Age of Discovery
| Part of a series on |
| Geography |
|---|
 |
| History of geography |
|---|
 |



The Age of Discovery (c. 1418 – c. 1620),[1] also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and largely overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the late 15th century to the 17th century, during which seafarers from a number of European countries explored, colonized, and conquered regions across the globe. The Age of Discovery was a transformative period in world history when previously isolated parts of the world became connected to form the world-system and laid the groundwork for globalization. The extensive overseas exploration, particularly the opening of maritime routes to the Indies and the European colonization of the Americas by the Spanish and Portuguese, later joined by the English, French and Dutch, spurred in the International global trade. The interconnected global economy of the 21st century has its origins in the expansion of trade networks during this era.
The exploration also created colonial empires and marked an increased adoption of colonialism as a government policy in several European states. As such, it is sometimes synonymous with the first wave of European colonization. The colonization reshaped power dynamics causing geopolitical shifts in Europe and creating new centers of power beyond Europe. Having set human history on the global common course, the legacy of the Age still shapes the world today.
European oceanic exploration started with the maritime expeditions of Portugal to the Canary Islands in 1336,[2][3] and later with the Portuguese discoveries of the Atlantic archipelagos of Madeira and Azores, the coast of West Africa in 1434, and the establishment of the sea route to India in 1498 by Vasco da Gama, which initiated the Portuguese maritime and trade presence in Kerala and the Indian Ocean.[4][5]
During the Age of Discovery, Spain sponsored and financed the transatlantic voyages of the Italian navigator Christopher Columbus, which from 1492 to 1504 marked the start of colonization in the Americas, and the expedition of the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan to open a route from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific, which later achieved the first circumnavigation of the globe between 1519 and 1522. These Spanish expeditions significantly impacted the European perceptions of the world. These discoveries led to numerous naval expeditions across the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, and land expeditions in the Americas, Asia, Africa, and Australia that continued into the late 19th century, followed by the exploration of the polar regions in the 20th century.
European exploration initiated the Columbian exchange between the Old World (Europe, Asia, and Africa) and the New World (the Americas and Australia). This exchange involved the transfer of plants, animals, human populations (including slaves), communicable diseases, and culture across the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The Age of Discovery and European exploration involved mapping of the world, shaping a new worldview and facilitating contact with distant civilizations. The continents drawn by European mapmakers of the Age developed from abstract "blobs" into the outlines more recognizable to us today.[6] Simultaneously, the spread of new diseases, especially affecting American Indians, led to rapid population declines. The era saw widespread enslavement, exploitation and military conquest of native populations, concurrent with the growing economic influence and spread of western and European culture, science and technology leading to a faster-than-exponential population growth world-wide.
Concept
The concept of discovery has been scrutinized, critically highlighting the history of the core term of this periodization.[7] The term "age of discovery" is in historical literature and still commonly used. J. H. Parry, calling the period the Age of Reconnaissance, argues that not only was the era one of European explorations, but it also produced the expansion of geographical knowledge and empirical science. "It saw also the first major victories of empirical inquiry over authority, the beginnings of that close association of science, technology, and everyday work which is an essential characteristic of the modern western world."[8] Anthony Pagden draws on the work of Edmundo O'Gorman for the statement that "For all Europeans, the events of October 1492 constituted a 'discovery'. Something of which they had no prior knowledge had suddenly presented itself to their gaze."[9] O'Gorman argues that the physical encounter with new territories was less important than the Europeans' effort to integrate this new knowledge into their worldview, what he calls "the invention of America".[10] Pagden examines the origins of the terms "discovery" and "invention". In English, "discovery" and its forms in romance languages derive from "disco-operio, meaning to uncover, to reveal, to expose to the gaze", what was revealed existed previously.[11] Few Europeans during the period used the term "invention" for the European encounters, with the exception of Martin Waldseemüller, whose map first used the term "America". [12]
A central legal concept of the discovery doctrine, expounded by the US Supreme Court in 1823, draws on assertions of European powers' right to claim land during their explorations. The concept of "discovery" has been used to enforce colonial claiming and discovery, but has been challenged by indigenous peoples[13] and researchers.[14] Many indigenous peoples have fundamentally challenged the concept of colonial claiming of "discovery" over their lands and people, as forced and negating indigenous presence.
The period alternatively called the Age of Exploration, has been scrutinized through reflections on the exploration. Its understanding and use, has been discussed as being framed and used for colonial ventures, discrimination and exploitation, by combining it with concepts such as the "frontier" (as in Frontier Thesis) and manifest destiny,[15] up to the contemporary age of space exploration.[16][17][18][19] Alternatively, the term contact, as in first contact, has been used to shed more light on the age of discovery and colonialism, using the alternative names of Age of Contact[20] or Contact Period,[21] discussing it as an "unfinished, diverse project".[22][23]
Overview
The Portuguese began systematically exploring the Atlantic coast of Africa in 1418, under the sponsorship of Prince Henry the Navigator. In 1488, Bartolomeu Dias reached the Indian Ocean by this route.[24]
In 1492, the Catholic Monarchs of Spain funded Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus's (Italian: Cristoforo Colombo) plan to sail west to reach the Indies, by crossing the Atlantic. Columbus encountered a continent uncharted by Europeans (though it had been explored and temporarily colonized by the Norse 500 years earlier).[25] Later, it was called America after Amerigo Vespucci, a trader working for Portugal.[26][27] Portugal quickly claimed those lands under the terms of the Treaty of Alcáçovas, but Castile was able to persuade the Pope, who was Castilian, to issue four papal bulls to divide the world into two regions of exploration, where each kingdom had exclusive rights to claim newly discovered lands. These were modified by the Treaty of Tordesillas, ratified by Pope Julius II.[28][29]

| Major discovery/ Destination |
Main explorer | Year | Funding by |
|---|---|---|---|
| Congo River | Diogo Cão | 1482 | John II of Portugal |
| Cape of Good Hope Indian Ocean |
Dias | 1488 | John II of Portugal |
| West Indies | Columbus | 1492 | Ferdinand and Isabella |
| India | Vasco da Gama | 1498 | Manuel I |
| Brazil | Cabral | 1500 | Manuel I |
| Spice Islands Australasia (Western Pacific Ocean) |
Albuquerque, Abreu, and Serrão | 1512 | Manuel I |
| Pacific Ocean | Vasco Balboa | 1513 | Ferdinand II of Aragon |
| Strait of Magellan | Magellan | 1520 | Charles I of Spain |
| Philippines | Magellan | 1521 | Charles I of Spain |
| Circumnavigation | Magellan and Elcano | 1522 | Charles I of Spain |
| Australia | Willem Janszoon | 1606 | United East India Company |
| New Zealand | Abel Tasman | 1642 | United East India Company |
| Islands Near Antarctica | James Cook | 1773 | George III |
| Hawaii | James Cook | 1778 | George III |
In 1498, a Portuguese expedition commanded by Vasco da Gama reached India by sailing around Africa, opening up direct trade with Asia.[30] While other exploratory fleets were sent from Portugal to northern North America, Portuguese India Armadas also extended this Eastern oceanic route, touching South America and opening a circuit from the New World to Asia (starting in 1500 by Pedro Álvares Cabral), and explored islands in the South Atlantic and Southern Indian Oceans. The Portuguese sailed further eastward, to the valuable Spice Islands in 1512, landing in China one year later. Japan was reached by the Portuguese in 1543. In 1513, Spanish Vasco Núñez de Balboa crossed the Isthmus of Panama and reached the "other sea" from the New World. Thus, Europe first received news of the eastern and western Pacific within a one-year span around 1512. East and west exploration overlapped in 1522, when a Spanish expedition sailing westward, led by Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan and, after his death by navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, completed the first circumnavigation of the world.[31] Spanish conquistadors explored the interior of the Americas, and some of the South Pacific islands. Their main objective was to disrupt Portuguese trade in the East.
From 1495, the French, English, and Dutch entered the race of exploration, after learning of Columbus' exploits, defying the Iberian monopoly on maritime trade by searching for new routes. The first expedition was John Cabot in 1497 to the north, in the service of England, followed by French expeditions to South America and later to North America. Later expeditions went to the Pacific Ocean around South America, and eventually by following the Portuguese around Africa, into the Indian Ocean; discovering Australia in 1606, New Zealand in 1642, and Hawaii in 1778. From the 1580s to the 1640s, Russians explored and conquered almost the whole of Siberia and Alaska in the 1730s.
Background
Rise of European trade
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire largely severed the connection between Europe, and lands further east, Christian Europe was largely a backwater compared to the Arab world, which conquered and incorporated large territories in the Middle East and North Africa. The Christian Crusades to retake the Holy Land, from the Muslims, were not a military success, but did bring Europe into contact with the Middle East and the valuable goods manufactured or traded there. From the 12th century, the European economy was transformed by the interconnecting of river and sea trade routes.[32]: 345
Before the 12th century, an obstacle to trade east of the Strait of Gibraltar, which divided the Mediterranean from the Atlantic Ocean, was Muslim control of territory, including the Iberian Peninsula and the trade monopolies of Christian city-states on the Italian Peninsula, especially Venice and Genoa. Economic growth of Iberia followed the Christian reconquest of Al-Andalus in what is now southern Spain and the siege of Lisbon (1147 AD), in Portugal. The decline of Fatimid Caliphate naval strength, which started before the First Crusade, helped the maritime Italian states, mainly Venice, Genoa and Pisa, dominate trade in the Eastern Mediterranean, with merchants there becoming wealthy and politically influential. Further changing the mercantile situation in the east Mediterranean, was the waning of Christian Byzantine naval power following the death of Emperor Manuel I Komnenos in 1180, whose dynasty had made notable treaties and concessions with Italian traders, permitting the use of Byzantine Christian ports. The Norman Conquest of England, in the late 11th century, allowed for peaceful trade on the North Sea. The Hanseatic League, a confederation of merchant guilds and their towns in north Germany, along the North Sea and Baltic Sea, was instrumental in the commercial development of the region. In the 12th century, the regions of Flanders, Hainault, and Brabant produced the finest quality textiles in northwest Europe, which encouraged merchants from Genoa and Venice to sail there from the Mediterranean, through the Strait of Gibraltar, and up the Atlantic coast.[32]: 316–38 Nicolòzzo Spinola made the first recorded direct voyage from Genoa to Flanders in 1277.[32]: 328
Technology: Ship design and the compass
Technological advancements that were important to the Age of Exploration were the adoption of the magnetic compass and advances in ship design.
The compass was an addition to the ancient method of navigation based on sightings of the sun and stars. It was invented during the Chinese Han dynasty and had been used for navigation in China by the 11th century. It was adopted by Arab traders in the Indian Ocean. The compass spread to Europe by the late 12th or early 13th century.[33] Use of the compass for navigation in the Indian Ocean was first mentioned in 1232.[32]: 351–2 The first mention of use of the compass in Europe was in 1180.[32]: 382 The Europeans used a "dry" compass, with a needle on a pivot. The compass card was also a European invention.[32]
Ships grew in size, required smaller crews and were able to sail longer distances without stopping. This led to significant lower long-distance shipping costs by the 14th century.[32]: 342 Cogs remained popular for trade because of their low cost. Galleys were also used in trade.[32]
Early geographical knowledge and maps

The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, a document from 40-60 AD, describes a newly discovered route through the Red Sea to India, with descriptions of the markets in towns around Red Sea, Persian Gulf and the Indian Ocean, including along the east coast of Africa, which states "for beyond these places the unexplored ocean curves around toward the west, and running along by the regions to the south of Aethiopia and Libya and Africa, it mingles with the western sea (possible reference to the Atlantic Ocean)". European medieval knowledge about Asia beyond the reach of the Byzantine Empire was sourced in partial reports, often obscured by legends,[34] dating back from the conquests of Alexander the Great and successors. Another source was the Radhanite Jewish trade networks of merchants established as go-betweens between Europe and the Muslim world during the time of the Crusader states.

In 1154, the Arab geographer Muhammad al-Idrisi created a description of the world and a world map, the Tabula Rogeriana, at the court of King Roger II of Sicily,[35][36] but still Africa was only partially known to either Christians, Genoese and Venetians, or the Arab seamen, and its southern extent was unknown. There were reports of great African Sahara, but the knowledge was limited for the Europeans, to the Mediterranean coast and little else, since the Arab blockade of North Africa precluded exploration inland. Knowledge about the Atlantic African coast was fragmented and derived mainly from old Greek and Roman maps based on Carthaginian knowledge, including Roman exploration of Mauritania. The Red Sea was barely known and only trade links with the Maritime republics, Venice especially, fostered the collection of accurate maritime knowledge.[37] Indian Ocean trade routes were sailed by Arab traders.
By 1400, a Latin translation of Ptolemy's Geographia reached Italy from Constantinople. The rediscovery of Roman geographical knowledge was a revelation,[38] both for map-making and worldview,[39] although reinforcing the idea that the Indian Ocean was landlocked.
Medieval European travel (1241–1438)


A prelude to the Age of Discovery was a series of European expeditions crossing Eurasia by land in the late Middle Ages.[40] The Mongols had threatened Europe, but Mongol states also unified much of Eurasia and, from 1206 on, the Pax Mongolica allowed safe trade routes and communication lines from the Middle East to China.[41][42] The close Italian links to the Levant raised curiosity and commercial interest in countries which lay further east.[43][page needed] There are a few accounts of merchants from North Africa and the Mediterranean, who traded in the Indian Ocean in late medieval times.[32]
Christian embassies were sent as far as Karakorum during the Mongol invasions of the Levant, from which they gained a greater understanding of the world.[44][45] The first of these travellers was Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, dispatched by Pope Innocent IV to the Great Khan, who journeyed to Mongolia and back from 1241 to 1247.[41] Russian prince Yaroslav of Vladimir, and his sons Alexander Nevsky and Andrey II of Vladimir, travelled to the Mongolian capital. Though having strong political implications, their journeys left no detailed accounts. Other travellers followed, like French André de Longjumeau and Flemish William of Rubruck, who reached China through Central Asia.[46] Marco Polo, a Venetian merchant, dictated an account of journeys throughout Asia from 1271 to 1295, describing being a guest at the Yuan dynasty court of Kublai Khan in Travels. It was read throughout Europe.[47]
The Muslim fleet guarding the Strait of Gibraltar was defeated by Genoa in 1291.[48] In that year, the Genoese attempted their first Atlantic exploration when merchant brothers Vadino and Ugolino Vivaldi sailed from Genoa with two galleys, but disappeared off the Moroccan coast, feeding fears of oceanic travel.[49][50] From 1325 to 1354, a Moroccan scholar from Tangier, Ibn Battuta, journeyed through North Africa, the Sahara desert, West Africa, Southern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Horn of Africa, the Middle East and Asia, having reached China. After returning, he dictated an account to a scholar he met in Granada, The Rihla ("The Journey"),[51] the unheralded source on his adventures.[52] Between 1357 and 1371 a book of supposed travels compiled by John Mandeville acquired popularity. Despite the unreliable and often fantastical nature of its accounts, it was used as a reference[53] for the East, Egypt, and the Levant in general, asserting the old belief that Jerusalem was the centre of the world. Following the period of Timurid relations with Europe, in 1439, Niccolò de' Conti published an account of his travels as a Muslim merchant to India and Southeast Asia. In 1466–1472, Russian merchant Afanasy Nikitin of Tver travelled to India, which he described in his book A Journey Beyond the Three Seas.
These overland journeys had little immediate effect. The Mongol Empire collapsed almost as quickly as it formed and soon the route to the east became more difficult and dangerous. The Black Death of the 14th century also blocked travel and trade for a time.[54]
Religion
Religion played a critical role in motivating European expansionism. In 1487, Portuguese envoys Pero da Covilhã and Afonso de Paiva were sent on a covert mission to gather intelligence on a potential sea route to India and inquire about Prester John, a Nestorian patriarch and king, believed to rule over parts of the subcontinent. Covilhã was warmly received upon his arrival in Ethiopia, but forbidden from leaving.[55]

During the Middle Ages, the spread of Christianity throughout Europe fueled the desire to sermonise in lands beyond. This evangelical effort became a significant part of the military conquests of European powers, like Portugal, Spain, and France, often leading to the conversion of indigenous peoples, voluntarily or forced.[56][57]
Religious orders such as the Franciscans, Dominicans, Augustinians, and Jesuits partook in most missionary endeavours in the New World. By the late 16th and 17th centuries, the latter's presence increased as they sought to reassert their power and revive the Catholic culture of Europe, which had been damaged by the Reformation.[58]
Chinese missions (1405–1433)

The Chinese had wide connections through trade in Asia and been sailing to Arabia, East Africa, and Egypt since the Tang dynasty (AD 618–907). Between 1405-21, the third Ming emperor Yongle sponsored long range tributary missions in the Indian Ocean under the command of admiral Zheng He.[59]
A large fleet of new junk ships was prepared for the international diplomatic expeditions. The largest of these junks—that the Chinese termed bao chuan (treasure ships)—may have measured 121 metres, and thousands of sailors were involved. The first expedition departed in 1405. At least seven well-documented expeditions were launched, each bigger and more expensive than the last. The fleets visited Arabia, East Africa, India, Malay Archipelago and Thailand (then called Siam), exchanging goods along the way.[60] They presented gifts of gold, silver, porcelain and silk; in return, received such novelties as ostriches, zebras, camels, ivory and giraffes.[61][62] After the emperor's death, Zheng He led a final expedition departing from Nanking in 1431 and returning to Beijing in 1433. It is likely this last expedition reached as far as Madagascar. The travels were reported by Ma Huan, a Muslim voyager and translator who accompanied Zheng He on three of the expeditions, his account published as the Yingya Shenglan (Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores) (1433).[63]
The voyages had a significant and lasting effect on the organization of a maritime network, using and creating nodes and conduits in its wake, thereby restructuring international and cross-cultural relationships and exchanges.[64] It was especially impactful as no other polity had exerted naval dominance over all sectors of the Indian Ocean, prior to these voyages.[65] The Ming promoted alternative nodes as a strategy to establish control over the network.[66] For instance, due to Chinese involvement, ports such as Malacca (in Southeast Asia), Cochin (Malabar Coast), and Malindi (Swahili Coast) had grown as key alternatives to other established ports.[a][67] The appearance of the Ming treasure fleet generated and intensified competition among contending polities and rivals, each seeking an alliance with the Ming.[64] The expeditions developed into a maritime trade enterprise, with imperial control over local markets and court-monitored transactions, generating revenue for China and its partners. They boosted regional trade and production, caused a supply shock in Eurasia and led to price spikes in Europe in the early 15th century.[68]
The tributary relations promoted during the voyages manifested a trend toward cross-regional interconnections and early globalization in Asia and Africa.[69] Diplomatic relations were built on mutually beneficial maritime trade and China's strong naval presence in foreign waters, with Chinese naval superiority being a key factor in these interactions.[70] The voyages brought about the Western Ocean's regional integration and increase in international circulation of people, ideas, and goods. It provided a platform for cosmopolitan discourses, which took place in locations such as the ships of the Ming treasure fleet, the Ming capitals of Nanjing as well as Beijing, and the banquet receptions organized by the Ming court for foreign representatives.[64] Diverse groups of people from maritime countries congregated, interacted, and traveled together as the treasure fleet sailed from and to China.[64] For the first time, the maritime region from China to Africa was under the dominance of a single imperial power and allowed for the creation of a cosmopolitan space.[71]
These long-distance journeys were not followed up, as the Ming dynasty retreated in the haijin, a policy of isolationism, having limited maritime trade. Travels were halted abruptly after the emperor's death, as the Chinese lost interest in what they termed barbarian lands, turning inward,[72] and successor emperors felt the expeditions were harmful to the Chinese state; Hongxi Emperor ended further expeditions and Xuande Emperor suppressed much of the information about Zheng He's voyages.
Atlantic Ocean (1419–1507)

From the 8th until the 15th century, the Republic of Venice and neighboring maritime republics held the monopoly of European trade with the Middle East. The silk and spice trade, involving spices, incense, herbs, drugs and opium, made these Mediterranean city-states phenomenally rich. Spices were among the most expensive and demanded products of the Middle Ages, as they were used in medieval medicine,[73] religious rituals, cosmetics, perfumery, as well as food additives and preservatives.[74] They were all imported from Asia and Africa.
Muslim traders dominated maritime routes throughout the Indian Ocean, tapping source regions in the Far East and shipping for trading emporiums in India, mainly Kozhikode, westward to Ormus in the Persian Gulf and Jeddah in the Red Sea. From there, overland routes led to the Mediterranean coasts. Venetian merchants distributed the goods through Europe until the rise of the Ottoman Empire, which eventually led to the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, barring Europeans from some important combined-land-sea routes in areas around the Aegean, Bosporus, and Black Sea.[citation needed] The Venetians and other maritime republics maintained more limited access to Asian goods, via south-eastern Mediterranean trade, in such ports as Antioch, Acre, and Alexandria.
Forced to reduce their activities in the Black Sea, and at war with Venice, the Genoese had turned to North African trade of wheat, olive oil and a search for silver and gold. Europeans had a constant deficit in silver and gold,[75] as it only went out, spent on eastern trade now cut off. Several European mines were exhausted,[76] The lack of bullion led to the development of a complex banking system to manage the risks in trade (the first state bank, Banco di San Giorgio, was founded in 1407 at Genoa). Sailing also into the ports of Bruges (Flanders) and England, Genoese communities were then established in Portugal,[77] who profited from their enterprise and financial expertise.
European sailing had been primarily close to land cabotage, guided by portolan charts. These charts specified proven ocean routes guided by coastal landmarks: sailors departed from a known point, followed a compass heading, and tried to identify their location by its landmarks.[78] For the first oceanic exploration Western Europeans used the compass, as well as progressive new advances in cartography and astronomy. Arab navigational tools like the astrolabe and quadrant were used for celestial navigation.
The Muslim lands in Asia were generally more economically developed and had better infrastructure than Europe at this time, despite Europe's economic changes brought about by the Black Death allowing for more freedoms for lower- and upper-class people.[79] The gunpowder empires concealed knowledge to European Christian traders about where lucrative locations such as Indonesia were, spurring a further desire for Christian trade with other Muslim nations besides the gunpowder empires despite European Christians generally having antipathy towards Muslims.[79]
Portuguese exploration


In 1297, King Denis of Portugal took a personal interest in exports. In 1317, he made an agreement with Genoese merchant sailor Manuel Pessanha, appointing him first admiral of the Portuguese Navy, to defend the country against Muslim pirate raids.[80] Outbreaks of bubonic plague led to severe depopulation in the second half of the 14th century: only the sea offered alternatives, with most population settling in fishing and trading coastal areas.[81] Between 1325 and 1357, Afonso IV of Portugal encouraged maritime commerce and ordered the first explorations.[82] The Canary Islands, already known to the Genoese, were claimed as officially discovered under the patronage of the Portuguese, but in 1344 Castile disputed them, expanding their rivalry into the sea.[83][84]
To ensure their monopoly on trade, Europeans (beginning with the Portuguese) attempted to install a Mediterranean system of trade which used military might and intimidation, to divert trade through ports they controlled; there it could be taxed.[85] In 1415, Ceuta was conquered by the Portuguese aiming to control navigation of the African coast. The young prince Henry the Navigator was there and became aware of profit possibilities in the trans-Saharan trade routes. For centuries slave and gold trade routes linking West Africa with the Mediterranean passed over the Western Sahara Desert, controlled by the Moors of North Africa.
Henry wished to know how far Muslim territories in Africa extended, hoping to bypass them and trade directly with West Africa by sea, find allies in legendary Christian lands to the south[86] like the supposed long-lost Christian kingdom of Prester John[87] and probe whether it was possible to reach the Indies by sea, the source of the lucrative spice trade. He invested in sponsoring voyages down the coast of Mauritania, gathering a group of merchants, shipowners and stakeholders interested in new sea lanes. Soon the Atlantic islands of Madeira (1419) and the Azores (1427) were reached. The expedition leader who established settlements on Madeira, was Portuguese explorer João Gonçalves Zarco.[88]
Europeans did not know what lay beyond Cape Non (Cape Chaunar) on the African coast, and whether it was possible to return once it was crossed.[89] Nautical myths warned of oceanic monsters or an edge of the world, but Henry's navigation challenged such beliefs: starting in 1421, systematic sailing overcame it, reaching the difficult Cape Bojador that in 1434 one of Henry's captains, Gil Eanes, finally passed.
From 1440 onwards, caravels were extensively used for the exploration of the coast of Africa. This was an existing Iberian ship type, used for fishing, commerce and military purposes. Unlike other vessels of the time, the caravel had a sternpost-mounted rudder (as opposed to a side-mounted steering oar). It had a shallow draft, which was helpful in exploring unknown coastlines. It had good sailing performance, with a windward ability that was notable by the standards of the time.[b] The lateen rig was less useful when sailing downwind – which explains Christopher Columbus (Italian: Cristoforo Colombo) re-rigging the Niña with square rig.[91]
For celestial navigation the Portuguese used the ephemerides, which experienced a remarkable diffusion in the 15th century. These were astronomical charts plotting the location of the stars over a distinct period of time. Published in 1496 by the Jewish astronomer, astrologer, and mathematician Abraham Zacuto, the Almanac Perpetuum included some of these tables for the movements of stars.[92] These tables revolutionized navigation, allowing the calculation of latitude. Exact longitude remained elusive from mariners for centuries.[93][94] Using the caravel, systematic exploration continued ever more southerly, advancing on average one degree a year.[95] Senegal and Cape Verde Peninsula were reached in 1445 and in 1446, Álvaro Fernandes pushed on almost as far as present-day Sierra Leone.
In 1453, the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottomans was a perceived blow to Christendom and established business links with the East. In 1455, Pope Nicholas V issued the bull Romanus Pontifex reinforcing the previous Dum Diversas (1452), granting all lands and seas discovered beyond Cape Bojador to King Afonso V of Portugal and his successors, as well as mostly cutting off trade to and permitting conquest and increased war against Muslims and pagans, initiating a mare clausum policy in the Atlantic.[96] The king, who had been inquiring of Genoese experts about a seaway to India, commissioned the Fra Mauro world map, which arrived in Lisbon in 1459.[97] In 1456, Diogo Gomes reached the Cape Verde archipelago. In the next decade captains at the service of Prince Henry, discovered the remaining islands which were occupied during the 15th century. The Gulf of Guinea would be reached in the 1460s.
Portuguese exploration after Prince Henry
In 1460, Pedro de Sintra reached Sierra Leone. Prince Henry died in November of that year after which, given the meagre revenues, exploration was granted to Lisbon merchant Fernão Gomes in 1469, who in exchange for the monopoly of trade in the Gulf of Guinea had to explore 100 miles (161 kilometres) each year for five years.[98] With his sponsorship, explorers João de Santarém, Pedro Escobar, Lopo Gonçalves, Fernão do Pó, and Pedro de Sintra made it beyond those goals. They reached the Southern Hemisphere and islands of the Gulf of Guinea, including São Tomé and Príncipe and Elmina on the Gold Coast in 1471. There, in what came to be called the "Gold Coast" in what is today Ghana, a thriving alluvial gold trade was found among the natives, Arab and Berber traders.
In 1478, during the War of the Castilian Succession, near the coast at Elmina a large battle was fought between a Castilian armada of 35 caravels, and a Portuguese fleet for the hegemony of the Guinea trade (gold, slaves, ivory, and malagueta pepper). The war ended with a Portuguese naval victory, followed by the official recognition by the Catholic Monarchs of Portuguese sovereignty over most of the disputed West African territories embodied in the Treaty of Alcáçovas, 1479. This was the first colonial war among European powers.[citation needed]
In 1481, João II decided to build São Jorge da Mina factory. In 1482 the Congo River was explored by Diogo Cão,[99] who in 1486 continued to Cape Cross (modern Namibia).

The next crucial breakthrough was in 1488, when Bartolomeu Dias rounded the southern tip of Africa, which he named Cabo das Tormentas, "Cape of Storms", anchoring at Mossel Bay and then sailing east as far as the mouth of the Great Fish River, proving the Indian Ocean was accessible from the Atlantic. Simultaneously Pero da Covilhã, sent out travelling secretly overland, had reached Ethiopia having collected important information about the Red Sea and Quenia coast, suggesting a sea route to the Indies would soon be forthcoming.[100] Soon the cape was renamed by King John II of Portugal the "Cape of Good Hope", because of the great optimism engendered by the possibility of a sea route to India, proving false the view that had existed since Ptolemy that the Indian Ocean was land-locked.
Based on many later stories of the phantom island known as Bacalao and the carvings on Dighton Rock some have speculated that Portuguese explorer João Vaz Corte-Real discovered Newfoundland in 1473, but the sources are considered unreliable.[101]
Spanish exploration: Columbus's landfall in the Americas

Portugal's Iberian rival, Castile, had begun to establish its rule over the Canary Islands in 1402 but became distracted by internal Iberian politics and the repelling of Islamic invasion attempts and raids through most of the 15th century. Late in the century, following the unification of the crowns of Castile and Aragon, an emerging modern Spain became fully committed to the search for new trade routes overseas. The Crown of Aragon had been an important maritime power in the Mediterranean, controlling territories in eastern Spain, southwestern France, major islands like Sicily, Malta, and the Kingdom of Naples and Sardinia, with mainland possessions as far as Greece. In 1492 the joint rulers conquered the Moorish kingdom of Granada, which had been providing Castile with African goods through tribute, and decided to fund Christopher Columbus's expedition in the hope of bypassing Portugal's monopoly on west African sea routes, to reach "the Indies" (east and south Asia) by travelling west.[102] Twice before, in 1485 and 1488, Columbus had presented the project to the king John II of Portugal, who rejected it.
On the evening of 3 August 1492, Columbus departed from Palos de la Frontera. The land was sighted on 12 October 1492, and Columbus called the island (one of the islands now comprising The Bahamas) San Salvador, in what he thought to be the "East Indies". Columbus explored the northeast coast of Cuba and the northern coast of Hispaniola, by 5 December. He was received by the native cacique Guacanagari, who gave him permission to leave some of his men behind.

Columbus left 39 men and founded the settlement of La Navidad in what is now Haiti.[103] Before returning to Spain, he kidnapped some ten to twenty-five natives and took them back with him. Only seven or eight of the native 'Indians' arrived in Spain alive, but they made an impression on Seville.[104] On 15 March 1493 he arrived in Barcelona, where he reported to Queen Isabella and King Ferdinand. Word of his discovery of new lands rapidly spread throughout Europe.[105]
Columbus and other Spanish explorers were initially disappointed with their discoveries—unlike Africa or Asia, the Caribbean islanders had little to trade with the Castilian ships. The islands thus became the focus of colonization efforts. It was not until the continent itself was explored that Spain found the wealth it had sought.
Treaty of Tordesillas (1494)

Shortly after Columbus's return from what would later be called the "West Indies", a division of influence became necessary to avoid conflict between the Spanish and Portuguese.[106] On 4 May 1493, two months after Columbus's arrival, the Catholic Monarchs received a bull (Inter caetera) from Pope Alexander VI stating all lands west and south of a pole-to-pole line 100 leagues west and south of the Azores or the Cape Verde Islands should belong to Castile and, later, all mainlands and islands then belonging to India. It did not mention Portugal, which could not claim newly discovered lands east of the line.
King John II of Portugal was displeased with the arrangement, feeling that it gave him far too little land—preventing him from reaching India, his main goal. He then negotiated directly with King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain to move the line west, allowing him to claim newly discovered lands east of it.[107] In 1494, the Treaty of Tordesillas divided the world between Portugal and Spain. Portugal gained control over Africa, Asia, and eastern South America (Brazil), encompassing everything outside Europe east of a line drawn 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde islands (already Portuguese). The Spanish (Castile) received everything west of this line, including the islands discovered by Columbus on his first voyage, named in the treaty as Cipangu and Antilia (Cuba and Hispaniola). The dividing line, situated about halfway between Portuguese Cape Verde and Spanish discoveries in the Caribbean, split the known world of Atlantic islands evenly.
In 1500, Pedro Álvares Cabral, initially considering the Brazilian coast as a large island, claimed it for Portugal east of the dividing line. This claim was acknowledged by the Spanish. Cabral, heading towards India, followed a corridor in the Atlantic negotiated by the treaty for favorable winds. While some speculate earlier secret Portuguese discovery of Brazil, there is no credible evidence for this. Similarly, suspicions about Duarte Pacheco Pereira alleged 1498 discovery lack credibility among historians.[citation needed]
Later the Spanish territory would prove to include huge areas of the continental mainland of North and South America, though Portuguese-controlled Brazil would expand across the line, and settlements by other European powers ignored the treaty.
The Americas: The New World

Little of the divided area had actually been seen by Europeans, as it was only divided by a geographical definition rather than control on the ground. The desire to compete with the Ottoman Empire and Columbus's first voyage in 1492 spurred further maritime exploration and, from 1497, several other explorers headed west.
North America
That year John Cabot (Italian: Giovanni Caboto), also a commissioned Italian, got letters patent from King Henry VII of England. Sailing from Bristol, probably backed by the local Society of Merchant Venturers, Cabot crossed the Atlantic from a northerly latitude hoping the voyage to the "West Indies" would be shorter[108] and made landfall somewhere in North America, possibly Newfoundland.
In 1499 João Fernandes Lavrador was licensed by the King of Portugal and together with Pero de Barcelos they first sighted Labrador, which was granted and named after him. After returning he possibly went to Bristol to sail in the name of England.[109]
Between 1499 and 1502 the brothers Gaspar and Miguel Corte Real explored and named the coasts of Greenland and Newfoundland.[110] Both explorations are noted in the 1502 Cantino planisphere.
The "True Indies" and Brazil
In 1497, newly crowned King Manuel I of Portugal sent an exploratory fleet eastwards, fulfilling his predecessor's project of finding a route to the Indies. In July 1499, news spread that the Portuguese had reached the "true Indies", as a letter was dispatched by the Portuguese king to the Spanish Catholic Monarchs.[111]
The third expedition by Columbus in 1498 was the beginning of the first successful Castilian (Spanish) colonization in the West Indies, on the island of Hispaniola. Despite growing doubts, Columbus refused to accept he had not reached the Indies. During the voyage he discovered the mouth of the Orinoco River on the north coast of South America (now Venezuela) and thought that the huge quantity of fresh water coming from it could only be from a continental land mass, which he was certain was the Asian mainland.
As shipping between Seville and the West Indies grew, knowledge of the Caribbean islands, Central America and the northern coast of South America increased. One of these Spanish fleets, that of Alonso de Ojeda and Amerigo Vespucci in 1499–1500 reached land at the coast of what is now Guyana, where the two explorers seem to have separated in opposite directions. Vespucci sailed southward, discovering the mouth of the Amazon River in July 1499,[112][113] and reaching 6°S, in present-day north east Brazil, before turning around.
In the beginning of 1500, Vicente Yáñez Pinzon was blown off course by a storm and reached what is now the northeast coast of Brazil on 26 January 1500, exploring as far south as the present-day state of Pernambuco. His fleet was the first to fully enter the Amazon River estuary, which he named Río Santa María de la Mar Dulce (Saint Mary's River of the Freshwater Sea).[114] The land was too far east for the Castilians to claim under the Treaty of Tordesillas, but the discovery created Castilian interest, with a second voyage by Pinzon in 1508 (the Pinzón–Solís voyage, which navigated the northern coast to the Central American mainland in search of a passage to the East) and a voyage in 1515–16 by a navigator of the 1508 expedition, Juan Díaz de Solís. The 1515–16 expedition was spurred on by reports of Portuguese exploration of the region (see below). It ended when de Solís and some of his crew disappeared when exploring the River Plata in a boat, but what they found reignited Spanish interest, and colonization began in 1531.
In April 1500, the second Portuguese India Armada, headed by Pedro Álvares Cabral, with a crew of expert captains, encountered the Brazilian coast as it swung westward in the Atlantic while performing a large "volta do mar" to avoid becalming in the Gulf of Guinea. On 21 April 1500, a mountain was seen and named Monte Pascoal, and on 22 April Cabral landed on the coast. On 25 April, the entire fleet sailed into the harbour they named Porto Seguro (Port Secure). Cabral perceived that the new land lay east of the line of Tordesillas, and sent an envoy to Portugal with the discovery in letters, including the letter of Pero Vaz de Caminha. Believing the land to be an island, he named it Ilha de Vera Cruz (Island of the True Cross).[115] Some historians have suggested that the Portuguese may have encountered the South American bulge earlier while sailing the "volta do mar", hence the insistence of John II in moving the line west of Tordesillas in 1494—so his landing in Brazil may not have been an accident; although John's motivation may have just been to claiming new lands in the Atlantic easier.[116] From the east coast, the fleet then turned eastward to resume the journey to the southern tip of Africa and India. Cabral was the first captain to touch four continents, leading the first expedition that connected and united Europe, Africa, the New World, and Asia.[117][118]
At the invitation of King Manuel I of Portugal, Amerigo Vespucci[119] participated as an observer in these exploratory voyages to the east coast of South America. The expeditions became widely known in Europe after two accounts attributed to him, published between 1502 and 1504, suggested the newly discovered lands were not the Indies but a "New World",[120] the Mundus novus; this is also the Latin title of a contemporary document based on Vespucci letters to Lorenzo di Pierfrancesco de' Medici, which had become popular in Europe.[121] It was soon understood that Columbus had not reached Asia but found a new continent, the Americas. The Americas were named in 1507 by cartographers Martin Waldseemüller and Matthias Ringmann, after Amerigo Vespucci.
From 1501 to 1502, one of these Portuguese expeditions, led by Gonçalo Coelho (and/or André Gonçalves or Gaspar de Lemos), sailed south along the coast of South America to the bay of present-day Rio de Janeiro. Vespucci's account states that the expedition reached the latitude "South Pole elevation 52° S", in the "cold" latitudes of what is now southern Patagonia, before turning back. Vespucci wrote that they headed toward the southwest and south, following "a long, unbending coastline", apparently coincident with the southern South American coast. This seems controversial, since he changed part of his description in the subsequent letter, stating a shift, from about 32° S (Southern Brazil) to the south-southeast, to open sea, maintaining that they reached 50°/52° S.[122][123]
In 1503, Binot Paulmier de Gonneville, challenging the Portuguese policy of mare clausum, led one of the earliest French Normand and Breton expeditions to Brazil. He intended to sail to the East Indies, but near the Cape of Good Hope, his ship was diverted to the west by a storm, and landed in the present-day state of Santa Catarina (southern Brazil), on 5 January 1504.

From 1511 to 1512, Portuguese captains João de Lisboa and Estevão de Fróis reached the River Plata estuary in present-day Uruguay and Argentina, and went as far south as the present-day Gulf of San Matias at 42°S.[124][125] The expedition reached a cape extending north to south which they called Cape of "Santa Maria" (Punta del Este, keeping the name the Cape nearby); and after 40°S they found a "Cape" or "a point or place extending into the sea", and a "Gulf" (in June and July). After they had navigated for nearly 300 km (186 mi) to round the cape, they again sighted the continent on the other side and steered towards the northwest, but a storm prevented them from making any headway. Driven away by the Tramontane or north wind, they retraced their course. Also gives the first news of the White King and the "people of the mountains" to the interior (the Inca Empire), and a gift, an ax of silver, obtained from the Charrúa natives on their return ("to the coast or side of Brazil"), and "to West" (along the coast and the River Plata estuary), and offered to King Manuel I.[126] Christopher de Haro, a Flemish of Sephardic origin (one of the financiers of the expedition along with D. Nuno Manuel), who would serve the Spanish Crown after 1516, believed the navigators had discovered a southern strait to west and Asia.
In 1519, an expedition sent by the Spanish Crown to find a way to Asia was led by the experienced Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan. The fleet explored the rivers and bays as it charted the South American coast until it found a way to the Pacific Ocean through the Strait of Magellan.
From 1524 to 1525, Aleixo Garcia, a Portuguese conquistador, led a private expedition of shipwrecked Castilian and Portuguese adventurers, who recruited about 2,000 Guaraní Indians. They explored the territories of present-day southern Brazil, Paraguay, and Bolivia, using the native trail network, the Peabiru. They were the first Europeans to cross the Chaco and reach the outer territories of the Inca Empire on the hills of the Andes.[127]
Indian Ocean (1497–1513)
Vasco da Gama's route to India

Protected from direct Spanish competition by the Treaty of Tordesillas, Portuguese eastward exploration and colonization continued apace. Twice, in 1485 and 1488, Portugal officially rejected Genoese Christopher Columbus's idea of reaching India by sailing westwards. King John II of Portugal's experts rejected it, for they held the opinion that Columbus's estimation of a travel distance of 2,400 miles (3,860 km) was low,[128] and in part because Bartolomeu Dias departed in 1487 trying the rounding of the southern tip of Africa. They believed that sailing east would require a far shorter journey. Dias's return from the Cape of Good Hope in 1488, and Pero da Covilhã's travel to Ethiopia overland indicated that the richness of the Indian Ocean was accessible from the Atlantic. A long-overdue expedition was prepared.

In July 1497, a small exploratory fleet of four ships and about 170 men left Lisbon under the command of Vasco da Gama. By December the fleet passed the Great Fish River—where Dias had turned back—and sailed into waters unknown to the Europeans. Sailing into the Indian Ocean, da Gama entered a maritime region that had three different and well-developed trade circuits. The one da Gama encountered connected Mogadishu on the east coast of Africa; Aden, at the tip of the Arabian peninsula; the Persian port of Hormuz; Cambay, in northwestern India; and Calicut, in southwestern India.[129] On 20 May 1498, they arrived at Calicut. The efforts of Vasco da Gama to get favorable trading conditions were hampered by the low value of their goods, compared with the valuable goods traded there.[130][page needed] Two years and two days after departure, Gama and a survivor crew of 55 men returned in glory to Portugal as the first ships to sail directly from Europe to India. Da Gama's voyage is romanticized in the Os Lusíadas, an epic poem by fellow discovery-era traveler Luís de Camões. The poem is widely regarded as Portugal's greatest literary achievement.[131][132]
In 1500, a second, larger fleet of thirteen ships and about 1500 men were sent to India. Under the command of Pedro Álvares Cabral, they made the first landfall on the Brazilian coast, giving Portugal its claim. Later, in the Indian Ocean, one of Cabral's ships reached Madagascar (1501), which was partly explored by Tristão da Cunha in 1507; Mauritius was discovered in 1507, Socotra occupied in 1506. In the same year Lourenço de Almeida landed in Sri Lanka, the eastern island named "Taprobane" in remote accounts of Alexander the Great's and 4th-century BC Greek geographer Megasthenes. On the Asiatic mainland, the first factories (trading-posts) were established at Kochi and Calicut (1501) and then Goa (1510).
The "Spice Islands" and China

The Portuguese continued sailing eastward from India, entering a second existing circuit of the Indian Ocean trade, from Calicut and Quillon in India, to southeast Asia, including Malacca, and Palembang.[129] In 1511, Afonso de Albuquerque conquered Malacca for Portugal, then the center of Asian trade. East of Malacca, Albuquerque sent several diplomatic missions: Duarte Fernandes as the first European envoy to the Kingdom of Siam (modern Thailand).
Learning the location of the so-called "spice islands", heretofore a secret from the Europeans, were the Maluku Islands, mainly the Banda, then the world's only source of nutmeg and cloves. Reaching these was the main purpose for the Portuguese voyages in the Indian Ocean. Albuquerque sent an expedition led by António de Abreu to Banda (via Java and the Lesser Sunda Islands), where they were the first Europeans to arrive in early 1512, after taking a route through which they also reached first the islands of Buru, Ambon and Seram.[133][134] From Banda Abreu returned to Malacca, while his vice-captain Francisco Serrão, after a separation forced by a shipwreck and heading north, reached once again Ambon and sank off Ternate, where he obtained a license to build a Portuguese fortress-factory: the Fort of São João Baptista de Ternate, which founded the Portuguese presence in the Malay Archipelago.
In May 1513 Jorge Álvares, one of the Portuguese envoys, reached China. Although he was the first to land on Lintin Island in the Pearl River Delta, it was Rafael Perestrello—a cousin of the famed Christopher Columbus—who became the first European explorer to land on the southern coast of mainland China and trade in Guangzhou in 1516, commanding a Portuguese vessel with crew from a Malaccan junk that had sailed from Malacca.[135][136] Fernão Pires de Andrade visited Canton in 1517 and opened up trade with China. The Portuguese were defeated by the Chinese in 1521 at the Battle of Tunmen and in 1522 at the Battle of Xicaowan, during which the Chinese captured Portuguese breech-loading swivel guns and reverse engineered the technology, calling them "Folangji" 佛郎機 (Frankish) guns, since the Portuguese were called "Folangji" by the Chinese. After a few decades, hostilities between the Portuguese and Chinese ceased and in 1557 the Chinese allowed the Portuguese to occupy Macau.
To enforce a trade monopoly, Muscat and Hormuz in the Persian Gulf were seized by Afonso de Albuquerque in 1507 and in 1515, respectively. He also entered into diplomatic relations with Persia. In 1513, while trying to conquer Aden, an expedition led by Albuquerque cruised the Red Sea inside the Bab al-Mandab and sheltered at Kamaran island. In 1521, a force under António Correia conquered Bahrain, ushering in a period of almost eighty years of Portuguese rule of the Gulf archipelago.[137] In the Red Sea, Massawa was the most northerly point frequented by the Portuguese until 1541, when a fleet under Estevão da Gama penetrated as far as Suez.
Pacific Ocean (1513–1529)

Balboa's expedition to the Pacific Ocean
In 1513, about 40 miles (64 kilometres) south of Acandí, in present-day Colombia, Spanish Vasco Núñez de Balboa heard unexpected news of an "other sea" rich in gold, which he received with great interest.[138] With few resources and using information given by caciques, he journeyed across the Isthmus of Panama with 190 Spaniards, a few native guides, and a pack of dogs.
Balboa, using a brigantine and ten native canoe, explored the coast, facing battles and dense jungles. On September 25, after crossing the Chucunaque River mountains, he became the first European to see the Pacific Ocean from the New World. The expedition briefly navigated the Pacific, naming the bay San Miguel and the sea Mar del Sur (South Sea). Seeking gold, Balboa traversed cacique lands to the islands, naming the largest Isla Rica (now Isla del Rey) and the group Archipiélago de las Perlas, names still in use today.[citation needed]
Subsequent developments to the east
From 1515 to 1516, the Spanish fleet led by Juan Díaz de Solís sailed down the east coast of South America as far as Río de la Plata, which Solís named shortly before he died while trying to find a passage to the "South Sea".
First circumnavigation

By 1516, several Portuguese navigators conflicting with King Manuel I of Portugal gathered in Seville to serve the newly crowned Charles I of Spain. Among them were explorers Diogo and Duarte Barbosa, Estêvão Gomes, João Serrão and Ferdinand Magellan, cartographers Jorge Reinel and Diogo Ribeiro, cosmographers Francisco and Ruy Faleiro and the Flemish merchant Christopher de Haro. Ferdinand Magellan had sailed in India for Portugal up to 1513, when the Maluku Islands were reached, and had kept contact with Francisco Serrão who was living there.[139][140] Magellan developed the theory that the Maluku Islands were in the Tordesillas Spanish area, based on studies by Faleiro brothers.
Aware of the efforts of the Spanish to find a route to India by sailing west, Magellan presented his plan to Charles I of Spain. The king and Christopher de Haro financed Magellan's expedition. A fleet was put together, and Spanish navigators such as Juan Sebastián Elcano joined the enterprise. On August 10, 1519, they departed from Seville with a fleet of five ships—the caravel flagship Trinidad under Magellan's command, and carracks San Antonio, Concepcion, Santiago and Victoria. They contained a crew of about 237 European men from several regions, with the goal of reaching the Maluku Islands by travelling west, trying to reclaim it under Spain's economic and political sphere.[141]

The fleet sailed south, avoiding Portuguese Brazil, and became the first to reach Tierra del Fuego. Starting on October 21, they navigated the 373-mile (600 km) Strait of Magellan, entering the Pacific on November 28, which Magellan named Mar Pacífico for its calm waters.[142] After crossing the Pacific, Magellan was killed in the battle of Mactan in the Philippines. Juan Sebastián Elcano completed the voyage, reaching the Spice Islands in 1521. On September 6, 1522, the Victoria returned to Spain, completing the first circumnavigation of the globe. Of the original crew, only 18 men completed the circumnavigation; 17 returned later, including twelve captured by the Portuguese and five survivors of the Trinidad. Antonio Pigafetta, a Venetian scholar, kept a detailed journal that is a key source of information about the voyage.[citation needed]
This round-the-world voyage gave Spain valuable knowledge of the world and its oceans which later helped in the exploration and settlement of the Philippines. Although this was not a realistic alternative to the Portuguese route around Africa[143] (the Strait of Magellan was too far south, and the Pacific Ocean too vast to cover in a single trip from Spain) successive Spanish expeditions used this information to explore the Pacific Ocean and discovered routes that opened up trade between Acapulco, New Spain (present-day Mexico) and Manila in the Philippines.[144]
Westward and eastward exploration meet


Soon after Magellan's expedition, the Portuguese rushed to seize the surviving crew and built a fort in Ternate.[145] In 1525, Charles I of Spain sent another expedition westward to colonize the Maluku Islands, claiming that they were in his zone of the Treaty of Tordesillas. The fleet of seven ships and 450 men was led by García Jofre de Loaísa and included the most notable Spanish navigators: Juan Sebastián Elcano and Loaísa, who died then, and the young Andrés de Urdaneta.
Near the Strait of Magellan one of the ships was pushed south by a storm, reaching 56° S, where they thought seeing "earth's end": so Cape Horn was crossed for the first time. The expedition reached the islands with great difficulty, docking at Tidore.[145] The conflict with the Portuguese established in nearby Ternate was inevitable, starting nearly a decade of skirmishes.[147][148]
As there was not a set eastern limit to the Tordesillas line, both kingdoms organized meetings to resolve the issue. From 1524 to 1529, Portuguese and Spanish experts met at Badajoz-Elvas trying to find the exact location of the antimeridian of Tordesillas, which would divide the world into two equal hemispheres. Each crown appointed three astronomers and cartographers, three pilots, and three mathematicians. Lopo Homem, Portuguese cartographer and cosmographer was on the board, along with cartographer Diogo Ribeiro of the Spanish delegation. The board met several times without reaching an agreement: the knowledge at that time was insufficient for an accurate calculation of longitude, and each group gave the islands to its sovereign. The issue was settled only in 1529, after a long negotiation, with the signing of Treaty of Zaragoza, which allocated the Maluku Islands to Portugal and the Philippines to Spain.[149]
From 1525 to 1528, Portugal sent several expeditions around the Maluku Islands. Gomes de Sequeira and Diogo da Rocha were sent north by the governor of Ternate Jorge de Menezes, being the first Europeans to reach the Caroline Islands, which they named "Islands de Sequeira".[150] In 1526, Jorge de Meneses docked on Biak and Waigeo islands, Papua New Guinea. Based on these explorations stands the theory of Portuguese discovery of Australia, one among several competing theories about the early discovery of Australia, supported by Australian historian Kenneth McIntyre, stating it was discovered by Cristóvão de Mendonça and Gomes de Sequeira.
In 1527, Hernán Cortés fitted out a fleet to find new lands in the "South Sea" (Pacific Ocean), asking his cousin Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón to take charge. On 31 October 1527, Saavedra sailed from New Spain, crossing the Pacific and touring the north of New Guinea, then named Isla de Oro. In October 1528, one of the vessels reached the Maluku Islands. In his attempt to return to New Spain he was diverted by the northeast trade winds, which threw him back, so he tried sailing back down, to the south. He returned to New Guinea and sailed northeast, where he sighted the Marshall Islands and the Admiralty Islands, but again was surprised by the winds, which brought him a third time to the Moluccas. This westbound return route was hard to find but was eventually discovered by Andrés de Urdaneta in 1565.[151]
Inland Spanish expeditions (1519–1532)
Rumors of undiscovered islands northwest of Hispaniola reached Spain by 1511, ushering King Ferdinand's interest in forestalling further exploration. While the Portuguese were making huge gains in the Indian Ocean, the Spanish invested in exploring inland in search of gold and other valuable resources. The members of these expeditions, the "conquistadors", were not soldiers in an army, but more like soldiers of fortune; they came from a variety of backgrounds including artisans, merchants, clergy, lawyers, lesser nobility and a few freed slaves. They usually supplied their own equipment or were extended credit to purchase it in exchange for a share in profits. They usually had no professional military training, but a number of them had previous experience on other expeditions.[152]
In the Americas, the Spanish encountered large indigenous empires and formed alliances with indigenous people through small expeditions. After establishing Spanish sovereignty and discovering wealth, the crown focused on implementing Spanish state and church institutions. A key element was the 'spiritual conquest' through Christian evangelization. The initial economy relied on a tribute and forced labor under the encomienda system. The discovery of vast silver deposits transformed both the colonial economies of Mexico and Peru and Spain’s economy. With global trade networks and valuable American crops, Spain's economy strengthened, enhancing its status as a world power.[citation needed]
During this time, pandemics of European diseases such as smallpox decimated the indigenous populations.[153]
In 1512, to reward Juan Ponce de León for exploring Puerto Rico in 1508, King Ferdinand urged him to seek these new lands. He would become governor of discovered lands but was to finance himself all exploration.[154] With three ships and about 200 men, Léon set out from Puerto Rico in March 1513. In April they sighted land and named it La Florida—because it was Easter (Florida) season—believing it was an island, becoming credited as the first European to land in the continent. The arrival location has been disputed between St. Augustine,[155] Ponce de León Inlet and Melbourne Beach. They headed south for further exploration and on April 8 encountered a current so strong that it pushed them backward: this was the first encounter with the Gulf Stream that would soon become the primary route for eastbound ships leaving the Spanish Indies bound for Europe.[156] They explored down the coast reaching Biscayne Bay, Dry Tortugas and then sailing southwest in an attempt to circle Cuba to return, reaching Grand Bahama on July.
Cortés' Mexico and the Aztec Empire
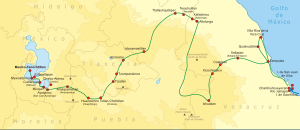
In 1517, Cuba's governor Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar commissioned a fleet under the command of Hernández de Córdoba to explore the Yucatán peninsula. They reached the coast where Mayans invited them to land. They were attacked at night and only a remnant of the crew returned. Velázquez then commissioned another expedition led by his nephew Juan de Grijalva, who sailed south along the coast to Tabasco, part of the Aztec empire.
In 1518, Velázquez gave the mayor of the capital of Cuba, Hernán Cortés, the command of an expedition to secure the interior of Mexico but, due to an old gripe between them, revoked the charter. In February 1519, Cortés went ahead anyway, in an act of open mutiny. With about 11 ships, 500 men, 13 horses and a small number of cannons he landed in Yucatán, in Mayan territory,[157] claiming the land for the Spanish crown. From Trinidad he proceeded to Tabasco and won a battle against the natives. Among the vanquished was Marina (La Malinche), his future mistress, who knew both (Aztec) Nahuatl language and Maya, becoming a valuable interpreter and counsellor. Cortés learned about the wealthy Aztec Empire through La Malinche,
In July, his men took over Veracruz and he placed himself under direct orders of new king Charles I of Spain.[157] There Cortés asked for a meeting with Aztec Emperor Montezuma II, who repeatedly refused. They headed to Tenochtitlan and on the way made alliances with several tribes. In October, accompanied by about 3,000 Tlaxcaltec they marched to Cholula, the second largest city in central Mexico. Either to instill fear upon the Aztecs waiting for him or (as he later claimed) wishing to make an example when he feared native treachery, they massacred thousands of unarmed members of the nobility gathered at the central plaza and partially burned the city.

On November 8, Cortés and his large army were welcomed by Moctezuma II in Tenochtitlan, who hoped to learn about them to eventually defeat them.[157] Moctezuma gave lavish gifts, which led Cortés to plunder the city. Cortés claimed the Aztecs saw him as an emissary or incarnation of the god Quetzalcoatl, though this is contested by few historians.[158] Upon learning that his men had been attacked on the coast, Cortés took Moctezuma hostage in his palace, demanding tribute for King Charles.
Meanwhile, Velasquez sent another expedition, led by Pánfilo de Narváez, to oppose Cortès, arriving in Mexico in April 1520 with 1,100 men.[157] Cortés left 200 men in Tenochtitlan and took the rest to confront Narvaez, whom he overcame, convincing his men to join him. In Tenochtitlán one of Cortés's lieutenants committed a massacre in the Great Temple, triggering local rebellion. Cortés speedily returned, attempting the support of Moctezuma but the Aztec emperor was killed, possibly stoned by his subjects.[159] The Spanish fled for the Tlaxcaltec during the Noche Triste, where they managed a narrow escape while their back guard was massacred. Much of the treasure looted was lost during this panicked escape.[157] After a battle in Otumba they reached Tlaxcala, having lost 870 men.[157] Having prevailed with the assistance of allies and reinforcements from Cuba, Cortés besieged Tenochtitlán and captured its ruler Cuauhtémoc in August 1521. As the Aztec Empire ended he claimed the city for Spain, renaming it Mexico City.
Pizarro's Peru and the Inca Empire

A first attempt to explore western South America was undertaken in 1522 by Pascual de Andagoya. Native South Americans told him about a gold-rich territory on a river called Pirú. Having reached San Juan River (Colombia), Andagoya fell ill and returned to Panama, where he spread the news about "Pirú" as the legendary El Dorado. These, along with the accounts of the success of Hernán Cortés, caught the attention of Pizarro.
Francisco Pizarro had accompanied Balboa in the crossing of the Isthmus of Panama. In 1524 he formed a partnership with priest Hernando de Luque and soldier Diego de Almagro to explore the south, agreeing to divide the profits. They dubbed the enterprise the "Empresa del Levante": Pizarro would command, Almagro would provide military and food supplies, and Luque would be in charge of finances and additional provisions.
On 13 September 1524, the first of three expeditions set out to conquer Peru with 80 men and 40 horses. The venture failed, halting in Colombia due to bad weather, hunger, and conflicts with locals; Almagro lost an eye. Their route was marked by Puerto Deseado (desired port), Puerto del Hambre (port of hunger), and Puerto quemado (burned port). Two years later, a second expedition began with reluctant permission from the Governor of Panama. In August 1526, they departed with two ships, 160 men, and horses. Upon reaching the San Juan River, Pizarro explored swampy coasts, while Almagro sought reinforcements. Pizarro's pilot, sailing south and crossing the equator, captured a raft from Tumbes. To his surprise, the raft carried coveted textiles, ceramics, gold, silver, and emeralds, becoming the expedition's main focus. Almagro later joined with reinforcements, and despite challenging conditions, they reached Atacames, where a sizable native population under Inca rule was observed, though they did not land.
Pizarro, safe near the coast, sent Almagro and Luque for reinforcements with proof if the rumoured gold. The new governor rejected a third expedition, ordering everyone back to Panama. Almagro and Luque seized the chance to rejoin Pizarro. At Isla de Gallo, Pizarro drew a line, presenting the choice between Peru's riches and Panama's poverty. Thirteen men, The Famous Thirteen, stayed and headed to La Isla Gorgona, staying seven months until provisions arrived.
They sailed south and by April 1528, reached northwestern Peru's Tumbes Region, warmly received by the Tumpis. Pizarro's men reported incredible riches, llama sightings, and the natives named them "Children of the Sun" for their fair complexion and brilliant armour. They decided to return to Panama to prepare a final expedition, sailing south through named territories like Cabo Blanco, port of Payta, Sechura, Punta de Aguja, Santa Cruz, and Trujillo, reaching the ninth degree south.
In the spring of 1528, Pizarro sailed for Spain, where he had an interview with king Charles I. The king heard of his expeditions in lands rich in gold and silver and promised to support him. The Capitulación de Toledo[160] authorized Pizarro to proceed with the conquest of Peru. Pizarro was then able to convince many friends and relatives to join: his brothers Hernándo Pizarro, Juan Pizarro, Gonzalo Pizarro and also Francisco de Orellana, who would later explore the Amazon River, as well as his cousin Pedro Pizarro.
Pizarro's third and final expedition left Panama for Peru on 27 December 1530. With three ships and one hundred and eighty men, they landed near Ecuador and sailed to Tumbes, finding the place destroyed. They entered the interior and established the first Spanish settlement in Peru, San Miguel de Piura. One of the men returned with an Incan envoy and an invitation for a meeting. Since the last meeting, the Inca had begun a civil war and Atahualpa had been resting in northern Peru following the defeat of his brother Huáscar. After marching for two months, they approached Atahualpa. He refused the Spanish, saying he would be "no man's tributary". There were fewer than 200 Spanish to his 80,000 soldiers, but Pizarro attacked and won the Incan army in the Battle of Cajamarca, taking Atahualpa captive at the so-called ransom room. Despite fulfilling his promise of filling one room with gold and two with silver, he was convicted for killing his brother and plotting against Pizarro, and was executed.
In 1533, Pizarro invaded Cuzco with indigenous troops and wrote to King Charles I: "This city is the greatest and the finest ever seen in this country or anywhere in the Indies ... it is so beautiful and has such fine buildings that it would be remarkable even in Spain." After the Spanish had sealed the conquest of Peru, Jauja in fertile Mantaro Valley was established as Peru's provisional capital, but it was too far up in the mountains, and Pizarro founded the city of Lima on 18 January 1535, which Pizarro considered one of the most important acts in his life.
Major new trade routes (1542–1565)
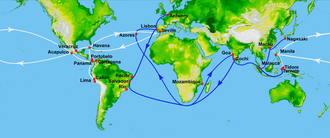
In 1543, three Portuguese traders accidentally became the first Westerners to reach and trade with Japan. According to Fernão Mendes Pinto, who claimed to be in this journey, they arrived at Tanegashima, where the locals were impressed by firearms that would be immediately made by the Japanese on a large scale.[161]
The Spanish conquest of the Philippines was ordered by Philip II of Spain, and Andrés de Urdaneta was the designated commander. Urdaneta agreed to accompany the expedition but refused to command and Miguel López de Legazpi was appointed instead. The expedition set sail on November 1564.[162] After spending some time on the islands, Legazpi sent Urdaneta back to find a better return route. Urdaneta set sail from San Miguel on the island of Cebu on 1 June 1565, but was obliged to sail as far as 38 degrees North latitude to obtain favorable winds.

He reasoned that the trade winds of the Pacific might move in a gyre as the Atlantic winds did. If in the Atlantic, ships made the Volta do mar to pick up winds that would bring them back from Madeira, then, he reasoned, by sailing far to the north before heading east, he would pick up trade winds to bring him back to North America. His hunch paid off, and he hit the coast near Cape Mendocino, California, then followed the coast south. The ship reached the port of Acapulco, on 8 October 1565, having traveled 12,000 miles (19,000 kilometres) in 130 days. Fourteen of his crew died; only Urdaneta and Felipe de Salcedo, nephew of López de Legazpi, had strength enough to cast the anchors.
Thus, a cross-Pacific Spanish route was established, between Mexico and the Philippines. For a long time, these routes were used by the Manila galleons, thereby creating a trade link joining China, the Americas, and Europe via the combined trans-Pacific and trans-Atlantic routes.
Northern European involvement (1595–17th century)

European nations outside Iberia did not recognize the Treaty of Tordesillas between Portugal and Castile, nor did they recognize Pope Alexander VI's donation of the Spanish finds in the New World. France, the Netherlands and England each had a long maritime tradition and had been engaging in privateering. Despite Iberian protections, the new technologies and maps soon made their way north.
After the marriage of Henry VIII of England and Catherine of Aragon failed to produce a male heir and Henry failed to obtain a papal dispensation to annul his marriage, he broke with the Roman Catholic Church and established himself as head of the Church of England. This added religious conflict to political conflict. When much of The Netherlands became Protestant, it sought political and religious independence from Catholic Spain. In 1568, the Dutch rebelled against the rule of Philip II of Spain leading to the Eighty Years' War. The war between England and Spain also broke out. In 1580, Philip II became King of Portugal, as heir to its Crown. Although he ruled Portugal and its empire as separate from the Spanish Empire, the union of the crowns produced a Catholic superpower, which England and the Netherlands challenged.
In the eighty-year Dutch War of Independence, Philip's troops conquered the important trading cities of Bruges and Ghent. Antwerp, then the most important port in the world, fell in 1585.[citation needed] The Protestant population was given two years to settle affairs before leaving the city.[163] Many settled in Amsterdam. Those were mainly skilled craftsmen, rich merchants of the port cities and refugees that fled religious persecution, particularly Sephardi Jews from Portugal and Spain and, later, the Huguenots from France. The Pilgrim Fathers also spent time there before going to the New World. This mass immigration was an important driving force: a small port in 1585, Amsterdam quickly transformed into one of the most important commercial centres in the world. After the failure of the Spanish Armada in 1588, there was a huge expansion of maritime trade even though the defeat of the English Armada would confirm the naval supremacy of the Spanish navy over the emergent competitors.
Dutch maritime power rose quickly as Dutch sailors, skilled in navigation and mapmaking, engaged with Portuguese voyages. In 1592, Cornelis de Houtman gathered information on the Spice Islands in Lisbon. The same year, Jan Huyghen van Linschoten published a detailed travel report in Amsterdam, providing navigation instructions for reaching the East Indies and Japan.[164] Following this, Houtman led the Dutch’s first exploratory voyage, discovering a new route from Madagascar to the Sunda Strait and securing a treaty with the Banten Sultan. The Dutch also demonstrated their maritime strength by seizing Malacca from Portugal in 1641, following a series of battles that began in 1602.
Dutch and British interest, fed on new information, led to a movement of commercial expansion, and the foundation of English (1600), and Dutch (1602) chartered companies. Dutch, French, and English sent ships which flouted the Portuguese monopoly, concentrated mostly on the coastal areas, which proved unable to defend against such a vast and dispersed venture.[165]
Exploring North America

The 1497 English expedition authorized by Henry VII of England was led by Italian Venetian John Cabot (Giovanni Caboto); it was the first of a series of French and English missions exploring North America. Mariners from the Italian peninsula played an important role in early explorations, most especially Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus. With its major conquests of central Mexico and Peru and discoveries of silver, Spain put limited efforts into exploring the northern part of the Americas; its resources were concentrated in Central and South America where more wealth had been found.[166] These other European expeditions were initially motivated by the same idea as Columbus, namely a westerly shortcut to the Asian mainland. After the existence of "another ocean" (the Pacific) was confirmed by Balboa in 1513, there still remained the motivation of potentially finding an oceanic Northwest Passage for Asian trade.[166] This was not discovered until the early twentieth century, but other possibilities were found, although nothing on the scale of the spectacular ones of the Spanish. In the early 17th century colonists from a number of Northern European states began to settle on the east coast of North America. Between 1520 and 1521, the Portuguese João Álvares Fagundes, accompanied by couples of mainland Portugal and the Azores, explored Newfoundland and Nova Scotia (possibly reaching the Bay of Fundy on the Minas Basin[167]), and established a fishing colony on the Cape Breton Island that would last until at least the 1570s or near the end of the century.[168]
In 1524, Italian Giovanni da Verrazzano sailed under the authority of Francis I of France, who was motivated by indignation over the division of the world between Portuguese and Spanish. Verrazzano explored the Atlantic Coast of North America, from South Carolina to Newfoundland, and was the first recorded European to visit what would later become the Virginia Colony and the United States. In the same year Estevão Gomes, a Portuguese cartographer who had sailed in Ferdinand Magellan's fleet, explored Nova Scotia, sailing South through Maine, where he entered what is now New York Harbor, the Hudson River and eventually reached Florida in August 1525. As a result of his expedition, the 1529 Diogo Ribeiro world map outlines the East coast of North America almost perfectly. From 1534 to 1536, French explorer Jacques Cartier, believed to have accompanied Verrazzano to Nova Scotia and Brazil, was the first European to travel inland in North America, describing the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, which he named "The Country of Canadas", after Iroquois names, claiming what is now Canada for Francis I of France.[169][170]

Europeans explored the Pacific Coast beginning in the mid-16th century. Spaniards Francisco de Ulloa explored the Pacific coast of present-day Mexico including the Gulf of California, proving that Baja California was a peninsula.[171] Despite his report based on first-hand information, the myth persisted in Europe that California was an island. His account provided the first recorded use of the name "California". João Rodrigues Cabrilho, a Portuguese navigator sailing for the Spanish Crown, was the first European to set foot in California, landing on September 28, 1542, on the shores of San Diego Bay and claiming California for Spain.[172] He also landed on San Miguel, one of the Channel Islands, and continued as far north as Point Reyes on the mainland. After his death, the crew continued exploring as far north as Oregon.
The English privateer Francis Drake sailed along the coast in 1579 north of Cabrillo's landing site while circumnavigating the world. Drake had a long and largely successful career attacking Spanish settlements in the Caribbean islands and the mainland so for the English, he was a great hero and fervent Protestant, but for the Spanish, he was "a frightening monster." Drake played a major role in the defeat of the Spanish Armada in 1588 but led an armada himself to the Spanish Caribbean that was unsuccessful in dislodging the Spanish.[173] On 5 June 1579, the ship briefly made first landfall at South Cove, Cape Arago, just south of Coos Bay, Oregon, and then sailed south while searching for a suitable harbor to repair his damaged ship.[174][175][176][177][178] On 17 June, Drake and his crew found a protected cove when they landed on the Pacific coast of what is now Northern California near Point Reyes.[179][177] While ashore, he claimed the area for Queen Elizabeth I of England as Nova Albion or New Albion.[180] To document and assert his claim, Drake posted an engraved plate of brass to claim sovereignty for Queen Elizabeth and her successors on the throne.[181] Drake's landfalls on the west coast of North America are one small part of his 1577-1580 circumnavigation of the globe, the first captain of his own ship to do so. Drake died in 1596 off the coast of Panama, following injuries from a raid.[182]
From 1609 to 1611, after several voyages on behalf of English merchants to explore a prospective Northeast Passage to India, English mariner Henry Hudson, under the auspices of the Dutch East India Company (VOC), explored the region around present-day New York City, while looking for a western route to Asia. He explored the Hudson River and laid the foundation for Dutch colonization of the region. Hudson's final expedition ranged farther north in search of the Northwest Passage, leading to his discovery of the Hudson Strait and Hudson Bay. After wintering in James Bay, Hudson tried to press on with his voyage in the spring of 1611, but his crew mutinied and they cast him adrift.
Search for a northern route

France, the Netherlands, and England sought a sea route to Asia after finding none through Africa or South America. With no route through the Americas, they focused on northern passages, driving European exploration of the Arctic coasts. The idea of a link between the Atlantic and Pacific was first proposed by Russian diplomat Gerasimov in 1525, though Russian Pomors had explored parts of the route as early as the 11th century.[citation needed]
In 1553, English explorer Hugh Willoughby with chief pilot Richard Chancellor were sent out with three vessels in search of a passage by London's Company of Merchant Adventurers to New Lands. During the voyage across the Barents Sea, Willoughby thought he saw islands to the north, and islands called Willoughby's Land were shown on maps published by Plancius and Mercator into the 1640s.[183] The vessels were separated by "terrible whirlwinds" in the Norwegian Sea and Willoughby sailed into a bay near the present border between Finland and Russia. His ships with the frozen crews, including Captain Willoughby and his journal, were found by Russian fishermen a year later. Richard Chancellor was able to drop anchor in the White Sea and make his way overland to Moscow and Ivan the Terrible's Court, opening trade with Russia and the Company of Merchant Adventurers became the Muscovy Company.
In June 1576, English mariner Martin Frobisher led an expedition consisting of three ships and 35 men to search for a north-west passage around North America. The voyage was supported by the Muscovy Company, the same merchants that hired Hugh Willoughby to find a northeast passage above Russia. Violent storms sank one ship and forced another to turn back but Frobisher and the remaining ship reached the coast of Labrador in July. A few days later they came upon the mouth of what is now Frobisher Bay. Frobisher believed it to be the entrance to a north-west passage and named it Frobisher's Strait and claimed Baffin Island for Queen Elizabeth. After some preliminary exploration, Frobisher returned to England. He commanded two subsequent voyages in 1577 and 1578 but failed to find the hoped-for passage.[184] Frobisher brought to England his ships laden with ore, but it was found to be worthless and damaged his reputation as an explorer. He remains an important early historical figure in Canada.[185]
Barentsz' Arctic exploration

On 5 June 1594, Dutch cartographer Willem Barentsz departed from Texel in a fleet of three ships to enter the Kara Sea, with the hopes of finding the Northeast Passage above Siberia.[186] At Williams Island the crew encountered a polar bear for the first time. They managed to bring it on board, but the bear rampaged and was killed. Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya and followed it northward, before being forced to turn back in the face of large icebergs.
The following year, Prince Maurice of Orange named him chief pilot of a new expedition of six ships, loaded with merchant wares that the Dutch hoped to trade with China.[187] The party came across Samoyed "wild men" but eventually turned back upon discovering the Kara Sea frozen. In 1596, the States-General offered a high reward for anybody who successfully navigated the Northeast Passage. The Town Council of Amsterdam purchased and outfitted two small ships, captained by Jan Rijp and Jacob van Heemskerk, to search for the elusive channel, under the command of Barents. They set off in May, and in June discovered Bear Island and Spitsbergen, sighting its northwest coast. They saw a large bay, later called Raudfjorden and entered Magdalenefjorden, which they named Tusk Bay, sailing into the northern entrance of Forlandsundet, which they called Keerwyck, but were forced to turn back because of a shoal. On 28 June they rounded the northern point of Prins Karls Forland, which they named Vogelhoek, on account of a large number of birds, and sailed south, passing Isfjorden and Bellsund, which were labelled on Barentsz's chart as Grooten Inwyck and Inwyck.

The ships once again reached Bear Island on 1 July, which led to a disagreement. They parted ways, with Barentsz continuing northeast, while Rijp headed north. Barentsz reached Novaya Zemlya and, to avoid becoming entrapped in ice, headed for the Vaigatch Strait but became stuck within the icebergs and floes. Stranded, the 16-man crew was forced to spend the winter on the ice. The crew used lumber from their ship to build a lodge they called Het Behouden Huys (The Kept House). Dealing with extreme cold, they used merchant fabrics to make additional blankets and clothing and caught Arctic foxes in primitive traps, as well as polar bears. When June arrived, and the ice had still not loosened its grip on the ship, scurvy-ridden survivors took two small boats out into the sea. Barentsz died at sea on 20 June 1597, while studying charts. It took seven more weeks for the boats to reach Kola where they were rescued by a Russian merchant vessel. Only 12 crewmen remained, reaching Amsterdam in November. Two of Barentsz' crewmembers later published their journals, Jan Huyghen van Linschoten, who had accompanied him on the first two voyages, and Gerrit de Veer who had acted as the ship's carpenter on the last.
In 1608, Henry Hudson made a second attempt, trying to go across the top of Russia. He made it to Novaya Zemlya but was forced to turn back. Between 1609 and 1611, Hudson, after several voyages on behalf of English merchants to explore a prospective Northern Sea Route to India, explored the region around modern New York City while looking for a western route to Asia under the auspices of the Dutch East India Company (VOC).
Dutch Australia and New Zealand

Terra Australis Ignota (Latin, "the unknown land of the south") was a hypothetical continent appearing on European maps from the 15th to the 18th centuries, with roots in a notion introduced by Aristotle. It was depicted on the mid-16th-century Dieppe maps, where its coastline appeared just south of the islands of the East Indies; it was often elaborately charted, with a wealth of fictitious detail. The discoveries reduced the area where the continent could be found. Many cartographers held to Aristotle's opinion, like Gerardus Mercator (1569) and Alexander Dalrymple even so late as 1767[188] argued for its existence, with such arguments as that there should be a large landmass in the Southern Hemisphere as a counterweight to the known landmasses in the Northern Hemisphere. As new lands were discovered, they were often assumed to be parts of this hypothetical continent.
Juan Fernández, sailing from Chile in 1576, claimed he had discovered the Southern Continent.[189] Luis Váez de Torres, a Galician navigator working for the Spanish Crown, proved the existence of a passage south of New Guinea, now known as Torres Strait. Pedro Fernandes de Queirós, a Portuguese navigator sailing for the Spanish Crown, saw a large island south of New Guinea in 1606, which he named La Australia del Espiritu Santo. He represented this to the King of Spain as the Terra Australis incognita. It was not Australia but an island in present-day Vanuatu.

Dutch navigator and colonial governor, Willem Janszoon sailed from the Netherlands for the East Indies for the third time on December 18, 1603, as captain of the Duyfken (or Duijfken, meaning "Little Dove"), one of twelve ships of the great fleet of Steven van der Hagen.[190] Once in the Indies, Janszoon was sent to search for other outlets of trade, particularly in "the great land of Nova Guinea and other East and Southlands." On November 18, 1605, the Duyfken sailed from Bantam to the coast of western New Guinea. Janszoon then crossed the eastern end of the Arafura Sea, without seeing the Torres Strait, into the Gulf of Carpentaria. On February 26, 1606, he made landfall at the Pennefather River on the western shore of Cape York in Queensland, near the modern town of Weipa. This is the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent. Janszoon proceeded to chart some 320 kilometres (199 miles) of the coastline, which he thought was a southerly extension of New Guinea. In 1615, Jacob Le Maire and Willem Schouten's rounding of Cape Horn proved that Tierra del Fuego was a relatively small island.
From 1642 to 1644, Abel Tasman, also a Dutch explorer and merchant in the service of the VOC, circumnavigated New Holland proving that Australia was not part of the mythical southern continent. He was the first known European expedition to reach the islands of Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania) and New Zealand and to sight the Fiji islands, which he did in 1643. Tasman, his navigator Visscher, and his merchant Gilsemans also mapped substantial portions of Australia, New Zealand, and the Pacific Islands.
Russian exploration of Siberia (1581–1660)

In the mid-16th century, the Tsardom of Russia conquered the Tatar khanates of Kazan and Astrakhan, thus annexing the entire Volga Region and opening the way to the Ural Mountains. The colonization of the new easternmost lands of Russia and further onslaught eastward was led by the rich merchants Stroganovs. Tsar Ivan IV granted vast estates near the Urals as well as tax privileges to Anikey Stroganov, who organized large-scale migration to these lands. Stroganovs developed farming, hunting, saltworks, fishing, and ore mining on the Urals and established trade with Siberian tribes.
Conquest of the Khanate of Sibir
Around 1577, Semyon Stroganov and other sons of Anikey Stroganov hired a Cossack leader called Yermak to protect their lands from the attacks of Khan Kuchum. By 1580, Stroganovs and Yermak came up with the idea of a military expedition to Siberia, to fight Kuchum in his own land. In 1581, Yermak began his voyage into the depths of Siberia. After a few victories over the Khan's army, Yermak's people defeated the main forces of Kuchum on Irtysh River in a 3-day Battle of Chuvash Cape in 1582. The remains of the Khan's army retreated to the steppes, and thus Yermak captured the Khanate of Sibir, including its capital Qashliq near modern Tobolsk. Kuchum still was strong and suddenly attacked Yermak in 1585 in the dead of night, killing most of his people. Yermak was wounded and tried to swim across the Wagay River (Irtysh's tributary), but drowned under the weight of his own chain mail. The Cossacks had to withdraw from Siberia completely, but thanks to Yermak's having explored all the main river routes in West Siberia, Russians successfully reclaimed all his conquests just several years later.

Siberian river routes
In the early 17th century, the eastward movement of Russians was slowed by the internal problems in the country during the Time of Troubles. Very soon, exploration and colonization of the huge territories of Siberia resumed, led mostly by Cossacks hunting for valuable furs and ivory. While Cossacks came from the Southern Urals, another wave of Russians came by the Arctic Ocean. These were Pomors from the Russian North, who already had been making fur trade with Mangazeya in the north of Western Siberia for quite a long time. In 1607, the settlement of Turukhansk was founded on the northern Yenisey River, near the mouth of Lower Tunguska. In 1619, Yeniseysk ostrog was founded on the mid-Yenisey at the mouth of the Upper Tunguska.
Between 1620 and 1624, a group of fur hunters led by Demid Pyanda left Turukhansk and explored some 1,430 miles (2,300 kilometres) of the Lower Tunguska, wintering in the proximity of the Vilyuy and Lena Rivers. According to later legendary accounts (folktales collected a century after the fact), Pyanda discovered the Lena. He allegedly explored some 1,500 miles (2,400 kilometres) of its length, reaching as far as central Yakutia. He returned up the Lena until it became too rocky and shallow, and portaged to the Angara River. In this way, Pyanda may have become the first Russian to meet Yakuts and Buryats. He built new boats and explored some 870 miles (1,400 kilometres) of the Angara, finally reaching Yeniseysk and discovering that the Angara (a Buryat name) and Upper Tunguska (Verkhnyaya Tunguska, as initially known by Russians) are one and the same river.
In 1627, Pyotr Beketov was appointed Yenisei voevoda in Siberia. He successfully carried out the voyage to collect taxes from the Zabaykalye Buryats, becoming the first Russian to step in Buryatia. He founded the first Russian settlement there, Rybinsky ostrog. Beketov was sent to the Lena River in 1631, where in 1632 he founded Yakutsk and sent his Cossacks to explore the Aldan River and farther down the Lena, to found new fortresses, and to collect taxes.[191]
Yakutsk soon turned into a major starting point for further Russian expeditions eastward, southward and northward. Maksim Perfilyev, who earlier had been one of the founders of Yeniseysk, founded Bratsk ostrog on the Angara in 1631. In 1638, Perfilyev became the first Russian to step into Transbaikalia, travelling there from Yakutsk.[192][193]

In 1643, Kurbat Ivanov led a group of Cossacks from Yakutsk to the south of the Baikal Mountains and discovered Lake Baikal, visiting its Olkhon Island. Ivanov later made the first chart and description of Baikal.[194]
Russians reach the Pacific
In 1639, a group of explorers led by Ivan Moskvitin became the first Russians to reach the Pacific Ocean and to discover the Sea of Okhotsk, having built a winter camp on its shore at the Ulya River mouth. The Cossacks learned from the locals about the large Amur River far to the south. In 1640, they apparently sailed south, and explored the south-eastern shores of the Okhotsk Sea, perhaps reaching the mouth of the Amur River and possibly discovering the Shantar Islands on their way back. Based on Moskvitin's account, Kurbat Ivanov drew the first Russian map of the Far East in 1642.
In 1643, Vasily Poyarkov crossed the Stanovoy Range and reached the upper Zeya River in the country of the Daurs, who were paying tribute to the Manchu Chinese. After wintering, in 1644, Poyarkov pushed down the Zeya and became the first Russian to reach the Amur River. He sailed down the Amur and finally discovered the mouth of that great river from land. Since his Cossacks provoked the enmity of the locals behind, Poyarkov chose a different way back. They built boats and in 1645, sailed along the Sea of Okhotsk coast to the Ulya River and spent the next winter in the huts that had been built by Ivan Moskvitin six years earlier. In 1646, they returned to Yakutsk.

In 1644, Mikhail Stadukhin discovered the Kolyma River and founded Srednekolymsk. A merchant named Fedot Alekseyev Popov organized a further expedition eastward, and Semyon Dezhnyov became a captain of one of the kochi. In 1648, they sailed from Srednekolymsk down to the Arctic and after some time they rounded Cape Dezhnyov, thus becoming the first explorers to pass through the Bering Strait and discover Chukotka and the Bering Sea. All their Kochi and most of their men (including Popov himself) were lost in storms and clashes with the natives. A small group led by Dezhnyov reached the mouth of the Anadyr River and sailed up it in 1649, having built new boats from the wreckage. They founded Anadyrsk and were stranded there until Stadukhin found them, coming from Kolyma by land.[195] Subsequently, Stadukhin set off south in 1651 and discovered Penzhin Bay on the northern coast of the Okhotsk Sea. He also may have explored the western shores of Kamchatka.
From 1649 to 1650, Yerofey Khabarov became the second Russian to explore the Amur River. Through Olyokma, Tungir and Shilka Rivers he reached Amur (Dauria), returned to Yakutsk and then back to Amur with a larger force in 1650–1653. This time he was met with armed resistance. He built winter quarters at Albazin, then sailed down Amur and found Achansk, which preceded the present-day Khabarovsk, defeating or evading large armies of Daurian Manchu Chinese and Koreans on his way. He charted the Amur in his Draft of the Amur river.[196] Subsequently, Russians held on to the Amur region until 1689, when by the Treaty of Nerchinsk this land was assigned to the Chinese Empire. It was returned by the Treaty of Aigun in 1858.
From 1659 to 1665, Kurbat Ivanov was the next head of Anadyrsky ostrog after Semyon Dezhnev. In 1660, he sailed from Anadyr Bay to Cape Dezhnyov. Atop his earlier pioneering charts, Ivanov is credited with the creation of the early map of Chukotka and the Bering Strait, which was the first to show on paper (very schematically) the yet undiscovered Wrangel Island, both Diomede Islands and Alaska, based on the data collected from the natives of Chukotka.
By the mid-17th century, Russians established the borders of their country close to modern ones, and explored almost the whole of Siberia, except the eastern Kamchatka and some regions north of the Arctic Circle. The conquest of Kamchatka later would be achieved in the early 1700s by Vladimir Atlasov, while the discovery of the Arctic coastline and Alaska would be completed by the Great Northern Expedition in 1733–1743.
Global impact

European overseas expansion led to contact between the Old and New Worlds producing the Columbian exchange.[197] It started the global silver trade and led to direct European involvement in the Chinese porcelain trade. It involved the transfer of goods unique from one hemisphere to another. Europeans brought cattle, horses, and sheep to the New World, and from the New World Europeans received tobacco, potatoes, tomatoes, and maize. Other items and commodities becoming important in global trade were the tobacco, sugarcane, and cotton crops of the Americas, along with the gold and silver brought from the American continent not only to Europe, but elsewhere in the Old World.[198][199][200][201]
The formation of new transoceanic links and expansion of European influence led to the Age of Imperialism, which began during the Age of Discovery, during which colonial powers from Europe colonized most territory on the planet. European demand for trade, commodities, colonies and slaves had a drastic impact on the rest of the world; during European colonization of the Americas, European colonial powers conquered and colonized numerous indigenous nations and cultures, and conducted numerous conversions and attempts at cultural assimilation both voluntary or forced. Combined with the introduction of infectious diseases from Europe, these events led to a drastic decrease of the indigenous American population. Indigenous accounts of European colonization were summarized by scholar Peter Mancall: "The arrival of Europeans brought death, displacement, sorrow, and despair to Native Americans".[202] In some areas, like North America, Central America, Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina, indigenous peoples were badly treated, driven off their lands, and reduced to dependent minorities in the territory.

Similarly, in East and West Africa, local states supplied the appetite of European slave traders, changing the complexion of coastal African states and fundamentally altering the nature of slavery in Africa, causing impacts on societies and economies deep inland.[200]
In North America, there were many conflicts between Europeans and indigenous peoples. The Europeans had many advantages over the indigenous people. Introduced Eurasian diseases wiped out 50–90% of the indigenous population because they had not been exposed before and lacked acquired immunity.[203]
Maize and manioc were introduced into Africa in the 16th century by the Portuguese.[204] They are now important staple foods, replacing native African crops.[205][206] Alfred W. Crosby speculated that increased production of maize, manioc, and other New World crops led to heavier concentrations of population in the areas from which slavers captured their victims.[207]
In the global silver trade, the Ming dynasty was stimulated by trade with the Portuguese, Spanish, and Dutch. Although global, much of that silver ended up with the Chinese, and China dominated silver imports.[208] Between 1600 and 1800 China received 100 tons of silver on average per year. A large populace near the Lower Yangtze averaged hundreds of taels of silver per household in the late 16th century.[209] More than 150,000 tons of silver were shipped from Potosí by the end of the 18th century. From 1500 to 1800, Mexico and Peru produced about 80%[210] of the world's silver, with more than 30% of it eventually ending up in China (largely because European merchants used it to purchase exotic Chinese commodities). In the late 16th and early 17th century, Japan was exporting heavily into China and foreign trade at large.[210] Trade with European powers and the Japanese brought in significant amounts of silver, which then replaced copper and paper banknotes as the common medium of exchange in China. During the last decades of the Ming Dynasty, the flow of silver into China was greatly diminished, thereby undermining state revenues and the entire Ming economy. This damage to the economy was compounded by the effects on agriculture of the incipient Little Ice Age, natural calamities, crop failure, and sudden epidemics. The ensuing breakdown of authority and people's livelihoods allowed rebel leaders such as Li Zicheng to challenge Ming authority.

New crops that had come to Asia from the Americas, via the Spanish colonizers in the 16th century, contributed to Asia's population growth.[211] Although the bulk of imports to China were silver, the Chinese also purchased New World crops from the Spanish Empire. This included sweet potatoes, maize, and peanuts, foods that could be cultivated in lands where traditional Chinese staple crops—wheat, millet, and rice—could not grow, hence facilitating a rise in the population of China.[212][213] In the Song dynasty (960–1279), rice had become the major staple crop of the poor;[214] after sweet potatoes were introduced to China around 1560, it gradually became the traditional food of the lower classes.[215]
The arrival of the Portuguese to Japan in 1543 initiated the Nanban trade period, with the Japanese adopting technologies and cultural practices, like the arquebus, European-style cuirasses, European ships, Christianity, decorative art, and language. After the Chinese had banned direct trade by Chinese merchants with Japan, the Portuguese filled this commercial vacuum as intermediaries. The Portuguese bought Chinese silk and sold it to the Japanese in return for Japanese-mined silver; since silver was more highly valued in China, the Portuguese could then use Japanese silver to buy even larger stocks of Chinese silk.[216] By 1573, after the Spanish established a trading base in Manila, the Portuguese intermediary trade was trumped by the prime source of incoming silver to China from the Spanish Americas.[217] Although China acted as the cog running the wheel of global trade during the 16th to 18th centuries, Japan's huge contribution of silver exports to China was critical to the world economy and China's liquidity and success with the commodity.[218]
Economic impact in Europe
| Renaissance |
|---|
 |
| Aspects |
| Regions |
| History and study |
As a wider variety of global luxury commodities entered the European markets by sea, previous European markets for luxury goods stagnated. The Atlantic trade largely supplanted pre-existing Italian and German trading powers which had relied on their Baltic, Russian, and Islamic trade links. The new commodities also caused social change, as sugar, spices, silks and chinawares entered the luxury markets of Europe.
The European economic centre shifted from the Mediterranean to Western Europe. The city of Antwerp, part of the Duchy of Brabant, became "the centre of the entire international economy",[219] and the richest city in Europe.[220] Centred in Antwerp first and then Amsterdam, the "Dutch Golden Age" was tightly linked to the Age of Discovery.
By 1549 the Portuguese were sending annual trade missions to Shangchuan Island in China. In 1557 they managed to convince the Ming court to agree on a legal port treaty that would establish Macau as an official Portuguese trade colony.[221] The Portuguese friar Gaspar da Cruz (c. 1520–70) wrote the first complete book on China published in Europe; it included information on its geography, provinces, royalty, official class, bureaucracy, shipping, architecture, farming, craftsmanship, merchant affairs, clothing, religious and social customs, music and instruments, writing, education, and justice.[222]

From China, the major exports were silk and porcelain, adapted to meet European tastes. The Chinese export porcelains were held in such great esteem in Europe that, in English, china became a commonly-used synonym for porcelain. Kraak porcelain was among the first Chinese ware to arrive in Europe in significant quantities; only the richest could afford these early imports.[223] Soon the Dutch East India Company established trade with the East, having imported 6 million porcelain items from China to Europe between the years 1602–82.[224][225] Kraak, mainly the blue and white porcelain, was imitated all over the world by potters in Arita, Japan and Persia—where Dutch merchants turned when the fall of the Ming dynasty rendered Chinese originals unavailable[226]—and ultimately in Delftware. Dutch and later English Delftware inspired by Chinese designs persisted from about 1630 to the mid-18th century alongside European patterns.
Antonio de Morga (1559–1636), a Spanish official in Manila, listed an extensive inventory of goods that were traded by Ming China at the turn of the 16th to 17th century, noting there were "rarities which, did I refer to them all, I would never finish, nor have sufficient paper for it".[227] Ebrey writes of the considerable size of commercial transactions: In one case a galleon to the Spanish territories in the New World carried over 50,000 pairs of silk stockings. In return China imported mostly silver from Peruvian and Mexican mines, transported via Manila. Chinese merchants were active in these trading ventures, and many emigrated to such places as the Philippines and Borneo to take advantage of the new commercial opportunities.[212]
The increase in gold and silver experienced by Spain coincided with a major inflationary cycle within Spain and Europe, known as the price revolution. Spain had amassed large quantities of gold and silver from the New World.[228] In the 1540s large scale extraction of silver from Mexico began. During the 16th century, Spain held the equivalent of US$1.5 trillion (1990 terms) in gold and silver from New Spain. Being the most powerful European monarch at a time full of war and religious conflicts, the Habsburg rulers spent their wealth in wars and arts across Europe. "I learnt a proverb here", said a French traveller in 1603: "Everything is dear in Spain except silver".[229] The spent silver, spread throughout a cash-starved Europe, caused widespread inflation.[230] The inflation was worsened by a growing population with a static production level, low salaries and a rising cost of living, which damaged local industry. Increasingly, Spain became dependent on the revenues flowing in from the mercantile empire, leading to Spain's first bankruptcy in 1557 due to rising military costs.[231] Philip II of Spain defaulted on debt payments in 1557, 1560, 1575, and 1596. The increase in prices as a result of currency circulation fuelled the growth of the commercial middle class in Europe, the bourgeoisie, which came to influence the politics and culture of many countries. One effect of the inflation, particularly in Great Britain, was that tenant farmers who held long-term leases from lords saw real decreases in rent. Some lords opted to sell their leased land, giving rise to small, landowning farmers such as yeoman and gentlemen farmers.[232]
See also
- Catholic Church and the Age of Discovery
- Exploration of North America
- European maritime exploration of Australia
- Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration
- History of navigation
- L'Anse aux Meadows
- List of explorations
- Maritime history
- Portuguese inventions
- Pre-Columbian transoceanic contact theories
- Scramble for Africa
- Timeline of European exploration
- Timeline of maritime migration and exploration
- Winds in the Age of Sail
Footnotes
- ^ Major ports in their respective regions included Palembang on the Malaccan Strait, Calicut on the Malabar coast, and Mombasa on the Swahili Coast (see Sen 2016).
- ^ Windward sailing ability, true for historic vessels as much as any other, is a combination of rig and hull shape. Other considerations are the amount of marine fouling on the hull, and a sternpost-mounted rudder gives a clear advantage over a steering oar, partly by producing less drag but also having the hydrodynamic effect of slightly reducing leeway.[90]
References
- ^ https://moonworldhistory.weebly.com/the-age-of-exploration.html
- ^ Butel, Paul (2002-03-11). The Atlantic. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-203-01044-0. Archived from the original on 2021-04-21. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ^ Kleinhenz, Christopher (2004). Medieval Italy: An Encyclopedia. Vol. 1. Routledge. p. 407.
- ^ "Portuguese, The – Banglapedia". en.banglapedia.org. Archived from the original on 1 April 2017.
- ^ Raychaudhuri, Tapan (1982). The Cambridge Economic History of India: Volume 1, C.1200-c.1750. CUP Archive. ISBN 978-0-521-22692-9. Archived from the original on 2014-07-04. Retrieved 2022-05-19.
- ^ Arnold, David (2006). The Age of Discovery, 1400-1600, (London: Routledge), p XI, https://books.google.com/books?id=SbIEAQAAQBAJ&q=The+Age+of+Discovery,+1400-1600
- ^ Washburn, Wilcomb E. (1962). "The Meaning of "Discovery" in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries". The American Historical Review. 68 (1). JSTOR: 1–21. doi:10.2307/1847180. ISSN 0002-8762. JSTOR 1847180.
- ^ Parry, J. H. (1973). The Age of Reconnaissance: Discovery, Exploration, and Settlement, 1450–1650. London: Cardinal. p. 13.
- ^ Pagden 1993, p. 5.
- ^ O'Gorman, Edmundo. The Invention of America. An Inquiry into the Historical Nature of the New World and the Meaning of History. Bloomington, IN 1961, 9–47.
- ^ Pagden 1993, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Pagden 1993, p. 6.
- ^ "Dismantling the Doctrine of Discovery" (PDF). Assembly of First Nations. 2018-01-22. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-09-04. Retrieved 2021-06-19.
- ^ Frichner, Tonya Gonnella. (2010). "Preliminary Study of the Impact on Indigenous Peoples of the International Legal Construct Known as the Doctrine of Discovery." Archived 2021-07-24 at the Wayback Machine E/C.19/2010/13. Presented at the Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues, Ninth Session, United Nations Economic and Social Council, New York, 27 Apr 2010.
- ^ Roy, Rohan Deb; Conversation, The (2018-04-09). "Science Still Bears the Fingerprints of Colonialism". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on 2021-08-03. Retrieved 2021-08-15.
- ^ Renstrom, Joelle (2021-03-18). "The Troubling Rhetoric of Space Exploration". Undark Magazine. Archived from the original on 2021-08-12. Retrieved 2021-08-15.
- ^ DNLee (26 March 2015). "When discussing Humanity's next move to space, the language we use matters". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 14 September 2019. Retrieved 20 September 2019.
- ^ Drake, Nadia (2018-11-09). "We need to change the way we talk about space exploration". National Geographic. Archived from the original on 2019-10-16. Retrieved 2019-10-19.
- ^ Marshall, Alan (February 1995). "Development and imperialism in space". Space Policy. 11 (1): 41–52. Bibcode:1995SpPol..11...41M. doi:10.1016/0265-9646(95)93233-B. Archived from the original on 2022-01-21. Retrieved 2020-06-28.
- ^ Whitehurst, Katie. "Age of Contact". PBS. Archived from the original on 15 August 2021. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ Nassaney, Michael Shakir (2014). "North America During the European Contact Period". In Smith, Claire (ed.). Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology. New York, NY: Springer. pp. 5350–5371. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-0465-2_1641. ISBN 978-1-4419-0426-3. Archived from the original on 10 September 2022. Retrieved 9 January 2021.
- ^ Silliman, Stephen W. (2005). "Culture Contact or Colonialism? Challenges in the Archaeology of Native North America". American Antiquity. 70 (1). Cambridge University Press (CUP): 55–74. doi:10.2307/40035268. ISSN 0002-7316. JSTOR 40035268. S2CID 161467685.
- ^ Wilson, Samuel (1999). The emperor's giraffe and other stories of cultures in contact. Boulder, Colo: Westview Press. ISBN 0-8133-3585-X. OCLC 40567393.
- ^ "Bartolomeu Dias". infoplease. Sandbox Networks, Inc. Archived from the original on 21 May 2015. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "BBC – History – Leif Erikson". www.bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2012-01-20. Retrieved 2020-10-06.
- ^ Fernández-Armesto, Felipe (2007). Amerigo: The Man Who Gave His Name to America. New York: Random House. p. 73. ISBN 978-1-4000-6281-2. Archived from the original on 2022-04-18. Retrieved 2020-10-06.
- ^ Davidson, M. H. (1997). Columbus Then and Now: A Life Re-examined. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, p. 417.
- ^ "Columbus to the Caribbean". fsmitha.com. Archived from the original on 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2016-01-31.
- ^ "Christopher Columbus – Exploration". history.com. Archived from the original on 2022-06-24. Retrieved 2016-01-31.
- ^ Diffie, Bailey W., and George D. Winius, "Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415–1580", p. 176
- ^ Zweig, Stefan, "Conqueror of the Seas – The Story of Magellan", Read Books, 2007, ISBN 1-4067-6006-4
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Paine, Lincoln (2013). The Sea and Civilization: A Maritime History of the World. New York: Random House, LLC.
- ^ Merson, John (1990). The Genius That Was China: East and West in the Making of the Modern World. Woodstock, NY: The Overlook Press. ISBN 978-0-87951-397-9. A companion to the PBS Series The Genius That Was China.
- ^ Arnold 2002, p. xi.
- ^ Houben, 2002, pp. 102–04.
- ^ Harley & Woodward, 1992, pp. 156–61.
- ^ Abu-Lughod 1991, p. 121.
- ^ Arnold 2002, p. 5.
- ^ Love 2006, p. 130.
- ^ silk-road 2008, web.
- ^ a b DeLamar 1992, p. 328.
- ^ Abu-Lughod 1991, p. 158.
- ^ Crowley, Roger (2011). City of Fortune (Main ed.). Faber & Faber. ISBN 978-0-571-24595-6.
- ^ Voegelin, Eric (1940). "The Mongol Orders of Submission to European Powers, 1245–1255". Byzantion. 15: 378–413. JSTOR 44168533.
- ^ Grousset, Empire, pp. 280–281.
- ^ Mancall 2006, p. 14.
- ^ Mancall 2006, p. 3.
- ^ Stark, Rodney (2005). The Victory of Reason: How Christianity Led to Freedom, Capitalism and Western Success. New York: Random House Trade Paperbacks. p. 137. ISBN 978-0-8129-7233-7.
- ^ Parry 2006, p. 69.[full citation needed]
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 24–25.
- ^ Dunn 2004, p. 310.
- ^ Chen, Yuan Julian (2021-10-11). "Between the Islamic and Chinese Universal Empires: The Ottoman Empire, Ming Dynasty, and Global Age of Explorations". Journal of Early Modern History. 25 (5): 422–456. doi:10.1163/15700658-bja10030. ISSN 1385-3783. S2CID 244587800. Archived from the original on 2022-04-17. Retrieved 2022-03-24.
- ^ Mancall 1999, p. 36.
- ^ DeLamar 1992, p. 329.
- ^ . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 344–345.
- ^ Viault, Birdsall (1991). Modern European History (II. Series ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 82–83. ISBN 0-07-067453-1.
- ^ Ricard, Robert (1966). An Essay on the Apostolate and the Evangelizing Methods of the Mendicant Orders in New Spain: 1523–1572, translated from French by Lesley Bird Simpson. University of California Press.
- ^ Campbell, Thomas J. The Jesuits, 1534–1921: A History of the Society of Jesus from Its Foundation to the Present Time. New York: The Encyclopedia Press. ISBN 978-0-87821-018-3. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ Arnold 2002, p. 7.
- ^ Tamura 1997, p. 70.
- ^ Cromer 1995, p. 117.
- ^ Tsai 2002, p. 206.
- ^ Mancall 2006, p. 115.
- ^ a b c d Sen (2016), 609–611 & 631–633.
- ^ Sen (2016), 609.
- ^ Sen (2016), 615.
- ^ Sen (2016), 620–621.
- ^ Sen (2016), 624–626.
- ^ Chen (2019), 41–42.
- ^ Sen (2016), 631–633.
- ^ Sen (2016), 611.
- ^ Mancall 2006, p. 17.
- ^ Spice importance for medieval humorism principles of medicine was such that shortly after entering the trade, apothecaries and physicians like Tomé Pires and Garcia da Orta (see Burns 2001, p. 14) were sent to India having studied spices in works like Suma Oriental (see Pires 1512, p. lxii) and Colóquios dos simples e drogas da India ("Conversations on the simples, drugs and materia medica of India)
- ^ ScienceDaily 1998, news.
- ^ Spufford 1989, pp. 339–49.
- ^ Spufford 1989, p. 343.
- ^ Abu-Lughod 1991, p. 122.
- ^ Parry 1981, p. 33.
- ^ a b Corbett, P. Scott; Janssen, Volker; Lund, John M.; Pfannestiel, Todd; Waskiewicz, Sylvie; Vickery, Paul (2024-01-11). "1.2 Europe on the Brink of Change". OpenStax. Retrieved 2024-04-22.
- ^ Diffie 1977, p. 210.
- ^ Newitt 2005, p. 9.
- ^ Diffie 1960, p. 49.
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 29–31.
- ^ Butel 1999, p. 36.
- ^ Chaudhuri, K.N. (1985). Trade and Civilization in the Indian Ocean: An Economic History from the Rise of Islam to 1750. Cambridge University Press. p. 64.
- ^ DeLamar 1992, p. 333.
- ^ Anderson 2000, p. 50.
- ^ Joaquinn Pedro Oliveira Martins, The Golden Age Of Prince Henry The Navigator. (New York: Dutton), p. 72.
- ^ Locke 1824, p. 385.
- ^ Palmer, Colin (September 2009). "Windward Sailing Capabilities of Ancient Vessels". International Journal of Nautical Archaeology. 38 (2): 314–330. Bibcode:2009IJNAr..38..314P. doi:10.1111/j.1095-9270.2008.00208.x. S2CID 111332443.
- ^ Elbl, Martin (1994). "The Caravel and the Galleon". In Gardiner, Robert; Unger, Richard W (eds.). Cogs, Caravels and Galleons: the sailing ship, 1000–1650. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-560-8.
- ^ Nissan Mindel, Rabbi Abraham Zacuto – (1450–1515), http://www.chabad.org/library/article_cdo/aid/111917/jewish/Rabbi-Abraham-Zacuto.htm Archived 2021-11-07 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Parry 1981, p. 145.
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 132–34.
- ^ Russell-Wood 1998, p. 9.
- ^ Daus 1983, p. 33.
- ^ Bagrow 1964, p. 72.
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 145–48.
- ^ DeLamar 1992, p. 335.
- ^ Anderson 2000, p. 59.
- ^ Lusa. "Portugueses chegaram à América 19 anos antes de Colombo". Expresso. Archived from the original on 2018-12-15. Retrieved 2018-07-29.
- ^ DeLamar 1992, p. 341.
- ^ Maclean 2008, web.
- ^ Forbes 1993, p. 22
- ^ Mancall 1999, p. 26.
- ^ DeLamar 1992, p. 345.
- ^ Davenport 1917, pp. 107–11.
- ^ Croxton 2007, web (on subscription)
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 463–64.
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 464–65.
- ^ Diffie 1977, p. 185.
- ^ Pohl, Frederick J. (1966). Amerigo Vespucci: Pilot Major. New York: Octagon Books. pp. 54–55.
- ^ [1] Archived 2021-11-08 at the Wayback Machine Arciniegas, German (1978) Amerigo and the New World: The Life & Times of Amerigo Vespucci: Octagon Press
- ^ Morison, Samuel (1974). The European Discovery of America: The Southern Voyages, 1492–1616. New York: Oxford University Press.
- ^ N. McAlister, Lyle. (1984) Spain and Portugal in the New World: 1492–1700. p. 75.
- ^ Crow 1992, p. 136.
- ^ Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415–1580 Archived 2016-02-08 at the Wayback Machine, Bailey Wallys Diffie and George D. Winius. The University of Minnesota Press, 1977 p. 187
- ^ The Coming of the Portuguese Archived 2014-10-31 at the Wayback Machine by Paul Lunde, London University's School of Oriental and African Studies, in Saudi Aramco World – July/August 2005 Volume 56, Number 4,
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 456–62.
- ^ Arciniegas 1978, pp. 295–300.
- ^ Diffie 1977, p. 458.
- ^ The Invention of America Archived 2018-12-15 at the Wayback Machine. Indiana University Press. pp. 106–07, by Edmundo O'Gorman
- ^ Imago Mvndi – Brill Archive – Leiden, Editorial Board Archived 2020-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. Leo Bagrow, Stockholm – New light on Vespucci's third voyage, By R. Levillier pp. 40–45
- ^ Bethell, Leslie (1984). The Cambridge History of Latin America, Volume 1, Colonial Latin America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 257. ISBN 978-0-521-23223-4. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2020-05-03.
- ^ Laguarda Trias, Rolando A. (1988). Pilotos portugueses en el Rio de La Plata durante el siglo XVI. Coimbra: UC Biblioteca Geral 1. pp. 59–61. Archived from the original on 2020-12-11. Retrieved 2020-11-08.
- ^ "Newen Zeytung auss Presillg Landt" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-06-02. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ^ Peabiru, the route lost Archived 2022-04-22 at the Wayback Machine in English
- ^ Morison 1942, pp. 65–75.
- ^ a b Abu-Lughod 1991, 252
- ^ Bernstein, William J. (2008). A Splendid Exchange: How Trade Shaped the World. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-4416-4.
- ^ "The Lusiads". the Guardian. 2001-05-21. Archived from the original on 2022-08-24. Retrieved 2022-08-24.
- ^ Magazine, Smithsonian; Fiegl, Amanda. "Adventures of a Portuguese Poet". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on 2022-08-24. Retrieved 2022-08-24.
- ^ Milton 1999, pp. 5–7.
- ^ Cortesão, Armando (1944). The Suma Oriental of Tomé Pires: an account of the east, from the Red Sea to Japan, written in Malacca and India in 1512–1515/The Book of Francisco Rodrigues rutter of a voyage in the Red Sea, nautical rules, almanack and maps, written and drawn in the east before 1515. The Hakluyt Society. ISBN 978-81-206-0535-0. Archived from the original on 2021-11-14. Retrieved 2016-02-10.
- ^ Pfoundes 1882, p. 89.
- ^ Nowell 1947, p. 8.
- ^ Cole 2002, p. 37.
- ^ Otfinoski 2004, p. 33
- ^ Zweig 1938, p. 51.
- ^ Donkin 2003, p. 29.
- ^ DeLamar 1992, p. 349.
- ^ Catholic Encyclopædia 2007, web.
- ^ Fernandez-Armesto 2006, p. 200.
- ^ "Magellan Killed in Philippine Skirmish". National Geographic Society. 2020-04-06. Archived from the original on 2022-05-24. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c Newitt 2005, p. 104.
- ^ Lach 1998, p. 1397
- ^ Lach 1998, p. 1397.
- ^ Diffie 1977, p. 375.
- ^ Diffie 1977, pp. 368, 473.
- ^ Galvano 1563, p. 168
- ^ Fernandez-Armesto 2006, p. 202.
- ^ U.C. 2009, web
- ^ Adetunji, Jo (February 19, 2019). "How smallpox devastated the Aztecs – and helped Spain conquer an American civilization 500 years ago". The Conversation. Retrieved April 16, 2024.
- ^ Lawson 2007, pp. 84–88.
- ^ Lawson 2007, pp. 29–32.
- ^ Weddle 1985, p. 42.
- ^ a b c d e f Grunberg 2007, magazine
- ^ Restall 2004, pp. 659–87.
- ^ Castillo 1963, p. 294.
- ^ Cervantes web, original text.
- ^ Pacey 1991, p. 88
- ^ N. McAlister, Lyle. (1984) Spain and Portugal in the New World: 1492–1700. p. 316.
- ^ Boxer 1977, p. 18.
- ^ Linschoten 1598, original book
- ^ Boxer 1969, p 109.
- ^ a b Paine 2000, p. xvi.
- ^ Mount Allison University, Marshlands: Records of Life on the Tantramar: European Contact and Mapping Archived 2021-04-19 at the Wayback Machine, 2004
- ^ Tratado das ilhas novas e descombrimento dellas e outras couzas, 1570 Francisco de Souza, p. 6 [2] Archived 2020-01-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Cartier E.B. 2009, web.
- ^ Histori.ca 2009, web.
- ^ Gutierrez 1998. pp. 81–82.
- ^ San Diego HS, web.
- ^ Pattridge, Blake D. "Francis Drake" in Encyclopedia of Latin American History and Culture, vol. 2, 402
- ^ Von der Porten, Edward (January 1975). "Drake's First Landfall". Pacific Discovery, California Academy of Sciences. 28 (1): 28–30.
- ^ Morison, Samuel Eliot (1978). The Great Explorere: The European Discovery of America. New York: Oxford University Press, Inc. p. 700. ISBN 978-0-19-504222-1.
- ^ Cassels, Sir Simon (August 2003). "Where Did Drake Careen The Golden Hind in June/July 1579? A Mariner's Assessment". The Mariner's Mirror. 89 (1): 263. doi:10.1080/00253359.2003.10659292. S2CID 161710358.
- ^ a b Gough, Barry (1980). Distant Dominion: Britain and the Northwest Coast of North America, 1579-1809. Vancouver: U Univ. of British Columbia Press. p. 15. ISBN 0-7748-0113-1.
- ^ Turner, Michael (2006). In Drake's Wake Volume 2 The World Voyage. United Kingdom: Paul Mould Publishing. p. 163. ISBN 978-1-904959-28-1.
- ^ Cassels, Sir Simon (August 2003). "Where Did Drake Careen The Golden Hind in June/July 1579? A Mariner's Assessment". The Mariner's Mirror. 89 (1): 263,264. doi:10.1080/00253359.2003.10659292. S2CID 161710358.
- ^ Sugden, John (2006). Sir Francis Drake. London: Pimlico. p. 136,137. ISBN 978-1-844-13762-6.
- ^ Turner, Michael (2006). In Drake's Wake Volume 2 The World Voyage. United Kingdom: Paul Mould Publishing. p. 173. ISBN 978-1-904959-28-1.
- ^ Pattridge, "Francis Drake", 406
- ^ Hacquebord 1995,
- ^ McDermott, James (28 May 2015). "Frobisher, Sir Martin". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/10191. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ^ [3] Archived 2022-05-22 at the Wayback Machine "Martin Frobisher", The Canadian Encyclopedia accessed 16 July 2021
- ^ Synge 1912, p. 258
- ^ ULT 2009, web
- ^ Wilford 1982, p. 139.
- ^ Medina 1918, pp. 136–246.
- ^ Mutch 1942, p. 17.
- ^ Lincoln 1994, p. 62
- ^ The Perfilyevs, web (in Russian)
- ^ Sbaikal, web (in Russian)
- ^ Lincoln 1994, p. 247
- ^ Fisher 1981, p. 30
- ^ Dymytryshyn 1985, web
- ^ McNeill 2019, web.
- ^ Hahn, Barbara (31 July 2019) [27 August 2018]. "Tobacco – Atlantic History". oxfordbibliographies.com. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/obo/9780199730414-0141. Archived from the original on 28 October 2020. Retrieved 4 September 2021.
- ^ Escudero, Antonio Gutiérrez (2014). "Hispaniola's Turn to Tobacco: Products from Santo Domingo in Atlantic Commerce". In Aram, Bethany; Yun-Casalilla, Bartolomé (eds.). Global Goods and the Spanish Empire, 1492–1824: Circulation, Resistance, and Diversity. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 216–229. doi:10.1057/9781137324054_12. ISBN 978-1-137-32405-4.
- ^ a b Knight, Frederick C. (2020). "3 Cultivating Knowledge: African Tobacco and Cotton Workers in Colonial British America". Working the Diaspora: The Impact of African Labor on the Anglo-American World, 1650–1850. New York and London: New York University Press. pp. 65–85. doi:10.18574/nyu/9780814748183.003.0004. ISBN 978-0-8147-4818-3. LCCN 2009026860. Archived from the original on 2021-09-04. Retrieved 2021-09-04.
- ^ Nater, Laura (2006). "Colonial Tobacco: Key Commodity of the Spanish Empire, 1500–1800". In Topik, Steven; Marichal, Carlos; Frank, Zephyr (eds.). From Silver to Cocaine: Latin American Commodity Chains and the Building of the World Economy, 1500–2000. Durham, North Carolina: Duke University Press. pp. 93–117. doi:10.1215/9780822388029-005. ISBN 978-0-8223-3753-9. Archived from the original on 2021-09-04. Retrieved 2021-09-04.
- ^ Mancall, Peter C. (1998). "The Age of Discovery". Reviews in American History. 26 (1): 35. doi:10.1353/rah.1998.0013. ISSN 0048-7511. JSTOR 30030873. S2CID 143822053.
Other documents from the sixteenth century, such as the magnificent Florentine Codex, contain testimony from native observers whose views were recorded by European witnesses to the conquest. These texts provide details about indigenous practices as well as views of the conquest from the perspective of the invaded. Some of these indigenous sources have been translated into English. On the issue of the encounter, these sources concur: the arrival of Europeans brought death, displacement, sorrow, and despair to Native Americans.
- ^ Cook 1998, p. 13
- ^ OSU 2006, news.
- ^ "The cassava transformation in Africa Archived 2014-06-09 at the Wayback Machine". The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO).
- ^ Scitizen 2007, web.
- ^ Crosby 1972, p. 188.
- ^ von Glahn, Richard (1996). "Myth and Reality of China's Seventeenth Century Monetary Crisis". Journal of Economic History. 2: 132.
... silver wanders throughout all the world... before flocking to China, where it remains as if at its natural center.
- ^ Huang, Ray (1975), "Financial management", Taxation and Governmental Finance in Sixteenth-Century Ming China, Cambridge University Press, pp. 266–305, doi:10.1017/cbo9780511735400.011, ISBN 978-0-511-73540-0
- ^ a b Flynn, Dennis O. (1995). "Born with a "Silver Spoon": The Origin of World Trade in 1571" (PDF). Journal of World History. University of Hawaii Press. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-04-23.
- ^ Columbia University 2009, web.
- ^ a b Ebrey 2006, p. 211.
- ^ Crosby 1972, pp. 198–201
- ^ Gernet 1962, p. 136.
- ^ Crosby 1972, p. 200.
- ^ Spence 1999, pp. 19–20.
- ^ Brook 1998, p. 205.
- ^ Flynn, Dennis Owen; Giraldez, Arturo (2002). "Cycles of Silver: Global Economic Unity through the Mid-Eighteenth Century". Journal of World History. 13 (2): 391–427. doi:10.1353/jwh.2002.0035. ISSN 1527-8050. S2CID 145805906.
- ^ Braudel 1985, p. 143.
- ^ Dunton 1896, p. 163.
- ^ Brook 1998, p. 124.
- ^ Aas 1976, pp. 410–11.
- ^ For a study on foreign objects in Dutch paintings, see Hochstrasser 2007, Still life and trade in the Dutch golden age.
- ^ Volker 1971, p. 22.
- ^ Brook 1998, p. 206.
- ^ Howard 1978, p. 7.
- ^ Brook 1998, pp. 205–206.
- ^ Walton 1994, pp. 43–44
- ^ Braudel 1979, p. 171.
- ^ Tracy 1994, p. 655.
- ^ Braudel 1979, pp. 523–25
- ^ Overton, Mark (1996). Agricultural Revolution in England: The transformation of the agrarian economy 1500–1850. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-56859-3.
Bibliography
Primary sources
- Castillo, Bernal Díaz del, John Michael Cohen (1963) [1632]. The conquest of New Spain. Penguin Classics. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-14-044123-9. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Galvano, Antonio (2004-03-01) [1563]. The Discoveries of the World from Their First Original Unto the Year of Our Lord 1555, issued by the Hakluyt Society. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7661-9022-1. Retrieved 2011-06-16.[permanent dead link]
- Linschoten, Jan Huyghen van (2004) [1598]. Voyage to Goa and Back, 1583–1592, with His Account of the East Indies: From Linschoten's Discourse of Voyages, in 1598. New Delhi, AES. ISBN 978-81-206-1928-9.
- Mancall, Peter C. (2006). Travel narratives from the age of discovery: an anthology. Oxford University Press US. ISBN 978-0-19-515597-6. Archived from the original on 2022-07-26. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Pires, Tomé, Armando Cortesão, Francisco Rodrigues (1990) [1512]. The Suma oriental of Tome Pires: an account of the East, from the Red Sea to China, written in Malacca and India in 1512–1515; and, The book of Francisco Rodrigues: Pilot-Major of the armada that discovered Banda and the Moluccas. Asian Educational Services. ISBN 978-81-206-0535-0. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Real Cédula aprobando la capitulación concedida por Carlos V a Francisco Pizarro para la conquista y población del Perú" (in Spanish). Biblioteca Virtual Miguel de Cervantes. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
Secondary works
- Abu-Lughod, Janet (1991). Before European Hegemony: The World System A.D. 1250–1350. Oxford University Press US. ISBN 978-0-19-506774-3. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Anderson, James Maxwell (2000). The history of Portugal. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-31106-2. Archived from the original on 2022-04-07. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Arciniegas, Germán (1978). Amerigo and the New World: The Life & Times of Amerigo Vespucci. Octagon Books. ISBN 978-0-374-90280-3.
- Armesto, Felipe Fernandez (2006). Pathfinders: A Global History of Exploration. W.W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-06259-5.
- Arnold, David (2002). The Age of Discovery, 1400–1600, Lancaster pamphlets. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-27996-3. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Boxer, Charles Ralph (1969). The Portuguese Seaborne Empire 1415–1825. Hutchinson. ISBN 978-0-09-131071-4. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Boxer, Charles Ralph (1977). The Dutch seaborne empire, 1600–1800. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-09-131051-6. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Braudel, Fernand (1992) [1979]. The Wheels of Commerce, vol. II of Civilization and Capitalism 15th–18th Century. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-08115-4. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Braudel, Fernand (1992) [1985]. The perspective of the world. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-08116-1. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Brook, Timothy (1998). The Confusions of Pleasure: Commerce and Culture in Ming China. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-22154-3. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Burns, William E. (2001). The scientific revolution: an encyclopædia. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-0-87436-875-8. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Butel, Paul (1999). The Atlantic. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-10690-0. Archived from the original on 2022-09-10. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Cole, Juan Ricardo (2002). Sacred Space and Holy War. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 978-1-86064-736-9. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Cook, Noble David (1998). Born to die: disease and New World conquest, 1492–1650. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62730-6. Archived from the original on 2022-04-07. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Crosby, Alfred W. Jr (2003) [1972]. The Columbian Exchange: Biological and Cultural Consequences of 1492 (30th Anniversary ed.). Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-275-98092-4. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Cromer, Alan (1995). Uncommon Sense: The Heretical Nature of Science. Oxford University Press US. ISBN 978-0-19-509636-1. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Crow, John A. (1992). The Epic of Latin America. University of California Press. p. 136. ISBN 978-0-520-07723-2. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Chen, Zhongping (2019). "Toward a Global Network Revolution: Zheng He's Maritime Voyages and Tribute-Trade Relations Between China and the Indian Ocean World". China and Asia. 1 (1): 3–49. doi:10.1163/2589465X-00101002.
- Daus, Ronald (1983). Die Erfindung des Kolonialismus. Wuppertal/Germany: Peter Hammer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-87294-202-9.
- Davenport, Frances Gardiner (1917). European Treaties Bearing on the History of the United States and Its Dependencies to 1648. Washington, DC: Carnegie Institute of Washington. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- De Lamar, Jensen (1992). Renaissance Europe: age of recovery and reconciliation. D.C. Heath. ISBN 978-0-669-20007-2.
- Diffie, Bailey (1977). Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415–1580. University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 978-0-8166-0782-2. Archived from the original on 2016-11-28. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Diffie, Bailey (1960). Prelude to empire: Portugal overseas before Henry the Navigator. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-5049-9. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Dymytryshyn, Basil, E.A.P. Crownhart-Vaughan, Thomas Vaughan (1985). Russia's conquest of Siberia, 1558–1700: a documentary record (in Russian). Western Imprints, The Press of the Oregon Historical Society. ISBN 978-0-8032-5049-9. Archived from the original on 2013-06-26. Retrieved 2016-02-10.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Donkin, R.A. (2003). Between East and West: the Moluccas and the Traffic in Spices up to the arrival of Europeans. Memoirs of the American Philosophical Society, Diane Publishing. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-87169-248-1. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Dunn, Ross E. (2004). The adventures of Ibn Battuta, a Muslim traveler of the fourteenth century. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24385-9. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Dunton, Larkin (1896). The World and Its People. Silver, Burdett.
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley, Anne Walthall, James B. Palais (2006–2008). East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History. Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-618-13384-0. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Fisher, Raymond H. (1981). The Voyage of Semen Dezhnev in 1648. The Hakluyt Society. ISBN 978-0-904180-07-7.
- Fiske, John (1892–2009). The Discovery of America: With Some Account of Ancient America and the Spanish Conquest. Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-1-110-32015-8. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Forbes, Jack D. (1993). Africans and Native Americans: the language of race and the evolution of Red-Black peoples. University of Illinois Press. ISBN 978-0-252-06321-3. Archived from the original on 2022-04-07. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Gernet, Jacques (1962). Daily life in China, on the eve of the Mongol invasion, 1250–1276. Stanford University Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-8047-0720-6. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Gitzen, Garry (2011). Francis Drake in Nehalem Bay 1579, Setting the Historical Record Straight. Fort Nehalem. Archived from the original on 2011-10-17. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Goodrich, Luther Carrington, Chao-ying Fang, Ming Biographical History Project Committee – Association for Asian Studies. (1976). Dictionary of Ming biography, 1368–1644. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-03833-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Gutierrez, Ramon A, and Richard J. Orsi (1998). Contested Eden: California before the Gold Rush. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-21274-9. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Hacquebord, Louwrens (September 1995). "In Search of Het Behouden Huys: A Survey of the Remains of the House of Willem Barentsz on Novaya Zemlya" (PDF). Arctic. 48 (3): 250. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.505.5702. doi:10.14430/arctic1246. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 March 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- Hochstrasser, Julie (2007). Still life and trade in the Dutch golden age. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-10038-9.
- Howard, David and John Ayers (1978). China for the West: Chinese Porcelain and other Decorative Arts for Export, Illustrated from the Mottahedeh Collection. London and New York: Sotheby Parke Bernet.
- Lach, Donald F., Edwin J. Van Kley (1998). Asia in the Making of Europe, Volume III: A Century of Advance. Book 3: Southeast Asia. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-46768-9. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Lawson, Edward W. (2007). The Discovery of Florida and Its Discoverer Juan Ponce de Leon. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4325-6124-6.
- Lincoln, W. Bruce (2007) [1994]. The Conquest of a Continent: Siberia and the Russians. Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-8922-8. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Locke, John (1824). The works of John Locke: in nine volumes, Volume 9" The history of navigation. C. and J. Rivington. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Love, Ronald S. (2006). Maritime Exploration in the Age of Discovery, 1415–1800. Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-313-32043-9. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Mancall, Peter C. (1999). "The Age of Discovery" in The Challenge of American History, ed. Louis Masur. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-6222-9. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Medina (1974) [1918]. El Piloto Juan Fernandez descubridor de las islas que ilevan su hombre, y Juan Jufre, armador de la expedicion que hizo en busca de otras en el mar del zur (in Spanish). Gabriela Mistral. ISBN 978-0-313-32043-9.
- Milton, Giles (1999). Nathaniel's Nutmeg. London: Sceptre. ISBN 978-0-340-69676-7.
- Morison, Samuel Eliot (2007) [1942]. Admiral of the Ocean Sea: The Life of Christopher Columbus. Read Books. ISBN 978-1-4067-5027-0. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Mutch, T.D. (1942). The First Discovery of Australia. Sydney: Journal of the Royal Australian Historical Society. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Newitt, Malyn D.D. (2005). A History of Portuguese Overseas Expansion, 1400–1668. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-23979-0. Archived from the original on 2011-12-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Nowell, Charles E. (1947). The Discovery of the Pacific: A Suggested Change of Approach. The Pacific Historical Review" (Volume XVI, Number 1).
- Otfinoski, Steven (2004). Vasco Nuñez de Balboa: explorer of the Pacific. Marshall Cavendish. ISBN 978-0-7614-1609-8. Archived from the original on 2022-09-10. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Pacey, Arnold (1991). Technology in world civilization: a thousand-year history. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-66072-3. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Pagden, Anthony (1993). European Encounters with the New World: From Renaissance to Romanticism. New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Paine, Lincoln P. (2000). Ships of discovery and exploration. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-395-98415-4. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Parry, J. H. (1981). The Age of Reconnaissance. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-04235-3. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Parry, J. H. (1981). The Discovery of the Sea. University of California Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-520-04237-7. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Penrose, Boies (1955). Travel and Discovery in the Renaissance:1420–1620. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-689-70153-5.
- Pfoundes, C. (1882). Notes on the History of Eastern Adventure, Exploration, and Discovery, and Foreign Intercourse with Japan. Transactions of the Royal Historical Society (Volume X).
- Restall, Matthew (2004). Seven Myths of the Spanish Conquest. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-517611-7. Archived from the original on 2022-09-10. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Russell-Wood, A.J.R. (1998). The Portuguese empire, 1415–1808: a world on the move. JHU Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-5955-7. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Sen, Tansen (2016). "The Impact of Zheng He's Expeditions on Indian Ocean Interactions". Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies. 79 (3): 609–636. doi:10.1017/S0041977X16001038.
- Spence, Jonathan D. (1999). The Chan's Great Continent: China in Western Minds. W.W. Norton & Co. ISBN 978-0-393-31989-7.
- Spufford, Peter (1989). Money and its Use in Medieval Europe. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-37590-0. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Bagrow, Leo, R.A. Skelton (1964). History of cartography. Transaction Publishers, 2009. ISBN 978-1-4128-1154-5. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Synge, J.B. (2007) [1912]. A Book of Discovery. Yesterday's Classics. ISBN 978-1-59915-192-2. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Tamura, Eileen H.; Mention, Linda K.; Lush, Noren W.; Tsui, Francis K.C.; Cohen, Warren (1997). China: Understanding Its Past. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-1923-1. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Tracy, James D. (1994). Handbook of European History 1400–1600: Late Middle Ages, Renaissance, and Reformation. Boston: Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 978-90-04-09762-9.
- Tsai, Shih-Shan Henry (2002). Perpetual Happiness: The Ming Emperor Yongle. University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0-295-98124-6. Archived from the original on 2021-04-14. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Volker, T. (1971). Porcelain and the Dutch East India Company: as recorded in the Dagh-registers of Batavia Castle, those of Hirado and Deshima and other contemporary papers, 1602–1682. E.J. Brill.
- Walton, Timothy R. (1994). The Spanish Treasure Fleets. Pineapple Press (FL). ISBN 978-1-56164-049-2. Archived from the original on 2022-05-22. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
- Weddle, Robert S. (1985). Spanish Sea: the Gulf Of Mexico in North American Discovery, 1500–1685. Texas A&M University Press. ISBN 978-0-89096-211-4.
- Wilford, John Noble (1982). The Mapmakers, the Story of the Great Pioneers in Cartography from Antiquity to Space Age. Vintage Books, Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-75303-4.
- Zweig, Stefan (2007) [1938]. Conqueror of the Seas – The Story of Magellan. Read Books. ISBN 978-1-4067-6006-4. Archived from the original on 2022-05-20. Retrieved 2011-06-16.
Web sources
- "Amerigo Vespucci". Catholic Encyclopædia (New Advent). Archived from the original on 5 September 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- "Ancient Silk Road Travelers". Silk Road Foundation. Archived from the original on 25 May 2017. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- "By the road of pathfinders" (in Russian). Sbaikal.ru. Archived from the original on 15 November 2011. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- "Discovering Francis Drake's California Harbor". Drake Navigators Guild. Archived from the original on 21 September 2011. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- "Oregon History of Francis Drake". Fort Nehalem Publishing. Archived from the original on 12 May 2014. Retrieved 10 May 2014.
- "Exploration–Jacques Cartier". The Historica Dominion Institute. Archived from the original on 1 March 2010. Retrieved 9 November 2009.
- "Ferdinand Magellan". Catholic Encyclopædia (New Advent). Archived from the original on 13 January 2007. Retrieved 14 January 2007.
- "Food Bacteria-Spice Survey Shows Why Some Cultures Like It Hot". ScienceDaily. March 5, 1998. Archived from the original on September 3, 2018. Retrieved February 28, 2018.
- Grunberg, Bernard (July–August 2007). "La folle aventure d'Hernan Cortés". L'Histoire. 322: 22. Archived from the original on 2011-06-29. Retrieved 2010-06-17.
- "Historic and contemporary political and physical maps of California, including early exploration". University of San Francisco. Archived from the original on 29 August 2011. Retrieved 14 January 2007.
- McNeill, J. R.; Sampaolo, Marco; Wallenfeldt, Jeff (30 September 2019) [28 September 2019]. "Columbian Exchange". Encyclopædia Britannica. Edinburgh: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Archived from the original on 21 April 2020. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- "Issues and Trends in China's Demographic History". Columbia University. Archived from the original on 22 June 2010. Retrieved 4 June 2010.
- Eccles, W.J. "Jacques Cartier". Britannica Online Encyclopædia. Archived from the original on 12 July 2010. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- "Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo". San Diego Historical Society. Archived from the original on 5 May 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- "Maize Streak Virus-Resistant Transgenic Maize: an African solution to an African Problem". www.scitizen.com. August 2007. Archived from the original on 27 December 2019. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- "The Cabot Dilemma: John Cabot's 1497 Voyage & the Limits of Historiography" ((on subscription)). Derek Croxton, University of Virginia. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 15 June 2010.
- "The European Voyages of Exploration". The Applied History Research Group, University of Calgary. Archived from the original on 22 July 2010. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- "The Lost Fort of Columbus". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on 21 December 2007. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- "The Perfilyevs family" (in Russian). VSP.ru. Archived from the original on 5 May 2010. Retrieved 19 June 2010.
- "Super-Sized Cassava Plants May Help Fight Hunger In Africa". Researchnews, The Ohio State University. May 24, 2006. Archived from the original on December 8, 2013.
- "Willem Barentsz and the Northeast passage". University Library of Tromsø – The Northern Lights Route. Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 18 June 2010.
External links
 Media related to Age of Discovery at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Age of Discovery at Wikimedia Commons- "The Faustian Impulse and European Exploration" at The Fortnightly Review (archived 27 April 2017)

