Zhu Zaiyu
| Zhu Zaiyu | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hereditary Prince of Zheng (鄭世子) | |||||||||
| Tenure | 1593–1611 | ||||||||
| Born | 1536 | ||||||||
| Died | 19 May 1611 | ||||||||
| Issue |
| ||||||||
| |||||||||
| House | Zhu | ||||||||
| Father | Zhu Houwan, Prince Gong of Zheng | ||||||||
| Occupation | Astronomer, historian, physicist, mathematician, choreographer, music theorist | ||||||||


Zhu Zaiyu (Chinese: 朱載堉; 1536 – 19 May 1611) was a Chinese scholar, mathematician and music theorist.[1] He was a prince of the Chinese Ming dynasty. In 1584, Zhu innovatively described the equal temperament via accurate mathematical calculation.[2]
Biography
Zhu was born in Qinyang, Henan Province to an aristocratic family, the sixth-generation descendant of the Hongxi Emperor, the fourth emperor of the Ming Dynasty. Zhu inherited the title the Prince of Zheng in 1593, but quickly resigned it to his cousin. On the emperor's order, he was granted a new princely title in 1606, the year he delivered a set of ten musicological treatises to the court, establishing his scholarly merit. His posthumous name was 鄭端靖世子 ("His Excellency The Dauphin of Zheng").
Zhu wrote on music theory and temperament (five treatises survive), music history (two treatises survive), dance and dance music (five treatises survive), and several other works. Three music theory works in particular are associated with the ideas of equal temperament, the Lü Xue Xin Shuo「律學新說」 ("on the equal temperament", 1584), Lü Lü Zheng Yi「律呂精義」("A clear explanation of that which concerns the equal temperament", 1595/96), and Suan Xue Xin Shuo「算學新說」("Reflection on mathematics", 1603). His work has been described as "the crowning achievement of two millennia of acoustical experiment and research" (Robinson 1962:224)[3] and he is described as "one of the most important historians of his nation's music".[4]
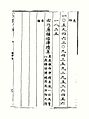
- Zhu Zaiyu's equal temperament ratio in Yue Lü Quan Shu「樂律全書」
Zhu also wrote treatises (three survive) on astronomy, physics, mathematics and calendrics, calculated the magnetic declination of Peking, the mass density of mercury and accurately described the duration of one tropical year to correct the Ming calendar.
Zhu's work on equal temperament did not get any official recognition during his lifetime nor during the Qing dynasty. This was due to the Ming and Qing emphasis on classical scholarship and discouragement of ideas based on empirical observation rather than textual interpretations.[5]
See also
- Book of Songs (Chinese)
- Chinese mathematics
- Chinese musicology
- Equal temperament
- Jing Fang
- Shen Kuo
- Shí-èr-lǜ
- Zhang Heng
References
- ^ Lam, Joseph S.C. (2001). "Zhu Zaiyu". Grove Music Online. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/gmo/9781561592630.article.49365. (subscription or UK public library membership required)
- ^ Hermann von Helmholtz,Die Lehre von den Tonempfindungen als physiologische Grundlage für die Theorie der Musik . p 258, 3rd edition, Longmans, Green and Co, London, 1895
- ^ Robinson, Kenneth. A critical study of Chu Tsai-yü's contribution to the theory of equal temperament in Chinese music. Wiesbaden : F. Steiner, 1980.
- ^ Fritz A. Kuttner. "Prince Chu Tsai-Yü's Life and Work: A Re-Evaluation of His Contribution to Equal Temperament Theory", p. 163, Ethnomusicology, Vol. 19, No. 2 (May 1975), pp. 163–206.
- ^ Dillon, Michael, ed. (1998). China: A Cultural and Historical Dictionary. London: Curzon. pp. 388. ISBN 0-7007-0439-6.
Further reading
- Cho, Gene J. The discovery of musical equal temperament in China and Europe in the sixteenth century. Lewiston, N.Y. : Edwin Mellen Press, 2003.
- Woo Shingkwan (January 2017). Floyd K. Grave; Nancy Y. Rao (eds.). "The Ceremonial Music of Zhu Zaiyu - A dissertation submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick". New Brunswick, New Jersey, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey.