Al-Anon/Alateen
 | |
| Founder | Lois W. Anne B. |
|---|---|
| Type | 501(c)(3) Nonprofit corporation |
| Purpose | Mutual support |
| Headquarters | Virginia Beach, Virginia, U.S. |
Area served | Worldwide |
| Website | al-anon |
Al-Anon Family Groups, founded in 1951, is an international mutual aid organization for people who have been impacted by another person's alcoholism. In the organization's own words, Al-Anon is a "worldwide fellowship that offers a program of recovery for the families and friends of alcoholics, whether or not the alcoholic recognizes the existence of an alcohol-related problem or seeks help."[1] Alateen "is part of the Al-Anon fellowship designed for the younger relatives and friends of alcoholics through the teen years".[2]
Background
Al-Anon defines itself as an independent fellowship with the stated purpose of helping relatives and friends of alcoholics.[3] According to the organization, alcoholism is a family illness.[3] Its "Preamble to the Twelve Steps" provides a general description:
The Al-Anon Family Groups are a fellowship of relatives and friends of alcoholics who share their experience, strength, and hope in order to solve their common problems. We believe alcoholism is a family illness and that changed attitudes can aid recovery.
Al-Anon is not allied with any sect, denomination, political entity, organization, or institution; does not engage in any controversy; neither endorses nor opposes any cause. There are no dues for membership. Al-Anon is self-supporting through its own voluntary contributions.[3]
Al-Anon has but one purpose: to help families of alcoholics. We do this by practicing the Twelve Steps[4] by welcoming and giving comfort to families of alcoholics, and by giving understanding and encouragement to the alcoholic.[3]
Not an intervention program, Al-Anon does not have the stated primary purpose of arresting another's compulsive drinking. Members meet in groups. Meetings are usually small (five to twenty-five); in larger meetings, members often split into smaller groups after the opening readings so everyone has a chance to speak.[5]
Many Al-Anon family group meetings begin with the "Suggested Al-Anon/Alateen Welcome", which starts:
We welcome you to the [Name of Group] Al-Anon Family Group and hope you will find in this fellowship the help and friendship we have been privileged to enjoy. We who live, or have lived, with the problem of alcoholism understand as perhaps few others can. We, too, were lonely and frustrated, but in Al-Anon we discover that no situation is really hopeless, and that it is possible for us to find contentment, and even happiness, whether the alcoholic is still drinking or not.[6]
History

Al-Anon was co-founded in 1951, 16 years after the founding of Alcoholics Anonymous on June 10, 1935,[7] by Anne B. and Lois W. (wife of AA co-founder Bill W.).[8] Before the formation of Al-Anon, independent groups of families of alcoholics met. "Bill thought the[se] groups could be consolidated and that Lois should be the one to take it on."[8]
Al-Anon adopted the Twelve Steps of Alcoholics Anonymous for their own use, changing the word "alcoholics" in the twelfth step to "others" ("we tried to carry this message to others").[9][10] Its name derives from the first parts of the words "Alcoholics Anonymous".[11] Alateen, part of Al-Anon, began in California in 1957 when a teenager named Bob "joined with five other young people who had been affected by the alcoholism of a family member."[12]
Purpose
Although people commonly turn to Al-Anon for help in stopping another's drinking, the organization recognizes that the friends and families of alcoholics are often traumatized themselves and in need of emotional support and understanding. According to Lois W.:
After a while I began to wonder why I was not as happy as I ought to be, since the one thing I had been yearning for all my married life [Bill's sobriety] had come to pass. Then one Sunday, Bill asked me if I was ready to go to the meeting with him. To my own astonishment as well as his, I burst forth with, "Damn your old meetings!" and threw a shoe as hard as I could.
This surprising display of temper over nothing pulled me up short and made me start to analyze my own attitudes ...
My life's purpose of sobering up Bill, which had made me feel desperately needed, had vanished ... I decided to strive for my own spiritual growth. I used the same principles as he did to learn how to change my attitudes ...
We began to learn ... that the partner of the alcoholic also needed to live by a spiritual program.[13]
Benefits
Problems
Al-Anon/Alateen literature focuses on problems common to family members and friends of alcoholics such as excessive care-taking, an inability to differentiate between love versus pity and loyalty to abusers, rather than the problems of the alcoholic.[5] The organization acknowledges that members may join with low self-esteem, largely a side-effect of unrealistically overestimating their agency and control: attempting to control another person's drinking behavior and, when they fail, blaming themselves for the other person's behavior.[5]
Improvement
Participation in Al-Anon has been associated with less personal blame by women who, as a whole, engage in more initial personal blame for the drinking than men.[14] Family members of alcoholics begin to improve as they learn to recognize family pathology, assign responsibility for the pathology to a disease, forgive themselves, accept that they were adversely affected by the pathology and learn to accept their family members' shortcomings.[15]
Al-Anon members are encouraged to keep the focus on themselves, rather than on the alcoholic. Although members believe that changed attitudes can aid recovery, they stress that one person did not cause, cannot cure and cannot control another person's alcohol-related choices and behaviors.[16]
Treatment of alcoholism
Al-Anon's primary purpose is to help families and friends of alcoholics,[3] rather than stopping alcoholism in others or assisting with interventions. When an alcoholic's spouse is active in Al-Anon and the alcoholic is active in AA, the alcoholic is more likely to be abstinent, marital happiness is more likely to be increased and parenting by both is more likely to improve.[17][18] A 1999 clinical analysis of methods used by concerned significant others (CSOs) to encourage alcoholics to seek treatment indicated that Al-Anon participation was "mostly ineffective" towards this goal. The psychologists found community reinforcement approach and family training (CRAFT) "significantly more" effective than Al-Anon participation in arresting alcoholism in others.[19][20]
Demographics
In 2015, Al-Anon Family Groups published its 2015 Member Survey Results of demographic and other information from Al-Anon members in Canada and the United States Of the 8,517 respondents, 93 percent identified as white, 83 percent as female and 61 percent as married. Twelve percent of the respondents had children under age 18 at home,[21] while "80 percent of respondents have been in a romantic relationship involving an alcoholic partner". And one side finding was that "40 percent of respondents initially joined Al-Anon because a person with a drug problem was negatively affecting their lives".[21]
For the 2006 Alateen Member Survey, conducted in the U.S., 139 Alateen members responded. Sixty-five percent of the respondents were female, 35 percent were male, 72 percent were white and 20 percent spoke Spanish fluently. The respondents' average age was 14.[22]
Structure
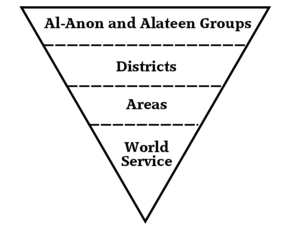
The structure of Al-Anon Family Groups may be depicted as an inverted pyramid, with the organization's headquarters (the World Service Office) at the bottom and the "autonomous"[23] groups at the top.
Groups
Al-Anon and Alateen members meet in Groups for fellowship and support. Each Group may elect a Group Representative (GR) to represent a group at District meetings.[24]
Districts
Al-Anon and Alateen Groups' Group Representatives (GRs) attend District meetings. At these meetings they discuss service activities, Group issues (their primary purpose being to be a forum for Groups) and information from their Area and the World Service Office (WSO) of Al-Anon and Alateen, with GRs having voting privileges. A District may host regular events, such as workshops and speaker meetings, for the local fellowship.[24]
Areas
An Area comprises several Districts. (For example, Texas is divided into two Al-Anon and Alateen Areas, East and West. Each Texas Area has about a dozen Al-Anon and Alateen Districts, for a total of about 24 in the state.[25]) Each Area has regular meetings (known as Assemblies) where Group Representatives (GRs) meet and vote on issues impacting that Area, host workshops and speakers and get Area information to bring back to their Groups.[24][26]
World Service
At Area Assembly, GRs elect a Delegate to the annual World Service Conference (WSC) (aka "The Conference"). The WSC meets annually to interface with the World Service Office (WSO), which is managed by administrators and overseen by the Board of Trustees (who meet more regularly themselves).
Democracy and accountability
Al-Anon promotes democracy and accountability. According to one of its General Warranties of the Conference, "That though the Conference serves Al-Anon it shall never perform any act of government; and that like the fellowship of Al-Anon Family Groups which it serves, it shall always remain democratic in thought and action." Another states "That no Conference member shall be placed in unqualified authority over other members."[27]
According to Tradition Two of Al-Anon's Twelve Traditions: "Our leaders are but trusted servants—they do not govern." Tradition Nine says: "Our groups, as such, ought never be organized; but we may create service boards or committees directly responsible to those they serve."[23] Districts and Areas are directly responsible to the Groups.
The World Service Office (WSO) is accountable to the World Service Conference (WSC). The WSC is responsible to the Areas through elected Delegates and ultimately responsible to the Groups. According to Concept One of Al-Anon's Twelve Concepts of Service: "The ultimate responsibility and authority for Al-Anon world services belongs to the Al-Anon Groups."[28]
In popular culture
When Love Is Not Enough: The Lois Wilson Story is a 2010 film about the wife of AA co-founder Bill Wilson and the beginnings of AA and Al-Anon.
The 1994 film When a Man Loves a Woman "...confronts the realities of substance abuse as it affects all members of one family with an alcoholic at its center."[29] The alcoholic is played by Meg Ryan and her husband, who makes his way to an Al-Anon meeting, is played by Andy García. The hosts of Beyond Belief Sobriety discuss the film in a 2019 podcast episode.[30]
In the Hulu show The Bear, the protagonist Carmen 'Carmy' Berzatto attends Al-Anon in response to his brother's painkiller addiction.
See also
- Alcoholics Anonymous
- Alcoholism in family systems
- Community Reinforcement and Family Training (CRAFT)
- List of twelve-step groups
- Nar-Anon
- National Association for Children of Alcoholics
References
- ^ Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. "Detachment" (PDF). Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Retrieved 2014-01-17.
- ^ Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. "Fact Sheet for Professionals" (PDF). Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2014-01-17.
- ^ a b c d e Al-Anon Family Groups. "Suggested Al-Anon Preamble to the Twelve Steps". www.al-anon.org. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Retrieved 2014-01-18.
- ^ "Twelve Steps". Al-Anon. Retrieved October 18, 2020.
- ^ a b c Humphreys, Keith; Kaskutas, Lee A (1995). "World Views of Alcoholics Anonymous, Women for Sobriety, and Adult Children of Alcoholics/Al-Anon Mutual Help Groups". Addiction Research & Theory. 3 (3): 231–243. doi:10.3109/16066359509005240.
- ^ Al-Anon Family Groups. "Al-Anon Guideline: A Meeting on Wheels, G-22" (PDF). www.al-anon.org. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. p. 1. Retrieved 2010-04-26., "Suggested Al-Anon/Alateen Welcome"
- ^ "AA Timeline". Alcoholics Anonymous. Retrieved 2014-01-17.
- ^ a b "Lois' Story". Stepping Stones: The Historic Home of Bill and Lois Wilson. Archived from the original on 2012-02-12. Retrieved 2014-01-17.
- ^ "The Twelve Steps". Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Retrieved 2014-01-19.
- ^ "Al-Anon's History". How Al-Anon Works for Families and Friends of Alcoholics. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. 1995. p. 127. ISBN 978-0-910034-26-5. OCLC 32951492.
- ^ 2014-2017 Al-Anon/Alateen Service Manual (PDF). Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. 2013. p. 139. Retrieved 2014-01-17.
- ^ "Al-Anon's History". How Al-Anon Works for Families and Friends of Alcoholics. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. 1995. p. 131. ISBN 978-0-910034-26-5. OCLC 32951492.
- ^ Lois W. (1995). "Lois's story". How Al-Anon Works for Families and Friends of Alcoholics. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. pp. 136–137. ISBN 978-0-910034-26-5. OCLC 32951492.
- ^ Kingree, J. B.; Thompson, Martie (2000). "Twelve-Step Groups, Attributions of Blame for Personal Sadness, Psychological Well-Being, and the Moderating Role of Gender". Journal of Applied Social Psychology. 30 (3): 499–517. doi:10.1111/j.1559-1816.2000.tb02493.x. ISSN 1559-1816.
- ^ Humphreys, K (April 1996). "World view change in adult children of Alcoholics/Al-Anon self-help groups: reconstructing the alcoholic family". International Journal of Group Psychotherapy. 46 (2): 255–63. doi:10.1080/00207284.1996.11491497. ISSN 0020-7284. PMID 8935765.
- ^ Al-Anon Family Groups (1997). "Step One". Paths to Recovery: Al-Anon's Steps, Traditions and Concepts. Al-Anon Family Groups. ISBN 978-0-910034-31-9.
- ^ Wright, KD; Scott, TB (September 1978). "The relationship of wives' treatment to the drinking status of alcoholics". Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 39 (9): 1577–1581. doi:10.15288/jsa.1978.39.1577. ISSN 0096-882X. PMID 215841.
- ^ Corenblum, B; Fischer, DG (May 1975). "Some correlates of Al-Anon group membership". Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 36 (5): 675–677. doi:10.15288/jsa.1975.36.675. ISSN 0096-882X. PMID 239290.
- ^ Miller, WR; Meyers, RJ; Tonigan, JS (October 1999). "Engaging the unmotivated in treatment for alcohol problems: a comparison of three strategies for intervention through family members". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 67 (5): 688–697. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.67.5.688. ISSN 0022-006X. PMID 10535235.
- ^ Meyers, RJ; Miller, WR; Smith, JE; Tonigan, JS (October 2002). "A randomized trial of two methods for engaging treatment-refusing drug users through concerned significant others". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 70 (5): 1182–1185. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.70.5.1182. ISSN 0022-006X. PMID 12362968.
- ^ a b Al-Anon Family Groups (2015). "2015 Member Survey Results" (PDF). al-anon.org. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. pp. 2–11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-06-28. Retrieved 2017-08-08.
- ^ Al-Anon Family Groups. "Survey among Alateen members, Fall 2006" (PDF). www.al-anon.org. Virginia Beach, Virginia: Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Retrieved 2010-04-27.
- ^ a b "The Twelve Traditions". Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Retrieved 2014-01-18.
- ^ a b c "2022-2025: Al-Anon/Alateen Groups at Work" (PDF) (2nd ed.). Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters. 2022.
- ^ "Texas al-Anon/Alateen". Retrieved August 28, 2015.
- ^ In keeping with Al-Anon's structure, only Group Representatives can vote on issues and officers here too.
- ^ "General Warranties of the Conference". Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Retrieved 2014-01-18.
- ^ "The Twelve Concepts of Service". Al-Anon Family Group Headquarters, Inc. Retrieved 2014-01-18.
- ^ "When a Man Loves a Woman - Movie Review". Common Sense Media. Retrieved 2023-07-04.
- ^ Sheldon, John (September 1, 2019). "Episode 120: When a Man Loves a Woman". Beyond Belief Sobriety. Retrieved July 4, 2023.
Further reading
- Kirby, K. C.; Marlowe, D. B.; Festinger, D. S.; Garvey, K. A.; LaMonaca, V. (August 1999). "Community reinforcement training for family and significant others of drug abusers: A unilateral intervention to increase treatment entry of drug users". Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 56 (1): 85–96. doi:10.1016/S0376-8716(99)00022-8. PMID 10462097.
- Rychtarik, R. G. & McGillicuddy, N. B. (April 2005). "Coping Skills Training and 12-Step Facilitation for Women Whose Partner Has Alcoholism: Effects on Depression, the Partner's Drinking, and Partner Physical Violence". Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 73 (2): 249–261. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.73.2.249. PMC 4652652. PMID 15796632.
- White, W. (2007). "Review of The Lois Wilson Story: When Love is not Enough". Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly. 24 (4): 159–162. doi:10.1300/J020v24n04_10. S2CID 218637411.
- Meyers, R. J.; Apodaca, T. R.; Flicker, S. M.; Slesnick, N. (July 2002). "Evidence-based approaches for the treatment of substance abusers by involving family members". The Family Journal. 10 (3): 281–288. doi:10.1177/10680702010003004. S2CID 71742028.
- Zajdow, G. (April 1998). "Civil society, social capital and the Twelve Step group". Community, Work & Family. 1 (1): 79–89. doi:10.1080/13668809808414699.
External links
