2020 Queensland state election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 93 seats in the Legislative Assembly of Queensland 47 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opinion polls | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered | 3,377,476 ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 2,969,347 (87.92%) ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2020 Queensland state election was held on 31 October to elect all 93 members to the 57th Legislative Assembly of Queensland. The Labor Party was returned to government for a third-term, led by incumbent premier Annastacia Palaszczuk.[2] With 47 seats needed to form a majority government, Labor won 52 seats, including all but five in Brisbane, while the Liberal National Party won 34 seats and formed opposition. On the crossbench, Katter's Australian Party retained its 3 seats, the Queensland Greens picked up South Brisbane for a total of 2, Pauline Hanson's One Nation retained Mirani and independent Sandy Bolton retained her seat of Noosa.
Both major parties managed a small swing to them on primary votes, as a result of One Nation's vote sharply declining. On the two-party-preferred vote, Labor had a small swing to it statewide, though the party did notably lose some ground to the LNP in some key seats, including the ultra-marginal seats of Burdekin and Whitsunday, and the LNP also won both Toowoomba-based seats with increased majorities. Labor picked up five seats from the LNP, but notably former Deputy Premier Jackie Trad lost her seat of South Brisbane to the Greens.
At 11pm on 31 October, Liberal National Party leader Deb Frecklington conceded defeat, congratulating Palaszczuk on her victory.[2] Frecklington initially indicated that she would stay on as party leader, but on 2 November announced that she would convene a party meeting and resign as leader.[3] David Crisafulli won the ensuing leadership spill and was elected LNP leader on 12 November 2020.[4]
Palaszczuk became the first female party leader to win three state elections in Australia,[5] as well as the first Queensland Premier to increase their party's seat total across three successive elections.[6]
Results
| 52 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 34 |
| ALP | GRN | IND | ONP | KAP | LNP |

| ||||||||||
| Party | Votes | % | Swing | Seats | +/– | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labor | 1,134,969 | 39.57 | +4.14 | 52 | ||||||
| Liberal National | 1,029,442 | 35.89 | +2.20 | 34 | ||||||
| Greens | 271,514 | 9.47 | −0.53 | 2 | ||||||
| One Nation | 204,316 | 7.12 | −6.60 | 1 | ||||||
| Katter's Australian | 72,168 | 2.52 | +0.20 | 3 | ||||||
| Legalise Cannabis | 26,146 | 0.91 | +0.91 | 0 | ||||||
| United Australia | 17,904 | 0.62 | +0.62 | 0 | ||||||
| Informed Medical Options | 17,546 | 0.61 | +0.61 | 0 | ||||||
| Animal Justice | 9,703 | 0.34 | +0.34 | 0 | ||||||
| North Queensland First | 5,616 | 0.20 | +0.20 | 0 | ||||||
| Civil Liberties and Motorists | 5,207 | 0.18 | −0.08[b] | 0 | ||||||
| Shooters, Fishers, Farmers | 2,801 | 0.10 | +0.10 | 0 | ||||||
| Independents | 70,992 | 2.48 | −2.10 | 1 | ||||||
| Formal votes | 2,868,324 | 96.60 | +0.94 | |||||||
| Informal votes | 101,023 | 3.40 | −0.94 | |||||||
| Total | 2,969,347 | 100 | 93 | |||||||
| Registered voters / turnout | 3,377,476 | 87.92 | +0.39 | |||||||
| Two-party-preferred vote[9] | ||||||||||
| Labor | 1,524,766 | 53.2 | ||||||||
| Liberal National | 1,343,558 | 46.8 | ||||||||
Vote summary
Seats changing hands
| Seat | 2017 Election | Swing | 2020 Election | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Member | Margin | Margin | Member | Party | ||||
| Bundaberg | Liberal National | David Batt | 4.20 | –4.21 | 0.01 | Tom Smith | Labor | ||
| Caloundra | Liberal National | Mark McArdle | 3.41 | –5.92 | 2.51 | Jason Hunt | Labor | ||
| Hervey Bay | Liberal National | Ted Sorensen | 9.10 | –11.12 | 2.02 | Adrian Tantari | Labor | ||
| Nicklin | Liberal National | Marty Hunt | 5.28 | –5.42 | 0.14 | Robert Skelton | Labor | ||
| Pumicestone | Liberal National | Simone Wilson | 0.84 | –6.11 | 5.27 | Ali King | Labor | ||
| South Brisbane | Labor | Jackie Trad | 3.55 | –8.90 | 5.35 | Amy MacMahon | Greens | ||
- Members listed in italics did not contest their seat at this election.
- The Liberal National Party also retained the seat of Whitsunday, where the sitting Liberal National member had resigned and contested the election as a member of their own party.
The swing between the major parties in each seat varied across the state. However, Labor managed a small statewide swing to it.
Queenslanders have been known to, at some points in time, vote for Labor on the state level and the LNP on the federal level; in 2019, when the federal Coalition government led by Scott Morrison was unexpectedly re-elected for a third consecutive term, the LNP won 23 of the 30 House of Representatives seats in Queensland and 58.44% of the two-party-preferred vote in the state, with Morrison's victory being credited to a stronger-than-expected performance in Queensland and Tasmania, despite Queensland having a state Labor government.
Ultimately, Labor managed to gain five seats from the LNP, including two Sunshine Coast seats (Caloundra and Nicklin), two seats in smaller regional cities (Bundaberg and Hervey Bay) and one seat in Brisbane (Pumicestone). However, Labor lost the seat of South Brisbane to the Greens, therefore giving Labor a net seat change of +4.
The seat of Bundaberg was won by Labor with a margin of just nine votes, currently the smallest margin of any federal or state electorate in Australia.
Labor's defeat in South Brisbane was significant in two ways. The Greens won their second state seat in Queensland, after winning Maiwar from the LNP in 2017. However, it also led to the defeat of sitting Deputy Premier Jackie Trad.[10] Trad became the first sitting Deputy Premier of Queensland to be unseated since 1947 (when Labor's Ted Walsh was unseated).
One Nation contested 90 seats at this election, but the party's vote dropped dramatically, having almost halved. One Nation finished second in many seats in 2017, but in 2020 the party only finished second in one seat: the Labor-held seat of Bundamba. Nevertheless, One Nation managed to get an increased majority in the only lower house seat in Australia that it currently holds: Mirani (represented by Stephen Andrew since 2017).
While Labor received a small swing to it in most seats, the party did lose some ground to the LNP in a few key seats, including Buderim, Cook, Mackay, Toowoomba North and Whitsunday.
The LNP managed to regain the seat of Whitsunday, where the sitting member (Jason Costigan) was expelled from the LNP and formed his own party, North Queensland First. The LNP candidate, Amanda Camm, managed to win the seat with an increased majority over the Labor Party.
Post-election pendulum
Subsequent changes
- On 10 June 2021, Duncan Pegg (Stretton) died. At the by-election on 24 July 2021, James Martin retained the seat for the Labor Party.
- On 29 March 2022, Colin Boyce (Callide) resigned. At the by-election on 18 June 2022, Bryson Head retained the seat for the Liberal National Party.
- On 31 December 2023, Premier Annastacia Palaszczuk (Inala) resigned. At the by-election on 16 March 2024, Margie Nightingale retained the seat for the Labor Party.
- On 27 January 2024, Jim Madden (Ipswich West) resigned. At the by-election on 16 March 2024, Darren Zanow gained the seat for the Liberal National Party.
Background
At the 2017 election, Labor won majority with 48 of 93 seats and formed government in the 56th Queensland Parliament. The LNP won 39 seats and formed opposition. Being allocated to crossbench, the Katter's Australian Party won three seats, One Nation won one seat, the Greens won one seat and Independent Sandy Bolton won the seat of Noosa.
Despite two by-elections, the composition of the 56th Parliament was unchanged, with the exception of the member for Whitsunday Jason Costigan. He was expelled from the LNP over allegations of behavioural impropriety, resulting in him joining the crossbench and eventually forming the North Queensland First party.
Labor has won all but one state election since 1989, and has only been out of government for five years since then. It lost its majority in 1996, giving way to a Coalition minority government that was defeated in 1998. In 2012, it suffered the worst defeat of a sitting government in the state's history, but regained power in 2015.
This election also marks the first time that both leaders of the current government and opposition have been female in a Queensland state election.[11] It is only the second time it has occurred in an Australian state, territory or federal election, the first time being the 1995 ACT election.
A record number of minor parties and candidates ran in the election, 342 minor party candidates, 69 as independents or not officially endorsed by any party. Labor, the LNP and the Greens ran candidates in every electorate, Pauline Hanson's One Nation ran in 90 electorates.[12]
Electoral system
Queensland has compulsory voting and uses full-preference instant-runoff voting for single-member electorates. The election was conducted by the Electoral Commission of Queensland (ECQ).
Of the political parties contesting the election, the party, or coalition, that win the majority of seats (at least 47) forms the government.
The party, or coalition that gains the next highest number of seats forms the opposition, with the remaining parties and independents candidates being allocated to the cross bench.
Queensland Parliament is the only unicameral state parliament in Australia. It has just one House—the Legislative Assembly.
Key dates
The election was for all 93 members of the Legislative Assembly. Pursuant to Constitution (Fixed Term Parliament) Amendment Act 2015 Queensland has fixed terms, with all elections following the 2020 vote scheduled every four years on the last Saturday of October. The Governor may call an election earlier than scheduled if the Government does not maintain confidence, or the annual appropriation bill fails to pass.
Under the legislation, the caretaker period commenced on 5 October 2020, 26 days prior to the election date.[13]
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, consideration was given to holding this election as a full postal ballot,[14] but this did not occur.[15] Despite this, a record number of postal votes was cast at the election, with a majority of Queenslanders voting before polling day.[15]
The election timetable is as follows:[16]
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 6 October 2020 | Queensland Parliament dissolved by Governor Paul de Jersey[17] |
| 10 October 2020 | Close of electoral rolls |
| 11 October 2020 | Close of nominations |
| 19 October 2020 | Early voting begins |
| 30 October 2020 | Early voting ends at 6 pm |
| 31 October 2020 | Polling day, between the hours of 8 am and 6 pm |
| 10 November 2020 | Last day for receipt of postal votes by 6 pm |
Registered parties
Since the previous election, 2017, six political parties were registered by Queensland's Electoral Commission: Shooters, Fishers and Farmers Party, North Queensland First, the Animal Justice Party, Clive Palmer's United Australia Party, Informed Medical Options Party, and Legalise Cannabis Queensland.
The following twelve registered parties contested the election, including a record number of minor parties:
|
Preferences
The LNP confirmed it would preference Labor candidates last on all of its how-to-vote cards.[19] An exception is for Maiwar, a seat held by the Greens, where the LNP put the sitting Greens member below the Labor candidate in the how-to-vote card.[20]
In response to LNP's preferences, Katter's Australia Party announced it would preference Greens candidates last on its party's how-to-vote cards, with party leader Robbie Katter suggesting the LNP's decision would lead to Greens candidates winning a number of seats in Brisbane.[21] Katter's Australia Party and Pauline Hanson's One Nation also announced a preference deal on 8 October, with the parties to preference each other in second place on their how-to-vote cards.[22]
Labor confirmed it would preference One Nation last on how-to-vote cards.[20]
Retiring MPs
Labor
- Kate Jones MP (Cooper) – announced 10 September 2020[23]
- Anthony Lynham MP (Stafford) – announced 10 September 2020[24]
- Coralee O'Rourke MP (Mundingburra) – announced 5 September 2020[25]
Liberal National
- Mark McArdle MP (Caloundra) – announced retirement 27 June 2019[26]
- Ted Sorensen MP (Hervey Bay) – announced retirement 25 May 2020[27]
- Simone Wilson MP (Pumicestone) – announced retirement 27 September 2019[28]
Candidates
At the close of nominations on 11 October 2020, 597 candidates had nominated for the state election—the highest number of candidates at a Queensland state election, surpassing the previous record of 453 candidates at the 2017 election.[29]
Leaders' debates
The first leaders' debate of the campaign between Palaszczuk and Frecklington was a People's Forum hosted by Sky News and the Courier Mail and was held on 28 October.[30] The selected audience consisted of undecided voters who post-debate were asked which party they would vote for based on the debate performance of the respective leaders. A majority of 53% opted for Labor, 30% for the LNP, whilst the remaining 17% were undecided.[31]
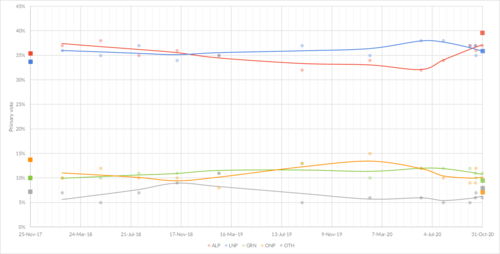
Polling
Several research, media and polling firms conduct opinion polls during the parliamentary term and prior to the state election in relation to voting. Most firms use an estimate of the flow of preferences at the previous election to determine the two-party-preferred vote; others ask respondents to nominate preferences.
Graphical summary
Opinion polling
Voting intention
| Date | Firm | Primary vote | 2pp vote | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP | LNP | ON | Green | Other | ALP | LNP | |||
| 31 October 2020 election | 39.6% | 35.9% | 7.1% | 9.5% | 7.9% | 53.2% | 46.8% | ||
| 25–30 Oct 2020 | Newspoll[32] | 37% | 36% | 10% | 11% | 6% | 51.5% | 48.5% | |
| 12–15 Oct 2020 | Roy Morgan[33] | 36% | 35% | 12% | 10% | 7% | 51% | 49% | |
| 9–14 Oct 2020 | Newspoll[34] | 37% | 37% | 9% | 11% | 6% | 52% | 48% | |
| 24 Sep–1 Oct 2020 | YouGov[35] | 37% | 37% | 9% | 12% | 5% | 52% | 48% | |
| 30 July 2020 | Newspoll[36] | 34% | 38% | 11% | 12% | 5% | 49% | 51% | |
| 7 June 2020 | YouGov[37] | 32% | 38% | 12% | 12% | 6% | 48% | 52% | |
| 7 February 2020 | YouGov[38] | 34% | 35% | 15% | 10% | 6% | 50% | 50% | |
| 30 August 2019 | YouGov[39] | 32% | 37% | 13% | 13% | 5% | 49% | 51% | |
| 13–14 February 2019 | YouGov[40] | 35% | 35% | 8% | 11% | 11% | 52% | 48% | |
| 7–8 November 2018 | YouGov[41] | 36% | 34% | 10% | 11% | 9% | 53% | 47% | |
| 8–9 August 2018 | YouGov[42] | 35% | 37% | 10% | 11% | 7% | 51% | 49% | |
| 9–10 May 2018 | YouGov[43] | 38% | 35% | 12% | 10% | 5% | 53% | 47% | |
| 7–8 Feb 2018 | YouGov[44] | 37% | 36% | 10% | 10% | 7% | 52% | 48% | |
| 12 December 2017 Deb Frecklington becomes leader of the Liberal National Party and Leader of the Opposition | |||||||||
| 25 Nov 2017 election | 35.4% | 33.7% | 13.7% | 10.0% | 7.2% | 51.2% | 48.8% | ||
| 21–24 Nov 2017 | Newspoll[45] | 36% | 34% | 13% | 10% | 7% | 52.5% | 47.5% | |
| 24 Nov 2017 | Galaxy[46] | 37% | 35% | 12% | 9% | 7% | 52% | 48% | |
| 20 Nov 2017 | ReachTEL[47] | 34% | 30% | 17% | 10% | 9% | 51% | 49% | |
Better premier and leadership approval polling
| Date | Firm | Better premier | Palaszczuk | Frecklington | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palaszczuk | Frecklington | Satisfied | Dissatisfied | Satisfied | Dissatisfied | |||
| 9–14 Oct 2020 | Newspoll[48] | 56% | 32% | 63% | 33% | 37% | 44% | |
| 24 Sep–1 Oct 2020 | YouGov[35] | 48% | 22% | 57% | 27% | 29% | 32% | |
| 21 September 2020 | Newspoll[49] | - | - | 63% | 33% | - | - | |
| 30 July 2020 | Newspoll[50] | 57% | 26% | 64% | 29% | 34% | 42% | |
| 12 June 2020 | Liberal National Party[51] | 42% | 19% | - | - | - | - | |
| 7 June 2020 | YouGov[38] | 44% | 23% | 49% | 33% | 26% | 29% | |
| 7 February 2020 | YouGov[38] | 34% | 22% | 29% | 44% | 23% | 33% | |
| 30 August 2019 | YouGov[52] | 34% | 29% | 34% | 45% | 30% | 30% | |
| 13–14 February 2019 | YouGov[40] | 47% | 27% | 48% | 38% | 31% | 35% | |
| 7–8 November 2018 | YouGov[41] | 43% | 26% | 46% | 37% | 35% | 29% | |
| 8–9 August 2018 | YouGov[42] | - | - | 41% | 38% | 31% | 26% | |
| 9–10 May 2018 | YouGov[43] | 47% | 27% | 46% | 38% | 31% | 28% | |
| 7–8 Feb 2018 | YouGov[44] | 42% | 31% | - | - | - | - | |
| 12 December 2017 Deb Frecklington becomes leader of the Liberal National Party and Leader of the Opposition | ||||||||
Electoral district polling
| Date | Firm | Electorate | Voting intention | 2cp vote | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP | LNP | ONP | GRN | KAP | UAP | LCA | OTH | ALP | LNP | GRN | |||
| 26 Oct 2020 | Newspoll[53] | South Brisbane | 32.0% | 24.0% | — | 39.0% | — | — | — | — | 45.5% | — | 54.5% |
| 24 Oct 2020 | Newspoll[54] | Mansfield | 41.0% | 45.0% | 2.0% | 9.0% | — | 0.5% | 1.5% | 1.0% | 50.5% | 49.5% | — |
| Mundingburra | 35.0% | 32.0% | 11.0% | 4.0% | 14.0% | 2.0% | 2.0% | — | 49.5% | 50.5% | — | ||
| Pumicestone | 45.0% | 37.0% | 9.0% | 6.0% | — | 1.0% | 2.0% | — | 54.0% | 46.0% | — | ||
Notes
- ^ a b At the previous election, Jason Costigan won the Electoral district of Whitsunday under the Liberal National Party, however was expelled from the party in February 2019.[1] After sitting as an Independent MP for over eight-months, Costigan established, and lead, his own party to the election.
- ^ Compared to 2017 election total of Consumer Rights, which was renamed to Civil Liberties and Motorists at the 2020 election.
References
- ^ "LNP expels north Queensland MP Jason Costigan". ABC News. 1 February 2019. Archived from the original on 6 February 2019. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ^ a b Maasdorp, James (31 October 2020). "Labor to clinch government in Queensland election, expected to win required 47 seats as Annastacia Palaszczuk claims third term as Premier". ABC News. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 1 November 2020.
- ^ Swanson, Tim (2 November 2020). "Queensland LNP leader Deb Frecklington stands down". ABC News. Archived from the original on 3 November 2020. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Lydia (12 November 2020). "LNP elects new leader and deputy while recount starts in two seats". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- ^ McKenna, Kate; Nothling, Lily (2 November 2020). "Annastacia Palaszczuk wins government in Queensland, making history". ABC News. Archived from the original on 2 November 2020. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Lydia (12 November 2020). "'We have to find a way to win': LNP to review election loss, policies". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 13 November 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ "2020 State General Election Results". Electoral Commission of Queensland. July 2019. Archived from the original on 10 November 2020. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ^ Green, Antony (13 November 2020). "QLD Election 2020 Results". ABC News. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ Estimate by Antony Green: "Analysis of the 2020 Queensland Election Result". Antony Green's Election Blog. 18 November 2020. Archived from the original on 18 November 2020. Retrieved 18 November 2020.
- ^ "Jackie Trad unseated in South Brisbane — a bruising election loss for a party high-flyer - ABC News". Archived from the original on 13 December 2023. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- ^ "What you need to know about Queensland's election campaign and how to cast your vote". ABC News. 6 October 2020. Archived from the original on 10 February 2022. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ "Record number of parties square up amid a 'fracturing' political landscape". 12 October 2020. Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
- ^ "Constitution (Fixed TermParliament) Amendment Act 2015". Queensland Government. 2015. Archived from the original on 10 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ Election could be a full postal vote Archived 11 April 2020 at the Wayback Machine Seniors News 10 April 2020
- ^ a b Hamilton-Smith, Lexy (18 October 2020). "How a staggering number of postal votes could change the face of Queensland's election". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 5 December 2020. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ^ "2020 State General Election". Electoral Commission of Queensland. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 26 October 2020.
- ^ Silk, Marty (6 October 2020). "Qld parliament dissolved ahead of election". The West Australian. Archived from the original on 2 February 2021.
- ^ "Record number of parties square up amid a 'fracturing' political landscape". 12 October 2020. Archived from the original on 17 October 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
- ^ Zillman, Stephanie (6 October 2020). "LNP to put Labor last in its Queensland election preferences, elevating the Greens". ABC News. Archived from the original on 5 October 2020. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- ^ a b "Labor's Queensland election candidates warned to toe party line on preferences after photos show signs saying 'put the LNP last'". ABC News. 20 October 2020. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ McKay, Jack (25 September 2020). "Robbie Katter appeals to LNP to preference Greens last". Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- ^ Barry, Derek (8 October 2020). "KAP and One Nation strike preference deal in Queensland election". North West Star. Archived from the original on 17 July 2022. Retrieved 8 October 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Lydia (10 September 2020). "Kate Jones becomes third Queensland Labor minister to call time". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 10 September 2020. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Lydia (10 September 2020). "Mines Minister Anthony Lynham will not contest his seat at election". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 17 September 2020. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
- ^ Stone, Lucy (5 September 2020). "Minister Coralie O'Rourke announces she will not contest election". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 5 September 2020. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Lydia (28 June 2019). "Sunshine Coast MP to stand down at next election for younger blood". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 3 July 2020. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Lydia (25 May 2020). "LNP's Ted Sorensen to retire after 26 years in local and state politics". Brisbane Times. Archived from the original on 3 July 2020. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- ^ "Member for Pumicestone Simone Wilson not to recontest in the next state election to be held October 2020". 1015 FM. Archived from the original on 2 July 2020. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- ^ Green, Antony (11 October 2020). "Close of Nominations for 2020 Queensland Election". Antony Green's Election Blog. Archived from the original on 25 October 2020. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- ^ Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: "FULL DEBATE: Frecklington and Palaszczuk go head-to-head at People's Forum". YouTube. 28 October 2020.
- ^ "Palaszczuk clear winner in election debate". 27 October 2020. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- ^ "Queensland election: Labor set for third term, but it's tight, Newspoll shows". The Australian. Archived from the original on 23 November 2021. Retrieved 31 October 2020.
- ^ "ALP Government leads with a slim majority in Queensland; small majority of Queenslanders don't want NSW border open now". Roy Morgan. Archived from the original on 22 October 2020. Retrieved 20 October 2020.
- ^ "Queensland ALP regains poll lead". The Australian. Archived from the original on 23 October 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
- ^ a b "Labor would win Queensland election if it was held today, YouGov poll shows". Courier Mail.
- ^ "Popular Queensland Premier Annastacia Palaszczuk but poll party postponed- The Australian". The Australian.
- ^ "YouGov: Labor's vote shrivels, as LNP surges". Courier Mail. Archived from the original on 6 October 2020. Retrieved 6 June 2020.
- ^ a b c "YouGov Galaxy: 50-50 in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 7 February 2020. Archived from the original on 7 February 2020. Retrieved 7 February 2020.
- ^ "YouGov Galaxy: 51-49 to state LNP in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 30 August 2019. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2019.
- ^ a b "YouGov Galaxy: Labor 35, LNP 35, Greens 11, One Nation 8 in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 10 November 2018. Archived from the original on 30 August 2019. Retrieved 30 August 2019.
- ^ a b "YouGov Galaxy: 53-47 to Labor in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 10 November 2018. Archived from the original on 10 November 2018. Retrieved 10 November 2018.
- ^ a b "YouGov Galaxy: 51-49 to state Labor in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 12 August 2018. Archived from the original on 12 August 2018. Retrieved 12 August 2018.
- ^ a b "YouGov Galaxy: 53-47 to state Labor in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 13 May 2018. Archived from the original on 16 April 2019. Retrieved 13 May 2018.
- ^ a b "YouGov Galaxy: 52-48 to state Labor in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 12 February 2018. Archived from the original on 13 February 2018. Retrieved 12 February 2018.
- ^ "Queensland election: swing to ALP but Hanson strings attached". The Australian. Archived from the original on 6 October 2020. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "Queensland Election 2017 galaxy poll predicts win for Labor and Premier Annastacia Palaszcuk". The Courier Mail. Archived from the original on 6 October 2020. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ^ "Labor leads LNP by 2 points in Qld: Poll". Sky News. Archived from the original on 23 November 2017. Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^ Bowe, William (16 October 2020). "Newspoll: 52-48 to Labor in Queensland". The Poll Bludger. Archived from the original on 18 October 2020. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- ^ "Majority support strict qld border lockdowns". The Australian. Archived from the original on 6 October 2020.
- ^ "Popular Queensland Premier Annastacia Palaszczuk but poll party postponed". The Australian.
- ^ Wardill, Steven (2020). "Deb Frecklington trails Annastacia Palaszczuk in popularity contest: LNP polling". Courier Mail. Archived from the original on 6 October 2020. Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ^ "YouGov Galaxy: 51–49 to State LNP in Queensland". Poll Bludger. 30 August 2019. Archived from the original on 24 December 2019. Retrieved 24 December 2019.
- ^ "South Brisbane - QLD Electorate, Candidates, Results". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 2 December 2023. Retrieved 6 February 2024.
- ^ Wardill, Steven (24 October 2020). "Newspoll results show Labor and LNP poised to claw marginal seats off each other". The Courier-Mail. Retrieved 11 February 2024.