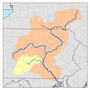
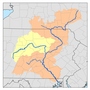
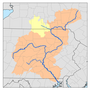
Tioga River (Chemung River tributary)
| Tioga River | |
|---|---|
 The Tioga River near the Pennsylvania–New York state line | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New York, Pennsylvania |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Armenia Township, Bradford County, Pennsylvania |
| • coordinates | 41°45′40″N 76°51′39″W / 41.76111°N 76.86083°W[1] |
| Mouth | Chemung River |
• location | Painted Post, Steuben County, New York |
• coordinates | 42°09′07″N 77°05′25″W / 42.15194°N 77.09028°W[1] |
| Length | 58 mi (93 km)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Lindley, New York[3] |
| • average | 821 cu ft/s (23.2 m3/s) |
| • minimum | 7.2 cu ft/s (0.20 m3/s) (September 1, 1939)[3] |
| • maximum | 63,000 cu ft/s (1,800 m3/s) (June 23, 1972)[3] |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Crooked Creek, Cowanesque River, Canisteo River |
The Tioga River (/ˈtaɪoʊɡə/ TY-o-gə) is a tributary of the Chemung River, approximately 58 miles (93 km) long,[2] in northern Pennsylvania and western New York in the United States. It drains a region of ridges in the northern Allegheny Plateau in the watershed of the Susquehanna River.
In the 19th century, trees logged in the Tioga Valley were extensively used in shipbuilding. Logs were floated down the Tioga to the Chemung and on to the Susquehanna River, the Chesapeake Bay, and the shipyards of Baltimore.
Course

The Tioga River rises in the mountains of western Bradford County and flows initially southwest into Tioga County, passing through Tioga State Forest. In southern Tioga County it turns north, cutting gaps in four separate ridges while flowing past Blossburg and Mansfield, then through Tioga Reservoir. North of Tioga it receives Crooked Creek from the west, then crosses into Steuben County, New York, near Lawrenceville, Pennsylvania. It receives the Cowanesque River from the west approximately one mile (1.6 km) north of the state line, then receives the Canisteo River from the west in southeastern Steuben County, approximately 10 miles (16 km) southwest of Corning. It joins the Cohocton River at Painted Post, just west of Corning, to form the Chemung River, a tributary of the Susquehanna.
Tioga Reservoir
The Tioga River has one major impoundment, the Tioga Reservoir, formed by a dam just before the borough of Tioga, Pennsylvania. The lake has a surface area of 498 acres (2.02 km2) and is administered by the United States Army Corps of Engineers, which built the Tioga Dam from 1973 to 1979. Built together with the adjoining Hammond Dam and Hammond Lake (on Crooked Creek), the total project cost $200 million.
The dam projects were initially authorized by the United States Congress in the Flood Control Act of 3 July 1958 (Public Law 85-500). Construction was begun in the aftermath of the devastating floods caused by Hurricane Agnes in June 1972, which resulted in widespread damage along the rivers. A channel connects the two lakes so that Hammond Lake (which has greater storage capacity) may be used to store excess (flood) water from Tioga Lake.
In addition to supporting flood control on the Chemung and Susquehanna rivers, the dams are also meant to help improve water quality by decreasing the acidity of water in the Tioga River downstream of the dams; it is diluted by addition of the more neutral waters of Crooked Creek. The Tioga River's acidity is caused by acid mine drainage.
The lakes also offer recreational opportunities, including camping, boating, fishing, swimming, and hiking on area trails.
See also
References
- ^ a b "Tioga River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
- ^ a b U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map, accessed August 8, 2011
- ^ a b c "01520500 Tioga River near Lindley, NY, Water Data Report 2013" (PDF). National Water Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1930–2013. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
External links
- U.S. Geological Survey: PA stream gaging stations
- Rootsweb: Tioga River history
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers page on Tioga-Hammond Lakes
- History of the Hammond-Tioga Dam Project
- Chesapeake Bay Program - The Tioga River Watershed
- Chesapeake Bay Program - Tioga River - Canisteo River To Chemung River Watershed