St. Thomas Evangelical Church of India
| St. Thomas Evangelical Church of India | |
|---|---|
 St Thomas Evangelical Church Of India Emblem | |
| Abbreviation | STECI |
| Type | Evangelical Protestant |
| Classification | Syrian Christian, Saint Thomas Syrian Christians |
| Scripture | Holy Bible |
| Polity | Episcopal |
| Governance | Democratic |
| Presiding Bishop | Most Rev Dr Thomas Abraham |
| Prathinidhi sabha Adhyakshan | Rt Rev Dr Abraham Chacko |
| Language | Malayalam, English, Hindi, Odia, Tamil, Kannada, Marathi, Gujrati, Telugu, |
| Liturgy | West Syriac Rite (Reformed) |
| Headquarters | Manjadi, Thiruvalla Kerala, India |
| Territory | Universal |
| Possessions | India, United States, Canada, Europe, Great Britain-London & Belfast, Middle East, Singapore |
| Origin | 26 January 1961 Thaimala, Thiruvalla |
| Independence | 1961 |
| Recognition | Independent Episcopal Church, 1961 |
| Separated from | Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church (1961) |
| Congregations | 350+ |
| Members | 100,000+ |
| Ministers | Bishops- 6, Clergy- 150+ |
| Missionaries | 400+ |
| Publications | suvisesha prakasini |
| Official website | http://steci.org/ |
| Slogan | FOR THE WORD OF GOD AND FOR THE TESTIMONY OF JESUS CHRIST (REV. 1:9) |
| Part of a series on |
| Christianity in India |
|---|
 |
St. Thomas Evangelical Church of India (STECI) is an Oriental Protestant (Reformed Orthodox) episcopal denomination based in Kerala, India.
The church originated from a schism in the Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church in 1961 and forms a part of the Saint Thomas Syrian Christian community.
The headquarters of the church is at Tiruvalla, Kerala.
History
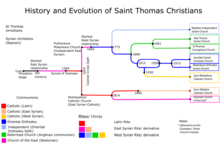
The St. Thomas Evangelical Church is one of several groups of Saint Thomas Christians who trace their origins to St. Thomas the Apostle who, according to their tradition, came to India in AD 52.[1]
Until 1961, the Church's history was deeply connected to the Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church.
In the 1800s, South Indian Christians were in contact with British missionaries during the time of British colonialism. The missionaries facilitated the translation of the Bible into Malayalam in 1811; this was the first vernacular Bible in Kerala. Further changes introduced by the influence of missionaries led to a schism within the Thomas Christians.[2]
By the 1830s, some clergy in the St Thomas Church were looking at reform, particularly in the area of rituals. This movement led to the St Thomas Church establishing the Mar Thoma Evangelistic Association (MTEA) in 1888.[3]
In the 1950s, reforms within the Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church led to some members creating the Mar Thoma Pathiopadesa Samathy (St Thomas Organisation for Sound Doctrine) in 1952. In 1960, four presbyters (P John Varghese, P I Mathal, CM Vaghese and KO John) were suspended. This led to the establishment of the St. Thomas Evangelical Church of India (STECI), on January 26, 1961, with 20 ministers and 25,000 lay Christians.[4]
STECI established the Jubilee Memorial Bible College in Chennai in August 1987.[5] The college trains students from almost 20 different denominations and has links to the Biblical Graduate School of Theology in Singapore and Columbia International University in the US.
Beliefs
Mission statement
STECI was formed with a three-pronged mission;
- Safeguarding sound doctrine
- Living a holy life
- Obeying the Great Commission to evangelise India [6]
Basic teachings
STECI believes in; the Trinity, the Second Coming, Sola Scriptura of 66 books of the Bible, salvation by faith (not works), safeguarding sound doctrine, evangelism and sharing the news about Jesus, royal priesthood and prayers to Jesus for the living.[7]
Sacraments
STECI members incorporate two sacraments into their lives; these are baptism and the Lord’s Supper.[8]
Diocese
In 2023, the Church has seven dioceses. Four of these are in Kerala; the others are "Bahya Kerala" ‘’Gulf and Singapore’’ and ‘’North America and Europe’’.[9] The dioceses cover 240 parishes.[10]

Bishops
- Bishop KN Oommen (Late)
- Bishop P John Varughese (Late)
- Bishop Dr. TC Cherian (Retd.)
- Bishop Dr. MK Koshy (Retd.)
- Bishop A.I Alexander (Retd.)
- Bishop Dr CV Mathew (Retd.)
- Bishop Most Rev Dr Thomas Abraham (Presiding Bishop from 2019)
- Bishop Rt Rev Dr Abraham Chacko (Prathinidhi sabha Adhyakshan from 2019)
STECI Boards
- Board for Evangelistic Work
- Board for Youth Work
- Board for Women's Work
- Board for Sunday School Work
- Education Board
- Department of Music & Communications
See also
External links
References
- ^ Curtin, D. P.; James, M.R. (June 2018). The Acts of St. Thomas in India. ISBN 9781087965710.
- ^ STECI Fellowship website
- ^ Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church website
- ^ STECI Fekllowship website
- ^ Jubilee Memorial Bible College official website
- ^ Indian Christians United website
- ^ SCETI Atlanta website
- ^ STECI Atlanta website
- ^ Official website, Retrieved 2023-05-29
- ^ STECI Kuwait website, Retrieved 2023-05-29

