Triisodontidae
| Triisodontidae | |
|---|---|

| |
| Skull and jaws of Triisodon quivirensis | |

| |
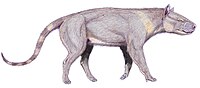
| Life restoration of Triisodon quivirensis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Mesonychia |
| Family: | †Triisodontidae Trouessart, 1904 |
| Type genus | |
| †Triisodon | |
| Genera | |
Triisodontidae is an extinct, probably paraphyletic, or possibly invalid family of mesonychian placental mammals. Most triisodontid genera lived during the Paleocene in North America, but the genus Andrewsarchus (if it is a mesonychian, and not an artiodactyl) is known from the middle Eocene of Asia.[2] Triisodontids were the first relatively large predatory mammals to appear in North America following the extinction of the non-bird dinosaurs.[3] They differ from other mesonychian families in having less highly modified teeth.[4]
Because of their comparatively simpler teeth, the triisodontids are regarded as basal mesonychids. A recent study found them to be a paraphyletic assemblage of stem-mesonychians.[5]
References
- ^ "Triisodontidae". paleobiodb.org. Retrieved 2021-08-27.
- ^ McKenna, M. C & S. K. Bell (1997). Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11012-X.
- ^ Clemens, W.A. & T.E. Williamson (2005). "A new species of Eoconodon (Triisodontidae, Mammalia) from the San Juan Basin, New Mexico". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 25 (1): 208–213. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2005)025[0208:ANSOET]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 86047162.
- ^ Matthew, W.D. (1937). "Paleocene faunas of the San Juan Basin, New Mexico". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. 30 (3532). American Philosophical Society: 1–510. Bibcode:1937Natur.140...46C. doi:10.2307/1005521. JSTOR 1005521.
- ^ Sarah L. Shelley, Thomas E. Williamson, Stephen L. Brusatte, Resolving the higher-level phylogenetic relationships of “Triisodontidae” (‘Condylarthra’) within Placentalia, October 2015, Society of Vertebrate Paleontology (abstract)