Steroid rosacea
| Steroid rosacea | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Steroid-induced rosacea is an iatrogenic condition (induced by the physician or patient) from the use of either systemic steroid or topical steroids. It is nearly identical to steroid induced acne from the standpoint of etiology.[1]
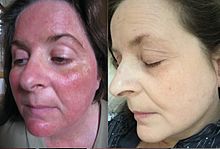
Cause
Steroid-induced rosacea can be caused by the prolonged used of a topical steroid on the face. Topical steroid comes in 7 different strengths (Some countries use 4 categories). Class I is super potent, and class VII is very weak. Usually, any categories of steroids over class VI can induce rosacea with prolonged use. The typical presentation is inflammatory acne lesions consisting of pustules, papules, and cysts. The patient often admits to the daily use of a topical steroid, often being under the advisement of a physician. Examination of the pustules often revealed inflammatory cells, and in many cases, numerous motile demodex mites.
Prevention
Physicians need to be aware of the danger of topical steroids. Only mild steroids should be applied to the face. The use of the topical steroid should be limited to the condition. Alternate week therapy or 3 consecutive days a week therapy is better than continuous therapy in preventing steroid-induced rosacea. Only the mildest topical steroid should be used on the face if a condition warrants such use. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) does not necessary prevent steroid induced rosacea. Similar conditions have been seen with both Elidel and Protopic, possibly from immunosuppression and Demodex or bacterial growth.
Treatment
Treatment often involves the gradual weaning off the topical steroid, and the use of a systemic anti-inflammatory antibiotic. If the patient is using a strong topical steroid, he or she is weaned to a weaker class VI or VII steroid. Usually, they are to use the substitute steroid daily, then only on weekends, then stop completely. The facial dermatitis and discomfort often worsen when they stop the offending steroid. The oral antibiotic will decrease the inflammatory nature of the lesions. The antibiotic of choice is usually a tetracycline antibiotic. Additionally, tacrolimus combined with oral antibiotics has proven to speed up the recovery process.[1]
