Uterine rupture
| Uterine rupture | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Obstetrics |
| Symptoms | Increased pain, vaginal bleeding, change in contractions[1][2] |
| Usual onset | During labor[3] |
| Risk factors | Vaginal birth after cesarean section, other uterine scars, obstructed labor, induction of labor, trauma, cocaine use[1][4] |
| Diagnostic method | Supported by a rapid drop in the baby's heart rate[1] |
| Treatment | Surgery[1] |
| Prognosis | 0.1%-10% risk of maternal death,[5] 6% risk of infant death[1] |
| Frequency | 1 in 12,000 vaginal deliveries with a normal uterus[1] 1 in 280 with vaginal birth after cesarean section[1] |
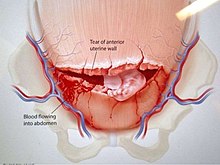
Uterine rupture is when the muscular wall of the uterus tears during pregnancy or childbirth.[3] Symptoms, while classically including increased pain, vaginal bleeding, or a change in contractions, are not always present.[1][2] Disability or death of the mother or baby may result.[1][3]
Risk factors include vaginal birth after cesarean section (VBAC), other uterine scars, obstructed labor, induction of labor, trauma, and cocaine use.[1][4] While typically rupture occurs during labor it may occasionally happen earlier in pregnancy.[3][1] Diagnosis may be suspected based on a rapid drop in the baby's heart rate during labor.[1][4] Uterine dehiscence is a less severe condition in which there is only incomplete separation of the old scar.[1]
Treatment involves rapid surgery to control bleeding and delivery of the baby.[1] A hysterectomy may be required to control the bleeding.[1] Blood transfusions may be given to replace blood loss.[1] Women who have had a prior rupture are generally recommended to have C-sections in subsequent pregnancies.[6]
Rates of uterine rupture during vaginal birth following one previous C-section, done by the typical technique, are estimated at 0.9%.[1] Rates are greater among those who have had multiple prior C-sections or an atypical type of C-section.[1] In those who do have uterine scarring, the risk during a vaginal birth is about 1 per 12,000.[1] Risk of death of the baby is about 6%.[1] Those in the developing world appear to be affected more often and have worse outcomes.[7][3]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of a rupture may be initially quite subtle. An old cesarean scar may undergo dehiscence; with further labor the woman may experience abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, though these signs are difficult to distinguish from normal labor. Often a deterioration of the fetal heart rate is a leading sign, but the cardinal sign of uterine rupture is loss of fetal station on manual vaginal exam. Intra-abdominal bleeding can lead to hypovolemic shock and death. Although the associated maternal mortality is now less than one percent, the fetal mortality rate is between two and six percent when rupture occurs in the hospital.
In pregnancy uterine rupture may cause a viable abdominal pregnancy. This is what accounts for most abdominal pregnancy births.
- Abdominal pain and tenderness. The pain may not be severe; it may occur suddenly at the peak of a contraction. The woman may describe a feeling that something "gave way" or "ripped."
- Chest pain, pain between the scapulae, or pain on inspiration—Pain occurs because of the irritation of blood below the woman's diaphragm
- Hypovolemic shock caused by bleeding, evidenced by falling blood pressure, tachycardia, tachypnea, pallor, cool and clammy skin, and anxiety. The fall in blood pressure is often a late sign of haemorrhage
- Signs associated with fetal oxygenation, such as late deceleration, reduced variability, tachycardia, and bradycardia
- Absent fetal heart sounds with a large disruption of the placenta; absent fetal heart activity by ultrasound examination
- Cessation of uterine contractions
- Palpation of the fetus outside the uterus (usually occurs only with a large, complete rupture). The fetus is likely to be dead at this point.
- Signs of an abdominal pregnancy
- Post-term pregnancy
Risk factors
A uterine scar from a previous cesarean section is the most common risk factor. (In one review, 52% had previous cesarean scars.)[8] Other forms of uterine surgery that result in full-thickness incisions (such as a myomectomy), dysfunctional labor, labor augmentation by oxytocin or prostaglandins, and high parity may also set the stage for uterine rupture. In 2006, an extremely rare case of uterine rupture in a first pregnancy with no risk factors was reported.[9]
Uterine rupture during pregnancy without a prior cesarean section is one of the major diagnostic criterion for vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (vEDS).[10]
Mechanism
In an incomplete rupture the peritoneum is still intact. With a complete rupture the contents of the uterus spill into the peritoneal cavity or the broad ligament.
Treatment
Emergency exploratory laparotomy with cesarean delivery accompanied by fluid and blood transfusion are indicated for the management of uterine rupture. Depending on the nature of the rupture and the condition of the patient, the uterus may be either repaired or removed (cesarean hysterectomy). Delay in management places both mother and child at significant risk.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Toppenberg, KS; Block WA, Jr (1 September 2002). "Uterine rupture: what family physicians need to know". American Family Physician. 66 (5): 823–8. PMID 12322775.
- ^ a b Lang, CT; Landon, MB (March 2010). "Uterine rupture as a source of obstetrical hemorrhage". Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology. 53 (1): 237–51. doi:10.1097/GRF.0b013e3181cc4538. PMID 20142660.
- ^ a b c d e Murphy, DJ (April 2006). "Uterine rupture". Current Opinion in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 18 (2): 135–40. doi:10.1097/01.gco.0000192989.45589.57. PMID 16601473. S2CID 23617249.
- ^ a b c Mirza, FG; Gaddipati, S (April 2009). "Obstetric emergencies". Seminars in Perinatology. 33 (2): 97–103. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2009.01.003. PMID 19324238.
- ^ Togioka, Brandon M.; Tonismae, Tiffany (June 27, 2022). "Uterine Rupture". StatPearls. PMID 32644635. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ Larrea, NA; Metz, TD (January 2018). "Pregnancy After Uterine Rupture". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 131 (1): 135–137. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000002373. PMID 29215521.
- ^ Berhe, Y; Wall, LL (November 2014). "Uterine rupture in resource-poor countries". Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey. 69 (11): 695–707. doi:10.1097/OGX.0000000000000123. PMID 25409161. S2CID 22593593.
- ^ Chibber R, El-Saleh E, Fadhli RA, Jassar WA, Harmi JA (March 2010). "Uterine rupture and subsequent pregnancy outcome - how safe is it? A 25-year study". J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 23 (5): 421–4. doi:10.3109/14767050903440489. PMID 20230321. S2CID 13566623.
- ^ Walsh CA, O'Sullivan RJ, Foley ME (2006). "Unexplained prelabor uterine rupture in a term primigravida". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 108 (3 Pt 2): 725–7. doi:10.1097/01.AOG.0000195065.38149.11. PMID 17018479. S2CID 8021433.
- ^ Byers, Peter H. (2019). Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. University of Washington, Seattle. PMID 20301667.
