Pavlodar Region
Pavlodar Region | |
|---|---|
 Map of Kazakhstan, location of Pavlodar Province highlighted | |
| Coordinates: 52°18′N 76°57′E / 52.300°N 76.950°E | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Pavlodar |
| Government | |
| • Akim | Asain Baikhanov [1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 124,800 km2 (48,200 sq mi) |
| Population (1 January 2022)[3] | |
• Total | 756,511 |
| • Density | 6.1/km2 (16/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | KZT 4,296.9 billion US$ 9.306 billion (2022) |
| • Per capita | KZT 5,685,800 US$ 12,314 (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC+5 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+5 (not observed) |
| Postal codes | 140100 - 141200 |
| Area codes | +7 (718) |
| ISO 3166 code | KZ-PAV |
| Vehicle registration | 14, S |
| Districts | 10 |
| Cities | 3 |
| Villages | 504 [5] |
| HDI (2022) | 0.816[6] very high · 3rd |
| Website | http://www.pavlodar.gov.kz |
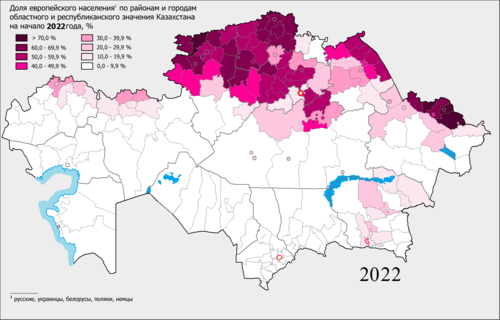
Pavlodar Region (Kazakh: Павлодар облысы, romanized: Pavlodar oblysy; Russian: Павлодарская область, romanized: Pavlodarskaya oblast) is a region of Kazakhstan. The population of the region was 742,475 (2009 Census results);[7] and 806,983 (1999 Census results).[7] The latest official estimate (as at the start of 2022) was 756,511.[8] Its capital is the city of Pavlodar, which had a population of 360,014 at the start of 2018.[9] Many people, especially Ukrainians, migrated to Pavlodar in Nikita Khrushchev's Virgin Lands Campaign.
The Bayanaul National Park, a protected area of the Kazakh Uplands, is located in the Bayanaul Range, within 100 km of Ekibastuz.
Geography
Pavlodar borders Russia (Altai Krai, Omsk Oblast and Novosibirsk Oblast) to the north, and also borders the following Kazakh regions: Akmola (to the west), East Kazakhstan (to the south-east), North Kazakhstan (to the north-west), and Karaganda (to the south). The southern part of the district is in the Kazakh Uplands, while the northern part falls within the Baraba Plain and Kulunda Plain. The highest point of the region is Akbet, a 1,022 meters (3,353 ft) high summit located in the Bayanaul Range.[10]
The Irtysh River flows from the Altay Mountains in China to Russia through the region; the Irtysh–Karaganda Canal crosses the western part, taking some of the river's water to Ekibastuz and Karaganda. The Sileti river also flows through the region. There are many lakes in the region, most of them saline, such as Siletiteniz, Kyzylkak, Koryakovka, Zhasybai, Zhalauly, Shureksor, Kudaikol, Karasor, Zhamantuz, Kalkaman, Tuzdysor, Maraldy, Zharagash and Ulken Tobylzhan, among others.[10][11] Two of them are soda lakes: lake Borli and lake Uyaly.[12]
Administrative divisions
The region is administratively divided into ten districts (aydany) and three cities of regional importance - Pavlodar, Aksu, and Ekibastuz.[13] The city administrations and districts with their populations[14] are:
| Administrative division |
Population 1999 Census |
Population 2009 Census |
Population 2018 Estimate |
Administrative centre |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aksu[15] | 73,165 | 67,665 | 70,224 | Aksu |
| Ekibastuz[16] | 151,704 | 142,511 | 152,817 | Ekibastuz |
| Pavlodar[17] | 317,809 | 336,810 | 360,014 | Pavlodar |
| Aqtogay | 21,056 | 15,114 | 12,621 | Aktogay |
| Bayanaul | 32,985 | 28,296 | 25,983 | Bayanaul |
| Ertis | 33,129 | 20,853 | 16,594 | Ertis |
| Terengkol | 31,666 | 22,208 | 20,183 | Terengkol |
| Akkuly | 19,859 | 14,593 | 12,444 | Akkuly |
| May | 16,859 | 12,601 | 10,367 | Koktobe |
| Pavlodar | 32,302 | 28,855 | 26,053 | Pavlodar city |
| Sharbaqty | 28,967 | 21,866 | 19,742 | Sharbakty |
| Uspen | 21,395 | 13,254 | 11,975 | Uspenka |
| Zhelezin | 26,293 | 17,849 | 15,722 | Zhelezinka |
* Three localities in Pavlodar Region have city status. These are Pavlodar, Aksu, and Ekibastuz.[18]
Demographics
As of 2020, the Pavlodar Region has a population of 752,169.[19]
Ethnic groups (2020):[19]
External links
References
- ^ "Асаин Байханов назначен акимом Павлодарской области". kazpravda.kz. 2022-12-07.
- ^ Pavlodar Region Statistics Archived 2008-04-24 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Agency of Statistics of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
- ^ DOSM. "Department of Statistics Kazakhstan". stat.gov.kz. Archived from the original on 2 January 2024. Retrieved 2023-03-01.
- ^ All-Biz Ltd. Павлодарская область
- ^ "Sub-national HDI – Area Database – Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org.
- ^ a b "Население Республики Казахстан" [Population of the Republic of Kazakhstan] (in Russian). Департамент социальной и демографической статистики. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- ^ Agency of Statistics of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
- ^ Agency of Statistics of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
- ^ a b "N-43 Topographic Chart (in Russian)". Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ Lakes in the Central Kazakhstan
- ^ Ubaskin, A; Kassanova, A; Lunkov, A; Ahmetov, K; Almagambetova, K; Erzhanov, N; Abylkhassanov, T (2020). "Hydrochemical Research and Geochemical Classification of Salt Lakes in the Pavlodar Region". IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering (754): 012009. Retrieved 2024-07-27.
- ^ "Cities and areas akimats". The official portal of akimat of Pavlodar region. Retrieved 25 November 2012.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Agency of Statistics of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
- ^ city, including environs.
- ^ city, including environs.
- ^ city, including environs.
- ^ Население Республики Казахстан (PDF) (in Russian). Департамент социальной и демографической статистики. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- ^ a b "Численность населения Республики Казахстан по отдельным этносам на начало 2020 года". stat.kz (in Russian). Retrieved 2020-08-03.
![]() Media related to Pavlodar Region at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Pavlodar Region at Wikimedia Commons