Portal:Language
Introduction




Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning.
Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between 5,000 and 7,000. Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whistling, signing, or braille. In other words, human language is modality-independent, but written or signed language is the way to inscribe or encode the natural human speech or gestures.
Depending on philosophical perspectives regarding the definition of language and meaning, when used as a general concept, "language" may refer to the cognitive ability to learn and use systems of complex communication, or to describe the set of rules that makes up these systems, or the set of utterances that can be produced from those rules. All languages rely on the process of semiosis to relate signs to particular meanings. Oral, manual and tactile languages contain a phonological system that governs how symbols are used to form sequences known as words or morphemes, and a syntactic system that governs how words and morphemes are combined to form phrases and utterances.
The scientific study of language is called linguistics. Critical examinations of languages, such as philosophy of language, the relationships between language and thought, how words represent experience, etc., have been debated at least since Gorgias and Plato in ancient Greek civilization. Thinkers such as Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712–1778) have argued that language originated from emotions, while others like Immanuel Kant (1724–1804) have argued that languages originated from rational and logical thought. Twentieth century philosophers such as Ludwig Wittgenstein (1889–1951) argued that philosophy is really the study of language itself. Major figures in contemporary linguistics of these times include Ferdinand de Saussure and Noam Chomsky. (Full article...)
Selected language -

Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic (/sləˈvɒnɪk, slæˈvɒn-/ slə-VON-ik, slav-ON-) is the first Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic subgroup of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family and remains the liturgical language of many Christian Orthodox churches. Until the reforms of Patriarch Nikon of Moscow between 1652 and 1666, Church Slavonic was the mandatory language of the Russian Orthodox Church.
Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with standardizing the language and undertaking the task of translating the Gospels and necessary liturgical books into it as part of the Christianization of the Slavs. It is thought to have been based primarily on the dialect of the 9th-century Byzantine Slavs living in the Province of Thessalonica (in present-day Greece). (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that a historian lamented the lack of English-language translations for the work of Aracy Amaral despite it being "a vital reference for the study of art history in Brazil"?
- ... that American educator Gilbert Eastman, who acted in and wrote American Sign Language plays, won an Emmy Award in 1993?
- ... that English missionary Reverend Thomas Sparshott co-wrote a book in Swahili, and his daughter Margaret Elwyn Sparshott was responsible as matron for 22 hospitals in World War I?
- ... that Navidades by Luis Miguel was the first Spanish-language album to enter the Billboard Top Holiday Albums since 1966?
- ... that Panzer Dragoon II Zwei features a villain inspired by Dune's Baron Harkonnen, visuals inspired by the work of Jean Giraud, and a fictional language?
- ... that the name of the International Institute of Modern Letters has been criticised by its founder Bill Manhire for being "almost at odds with the fine use of language"?
More did you know -
- ...that most of the 8,000 speakers of the Niuean language live outside the borders of Niue?
- ...that hundreds of words still in use today, including accident, cinnamon, desk, scissors, vacation, and Valentine, first appear in manuscripts written by Geoffrey Chaucer in the 1300s?
- ...that the Jru' language, an indigenous language of Laos, was once written in a secret script?
- ...that during the filming of The Linguists in the Andes, the cast coped with altitude sickness by drinking coca leaf tea?
Categories
Linguistics: Computational linguistics • Grammar • Historical linguistics • Morphology • Phonetics • Phonology • Pragmatics • Reading • Semantics • Sociolinguistics • Syntax • Writing
Languages: Language families • Pidgins and creoles • Sign languages
Linguists: By nationality • Historical linguists • Morphologists • Phoneticians • Phonologists • Sociolinguists • Syntacticians • Translators
Stubs: Constructed languages • Languages • Linguists • Pidgins and creoles • Typography • Vocabulary and usage • Writing systems
Full Language category tree |
|---|
Select [►] to view subcategories |
Related portals
Selected topic -
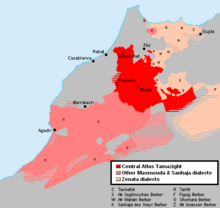
Central Atlas Tamazight or Atlasic (native name: ⵜⴰⵎⴰⵣⵉⵖⵜ Tamazight [tæmæˈzɪxt, θæmæˈzɪxθ]; Arabic: أمازيغية أطلس الأوسط) is a Berber language of the Afroasiatic language family spoken by 3.1 million speakers.
Central Atlas Tamazight is one of the most-spoken Berber languages, along with Tachelhit, Kabyle, Riffian, Shawiya and Tuareg. In Morocco, it comes second as the most-spoken after Tachelhit. All five languages may be referred to as "Tamazight", but Central Atlas speakers are the only ones who use the term exclusively. As is typical of Afroasiatic languages, Tamazight has a series of "emphatic consonants" (realized as pharyngealized), uvulars, pharyngeals and lacks the phoneme /p/. Tamazight has a phonemic three-vowel system but also has numerous words without vowels. (Full article...)
Selected picture -

The Phoenician alphabet was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It became one of the most widely used writing systems, spread by Phoenician merchants across the Mediterranean world, where it evolved and was assimilated by many other cultures. The Aramaic alphabet, a modified form of Phoenician, was the ancestor of modern Arabic script, while Hebrew script is a stylistic variant of the Aramaic script. The Greek alphabet (and by extension its descendants such as the Latin, the Cyrillic and the Coptic), was a direct successor of Phoenician, though certain letter values were changed to represent vowels.
Language News
- 22 November 2024 – Censorship in Belarus
- In a speech at Minsk State Linguistic University, Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko threatens to shut down the Internet in his country if there are mass protests before the upcoming presidential election after the previous election saw mass protests. (Rferl)
- 20 August 2024 – Germany–Iran relations
- Following the ordered closure of the Islamic Centre Hamburg in Hamburg, Germany, Iran orders the closure of two branches of a German language school in Tehran for "breaching Iranian law, committing various illegal actions and extensive financial violations." In response, Germany summons the Iranian ambassador. (DW)
- 19 July 2024 –
- Ukrainian linguist, nationalist politician, and former People's Deputy Iryna Farion is shot and killed in Lviv, Ukraine by an unknown assailant. (Reuters)
- 27 June 2024 –
- Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy signs a law establishing English as an official language of international communication in Ukraine. (The Kyiv Independent)
Topics

Languages of Africa: Arabic, Chadic, Cushitic, Kanuri, Maasai, Setswana, Swahili, Turkana, Xhosa, Yoruba, Zulu, more...
Languages of the Americas: Aleut, Carib, Cherokee, Inuktitut, Iroquois, Kootenai, Mayan, Nahuatl, Navajo, Quechuan, Salish, American Sign Language, more...
Languages of Asia: Arabic, Assamese, Balochi, Bengali, Chinese, Japanese, Hajong, Hebrew, Hindustani, Kannada, Kokborok, Marathi, Khasi, Korean, Kurdish, Malayalam, Manipuri, Meithei, Mongolian, Persian, Rajasthani, Sindhi, Sanskrit, Sylheti, Tamil, Tanchangya, Tulu, Telugu, Tibetan, Thai, Turkish, Vietnamese, Khowar, more...
Languages of Austronesia: Austric, Fijian, Hawaiian, Javanese, Malagasy, Malay, Maori, Marshallese, Samoan, Tahitian, Tagalog, Tongan, Auslan, more...
Languages of Europe: Basque, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English (book), French, German, Greek, Italian, Latin, Leonese, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Slovak, Spanish, Ukrainian more...
Constructed languages: Esperanto, Ido, Volapük, more...
Agglutinative language, Analytic language, Constructed language, Creole, Context-free language, Extinct language, Dialect, Fusional language, Inflectional language, International language, Isolating language, Language isolate, National language, Natural language, Pidgin, Pluricentric language, Polysynthetic language, Proto-language, Sign language, Spoken language, Synthetic language, Variety (linguistics)

Applied linguistics, Cognitive linguistics, Accent (dialect), Computational linguistics, Descriptive linguistics, Eurolinguistics, Generative linguistics, Historical linguistics, Lexicology, Lexical semantics, Morphology, Onomasiology, Phonetics, Phonology, Pragmatics, Prescription, Prototype semantics, Psycholinguistics, Semantics, Stylistics, Sociolinguistics, Syntax
See also: List of linguists

Alphabets: Arabic alphabet, Bengali alphabet, Cyrillic alphabet, Hebrew alphabet, Latin alphabet, more...
Other writing systems: Abjad, Abugida, Braille, Hieroglyphics, Logogram, Syllabary, SignWriting, more..
See also: History of the alphabet, Script
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Find a language
| Enter an ISO 639 code to find the corresponding language article |




- Random portal









