West Sudanian savanna
| West Sudanian savanna | |
|---|---|
 | |
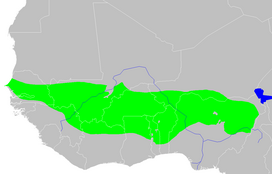 Map of the West Sudanian savanna ecoregion | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Afrotropical |
| Biome | tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
| Borders | |
| Geography | |
| Area | 1,632,821 km2 (630,436 sq mi) |
| Countries | |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | Critical/endangered |
| Protected | 233,942 km2 (14%)[1] |
The West Sudanian savanna is a tropical savanna ecoregion that extends across West Africa.
Geography
The ecoregion stretches east and west across West Africa, from the Atlantic coast of Senegal to the Mandara Mountains on Nigeria's eastern border.
The drier Sahelian Acacia savanna lies to the north, and the more humid Guinean forest-savanna mosaic lies to the south.
Climate
The climate is a tropical savanna climate and a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification Aw and BSh) with a dry season and a wet season and the temperature being warm and hot year-round. Annual rainfall ranges from 1000 mm in the south to 600 mm in the north on the edge of the Sahel. Rainfall and temperature vary seasonally, with a hot rainy season from May to September, and a cooler dry season from October to April. Temperatures range from 30 °C to 33 °C during the hottest month, and 18 °C to 21 °C during the coolest month.[2]
Examples
| Climate data for Dakar, Senegal (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 39.6 (103.3) |
38.7 (101.7) |
40.4 (104.7) |
38.4 (101.1) |
36.2 (97.2) |
36.6 (97.9) |
36.9 (98.4) |
35.0 (95.0) |
36.2 (97.2) |
39.3 (102.7) |
40.3 (104.5) |
39.5 (103.1) |
40.4 (104.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 25.3 (77.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.0 (77.0) |
26.0 (78.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.7 (87.3) |
31.0 (87.8) |
29.8 (85.6) |
27.4 (81.3) |
27.9 (82.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 18.3 (64.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
18.5 (65.3) |
19.2 (66.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
23.5 (74.3) |
25.1 (77.2) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.3 (77.5) |
23.3 (73.9) |
21.0 (69.8) |
22.0 (71.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 11.0 (51.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
10.9 (51.6) |
14.0 (57.2) |
15.4 (59.7) |
17.0 (62.6) |
17.2 (63.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
17.2 (63.0) |
17.0 (62.6) |
12.4 (54.3) |
10.7 (51.3) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 1.0 (0.04) |
2.0 (0.08) |
0.3 (0.01) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.00) |
14.0 (0.55) |
51.0 (2.01) |
154.0 (6.06) |
133.0 (5.24) |
26.0 (1.02) |
9.2 (0.36) |
1.0 (0.04) |
391.6 (15.41) |
| Average rainy days | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 3.0 | 8.0 | 15.0 | 12.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 47.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 68 | 74 | 77 | 81 | 81 | 80 | 78 | 81 | 83 | 80 | 72 | 68 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 244.9 | 245.8 | 276.0 | 288.0 | 291.4 | 252.0 | 232.5 | 223.2 | 219.0 | 257.3 | 249.0 | 238.7 | 3,017.8 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 70 | 74 | 74 | 74 | 73 | 65 | 58 | 57 | 60 | 70 | 73 | 69 | 68 |
| Source 1: Pogoda.ru.net[3] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Spiegel Online Wetter[4] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Bamako (1950–2000, extremes 1949–2015) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 38.9 (102.0) |
42.8 (109.0) |
43.9 (111.0) |
43.5 (110.3) |
45.0 (113.0) |
42.0 (107.6) |
40.0 (104.0) |
37.8 (100.0) |
38.4 (101.1) |
38.9 (102.0) |
42.0 (107.6) |
40.0 (104.0) |
45.0 (113.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 33.4 (92.1) |
36.4 (97.5) |
38.5 (101.3) |
39.6 (103.3) |
38.5 (101.3) |
35.3 (95.5) |
32.1 (89.8) |
31.1 (88.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
34.6 (94.3) |
35.3 (95.5) |
33.4 (92.1) |
35.0 (95.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
22.9 (73.2) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
23.6 (74.5) |
22.2 (72.0) |
21.8 (71.2) |
21.6 (70.9) |
21.3 (70.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
16.8 (62.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8.7 (47.7) |
9.0 (48.2) |
12.0 (53.6) |
15.8 (60.4) |
17.8 (64.0) |
16.1 (61.0) |
17.5 (63.5) |
17.2 (63.0) |
18.0 (64.4) |
14.7 (58.5) |
10.8 (51.4) |
6.0 (42.8) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.6 (0.02) |
0.7 (0.03) |
2.1 (0.08) |
19.7 (0.78) |
54.1 (2.13) |
132.1 (5.20) |
224.1 (8.82) |
290.2 (11.43) |
195.9 (7.71) |
66.1 (2.60) |
5.2 (0.20) |
0.5 (0.02) |
991.3 (39.03) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 3.3 | 6.3 | 7.7 | 16.7 | 17.9 | 14.7 | 5.7 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 73.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 24 | 20 | 22 | 33 | 50 | 67 | 77 | 81 | 78 | 65 | 38 | 27 | 49 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 277.4 | 253.0 | 268.1 | 230.4 | 242.6 | 233.6 | 216.6 | 218.3 | 221.7 | 253.7 | 270.7 | 268.6 | 2,954.7 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization[5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun 1961–1990),[6] Deutscher Wetterdienst (extremes and humidity)[7] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Ouagadougou (1971-2000, extremes 1902-present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 39.8 (103.6) |
42.3 (108.1) |
43.8 (110.8) |
46.1 (115.0) |
44.5 (112.1) |
41.3 (106.3) |
38.8 (101.8) |
36.6 (97.9) |
38.6 (101.5) |
41.0 (105.8) |
40.5 (104.9) |
40.1 (104.2) |
46.1 (115.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32.9 (91.2) |
35.8 (96.4) |
38.3 (100.9) |
39.3 (102.7) |
37.7 (99.9) |
34.7 (94.5) |
32.1 (89.8) |
31.1 (88.0) |
32.5 (90.5) |
35.6 (96.1) |
35.9 (96.6) |
33.4 (92.1) |
34.9 (94.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 16.5 (61.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
24.1 (75.4) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.0 (73.4) |
19.6 (67.3) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.9 (71.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) |
10.4 (50.7) |
14.8 (58.6) |
16.2 (61.2) |
17.0 (62.6) |
17.0 (62.6) |
15.0 (59.0) |
17.9 (64.2) |
17.6 (63.7) |
17.6 (63.7) |
13.0 (55.4) |
9.5 (49.1) |
8.5 (47.3) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.1 (0.00) |
0.5 (0.02) |
5.9 (0.23) |
26.5 (1.04) |
66.8 (2.63) |
97.5 (3.84) |
176.2 (6.94) |
214.2 (8.43) |
121.2 (4.77) |
33.5 (1.32) |
1.2 (0.05) |
0.2 (0.01) |
743.8 (29.28) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 16 | 11 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 68 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 24 | 21 | 22 | 36 | 50 | 64 | 72 | 80 | 77 | 60 | 38 | 29 | 48 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 287 | 263 | 264 | 256 | 277 | 264 | 240 | 223 | 217 | 273 | 288 | 284 | 3,136 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization,[8] Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[9] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Deutscher Wetterdienst (humidity, 1961–1967, and sun, 1961–1990)[10][11][a] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Niamey, Niger (1961–1990, extremes: 1961–2015) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 38.2 (100.8) |
44.0 (111.2) |
45.0 (113.0) |
45.6 (114.1) |
45.1 (113.2) |
43.5 (110.3) |
41.0 (105.8) |
39.6 (103.3) |
41.8 (107.2) |
41.2 (106.2) |
40.7 (105.3) |
40.0 (104.0) |
45.6 (114.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32.5 (90.5) |
35.7 (96.3) |
39.1 (102.4) |
40.9 (105.6) |
40.2 (104.4) |
37.2 (99.0) |
34.0 (93.2) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.4 (93.9) |
37.8 (100.0) |
36.2 (97.2) |
33.3 (91.9) |
36.2 (97.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 24.3 (75.7) |
27.3 (81.1) |
30.9 (87.6) |
33.8 (92.8) |
34.0 (93.2) |
31.5 (88.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
27.9 (82.2) |
29.0 (84.2) |
30.8 (87.4) |
27.9 (82.2) |
25.0 (77.0) |
29.3 (84.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 16.1 (61.0) |
19.0 (66.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
26.5 (79.7) |
27.7 (81.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.6 (74.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
16.7 (62.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 12.6 (54.7) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.0 (64.4) |
21.6 (70.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
20.5 (68.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.3 (68.5) |
15.8 (60.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
12.6 (54.7) |
12.6 (54.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
3.9 (0.15) |
5.7 (0.22) |
34.7 (1.37) |
68.8 (2.71) |
154.3 (6.07) |
170.8 (6.72) |
92.2 (3.63) |
9.7 (0.38) |
0.7 (0.03) |
0.0 (0.0) |
540.8 (21.28) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 2.9 | 5.9 | 9.9 | 12.2 | 7.4 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 41 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 22 | 17 | 18 | 27 | 42 | 55 | 67 | 74 | 73 | 53 | 34 | 27 | 42 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 280 | 264 | 264 | 251 | 257 | 251 | 238 | 203 | 228 | 285 | 285 | 276 | 3,082 |
| Source 1: Deutscher Wetterdienst[12] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Danish Meteorological Institute[13] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Maiduguri | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 40 (104) |
42 (108) |
44 (111) |
46 (115) |
47 (117) |
42 (108) |
43 (109) |
36 (97) |
38 (100) |
39 (102) |
39 (102) |
38 (100) |
47 (117) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 31.9 (89.4) |
34.6 (94.3) |
37.8 (100.0) |
40.1 (104.2) |
39.4 (102.9) |
36.4 (97.5) |
33.2 (91.8) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.7 (92.7) |
36.4 (97.5) |
34.2 (93.6) |
32.3 (90.1) |
35.2 (95.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 21.8 (71.2) |
24.8 (76.6) |
29.3 (84.7) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.5 (90.5) |
30.2 (86.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
24.9 (76.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
27.4 (81.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 12.6 (54.7) |
15.3 (59.5) |
19.7 (67.5) |
21.9 (71.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
24.5 (76.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.4 (72.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
13.1 (55.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 8 (46) |
10 (50) |
15 (59) |
12 (54) |
18 (64) |
19 (66) |
20 (68) |
19 (66) |
20 (68) |
15 (59) |
10 (50) |
5 (41) |
5 (41) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.3 (0.01) |
13.0 (0.51) |
30.5 (1.20) |
73.8 (2.91) |
147.1 (5.79) |
193.2 (7.61) |
83.0 (3.27) |
11.1 (0.44) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.00) |
552.1 (21.74) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 4.0 | 7.0 | 10.7 | 10.7 | 6.8 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 42.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 15:00 LST) | 15.4 | 11.2 | 12.0 | 17.5 | 28.4 | 38.4 | 55.5 | 63.4 | 54.8 | 30.2 | 19.0 | 19.6 | 30.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 266.6 | 249.2 | 257.3 | 237.0 | 263.5 | 249.0 | 217.0 | 204.6 | 225.0 | 285.2 | 282.0 | 275.9 | 3,012.3 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 8.6 | 8.9 | 8.3 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 8.3 | 7.0 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 9.2 | 9.4 | 8.9 | 8.3 |
| Source 1: NOAA,[14] Climate Charts (latitude: 11°51'N; longitude: 013°05'E; elevation: 354m, 1161')[15] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Voodoo Skies for record temperatures[16] | |||||||||||||
Flora

Savanna and open woodland are the characteristic vegetation types. Species of Combretum and Terminalia are the typical savanna trees, and the ground is covered with long grasses, herbs, and shrubs. Species of Hyparrhenia, or elephant grass, is the predominant grass, and often grows 1 meter or more in height. Trees in the drier woodlands generally less than 10 meters high, and include Anogeissus spp. with Acacia spp., Balanites aegyptiaca, Combretum glutinosum, Commiphora africana, Prosopis africana, Tamarindus indica, and Ziziphus mucronata. Many trees lose their leaves during the height of the dry season, and the grasses often dry out.[2]
Acacia is less common in the wetter woodlands in higher-rainfall areas and along watercourses, where Afzelia africana, Burkea africana, Combretum spp. and Terminalia spp. are predominant. Smaller areas of Isoberlinia woodland occur in more humid portions of the southern ecoregion.[2]
Fauna
The ecoregion is home to many large mammals, including African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana), West African giraffe (Giraffa camelopardalis peralta), giant eland (Taurotragus derbianus derbianus), roan antelope (Hippotragus equinus), African buffalo (Syncerus caffer brachyceros), lion (Panthera leo), leopard (Panthera pardus) cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus), and African wild dog (Lycaon pictus). Most large mammals are now very limited in range and numbers.[2]
Conservation
A 2017 assessment found that 233,942 km2, or 14%, of the ecoregion is in protected areas.[1]
Notes
- ^ Station ID for Ouagadougou is 65503 Use this station ID to locate the sunshine duration
External links
- "West Sudanian savanna". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
 Media related to West Sudanian savanna at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to West Sudanian savanna at Wikimedia Commons
References
- ^ a b Eric Dinerstein, David Olson, et al. (2017). An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm, BioScience, Volume 67, Issue 6, June 2017, Pages 534–545; Supplemental material 2 table S1b. [1] Archived 2020-10-09 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c d "West Sudanian savanna". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- ^ "Climate Averages for Dakar" (in Russian). Weather and Climate (Погода и климат). Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- ^ "Africa, Senegal, Dakar". Spiegel Online Wetter. Archived from the original on 2014-02-01. Retrieved 2014-02-17.
- ^ "World Weather Information Service – Bamako". World Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 13 March 2013. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ "BKO–s (Bamako) Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
- ^ "Klimatafel von Bamako (Flughafen) / Mali" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961–1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 June 2020. Retrieved 3 February 2019.
- ^ "World Weather Information Service – Ouagadougou Aero". World Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 26 January 2022. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ^ "Station Ouagadougou" (in French). Meteo Climat. Archived from the original on 9 August 2020. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ^ "Klimatafel von Ouagadougou / Burkina Faso (Obervolta)" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961–1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 November 2021. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ^ "Station 65503: Ouagadougou". Global station data 1961–1990—Sunshine Duration. Deutscher Wetterdienst. Archived from the original on 2017-10-17. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ^ "Klimatafel von Niamey (Aéro) / Niger" (PDF). Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 September 2019. Retrieved 14 June 2016.
- ^ "Stationsnummer 61052" (PDF). Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2016.
- ^ "Maiduguri Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 14 October 2020. Retrieved 22 July 2016.
- ^ "Maiduguri, Nigeria Climate, Global Warming, and Daylight Charts and Data". Climate Charts. Archived from the original on 19 September 2017. Retrieved 3 December 2013.
- ^ "Maiduguri, Nigeria". Voodoo Skies. Archived from the original on 6 December 2013. Retrieved 3 December 2013.
