetto G, van der Marel GA, van Boom JH, Rich A, Wang AH (March 1990). "Structural comparison of anticancer drug-DNA complexes: adriamycin and daunomycin". Biochemistry. 29 (10): 2538–49. doi:10.1021/bi00462a016. PMID 2334681.
- ^ Trevor AJ, Katzung BG, Masters SB, Kruidering-Hall M (2010). "Chapter 54: Cancer Chemotherapy: Anthracycline Antibiotics". Pharmacology Examination & Board Review. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical.
- ^ Fujiwara A, Hoshino T, Westley J (1985). "Anthracycline Antibiotics". Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 3 (2): 133–157. doi:10.3109/07388558509150782.
- ^ a b c McGowan JV, Chung R, Maulik A, Piotrowska I, Walker JM, Yellon DM (February 2017). "Anthracycline Chemotherapy and Cardiotoxicity". Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy. 31 (1): 63–75. doi:10.1007/s10557-016-6711-0. PMC 5346598. PMID 28185035.
- ^ a b c d Weiss RB (December 1992). "The anthracyclines: will we ever find a better doxorubicin?". Seminars in Oncology. 19 (6): 670–86. PMID 1462166.
- ^ a b c Minotti G, Menna P, Salvatorelli E, Cairo G, Gianni L (June 2004). "Anthracyclines: molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity". Pharmacological Reviews. 56 (2): 185–229. doi:10.1124/pr.56.2.6. PMID 15169927. S2CID 13138853.
- ^ Peng X, Chen B, Lim CC, Sawyer DB (June 2005). "The cardiotoxicology of anthracycline chemotherapeutics: translating molecular mechanism into preventative medicine". Molecular Interventions. 5 (3): 163–71. doi:10.1124/mi.5.3.6. PMID 15994456.
- ^ Lyman GH, Kuderer NM, Crawford J, Wolff DA, Culakova E, Poniewierski MS, Dale DC (May 2011). "Predicting individual risk of neutropenic complications in patients receiving cancer chemotherapy". Cancer. 117 (9): 1917–27. doi:10.1002/cncr.25691. PMC 3640637. PMID 21509769.
- ^ Dimarco A, Gaetani M, Orezzi P, Scarpinato BM, Silvestrini R, Soldati M, Dasdia T, Valentini L (February 1964). "'Daunomycin', a new antibiotic of the rhodomycin group". Nature. 201 (4920): 706–7. Bibcode:1964Natur.201..706D. doi:10.1038/201706a0. PMID 14142092. S2CID 4292271.
- ^ Dubost M, Ganter P, Maral R, Ninet L, Pinnert S, Preudhomme J, Werner GH (September 1964). "Rubidomycin: a new antibiotic with cytostatic properties". Cancer Chemotherapy Reports. 41: 35–6. PMID 14213139.
- ^ Arcamone F, Cassinelli G, Fantini G, Grein A, Orezzi P, Pol C, Spalla C (November 1969). "Adriamycin, 14-hydroxydaunomycin, a new antitumor antibiotic from S. peucetius var. caesius". Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 11 (6): 1101–10. doi:10.1002/bit.260110607. PMID 5365804. S2CID 21897153.
- ^ Blum RH, Carter SK (February 1974). "Adriamycin. A new anticancer drug with significant clinical activity". Annals of Internal Medicine. 80 (2): 249–59. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-249. PMID 4590654.
- ^ Cancer management in man : chemotherapy, biological therapy, hyperthermia and supporting measures. Minev, Boris R. Dordrecht: Springer. 2011. ISBN 9789048197040. OCLC 704395391.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg's cancer : principles & practice of oncology. DeVita, Vincent T., Jr., 1935-, Lawrence, Theodore S., Rosenberg, Steven A. (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2008. ISBN 9780781772075. OCLC 192027662.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Takemura G, Fujiwara H (March 2007). "Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy from the cardiotoxic mechanisms to management". Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. 49 (5): 330–52. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2006.10.002. PMID 17329180.
- ^ Arcamone F, Penco S, Vigevani A (1975). "Adriamycin (NSC 123127): new chemical developments and analogs". Cancer Chemotherapy Reports. 6: 123–129.
- ^ Arcamone F, Bernardi L, Giardino P, Patelli B, Di Marco A, Casazza AM, Pratesi G, Reggiani P (July 1976). "Synthesis and antitumor activity of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin, 4-demethoxy-7,9-diepidaunorubicin, and their beta anomers". Cancer Treatment Reports. 60 (7): 829–34. PMID 1009518.
- ^ Evison BJ, Sleebs BE, Watson KG, Phillips DR, Cutts SM (March 2016). "Mitoxantrone, More than Just Another Topoisomerase II Poison". Medicinal Research Reviews. 36 (2): 248–99. doi:10.1002/med.21364. PMID 26286294. S2CID 8973790.
- ^ a b Marinello J, Delcuratolo M, Capranico G (November 2018). "Anthracyclines as Topoisomerase II Poisons: From Early Studies to New Perspectives". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (11): 3480. doi:10.3390/ijms19113480. PMC 6275052. PMID 30404148.
- ^ a b Wahba HA, El-Hadaad HA (June 2015). "Current approaches in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer". Cancer Biology & Medicine. 12 (2): 106–16. doi:10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2015.0030 (inactive 1 November 2024). PMC 4493381. PMID 26175926.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ a b c d Cagel M, Grotz E, Bernabeu E, Moretton MA, Chiappetta DA (February 2017). "Doxorubicin: nanotechnological overviews from bench to bedside". Drug Discovery Today. 22 (2): 270–281. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2016.11.005. hdl:11336/47838. PMID 27890669.
- ^ Poon RT, Borys N (February 2009). "Lyso-thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin: a novel approach to enhance efficacy of thermal ablation of liver cancer". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 10 (2): 333–43. doi:10.1517/14656560802677874. PMID 19236203. S2CID 73112213.
- ^ Mukai H, Kogawa T, Matsubara N, Naito Y, Sasaki M, Hosono A (June 2017). "A first-in-human Phase 1 study of epirubicin-conjugated polymer micelles (K-912/NC-6300) in patients with advanced or recurrent solid tumors". Investigational New Drugs. 35 (3): 307–314. doi:10.1007/s10637-016-0422-z. PMID 28054329. S2CID 596267.
- ^ Nishiyama N, Matsumura Y, Kataoka K (July 2016). "Development of polymeric micelles for targeting intractable cancers". Cancer Science. 107 (7): 867–74. doi:10.1111/cas.12960. PMC 4946707. PMID 27116635.
- ^ Guo B, Tam A, Santi SA, Parissenti AM (September 2016). "Role of autophagy and lysosomal drug sequestration in acquired resistance to doxorubicin in MCF-7 cells". BMC Cancer. 16 (1): 762. doi:10.1186/s12885-016-2790-3. PMC 5043608. PMID 27687594.
- ^ a b c d Gewirtz DA (April 1999). "A critical evaluation of the mechanisms of action proposed for the antitumor effects of the anthracycline antibiotics adriamycin and daunorubicin". Biochemical Pharmacology. 57 (7): 727–41. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(98)00307-4. PMID 10075079.
- ^ Binaschi M, Bigioni M, Cipollone A, Rossi C, Goso C, Maggi CA, Capranico G, Animati F (August 2001). "Anthracyclines: selected new developments". Current Medicinal Chemistry. Anti-Cancer Agents. 1 (2): 113–30. doi:10.2174/1568011013354723. PMID 12678762.
- ^ a b c Angsutararux P, Luanpitpong S, Issaragrisil S (2015). "Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Overview of the Roles of Oxidative Stress". Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2015: 795602. doi:10.1155/2015/795602. PMC 4602327. PMID 26491536.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Simůnek T, Stérba M, Popelová O, Adamcová M, Hrdina R, Gersl V (January 2009). "Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: overview of studies examining the roles of oxidative stress and free cellular iron". Pharmacological Reports. 61 (1): 154–71. doi:10.1016/S1734-1140(09)70018-0. PMID 19307704. S2CID 4728513.
- ^ a b Cutts SM, Rephaeli A, Nudelman A, Ugarenko M, Phillips DR (2015). "Potential Therapeutic Advantages of Doxorubicin when Activated by Formaldehyde to Function as a DNA Adduct-Forming Agent". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 15 (14): 1409–22. doi:10.2174/1568026615666150413154512. PMID 25866273.
- ^ Cutts SM, Nudelman A, Rephaeli A, Phillips DR (February 2005). "The power and potential of doxorubicin-DNA adducts". IUBMB Life. 57 (2): 73–81. doi:10.1080/15216540500079093. PMID 16036566. S2CID 6784020.
- ^ a b Bartlett JM, McConkey CC, Munro AF, Desmedt C, Dunn JA, Larsimont DP, et al. (May 2015). "Predicting Anthracycline Benefit: TOP2A and CEP17-Not Only but Also". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 33 (15): 1680–7. doi:10.1200/JCO.2013.54.7869. PMID 25897160.
- ^ Jing Liu; Sarah Lane (December 23, 2022). "Circulating hemopexin modulates anthracycline cardiac toxicity in patients and in mice". Science Advances. 8 (51): eadc9245. Bibcode:2022SciA....8C9245L. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adc9245. PMC 9788780. PMID 36563141. (research conducted on patients affected by breast cancer).
- ^ Scully RE, Lipshultz SE (2007). "Anthracycline cardiotoxicity in long-term survivors of childhood cancer". Cardiovascular Toxicology. 7 (2): 122–8. doi:10.1007/s12012-007-0006-4. PMID 17652816. S2CID 834412.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Ewer MS, Ewer SM (September 2015). "Cardiotoxicity of anticancer treatments". Nature Reviews. Cardiology. 12 (9): 547–58. doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2015.65. PMID 25962976. S2CID 9317756.
- ^ Vejpongsa P, Yeh ET (January 2014). "Topoisomerase 2β: a promising molecular target for primary prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 95 (1): 45–52. doi:10.1038/clpt.2013.201. PMID 24091715. S2CID 565837.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Gabizon A, Shmeeda H, Barenholz Y (2003). "Pharmacokinetics of pegylated liposomal Doxorubicin: review of animal and human studies". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 42 (5): 419–36. doi:10.2165/00003088-200342050-00002. PMID 12739982. S2CID 29494837.
- ^ a b c Jordan K, Behlendorf T, Mueller F, Schmoll HJ (April 2009). "Anthracycline extravasation injuries: management with dexrazoxane". Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 5 (2): 361–6. doi:10.2147/tcrm.s3694. PMC 2697522. PMID 19536310.
- ^ Chou H, Lin H, Liu JM (2015-07-13). "A tale of the two PEGylated liposomal doxorubicins". OncoTargets and Therapy. 8: 1719–20. doi:10.2147/OTT.S79089. PMC 4508070. PMID 26203262.
- ^ van Dalen EC, Caron HN, Dickinson HO, Kremer LC (June 2011). "Cardioprotective interventions for cancer patients receiving anthracyclines". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016 (6): CD003917. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd003917.pub4. PMC 6457676. PMID 21678342.
- ^ Araujo FI, Proença FP, Ferreira CG, Ventilari SC, Rosado de Castro PH, Moreira RD, Fonseca LM, Souza SA, Gutfilen B (August 2015). "Use of (99m)Tc-doxorubicin scintigraphy in females with breast cancer: a pilot study". The British Journal of Radiology. 88 (1052): 20150268. doi:10.1259/bjr.20150268. PMC 4651371. PMID 26111270.
- ^ a b Perez EA (March 2009). "Impact, mechanisms, and novel chemotherapy strategies for overcoming resistance to anthracyclines and taxanes in metastatic breast cancer". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 114 (2): 195–201. doi:10.1007/s10549-008-0005-6. PMID 18443902. S2CID 7302079.
- ^ a b Arnason T, Harkness T (October 2015). "Development, Maintenance, and Reversal of Multiple Drug Resistance: At the Crossroads of TFPI1, ABC Transporters, and HIF1". Cancers. 7 (4): 2063–82. doi:10.3390/cancers7040877. PMC 4695877. PMID 26501324.
- ^ Fan Y, Zhang Q (April 2013). "Development of liposomal formulations: From concept to clinical investigations". Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 8 (2): 81–87. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2013.07.010.
- ^ a b Sercombe L, Veerati T, Moheimani F, Wu SY, Sood AK, Hua S (2015-12-01). "Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 6: 286. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00286. PMC 4664963. PMID 26648870.
- ^ Barenholz Y (June 2012). "Doxil®--the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned". Journal of Controlled Release. 160 (2): 117–34. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.03.020. PMID 22484195.
- ^ Udhrain A, Skubitz KM, Northfelt DW (2007). "Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma". International Journal of Nanomedicine. 2 (3): 345–52. PMC 2676669. PMID 18019833.
- ^ a b c Soloman R, Gabizon AA (February 2008). "Clinical pharmacology of liposomal anthracyclines: focus on pegylated liposomal Doxorubicin". Clinical Lymphoma & Myeloma. 8 (1): 21–32. doi:10.3816/CLM.2008.n.001. PMID 18501085.
- ^ Haran G, Cohen R, Bar LK, Barenholz Y (September 1993). "Transmembrane ammonium sulfate gradients in liposomes produce efficient and stable entrapment of amphipathic weak bases". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1151 (2): 201–15. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(93)90105-9. PMID 8373796.
- ^ Maeda H, Nakamura H, Fang J (January 2013). "The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: Improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo". Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 65 (1): 71–9. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.10.002. PMID 23088862.
- ^ Batist G (2007). "Cardiac safety of liposomal anthracyclines". Cardiovascular Toxicology. 7 (2): 72–4. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.529.9071. doi:10.1007/s12012-007-0014-4. PMID 17652807. S2CID 2815965.
- ^ Batist G, Barton J, Chaikin P, Swenson C, Welles L (December 2002). "Myocet (liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin citrate): a new approach in breast cancer therapy". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 3 (12): 1739–51. doi:10.1517/14656566.3.12.1739. PMID 12472371. S2CID 46242391.
- ^ Leonard RC, Williams S, Tulpule A, Levine AM, Oliveros S (August 2009). "Improving the therapeutic index of anthracycline chemotherapy: focus on liposomal doxorubicin (Myocet)". Breast. 18 (4): 218–24. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2009.05.004. PMID 19656681.
- ^ a b Swenson CE, Perkins WR, Roberts P, Janoff AS (June 2001). "Liposome technology and the development of Myocet™(liposomal doxorubicin citrate)". The Breast. 10: 1–7. doi:10.1016/S0960-9776(01)80001-1.
- ^ Bulbake U, Doppalapudi S, Kommineni N, Khan W (March 2017). "Liposomal Formulations in Clinical Use: An Updated Review". Pharmaceutics. 9 (2): 12. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics9020012. PMC 5489929. PMID 28346375.
- ^ Mross K, Niemann B, Massing U, Drevs J, Unger C, Bhamra R, Swenson CE (December 2004). "Pharmacokinetics of liposomal doxorubicin (TLC-D99; Myocet) in patients with solid tumors: an open-label, single-dose study". Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology. 54 (6): 514–24. doi:10.1007/s00280-004-0825-y. PMID 15322827. S2CID 24630910.
- ^ Kivistö KT, Kroemer HK, Eichelbaum M (December 1995). "The role of human cytochrome P450 enzymes in the metabolism of anticancer agents: implications for drug interactions". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 40 (6): 523–30. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1995.tb05796.x. PMC 1365206. PMID 8703657.
- ^ a b "Product Information: Adriamcycin (Doxorubcin HCl) for Injection, USP. In (pp. 8)" (PDF). Ohio: Bedford Laboratories. 2012.
- ^ Tacar O, Sriamornsak P, Dass CR (February 2013). "Doxorubicin: an update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 65 (2): 157–70. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01567.x. PMID 23278683. S2CID 34737360.
- ^ Lyu YL, Kerrigan JE, Lin CP, Azarova AM, Tsai YC, Ban Y, Liu LF (September 2007). "Topoisomerase IIbeta mediated DNA double-strand breaks: implications in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity and prevention by dexrazoxane". Cancer Research. 67 (18): 8839–46. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1649. PMID 17875725.
- ^ Ewer MS, Ewer SM (September 2010). "Troponin I provides insight into cardiotoxicity and the anthracycline-trastuzumab interaction". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 28 (25): 3901–4. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.6274. PMID 20679626.
- ^ Rayson D, Richel D, Chia S, Jackisch C, van der Vegt S, Suter T (September 2008). "Anthracycline-trastuzumab regimens for HER2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer: current experience and future strategies". Annals of Oncology. 19 (9): 1530–9. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn292. PMID 18480068.
- ^ Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M, Baselga J, Norton L (March 2001). "Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2". The New England Journal of Medicine. 344 (11): 783–92. doi:10.1056/NEJM200103153441101. PMID 11248153.
- ^ Gianni L, Viganò L, Locatelli A, Capri G, Giani A, Tarenzi E, Bonadonna G (May 1997). "Human pharmacokinetic characterization and in vitro study of the interaction between doxorubicin and paclitaxel in patients with breast cancer". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 15 (5): 1906–15. doi:10.1200/JCO.1997.15.5.1906. PMID 9164201.
Notes
External links
 Media related to Anthracyclines at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Anthracyclines at Wikimedia Commons