Piri Reis
Piri Reis | |
|---|---|
 Statue of Piri Reis | |
| Born | Muhiddin Piri c. 1470 |
| Died | 1553 (aged 82–83) Cairo, Egypt Eyalet, Ottoman Empire |
| Notable work | |
| Relatives | Kemal Reis (uncle) |

Muhiddin Piri (c. 1470 – 1553), better known as Piri Reis (Turkish: Pîrî Reis), was an Ottoman corsair, navigator, geographer, and cartographer. He is primarily known today for his cartographic works, including his 1513 world map and the Kitab-ı Bahriye (Book of the Sea), a book with detailed information on early navigational techniques as well as relatively accurate charts for their time, describing the ports and cities of the Mediterranean Sea.
He was born in Gallipoli—a major Ottoman naval base—and sailed from an early age with his uncle Kemal Reis. They fought as corsairs in the Western Mediterranean until they were brought into the Ottoman Navy. Piri Reis fought alongside Kemal Reis in the Ottoman–Venetian wars. When his uncle died in 1511, Piri Reis returned to Gallipoli to begin his cartographic works. He created his first world map and likely began drafting the charts and notes that would form the basis of the Kitab-ı Bahriye. By 1516, he returned to the navy and took part in the Ottoman conquest of Egypt. After their victory, he presented the world map to Sultan Selim I. When Suleiman the Magnificent became sultan, Piri Reis completed the first version of the Kitab-ı Bahriye, which he dedicated and gifted to the sultan by 1521. Several years later, he created a more elaborate version at the urging of Grand Vizier Pargalı Ibrahim Pasha. His final surviving work is a 1528 world map, of which only the northwest corner remains (showing Greenland, Labrador, Newfoundland, Florida, Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica, and Central America).
In 1546, Piri Reis became Hind Kapudan-ı Derya, or grand admiral of the Ottoman Fleet in the Indian Ocean, as well as admiral of the fleet in Egypt. He expanded the Indian Ocean fleet, retook several ports, and pushed the Portuguese out of the Red Sea. In the 1550s, he began a campaign to capture the Portuguese-controlled Hormuz Island at the mouth of the Persian Gulf. He abandoned the siege of Hormuz after several weeks, sacked the city, and looted the nearby Qeshm Island, where wealthy residents of Hormuz had evacuated. For failing to capture Hormuz, he was executed in 1553 in Cairo.
His cartographic work received little appreciation during his own life. There is no evidence that the Kitab-ı Bahriye circulated outside the royal palace before 1550. After his death, hundreds of copies of the book were likely made. Over 40 copies survive today, spanning several centuries. When his 1513 world map was unearthed at the Topkapı Palace in Istanbul, it drew international attention. The map relies on many sources, including a lost map of the Caribbean from Christopher Columbus. This sparked greater interest in the Kitab-ı Bahriye, and facsimiles of both were published. Piri Reis and his cartography have since become a point of national pride for Turkey.
Biography
Early life and piracy
Little is known about Piri Reis' background and early life.[1] He was likely born around 1470 in Gallipoli on the Dardanelles.[2] At the time, Gallipoli was a major naval base for the Ottoman Empire.[1] He was born Muhiddin Piri; Reis was a military rank equivalent to captain.[3] His uncle was Kemal Reis.[4] Little is known about his parents.[5] Piri Reis gives his father's name as Hacı Mehmed.[4] It is not clear from historical records whether Piri was the son of Kemal Reis' brother or sister.[5] Kemal Reis had a brother-in-law from Nafpaktos who was arrested and tortured in Venice for alleged spying during the Ottoman–Venetian wars. He was possibly Piri Reis' father.[6]
By age 12, he began sailing with his uncle Kemal Reis.[4] Kemal was a notable corsair,[7] a type of pirate who acted with the approval of a sovereign state.[8] Led by Kemal Reis, the Barbary pirates threatened European maritime traffic.[9] Piri Reis wrote of his early years, "We sailed on the Mediterranean and fought the enemies of our religion mercilessly."[10] He sailed with his uncle on raids, mainly on the coasts of Italy and Spain.[2] By 1490, they were operating out of Béjaïa, Algeria.[11] As a corsair, Piri Reis captured many ships, a fortress near Mallorca, and Pianosa near Corsica.[2] During the Granada War, Piri Reis transported Muslims and Jews from Spain to North Africa.[10] During the winters, he and his uncle took shelter in favorable harbors on the Barbary Coast.[12]
Naval career and cartography

Piri Reis sailed under his uncle and later Hayreddin Barbarossa in the Ottoman Navy.[13] To bolster the empire's navy, Ottoman Sultan Bayezid II recruited Barbary and Aegean corsairs, including Piri and Kemal.[14] Before Barbarossa reorganized the navy, sultans commonly employed former pirates.[15] The addition of experienced corsairs raised the Ottoman Navy's competence in open-sea combat and knowledge of the Mediterranean.[14]
In 1495, Kemal Reis was imprisoned on Euboea for piracy and brought to the capital, Constantinople. Rather than being sentenced, he was given an official position in the navy. Piri Reis was with his uncle through this and later documented it in the Kitab-ı Bahriye.[16] In the empire's navy, Kemal and Piri advocated taking the Venetian coastal fortresses of the Peloponnese and the small but strategically valuable island of Rhodes.[17] In his Kitab-ı Bahriye, Piri Reis reports that his uncle had told Sultan Bayezid II, "Venice has two eyes: Her left eye is the [harbor] fortress of Modon. Her right eye is that of Corfu."[18]
Piri Reis took part in the Ottoman–Venetian wars, including the First Battle of Lepanto (Battle of Zonchio), Second Battle of Lepanto (Battle of Modon), and 1501 conquest of Navarino.[2][19] During the First Battle of Lepanto, Piri Reis was one of many corsairs in a fleet of about 270 ships that fought through the Venetian fleet and entered the Gulf of Corinth, forcing the governor to surrender.[20] Kemal Reis led the Ottomans in the battles to take the fortresses at Modon and Navarino.[21] After the Ottoman navy defeated the Venetian fleet at the Peloponnese, they began to take control of the Eastern Mediterranean.[22] In the early 1500s, Kemal Reis led raids on the Balearic Islands, Sardinia, and Pianosa in the western Mediterranean.[23] In one naval battle, Piri Reis and his uncle captured a Spaniard who had participated in Columbus's voyages,[24][25] and likely possessed an early map of the Americas that Piri Reis would use as a source for his maps.[26]
When his uncle died in a 1511 shipwreck in the Mediterranean, Piri Reis returned to Gallipoli to work on his navigational studies.[27] The finished manuscript of his first world map was dated to the month of Muharram in the Islamic year 919 AH, equivalent to March 1513 AD.[28][29] This work included the recently explored shores of the Americas and Africa.[30] Although he had never sailed the Atlantic, he compiled over twenty maps of Arab, Spanish, Portuguese, Indian and older Greek origins into a comprehensive representation of the known world of his era.[31] At least by 1513, Piri Reis was sailing again for the Ottomans under Hayreddin Barbarossa along the coast of North Africa.[32]
By 1516, Piri Reis returned to the navy as captain of a galley in the Ottoman fleet and took part in the 1516–17 Ottoman conquest of Egypt.[2][33] He was the commander of the Turkish fleet that blockaded Alexandria.[34] After the Ottoman victory,[33] Piri Reis presented the 1513 world map to Sultan Selim I (r. 1512–1520).[35] It is unknown how Selim used the map, if at all, as it vanished from history until its rediscovery centuries later.[36] According to Venetian documents, Piri Reis was no longer with the Ottoman navy in 1518 and was engaging in piracy in the Aegean Sea.[37]

Piri Reis advocated for and took part in Suleiman the Magnificent's 1522 Siege of Rhodes.[38][39] The first version of his Kitab-ı Bahriye—a nautical atlas gifted and dedicated to Suleiman—included advice on conquering Rhodes.[38][40] The island of Rhodes had a secure harbor and was 20 km (12 mi) off the coast of Anatolia. Controlled by an adversary, it could threaten maritime communication between the empire's capital and Mediterranean ports.[41] The Knights of St. John controlled the island, took Muslim captives, and provided shelter to Christian pirates.[42] During the siege, the Knights' fleet of ten ships remained in the harbor rather than confront the larger Ottoman force.[43] The Ottoman Navy conducted an amphibious operation, transporting many troops to the small island,[43] and the island surrendered in December 1522. The Knights of St. John later relocated to Malta.[44][45] The second version of the Kitab-ı Bahriye, completed after the conquest of Rhodes, only discusses the events in terms of the practical concerns of acquiring drinking water from Karabağ in Bodrum prior to the siege.[46]
The longer second version of the Kitab-ı Bahriye resulted from a conversation with the empire's grand vizier.[47] Suleiman's reign was the beginning of a shift towards power concentrating in a group of viziers, advisers, governors, and royal family members, including Suleiman's childhood friend Pargalı Ibrahim Pasha who rose to grand vizier of the empire.[48] When putting down Hain Ahmed Pasha's 1524 rebellion in Egypt, Ibrahim rode aboard the navy's flagship, commanded by Piri Reis.[49][14] Piri Reis said they discussed cartography after Ibrahim asked him about the maps and charts being consulted aboard the ship.[50] Ibrahim commissioned Piri Reis to create an expanded version of the Kitab-ı Bahriye.[51] He finished it and gifted it to the sultan by 1526. In later centuries, many copies were made of both versions of the book.[52] Piri Reis completed a second world map in 1528 or 1529.[53] According to Sevim Tekeli, the changes from the first world map demonstrate that Piri Reis was actively following European voyages of discovery.[54]
In both the 1513 world map and the Kitab-ı Bahriye preface, Piri Reis rhetorically undermines the significance of European discoveries by reframing them as the rediscovery of ancient knowledge.[55] He invokes Alexander the Great when explaining the discoveries of Columbus.[56] According to the Quran and Turkish literary tradition, Dhu al-Qarnayn—believed to be a Quranic reference to Alexander the Great—traveled to every corner of the world, thereby defining its limits.[57] Marginal inscriptions on the world map mention "charts drawn in the days of Alexander" and a book that "fell into the hands" of Columbus describing lands "at the end of the Western Sea".[58][59] In the 1526 version of the Kitab-ı Bahriye, he explicitly credits European discoveries to lost works created during legendary voyages of Alexander, "My friend, the Franks both read and write everything there is to know about the science of the sea. But do not suppose that they invented such knowledge on their own; and if you wish, I will explain why. During his time, the famous ruler Alexander traveled over all the seas, and whatever he saw and whatever he heard he had recorded, item by item, by a competent person."[60]
Venice saw Piri Reis as an adversary and obstacle to their aims in the Middle East during the 1530s.[61] In 1532, he fought back Dalmatian pirates in the Adriatic.[62] He attacked the Venetian-held castle at Coron in 1533, captured a Venetian galley in 1536, and chased Venetian ships out of the eastern Mediterranean.[61]
Grand Admiral of the Indian Ocean Fleet

After Sinan Reis died in 1546,[61] Piri Reis took his position as Hind Kapudan-ı Derya, or grand admiral of the Ottoman Fleet in the Indian Ocean, as well as admiral of the fleet in Egypt.[63] Portuguese ships had raided the Red Sea as far as Suez and taken the port city of Aden in Yemen.[63] The Portuguese navy employed sailing ships capable of navigation and combat in open seas, while the Ottoman navy relied mainly on galleys, which were more effective along the coasts. This limited Ottoman naval warfare to the Red Sea, Persian Gulf, and narrow straits around Arabia. The empire focused on using its navy to continue land-based expansion into new areas for tax revenue and agriculture.[64]
Using his fleet based out of Suez, Egypt, Piri Reis led campaigns in the Red Sea and Persian Gulf.[10] On 26 February 1548, he recaptured Aden from the Portuguese.[63] Piri Reis subdued the local Bedouin rulers of Basra in 1547 and began building a Persian Gulf fleet.[65] The fleet conducted annual expansions in the Indian Ocean, and some local rulers began to ally with the Portuguese.[65]

The sultan instructed Piri Reis to take the Portuguese-controlled Hormuz Island at the mouth of the Persian Gulf.[66] Taking Bahrain Island was a secondary objective.[67] In April 1552,[68] Piri Reis left Suez with 25 galleys, 5 ships, and 850 soldiers.[69] In 1552, the Turkish fleet took Muscat after a one-month siege.[63][70] The expedition took control of coastal lands in Yemen, Oman, and Arabia.[71] The Portuguese prepared for the attack on Hormuz by evacuating most of the island. Wealthy residents took refuge on the nearby island of Qeshm, and the soldiers and royal family retreated to the fortress.[70]
The Turkish soldiers took the City of Hormuz, but could not take the fortress.[72] They besieged and bombarded the fortress for several weeks, but Piri Reis grew concerned about the Portuguese fleet attacking them during the siege.[73] The Ottoman forces ran low on gunpowder, and Kubad Pasha the governor of Basra did not send supplies to the siege.[74] On 9 October 1552, the Ottomans retreated.[75][70] They sacked the city, looted Qeshm, and retreated into the gulf with over a million pieces of gold.[70] The fleet arrived at Basra by 1553.[76] A letter from the Portuguese governor inside the fortress, dated 31 October 1552, said that the walls had been near collapsing, but that the Ottomans had run low on "munitions, gunpowder, and other war materials" much of which they had lost when a galleon sank on the way to Hormuz.[77] The Portuguese governor of India, Afonso de Noronha organized a fleet of 40 ships led by his nephew Antão de Noronha that reached Hormuz in November 1552.[78]
In his 80s, Piri Reis was executed following his retreat at Hormuz.[10] After the expedition's failure, Kubad Pasha denied Piri Reis rowers for his galleys.[66][70] Piri Reis returned to Egypt in 1553 with only two ships, loaded with gold.[79][70] The sultan had him beheaded in Cairo; the exact date of his execution is unknown.[79] A letter—dated 15 November 1553—written from diplomats in Constantinople to Venice said that he had been "charged with having raised the siege of the fortress of Hormuz".[79] He was possibly survived by a son, Mehmed Reis, who is known only from a single portolan map of the Aegean.[80]
Works
Three of his cartographic works survive in some form to the present day.[81] Fragments of his 1513 world map and his 1528 world map are kept in museums in Istanbul.[82][83] Copies of the Kitab-ı Bahriye, a navigational atlas, are kept in many libraries and museums around the world, although the two created by Piri Reis himself are lost.[84]
Piri Reis map of 1513
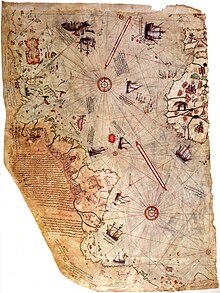
The Piri Reis map of 1513 is a world map compiled from a range of contemporary and classical sources.[85] Approximately one third of the map survives,[86] housed in the Topkapı Palace in Istanbul.[87] The finished manuscript was dated to the Islamic year 919 AH, equivalent to 1513 AD.[88] After the empire's 1517 conquest of Egypt,[33] Piri Reis presented the 1513 world map to Ottoman Sultan Selim I (r. 1512–1520).[89] It is unknown how Selim used the map, if at all, as it vanished from history until its rediscovery centuries later.[36] When rediscovered in 1929,[90] the remaining fragment garnered international attention for including a partial copy of an otherwise lost map by Christopher Columbus.[91]
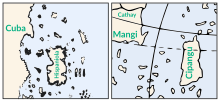
The map is a portolan chart with compass roses from which lines of bearing radiate.[92] Designed for navigation via dead reckoning,[93] portolan charts use a windrose network rather than a longitude and latitude grid.[92] It contains extensive notes primarily in Ottoman Turkish.[94] The colophon in Arabic is written in a different handwriting,[95] likely that of Piri Reis himself.[29] The depiction of South America is detailed and accurate for its time.[96][97] Scholars attribute the peculiar arrangement of the Caribbean to a now-lost map from Columbus that depicted Cuba as part of the Asian mainland and Hispaniola according to Marco Polo's description of Japan.[98][99] This reflects Columbus's erroneous claim that he had found a new route to Asia.[100][a] The southern coast of the Atlantic Ocean is most likely a version of Terra Australis.[106][107]
The map is visually distinct from European portolan charts, influenced by the Islamic miniature tradition.[108] It was unusual in the Islamic cartographic tradition for incorporating many non-Muslim sources.[109] Historian Karen Pinto has described the positive portrayal of legendary creatures from the edge of the known world in the Americas as breaking away from the medieval Islamic idea of an impassable "Encircling Ocean" surrounding the Old World.[110] Piri Reis adapted the elements of iconography from the traditional maps—which illustrated well-known routes, cities, and peoples—to the portolan portrayals of newly discovered coasts.[111]
There are conflicting interpretations of the map.[112] Scholarly debate exists over the specific sources used in the map's creation and the number of source maps.[113] Many areas on the map have not been conclusively identified with real or mythical places.[114] Some authors have noted visual similarities to parts of the Americas not officially discovered by 1513,[115] but there is no textual or historical evidence that the map represents land south of present-day Cananéia.[116] A disproven 20th-century hypothesis identified the southern landmass with an ice-free Antarctic coast.[117]
Kitab-ı Bahriye

The Kitab-ı Bahriye (كتاب بحرية), or Book of the Sea, is a navigational atlas.[b][51] Piri Reis compiled navigational charts and notes into the most detailed portolan atlas of the sixteenth century.[52][119] There are two versions of the book.[51] The first version was composed between 1511 and 1521.[c] Both versions begin with a preface and were dedicated to the sultan Suleiman the Magnificent (r. 1520–1566).[84]
The second version—completed by 1526—includes a longer introduction written in verse.[51] It offers information on storms, winds, navigating with a compass, navigating by the stars, reading portolan charts, and the oceans.[84] It includes information on recent Portuguese and Spanish voyages including the voyages of Christopher Columbus to the Americas and Vasco da Gama's discovery of a sea route to India.[51] It offers the first detailed Ottoman description of the Indian Ocean,[123] and gives special attention to Hormuz Island at the strait leading into the Persian Gulf.[95]
The main part of both versions is a nautical guide to the Mediterranean Sea. Separate chapters cover different locations with corresponding portolan charts.[84] There are 130 chapters in the first version and 210 in the second.[84] Piri Reis says he composed an atlas because any single map has limited space for written details, and some "knowledge cannot be known from maps; it must be explained."[84] The chapters start at the Dardanelles and move counter-clockwise around the Mediterranean.[124] The Kitab-ı Bahriye combines information from a range of sources and Piri Reis' personal experience. The coast of North Africa relies little on outside sources.[125] Its maps have compass roses indicating North for each page.[126][119] Scale is indicated only in the textual descriptions, not with scale bars.[119] Standard portolan symbols indicate hazards, like dots for shallow water and crosses for rocks.[126] Written when Ottoman sailors relied on oar-driven galleys and galiots, the Kitab-ı Bahriye reflects their needs and capabilities. It gives information on coastal waters, safe harbors, hazards, and sources of fresh water.[127]
The known surviving manuscripts are all copies created beginning in the later 1500s.[118] The book achieved fame only after Piri Reis' death.[128] At least some portion of the book has been translated into English, modern Turkish, Greek, French, German, and Italian.[129]
1528 world map

Piri Reis compiled a second world map in 1528.[130] Only a fragment of the map—the northwest corner—remains.[130] The parchment fragment is approximately 70 centimeters (28 in) square.[130] As with the 1513 map, the 1528 map has calligraphic inscriptions in Ottoman-Turkish written in the Arabic alphabet. The colophon is in Arabic, likely handwritten by Piri Reis himself.[131] According to the colophon, Piri Reis compiled the map in 1528 in Gallipoli.[131] However, he may not have completed it until 1529.[130]
The 1528 map was a portolan chart like his earlier works. It uses a windrose network radiating out from compass roses.[132] The map does include one line of latitude, the Tropic of Cancer; it is slightly south of the correct position for Cuba and the Yucatan.[133] The map uses standard portolan colors and symbols. Dots indicate shallow waters and sand banks. Crosses indicate rocks and reefs.[132] The ships painted on the map are two caravels and a carrack.[131] The scale bars indicate 80 km (50 mi) between the sections of the scales.[134]
Based on the design of recently explored geographical features like Greenland, Newfoundland, and Florida, the map likely relied on Spanish, Portuguese, and Italian maps from the 1520s.[130] Notes on the map cite recent Portuguese voyages to Labrador and Newfoundland.[135] Hispaniola and Cuba are much more accurate compared to the 1513 world map. Cuba, labeled "Isla di Vana", is now correctly positioned as an island in the Caribbean.[136][137] In contrast to the 1513 map, Piri Reis leaves areas that have not been explored blank.[138] Only the explored southern coasts of the Florida peninsula are on the map. The geography of Florida is left ambiguous as potentially an island or peninsula.[139] The Spanish Empire's master map, the Padrón Real, included this type of ambiguous Florida until 1520, and it influenced Italian cartography like the Freducci map.[140]
Legacy

During his own life, there was limited appreciation for Piri Reis' cartography. Historian Svat Soucek said of the cartographic works of Piri Reis, "They show that although the Ottoman Empire had the potential to participate in the discoveries, its ruling elite spurned the attempt to blaze a trail in this direction".[141] The 1513 world map disappeared from the historical record until its rediscovery centuries later.[36] There is no evidence that either version of his atlas circulated outside the royal palace prior to 1550.[128] The copies produced in the following centuries were often created for their aesthetic or artistic value.[53] No Turkish school of cartography or navigation was established to build on his work.[142] Murat Reis the Elder's expedition to the Canary Islands and the 1586 Sack of Lanzarote were some of the few times when Piri Reis' Atlantic cartography was likely used by the Ottoman Navy.[143] The empire's navy—even during the Canary Islands expedition—remained largely composed of oar-driven galleys after the point where other naval powers were moving to sailing ships that were more suited to the open oceans.[143] Ottoman scholar Kâtip Çelebi built on the Kitab-i Bahriye in his seventeenth-century work, Müntehab-ı Bahriyye.[144] By the eighteenth century, major works of cartography from Western Europe were being translated into Turkish.[145]
When Piri Reis' world map was unearthed in 1929, it received international media attention for containing the surviving piece of an otherwise lost map of Christopher Columbus.[91] Turkey's first president, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, took an interest in the map and initiated projects to publish facsimiles and conduct research.[146] Discovered during Atatürk's reforms, the map was a point of national pride. Its rediscovery also sparked interest in the Kitab-ı Bahriye.[147][142] A facsimile of the book's second version was published by the Turkish Historical Society in 1935,[148] and a four-volume facsimile with photographic quality was published in 1988.[149] Several ships and submarines have been named after him, including the RV K. Piri Reis and TCG Pirireis.[150][151][152] The Piri Reis University for maritime studies was founded in 2008.[153] In the Turkish TV series Barbaros: Sword of the Mediterranean, he is portrayed by actor Emir Benderlioğlu.[154]
Piri Reis' 1513 world map is the target of various pseudoscientific claims and is sometimes invoked in broader pop culture as an unsolved mystery. Civil engineer Arlington Mallery, professor Charles Hapgood, and Hapgood's students developed the hypothesis that the 1513 world map contained cartographic information, notably from an ice-free Antarctic coast, that exceeded the map-making abilities of the sixteenth century. In his 1966 book Maps of the Ancient Sea Kings, Hapgood claims islands along the map's southern Atlantic shore to be ice-covered mountains in Antarctica's Queen Maud Land region.[155] Hapgood's book was met with skepticism due to its lack of evidence and reliance on polar shift.[156] According to geologist Paul Heinrich, the book also did not account for post-glacial rebound, and the 1949 survey initially cited by Mallery could not measure even one percent of the area drawn in the Piri Reis map. Subsequent studies have shown no significant similarities to Antarctica's coast.[157] Hapgood's claims have been uncritically repeated by Erich von Däniken in support of ancient astronauts and by Graham Hancock in support of an advanced lost civilization.[158][159] The map and polar shift were key plot elements in Allan W. Eckert's science fiction novel The HAB Theory.[160] Piri Reis is a character in the Assassin's Creed franchise. In the 2010 video game Assassin's Creed: Brotherhood, a group of Italian Assassins sent from Rome to Constantinople by Ezio Auditore da Firenze infiltrates Piri Reis' shop to steal some of his maps detailing the New World, to match the Templars' expansion into the new lands.[161] He appears in its 2011 sequel Assassin's Creed: Revelations, set in early sixteenth-century Constantinople.[162][163]
Notes
- ^ There is disagreement on how much of the map draws from Columbus. Paul Kahle and most later scholars attributed everything north and west of the phantom island Antilia to this source.[101] Svat Soucek expressed doubts about Kahle's "supposed connection",[102] and commented that "as for the 'map made by Columbus', Piri Reis' own map shows that he must also have used other sources depicting South America (specifically, the eastern bulge of the continent, thus Brazil), which Columbus could not have known" about when the map would have been produced.[103] Gregory McIntosh found that Cuba, Central America, and Hispaniola could be clearly attributed to an early map from Columbus,[104] but not necessarily the Lesser Antilles. McIntosh noted that the duplication of some features like the Virgin Islands indicated an attempt to join a second map in that area.[105]
- ^ Other translations of the title:
- ^ Soucek (1992) notes that work on the book began in 1511 around the same time as work on the 1513 world map.[120] Soucek (2013) gives 1520 as the completion date.[121] Hepworth (2005) says the book was "presented" in 1521.[52] Lepore, Piccardi, and Rombai (2013) say the book "appeared" in 1521.[122]
References
- ^ a b c Soucek 1992, p. 266.
- ^ a b c d e Bostan 2014.
- ^
- İnan 1954, p. 6;
- McIntosh 2000a, p. 5;
- "Reis". Tureng Multilingual Dictionary.
- ^ a b c McIntosh 2000a, p. 5.
- ^ a b Pedani 2015, p. 320.
- ^ Pedani 2015, p. 321.
- ^ Khair 2006, p. 127.
- ^ "Corsair". Cambridge Dictionary.
- ^ Pryor 1988, p. 193.
- ^ a b c d McIntosh 2000a, p. 6.
- ^ Isom-Verhaaren 2022, p. 91.
- ^ İnan 1954, p. 9.
- ^ Ayyubi 1989, p. 737.
- ^ a b c Hess 1970, p. 1905.
- ^ Pedani 2015, p. 319.
- ^ Pedani 2015, pp. 319–320.
- ^ Soucek 2004, pp. 222, 232.
- ^ Soucek 2004, p. 232.
- ^ Zarinebaf, Bennet & Davis 2005, p. 11.
- ^ Isom-Verhaaren 2022, pp. 92–93.
- ^ Isom-Verhaaren 2022, pp. 94–95.
- ^ Hess 1970, pp. 1905–1907.
- ^ Pitcher 1972, p. 99.
- ^ Soucek 1992, pp. 270–271.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, p. 73.
- ^ Nebenzahl 1990, p. 62.
- ^ Urguplu 2015.
- ^ Massetti & Veracini 2016, pp. 41–42.
- ^ a b McIntosh 2000a, p. 15.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, p. 9.
- ^ Brotton 1998, pp. 108–110.
- ^ Isom-Verhaaren 2022, p. 109.
- ^ a b c Tekeli 1985, pp. 675–676.
- ^ Ayyubi 1989, p. 738.
- ^ Kahle 1933, p. 621.
- ^ a b c Soucek 1992, p. 270.
- ^ Pedani 2015, pp. 321–322.
- ^ a b Soucek 2004, p. 222.
- ^ İnan 1954, p. 14.
- ^ Soucek 2013, p. 137.
- ^ Soucek 2004, p. 220.
- ^ Soucek 2004, p. 221.
- ^ a b Soucek 2004, p. 223.
- ^ Grima 2021.
- ^ Yaldız, Kaymakçı & Özgün 2019, pp. 224–225.
- ^ Isom-Verhaaren 2022, p. 101.
- ^ Soucek 2013, pp. 137–138.
- ^ Casale 2010, pp. 34–35.
- ^ Casale 2010, p. 36.
- ^ Casale 2010, pp. 36–37.
- ^ a b c d e Casale 2010, p. 37.
- ^ a b c d Hepworth 2005, p. 73.
- ^ a b Soucek 2013, p. 141.
- ^ Ayyubi 1989, p. 739.
- ^ Casale 2019, p. 876.
- ^ Casale 2019, pp. 871, 874–875.
- ^ Casale 2019, pp. 864–867, 875.
- ^ Akçura 1935, sec. V.
- ^ Akçura 1935, sec. VI.
- ^ Casale 2019, p. 875.
- ^ a b c Pedani 2015, p. 323.
- ^ Pedani 2015, pp. 322–323.
- ^ a b c d Shaw 1976, p. 107.
- ^ Hess 1970, pp. 1916–1917.
- ^ a b Shaw 1976, pp. 106–107.
- ^ a b Önalp 2010, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Özbaran 2009, p. 107.
- ^ Özbaran 2009, p. 108.
- ^ Floor 2006, p. 175.
- ^ a b c d e f Floor 2006, p. 176.
- ^ Malekandathil 2010, p. 117.
- ^ Finkel 2007, p. 136.
- ^ Özbaran 2009, p. 110.
- ^ Soucek 2011, p. 61.
- ^ Özbaran 2009, p. 110.
- ^ Isom-Verhaaren 2022, p. 104.
- ^ Özbaran 2009, p. 111.
- ^ Özbaran 2009, pp. 110–111.
- ^ a b c Pedani 2015, p. 324.
- ^ Angelov, Bazzaz & Batsaki 2013, p. 84.
- ^ Robinson 1996, p. 70.
- ^ Anatolia News Agency 2013.
- ^ McIntosh 2015, p. 317.
- ^ a b c d e f Soucek 1992, p. 272.
- ^ Soucek 2013, p. 140.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 8–9.
- ^ Massetti & Veracini 2016, p. 41.
- ^ Massetti & Veracini 2016, p. 42.
- ^ Casale 2019, p. 871.
- ^
- Şengör 2004 cites:
- Adıvar 1939, pp. 59–60.
- ^ a b Gerber 2010, p. 199.
- ^ a b Dutch 2010.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 60–61.
- ^ McIntosh 2000b, p. 21.
- ^ a b Soucek 2013, p. 139.
- ^ İnan 1954, pp. 35, 38.
- ^ Soucek 1996, pp. 58, 73–74.
- ^ Gaspar 2015, pp. 1–3.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, p. 91.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 114, 136.
- ^
- Kahle 1933, p. 628;
- İnan 1954, pp. 37–40;
- McIntosh 2000a, pp. 131–133.
- ^ Soucek 1992, pp. 270–271.
- ^ Soucek 2013, p. 140.
- ^ McIntosh 2014, p. 372.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 134–139.
- ^ Cuoghi 2002.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, p. 68.
- ^ Pinto 2012, p. 71.
- ^ Soucek 1994, pp. 123, 129.
- ^ Pinto 2012, pp. 80, 90.
- ^ Pinto 2012.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, p. 2.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 15–18.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 26, 30, 41, 100.
- ^
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 37–38.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, ch. 6.
- ^ a b Goodrich 2004.
- ^ a b c Goodrich 2004, pt. 1.
- ^ Soucek 1992, p. 267.
- ^ Soucek 2013, p. 135.
- ^ Lepore, Piccardi & Rombai 2013, p. 85.
- ^ Casale 2010, p. 37
- ^ İnan 1954, pp. 21–22.
- ^ Soucek 1992, pp. 277–279.
- ^ a b Soucek 1992, p. 277.
- ^ Soucek 1992, pp. 273–274.
- ^ a b Casale 2010, p. 186.
- ^ Lepore, Piccardi & Rombai 2013, p. 86.
- ^ a b c d e McIntosh 2015, p. 303.
- ^ a b c McIntosh 2015, p. 306.
- ^ a b McIntosh 2015, p. 305.
- ^ Tekeli 1985, p. 681.
- ^ İnan 1954, p. 45.
- ^ İnan 1954, pp. 43–45.
- ^ Tekeli 1985, p. 681
- ^ McIntosh 2015, p. 307.
- ^ İnan 1954, p. 48.
- ^ McIntosh 2015, pp. 307–308.
- ^ McIntosh 2015, pp. 308–309.
- ^ Soucek 2013, p. 143.
- ^ a b Soucek 1994, p. 135.
- ^ a b Muhaj 2014, p. 265.
- ^ Sarıcaoğlu 2009, p. 120.
- ^ Sarıcaoğlu 2009, pp. 123–124.
- ^ İnan 1954, p. 4.
- ^ Soucek 2013, p. 141
- ^ Soucek 2013, pp. 135–144.
- ^ Goodrich 2004, pt. 2.
- ^ Ozberk 2024.
- ^ NHHC 2016.
- ^ Newsroom 2024.
- ^ Tethys 2024.
- ^ Tarihi 2022.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, pp. 53–58.
- ^
- McIntosh 2000a, pp. 60–62;
- Stunkel 1967;
- Davies 1985.
- ^ Heinrich 2001.
- ^ Fagan 2006, p. 35.
- ^ McIntosh 2000a, p. 58.
- ^ Pinto 2012, pp. 65–67.
- ^ Ubisoft Montreal 2010.
- ^ Hoekstra 2024.
- ^ Ritman 2011.
Bibliography
- Adıvar, Abdülhak Adnan (1939). La Science Chez les Turcs Ottomans (1st ed.). Paris: G.P. Maisonneuve et Larose. OCLC 11676376.
- Akçura, Yusuf (1935). "Piri Reis' Map". Piri Reis Haritasi (PDF) (1st ed.). Istanbul: Türk Tarih Kurumu (Turkis HistoricalSociety). OCLC 42754605.
- Anatolia News Agency (23 January 2013). "Topkapı Palace Museum features Piri Reis collection". Hürriyet Daily News.
- Angelov, Dimiter; Bazzaz, Sahar; Batsaki, Yota (2013). Imperial Geographies in Byzantine and Ottoman Space. Washington, DC: Center for Hellenic Studies.
- Ayyubi, N. Akmal (1989). "Contribution of Piri Reis to Cartography". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 50: 737–740. ISSN 2249-1937. JSTOR 44146128.
- Bostan, İdris (30 January 2014). "Piri Reis: Ottoman Sailor of the Exploration Age". SeaNews.
- Brotton, Jerry (1998). Trading Territories : Mapping the early modern world. Ithaca, N.Y.: Cornell University Press. ISBN 0-8014-3499-8.
- Casale, Giancarlo (28 January 2010). The Ottoman Age of Exploration. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195377828.003.0003. ISBN 978-0-19-537782-8.
- Casale, Giancarlo (2019). "Did Alexander the Great Discover America? Debating Space and Time in Renaissance Istanbul". Renaissance Quarterly. 72 (3): 863–909. doi:10.1017/rqx.2019.252. JSTOR 26845906. S2CID 204482631.
- Cuoghi, Diego (2002). "Part 1 (Piri Reis)". The Mysteries of the Piri Reis map. Archived from the original on 10 March 2004. Translation of: Cuoghi, Diego (2003). "I Misteri Della Mappa di Piri Reis". Gli enigmi della storia. Milan: Edizioni Piemme.
- Davies, Gordon L. Herries (1985). "Reviewed Work(s): Maps of the Ancient Sea Kings. Evidence of Advanced Civilization in the Ice Age by Charles H. Hapgood". Imago Mundi. 37: 108–109. JSTOR 1150840.
- Dutch, Steven (2010) [1998]. "The Piri Reis Map". Science, Pseudoscience, and Irrationalism. Archived from the original on 13 August 2013 – via University of Wisconsin–Green Bay.
- Fagan, Garrett G. (2006). Archaeological Fantasies: How Pseudoarchaeology Misrepresents the Past and Misleads the Public. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-041530-592-1.
- Finkel, Caroline (2007). Osman's dream: the story of the Ottoman Empire, 1300-1923. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-02397-4.
- Floor, Willem M. (2006). The Persian Gulf: A Political and Economic History of Five Port Cities, 1500-1730. Mage Publishers. ISBN 978-1-93382-312-6.
- Gaspar, Joaquim Alves (2015). "The Representation of the West Indies in Early Iberian Cartography: A Cartometric Approach". Terrae Incognitae. 47 (1): 10–32. doi:10.1179/0082288415Z.00000000041. S2CID 128885931.
- Gerber, Albrecht (2010). Deissmann the Philologist (1st ed.). Berlin: De Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11022-432-0.
- Goodrich, Thomas D. (2004). "The maps of the Kitab-i Bahriye of Piri Reis". Piri Reis Sempozyumu. Istanbul Military Museum. Archived from the original on 16 May 2015.
- Grima, Joseph F. (24 October 2021). "The Order of St John's arrival in Malta in 1530". Times of Malta.
- Heinrich, Paul (2001). Fingerprints of the Gods Re: Piri Reis Map, Geologist and Archaeological Geologist at Louisiana State University.
- Hepworth, Paul (2005). "Production and Date of the Walters' "Kitab-i Bahriye"". The Journal of the Walters Art Museum. 63: 73–80. ISSN 1946-0988. JSTOR 20650882.
- Hess, Andrew C. (1970). "The Evolution of the Ottoman Seaborne Empire in the Age of the Oceanic Discoveries, 1453-1525". The American Historical Review. 75 (7): 1892–1919. doi:10.2307/1848022. ISSN 0002-8762. JSTOR 1848022.
- Hoekstra, Kyle (20 May 2024). "Assassin's Creed Games in Order: a Brief History". History Hit.
- İnan, Afet; Yolaç, Leman (trans.) (1954). The Oldest Map of America, Drawn by Piri Reis. Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu Basimevi. OCLC 2435662.
- Isom-Verhaaren, Christine (2022). The Sultan's fleet: seafarers of the Ottoman empire (First published ed.). London New York Oxford New Delhi Sydney: I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-0-7556-4173-4.
- Kahle, Paul E. (October 1933). "A Lost Map of Columbus". Geographical Review. 23 (4): 621–638. Bibcode:1933GeoRv..23..621K. doi:10.2307/209247. JSTOR 209247.
- Khair, Tabish, ed. (2006). "Piri Reis: The Voyages of a 'Corsair' (c. 1526)". Other routes: 1500 years of African and Asian travel writing. Oxford: Signal. pp. 127–131. ISBN 978-1-90495-512-2. OCLC 61177562.
- Lepore, Fortunato; Piccardi, Marco; Rombai, Leonardo (2013). "Looking at the Kitab-i Bahriye of Piri Reis" (PDF). E-Perimetron. 8 (2).
- Malekandathil, Pius (2010). Maritime India-Trade, Religion and Polity In the Indian Ocean. Primus Books. ISBN 978-9-38060-701-6.
- Massetti, Marco; Veracini, Cecilia (2016). "The zoomorphic representations of the Pîrî Reis map (1513)" (PDF). Anthropozoologica. 51 (1): 41–54. doi:10.5252/az2016n1a3. hdl:10400.5/28972. S2CID 192924551.
- McIntosh, Gregory C. (2000a). The Piri Reis Map of 1513. Athens, Georgia: University of Georgia Press. ISBN 978-0-82034-359-4.
- McIntosh, Gregory C. (2000b). "The Tale of Two Admirals: Columbus and the Piri Reis Map of 1513". Mercator's World. Vol. 5, no. 3. Aster. pp. 18–23.
- McIntosh, Gregory C. (2014). "The Piri Reis Map of 1513: Art and Literature in the Service of Science". Seapower, Technology, and Trade: Studies in Turkish Maritime History (Digital ed.). Istanbul: Piri Reis University. ISBN 978-9-94426-451-8..
- McIntosh, Gregory C. (August 2015). "The Piri Reis Map of 1528: A Comparative Study with Other Maps of the Time". Mediterranea. Ricerche Storiche. (34). Palermo: Mediterranea. ISSN 1828-230X.
- Muhaj, Ardian (December 2014). Ottoman corsairs in the Atlantic during the 16th century: Murat Rais, the Albanian and the first Ottoman expedition to the Canary Islands. International Symposium of Piri Reis and Turkish Maritime History. Istanbul.
- Nebenzahl, Kenneth (1990). Atlas of Columbus and the Great Discoveries. Chicago: Rand McNally. ISBN 978-0-52883-407-3.
- Newsroom (2024). "Experts investigate fish deaths, pollution crisis in Izmir Bay - Türkiye Today". 31 August 2024.
- NHHC (21 April 2016). "Mapiro (SS-376)". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Naval History and Heritage Command.
- Önalp, Ertuğrul (2010). "The Military Expedition of Piri Reis to Hormuz and the Considerations of Turkish and Portugese Historians About his Execution" (PDF). Ankara Üniversitesi Dil ve Tarih-Coğrafya Fakültesi Tarih Bölümü Tarih Araştırmaları Dergisi (in Turkish). 29 (47). doi:10.1501/Tarar_0000000453. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 December 2013.
- Özbaran, Salih (2009). Ottoman expansion toward the Indian Ocean in the 16th century (1st ed.). Şişli, İstanbul: İstanbul Bilgi University Press. ISBN 978-605-399-062-8.
- Ozberk, Tayfun (25 August 2024). "Turkish Navy commissions first Reis-class AIP submarine TCG Piri Reis". Naval News.
- Pedani, Maria Pia (August 2015). "Piri Reis in Venetian Documents". Mediterranea. Ricerche Storiche. (34). Palermo: Mediterranea. ISSN 1828-230X.
- Pinto, Karen (2012). "Searchin' His Eyes, Lookin' for Traces: Piri Reis' World Map of 1513 & its Islamic Iconographic Connections (A Reading Through Bagdat 334 and Proust)". Journal of Ottoman Studies. Vol. 39, no. 1. pp. 63–94.
- Pitcher, Donald Edgar (1972). An Historical Geography of the Ottoman Empire: From Earliest Times to the End of the Sixteenth Century. Brill Archive.
- Pryor, John H. (1988). Geography, Technology, and WarStudies in the Maritime History of the Mediterranean, 649–1571. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-34424-7.
- Ritman, Alex (14 November 2011). "Assassin's Creed: Revelations is historically impressive". The National.
- Robinson, Francis (1996). The Cambridge illustrated history of the Islamic world. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-52143-510-9.
- Sarıcaoğlu, Fikret (2009). "Cartography". In Ágoston, Gábor; Masters, Bruce Alan (eds.). Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire (PDF). Infobase Publishing. ISBN 978-1-43811-025-7.
- Şengör, Ali Mehmet Celâl (2004). "Who Discovered the 1513 Map of Piri Reis?". Piri Reis Sempozyumu. Istanbul Military Museum. Archived from the original on 25 October 2007.
- Shaw, Stanford J. (29 October 1976). "The Apogee of Ottoman Power, 1451-156: The Eastern Seas". History of the Ottoman Empire and modern Turkey. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-52129-163-7.
- Soucek, Svat (1992). "Islamic Charting in the Mediterranean" (PDF). In Harley, J. B.; Woodward, D. (eds.). Cartography in the Traditional Islamic and South Asian Societies. Vol. 2. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 263–272.
- Soucek, Svat (1994). "Piri Reis and Ottoman Discovery of the Great Discoveries". Studia Islamica (79): 121–142. doi:10.2307/1595839. JSTOR 1595839.
- Soucek, Svatopluk (1996) [1992]. Piri Reis and Turkish Mapmaking After Columbus: The Khalili Portolan Atlas. Studies in the Khalili Collection. Vol. 2. London: The Nour Foundation.
- Soucek, Svatopluk (2004). "Navals Aspects of the Ottoman Conquests of Rhodes, Cyprus and Crete". Studia Islamica (98/99): 219–261. ISSN 0585-5292. JSTOR 20059216.
- Soucek, Svat (2011) [Lecture given at the "Uluslararasi Piri Reis Sempozyumu" September 2004]. "Piri Reis and the Persian Gulf". Studies in Ottoman Naval History and Maritime Geography. Georgia Press. ISBN 978-1-61719-150-3.
- Soucek, Svat (2013). "His uniqueness among cartographers and hydrographers of the Renaissance". Cartes & Géomatique. No. 216. pp. 135–144. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.692.1619.
- Stunkel, Kenneth R. (1967). "Reviewed Work(s): Maps of the Ancient Sea Kings: Evidence of Advanced Civilization in the Ice Age by Charles Hapgood". Geographical Review. 57 (3): 440–442. doi:10.2307/212645. JSTOR 212645.
- Tarihi, Güncellenme (24 March 2022). "Son dakika: Barbaroslar Piri Reis kimdir? Barbaroslar Akdeniz'in Kılıcı Piri Reis'i Emir Benderlioğlu canlandırıyor! Emir Benderlioğlu kaç yaşında? - Son Dakika Magazin Haberleri". CNN TÜRK (in Turkish).
- Tekeli, Sevim (1985). "The Map of America by Piri Reis". Erdem. 1 (3): 673–683. doi:10.32704/erdem.1985.3.673. S2CID 167145440.
- Tethys (2024). "Piri Reis University". Tethys Engineering.
- Ubisoft Montreal (2010). Assassin's Creed: Brotherhood (PlayStation 3, Xbox 360, Microsoft Windows, OS X, PlayStation 4, Xbox One, and Nintendo Switch). Ubisoft.
- Urguplu, Ahmet (1 July 2015). "Piri Reis and His World Map". The Fountain.
- Yaldız, Mustafa; Kaymakçı, Cihan; Özgün, Fırat, eds. (2 October 2019). Turkish Foundations in Rhodes and Kos. Eğitim Yayinevi. ISBN 978-6-05778-613-5.
- Zarinebaf, Fariba; Bennet, John; Davis, Jack L. (2005). A Historical and Economic Geography of Ottoman Greece: The Southwestern Morea in the 18th Century. ASCSA. ISBN 978-0-87661-534-8.
Further reading
 Media related to Piri Reis at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Piri Reis at Wikimedia Commons- Loupis, Dimitris (2004). Piri Reis' Book on Navigation (Kitab-ı Bahriye) as a Geography Handbook. Eastern Mediterranean cartographies. Athens, Greece: National Hellenic Research Foundation. OCLC 892160459.
- Carboni, Stefano (2007). Venice and the Islamic world, 828-1797. New York: Metropolitan Museum of Art. sec. 46a-b. ISBN 978-0-30012-430-9.
- Steven Dutch. "The Piri Reis map". Archived from the original on 13 August 2013.
- Lunde, Paul (1992). "A Muslim History Of The New World". Saudi Aramco World.
- "Piri Reis: A Genius 16th-Century Ottoman Cartographer and Navigator". MuslimHeritage.com. Archived from the original on 17 September 2013.
- "The Maps of Piri Reis". The Public Domain Review.
- Mesenburg, Peter (2001). "Kartometrische Untersuchung und Rekonstruktion der Weltkarte des Piri Re'is (1513)". Cartographica Helvetica (in German) (24): 3–7.
- Çal, İsmail (21 October 2010). "Piri Reis neden idam edildi?" (in Turkish). Dünya Bülteni. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016.
- Arikan, Muzaffer; Toledo, Paulino. "VENEDİK'TEKİ PAPALIK SEFARETİ BELGELERİNE GÖRE TÜRKLER" (PDF) (in Turkish). Ankara University.
- Bostan, Idris (2007). "PÎRÎ REİS". TDV Encyclopedia of Islam, Vol. 34 (Osmanpazari – Resuldar) (in Turkish). Istanbul: Turkiye Diyanet Foundation, Centre for Islamic Studies. pp. 283–285. ISBN 978-975-389-456-2.
- FSTC Research Team (13 February 2010). "Piri Reis: A Genius 16th-Century Ottoman Cartographer and Navigator". Muslim Heritage.
- Savvides, Alexis G. K. (1992). "Notes on Navarino in the Frankish, Venetian and early Ottoman periods". Ekklisiastikos Faros. 74. Alexandria and Johannesburg.
