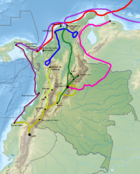
Spanish conquest of New Granada
| Conquest of New Granada | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Spanish colonization of the Americas | |||||||
 Conquest map of Colombia | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
Calima Nariño Quimbaya San Agustín Tairona Zenú | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 5,250,000 deaths as a result of the conquest (87.5% of the population)[1][2] | |||||||

Alonso de Ojeda (1499-1501)
Vasco Núñez de Balboa (1513)
Pedro Arias Dávila (1513-1519)
Pascual de Andagoya, Diego de Almagro and Francisco Pizarro (1515-1529)
Pedro de Heredia and his lieutenants (1532-1538)
Sebastián de Belalcázar (1533-1539)
Lieutenants of Sebastián de Belalcázar (1533-1539)
Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada (1536-1538)
Nikolaus Federmann (1537-1539)


Sebastián de Belalcázar (1514–1539)
The Spanish conquest of New Granada refers to the conquest between 1525 and 1540 by the Spanish monarchy of the Chibcha language-speaking nations of modern-day Colombia and Panama, mainly the Muisca and Tairona that inhabited present-day Colombia, beginning the Spanish colonization of the Americas.[3] It is estimated that around 5.25 million people died as a result of Spanish Conquest, either by disease or direct conflict. This represents 87.5% of the Pre-Columbian population of Colombia.[4][2]
Pre-Columbian

The first inhabitants of Colombia were migrating members of the Mesoamericans who established themselves in the area c. 1200 BC followed by two other waves c. 500 BC and a third one between 400 and 300 BC. Later on the group of Arawak coming from southern South America made presence in the area, and a third wave of migrating groups, the warring Caribs established in the lower lands and pushed the Mesoamericans to the mountains. The southern areas of present-day Colombia were also part of the Inca Empire.[5]
There were two main tribes that were socially and economically developed at the time of the Spanish arrival: the Muisca, and the Tairona. Both were within the Chibchan Nations.
By the 16th century, the Chibchas, were divided into two main groups: the Muisca, located in the plateaus of Cundinamarca and Boyacá, and the Tairona, who settled along the northern spur of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta in present-day Magdalena, Cesar and La Guajira departments.
Spanish conquest
The territory was first sighted by Spanish explorer Alonso de Ojeda in 1499,[6] though he never landed. A short time later, Juan de la Cosa, another Spanish explorer, landed on what is today called Cabo de la Vela (Cape of Sails) in the Guajira Peninsula.[7]
In 1502, on another coast of present-day Colombia, near the Gulf of Urabá, Spanish explorers led by Vasco Núñez de Balboa explored and conquered the area near the Atrato River. There they founded Santa María la Antigua del Darién (c. 1509) and the now-vanished town of San Sebastian de Urabá (c. 1508–1510), the first two European settlements on the mainland of the Americas.[8]
On July 29, 1525, the city of Santa Marta was founded in the northern coast of Colombia by the Spanish conqueror Rodrigo de Bastidas.
In April 1536 the Spanish conquistador Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada led the main expedition into the heart of the Andes, where the Muisca Confederation was located, with around 800 Spanish soldiers and 85 horses. Around the settlements of Suesca and Nemocón the de Quesada expedition faced the first attempt of Muisca active resistance in March 1537: the Muisca zipa Tisquesusa made a failed effort to oust the invaders who then gave the first demonstration of their superior weaponry.
In April of the same year, De Quesada, was continuously attacked by Tisquesusa's subjects on the Bogotá savanna, but managed to take advantage of rivalries among various indigenous chiefs to go weakening the power of the zipa of Bacatá. The caciques of Chía and Suba were among the first to submit and collaborate with the Spanish, while men of Tisquesusa suffered defeat after defeat and failed to oppose the Spanish, who had horses, dogs, and firearms, rather than primitive wooden weapons: spears, clubs, and darts thrown with shuttles. Tisquesusa continued to harass and attack the Spanish, but in some obscure skirmish, late 1537, he died, without the Spanish knowing immediately and without knowing anything of his treasure.[9]
Tisquesusa's successor, his nephew Sagipa (also described as Saquesazipa), submitted soon to the conquistadors. Soon the relations between the Spanish and Sagipa deteriorated. Those eager to locate the lost treasure of the zipa apprehended Sagipa and subjected to trial, accusing him of rebellion against the Spaniards and refusing to reveal the site where the fabulous treasure was hidden.
Tundama was another cacique who had appeared ready to fight. This bellicose leader called his subjects and requested the assistance of neighboring caciques from Cerinza, so when Hernán Pérez de Quesada, brother of Gonzalo, came, he found the most ordered troops and more martial aspect to here they had been among Muisca, formed by steps in different bodies, all festooned with feathers of different colors. In this battle, called the Battle of Bonza, indigenous forces formed a desperate resistance. Hernán de Quesada was in danger of losing his life by falling from his horse in the midst of enemies, but at last, broke the indigenous people and trampled them by horses, staining the marshes of Bonza with indigenous blood.[10]
Finally on August 6, 1538, the city of Bogotá (named originally Santa Fé de Bogotá) was founded on the remains of the original southern Muisca capital Bacatá.

Isolated Chibcha
Dorasque
Waimi
Ngäbe
The Ngäbe or Guaymí people are an indigenous group living mainly within the Ngäbe-Buglé comarca in the Western Panamanian provinces of Veraguas, Chiriquí and Bocas del Toro. The Ngäbe also have five indigenous territories in southwestern Costa Rica encompassing 23,600 hectares: Coto Brus, Abrojos Montezuma, Conte Burica, Altos de San Antonio and Guaymi de Osa.[11] There are approximately 200,000-250,000 speakers of Ngäbere today.
Guaymí is an outdated name derived from the Buglere term for them (guaymiri). Local newspapers and other media often alternatively spell the name Ngäbe as Ngobe or Ngöbe because Spanish does not contain the sound represented by ä, a low-back rounded a, slightly higher than the English aw in the word saw and Spanish speakers hear ä as either an o or an a. Ngäbe means people in their native language- Ngäbere. A sizable number of Ngäbe have migrated to Costa Rica in search of work on the coffee fincas. Ngäbere and Buglere are distinct languages in the Chibchan language family. They are mutually unintelligible.
Bokota
The Bokota people, also called Bogotá,[12] or Buglere, are an Amerindian ethnical group in Panama. They live in Bocas del Toro and north of Veraguas.[13] Bokota Indians live in the same region as the Teribe or Naso Indians.
As of 2000, there were 993 Bogota living in Panama. They are the smallest tribe in Panama and live in the west of the country.[13]
Arwako-Chimila

This region was the first explored when Santa Marta was founded in 1525
Tairona
- Main explorers and conquistadors
- Rodrigo de Bastidas (1524–25), Juan de Céspedes (1524–1529, 1543–1546)
- Ambrosius Ehinger (1529–1533)
- Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, Hernán Pérez de Quesada, 800 more (1536)
- Pedro de Ursúa (1545–1561)
The Tairona inhabit the northern and central parts of the isolated mountain range of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta. The Tairona were divided into two groups the coastal Tairona by the Caribbean Sea, and the mountain Tairona in higher altitude cloud forests of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta. The lowland Tairona fished and produced salt, which they traded for cotton cloth and blankets with the Andes civilisation of the Muisca, the Guane and Chimila and other neighbouring groups. Both Tairona populations lived in numerous small and well-organized towns, connected by stone roads.
Kankuamo
Of the four indigenous groups living in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, the Kankuamo are the least contacted and still retained their independency.
Kogi
Arhuaco
The Arhuacos live in the upper valleys of the Piedras River, San Sebastian River, Chichicua River, Ariguani River, and Guatapuri River, in an indigenous territory in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta. Their traditional territory before the Spanish colonization, was larger than today's boundaries which exclude many of their sacred sites that they continue to visit today, to pay offerings. These lost territories are the lower parts by the steps of the mountains, lost to colonization and farming.
Chimila


The Chitarero inhabit the northern flank of the Andes in the Maracaibo Basin, Norte de Santander
- Main explorers and conquistadors
- Ambrosius Ehinger (1529–33)
- Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, Hernán Pérez de Quesada, and others (1536)
Chitarero
- Main explorers and conquistadors
- Ambrosius Ehinger (1529–33)
- Georg von Speyer (1535–38), Nikolaus Federmann, Miguel Holguín y Figueroa (1535–39)
- Hernán Pérez de Quesada (1541)
- Juan Maldonado (1543–72)
- Pedro de Ursúa (1545–61)
Kuna-Colombian
Kuna
- Main explorers and conquistadors
- Columbus (1502)
- Alonso de Heredia, Francisco Pizarro (1509–10)
- Vasco Núñez de Balboa, Francisco Pizarro, Pedro Arias Dávila (1513)
- Francisco Pizarro, Pascual de Andagoya, Diego de Almagro, Bartolomé Ruiz (1515–29)
Nutabe[14]
- Main conquistadors
- Juan de Ampudia (1535–41), Jorge Robledo (1535–46)
- Gaspar de Rodas (1539–81)
The Nutabe traded with neighboring tribes, for which they used a strategic bridge over the San Andreas River.
Their society was organized into small hereditary chiefdoms, individually scattered and lacking any central power. However, faced with the Spanish conquest (and against other situations overall incidence), these tribes used to work together in confederations. Mainly a peaceful group, when the Spanish conquistadors arrived, they defended their territories When the Spanish arrived, the leadership of the tribe was exercised by a cacique named Guarcama.
Motilon
- Main conquistadors
- Ambrosius Ehinger (1529–33)
- Georg von Speyer (1535–38), Nikolaus Federmann, Miguel Holguín y Figueroa (1535–39)

Their western neighbours were the Guane, southern the Muisca, northwest the Chitarero, and north and east the U'wa
U'wa
- Main conquistadors
- Nikolaus Federmann, Miguel Holguín y Figueroa (1535–39)
Lache
- Main conquistadors
- Nikolaus Federmann, Miguel Holguín y Figueroa (1535–39)
- Hernán Pérez de Quesada (1541)
- soldier Lázaro Fonte
| Settlement | Department | Year explored | Note(s) | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jericó | Boyacá | 1541 | [15] |  |
| Guacamayas | Boyacá | 1541 | [16] |  |
| Chiscas | Boyacá | 1541 | [17] |  |
| Chita | Boyacá | 1541 | [16] |  |
| Panqueba | Boyacá | 1541 | [16] |  |
| Güicán | Boyacá | 1541 | [18] |  |
| El Cocuy | Boyacá | 1541 | [16][19] |  |
Guane

- Main conquistador Martín Galeano
| Name bold is founded |
Department | Date | Year | Note(s) | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vélez | Santander | 14 September | 1539 | [20] |  |
| Oiba | Santander | 28 February | 1540 | [21] |  |
| Charalá | Santander | 23 July | 1540 | [22] |  |
| Simacota | Santander | 1551 |  |
Muisca
 |
Feb 1537 | First contact @ Chipatá | ||
| Mar-Apr 1537 | Expedition into Muisca Confederation | |||
| 20 Apr 1537 | Conquest of Funza upon zipa Tisquesusa | |||
| May-Aug 1537 | Expedition & conquest in Tenza Valley | |||
| 20 Aug 1537 | Conquest Hunza, zaque Quemuenchatocha | |||
| Early Sep 1537 | Conquest Sugamuxi, iraca Sugamuxi | |||
 |
Oct 1537-Feb 1538 | Other foundations on Altiplano & valleys | ||
| 6 Aug 1538 | Foundation Santafé de Bogotá, by Gonzalo | |||
| 20 Aug 1538 | B. of Tocarema; Spanish & zipa beat Panche | |||
| 6 Aug 1539 | Foundation Tunja, by Gonzalo Suárez | |||
| 15 Dec 1539 | Conquest Tundama, by Baltasar Maldonado | |||
| Early 1540 | Decapitation last zaque Aquiminzaque, Hernán | |||
| The Muisca established on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense one of the four grand civilisations of the pre-Columbian Americas | ||||
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| El Dorado | Sun Temple | tunjo | El Infiernito | |
| Their southwestern neighbours, inhabiting the highest parts under páramo conditions; the Sutagao were the southernmost Chibcha speakers | ||||
In the centuries before the Spanish conquest of the Muisca in 1537, the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, high plateau of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes, was inhabited by the Muisca people. They were an advanced civilisation of mainly farmers and traders.[23]
The Muisca did not construct stone architecture, as the Maya, Aztec and Inca did; their houses, temples and shrines were built with wood and clay. They were called "Salt People" because of their extraction of halite from various salt mines on the Altiplano, predominantly in Zipaquirá, Nemocón and Tausa.
The Muisca were polytheistic and their religion and mythology was closely connected with the natural area they were inhabiting. They had a thorough understanding of astronomical parameters and developed a complex luni-solar calendar; the Muisca calendar. According to the calendar they had specific times for sowing, harvest and the organisation of festivals where they sang, danced and played music and drank their national drink chicha in great quantities.
The most respected members of the community were mummified and the mummies were not buried, yet displayed in their temples, in natural locations such as caves and even carried on their backs during warfare to impress their enemies.
Their art is the most famous remnant of their culture, as living spaces, temples and other existing structures have been destroyed by the Spanish who colonised the Muisca territories. A primary example of their fine goldworking is the Muisca raft, together with more objects made of gold, tumbaga, ceramics and cotton displayed in the Museo del Oro in Bogotá, the ancient capital of the southern Muisca.
The Muisca were a predominantly agricultural society with small-scale farmfields, part of more extensive terrains. To diversify their diet, they traded mantles, gold, emeralds and salt for fruits, vegetables, coca, yopo and cotton cultivated in lower altitude warmer terrains populated by their neighbours, the Muzo, Panche, Yarigui, Guane, Guayupe, Achagua, Tegua, Lache, Sutagao and U'wa. Trade of products grown farther away happened with the Calima, Pijao and Caribbean coastal communities around the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta.
The people used a decimal counting system and counted with their fingers. Their system went from 1 to 10 and for higher numerations they used the prefix quihicha or qhicha, which means "foot" in their Chibcha language Muysccubun. Eleven became thus "foot one", twelve "foot two", etc. As in the other pre-Columbian civilizations, the number 20 was special. It was the total number of all body extremities; fingers and toes. The Muisca used two forms to express twenty: "foot ten"; quihícha ubchihica or their exclusive word gueta, derived from gue, which means "house". Numbers between 20 and 30 were counted gueta asaqui ata ("twenty plus one"; 21), gueta asaqui ubchihica ("twenty plus ten"; 30). Larger numbers were counted as multiples of twenty; gue-bosa ("20 times 2"; 40), gue-hisca ("20 times 5"; 100). The Muisca script consisted of hieroglyphs, only used for numerals.[24]
The conquest of the Muisca was the heaviest of all four Spanish expeditions to the great civilisations of the Americas.[25] More than 80 percent of the soldiers and horses that started the journey of a year to the northern Muisca Confederation didn't make it.[26][27][28] Various settlements were founded by the Spanish between 1537 and 1539.[29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38]

Sutagao
The Sutagao are the Chibcha-speaking[39] indigenous people from the region of Fusagasugá, Bogotá savanna, Cundinamarca, Colombia. Knowledge about the Sutagao has been provided by scholar Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita.[40]
Before the Spanish conquest, the Sutagao were in conflict with the Muisca to the northeast. Zipa Saguamanchica conquered the Sutagao around 1470 when the cacique of the Sutagao lost the Battle of Pasca. Conquistador Juan de Céspedes, under command of Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada submitted the Sutagao to the new rule of the New Kingdom of Granada.[39][41]
The Sutagao inhabited the region until a new town was founded by Bernardino Albornoz between 5 and 13 February in 1592. During the visit of Miguel de Ibarra there were 759 indigenous people residing in Fusagasugá.
When Aróstequi arrived in February 1760, the indigenous population had dwindled to 85, and there were 644 new settlers divided among 109 families.
See also
- List of conquistadors in Colombia
- Comparison Chibcha words[broken anchor]
- Spanish conquest of the Muisca
- Spanish conquest of Honduras
- Hernán de Quesada, Juan de Céspedes
- Gonzalo de Quesada, Sebastián de Belalcázar, New Kingdom of Granada
References
- ^ Jaime Jaramillo Uribe (1989). Ensayos de historia social: La sociedad neogranadina. Santa Fe de Bogotá: Tercer Mundo, págs. 87. ISBN 978-9-58601-236-2.
- ^ a b "Caída de la población indígena en Colombia, 1500-1630: tres escenarios" [Decline of the indigenous population in Colombia, 1500-1630: three scenarios] (PDF). Banco de la República.
- ^ Tairona Heritage Trust: Tairona history to the time of the Spanish Invasion Tairona Heritage Trust Accessed 21 August 2007.
- ^ Jaime Jaramillo Uribe (1989). Ensayos de historia social: La sociedad neogranadina. Santa Fe de Bogotá: Tercer Mundo, pp. 87. ISBN 978-9-58601-236-2.
- ^ All Empires: Central Andes Allempires.info Accessed 22 August 2007.
- ^ (in Spanish) Biography Alonso de Ojeda
- ^ "Bienvenido a Fuerza Aérea Colombiana".
- ^ Víctor Manuel Patiño, Historia dela Cultura Material en la América Equinoccial, Chapter 21. Accessed 15 Nov. 2010. Archived 2007-09-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Langebaek, Carl (1996). Historia de Colombia: el establecimiento de la dominación española (in Spanish). Bogotá, Biblioteca Luis Ángel Arango: Imprenta Nacional de Colombia.
- ^ Acosta, Joaquín (1901). Compendio histórico del descubrimiento y colonización de la Nueva Granada en el siglo XVI. Bogotá, Biblioteca Luis Ángel Arango: Imprenta De La Luz. pp. Chapter XIII.
- ^ Hugh Govan and Rigoberto Carrera (2010) Strengthening Indigenous Cultural Heritage through Capacity Building in Costa Rica. In Biocultural Diversity Conservation eds Luisa Maffi and Ellen Woodley. Earthsacan.
- ^ "Bogota Language (Bogotá, Bocota)." Native Languages. (retrieved 23 Feb 2011)
- ^ a b "Indigenous Peoples in Panama." Archived 2011-03-02 at the Wayback Machine International Work Group for Indian Affairs. (retrieved 23 Feb 2011)
- ^ Note: Nutabes is Spanish plural; convention is <singular name> <people>
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Jericó
- ^ a b c d (in Spanish) Official website Guacamayas
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Chiscas
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Güicán
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website El Cocuy
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Vélez
- ^ (in Spanish) Fundaciones de ciudades y poblaciones - Banco de la República
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Charalá
- ^ Ocampo López, 2007, p.26
- ^ Izquierdo Peña, 2009
- ^ (in Spanish) Personajes de la Conquista a América - Banco de la República
- ^ (in Spanish) List of conquistadors led by Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada - Banco de la República
- ^ (in Spanish) Biography Hernán Pérez de Quesada - Banco de la República
- ^ (in Spanish) Conquista rápida y saqueo cuantioso de Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Chipatá
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Guachetá
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Lenguazaque
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Suesca
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Funza
- ^ (in Spanish) Engativá celebra hoy sus 458 años - El Tiempo
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Chocontá
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Tenza
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Turmequé
- ^ (in Spanish) Official website Sutatausa
- ^ a b (in Spanish) Indios Sutagaos
- ^ (in Spanish) Los Sutagaos
- ^ (in Spanish) Historia de Fusagasugá Archived 2015-05-03 at the Wayback Machine
Bibliography and further reading
- Casilimas Rojas, Clara Inés (2005), "Expresión de la modalidad en la lengua uwa" (PDF), Amerindia (in Spanish), 29/30: 247–262, retrieved 2016-07-11
- Izquierdo Peña, Manuel Arturo (2009), The Muisca Calendar: An approximation to the timekeeping system of the ancient native people of the northeastern Andes of Colombia (PhD), Université de Montréal, pp. 1–170, arXiv:0812.0574
- Ocampo López, Javier (2007), Grandes culturas indígenas de América - Great indigenous cultures of the Americas (in Spanish), Bogotá, Colombia: Plaza & Janes Editores Colombia S.A., pp. 1–238, ISBN 978-958-14-0368-4
- Quesada Pacheco, Miguel Ángel; Rojas Chaves, Carmen (1999), Diccionario boruca - español, español - boruca (in Spanish), Universidad de Costa Rica, pp. 1–207, ISBN 978-9977-67-548-0, retrieved 2016-07-11
- Reichel-Dolmatoff, Gerardo (1947), "La lengua chimila - The Chimila language", Journal de la Société des Américanistes (in Spanish), 36: 15–50, doi:10.3406/jsa.1947.2358, retrieved 2016-07-11
- Saravia, Facundo Manuel (2015), Curso de aproximación a la lengua chibcha o muisca - Nivel 1 - Introduction course to the Chibcha or Muisca language - Level 1 (PDF) (in Spanish), Fundación Zaquenzipa, pp. 1–81, retrieved 2016-07-08
- Zerda, Liborio (1947) [1883], El Dorado (PDF) (in Spanish), retrieved 2016-07-08
- Andagoya, Pascual de. "Narrative of Pascual de Andagoya". Narrative of the Proceedings of Pedrarias Davila. The Hakluyt Society. Retrieved 21 June 2019 – via Wikisource.