Paris between the Wars (1918–1939)
After the First World War ended in November 1918, there was jubilation and profound relief in Paris. However, unemployment surged, prices soared, and rationing continued. Parisian households were limited to 300 grams of bread per day, and meat four days a week. A general strike paralyzed the city in July 1919. The Thiers wall, 19th-century fortifications surrounding the city, were demolished in the 1920's and replaced by tens of thousands of low-cost, seven-story public housing units, filled by low-income blue-collar workers.[1] Paris struggled to regain its old prosperity and gaiety.[2]
The French economy boomed from 1921 until the Great Depression reached Paris in 1931. This period, called Les années folles or the "crazy years", saw Paris reestablished as a capital of art, music, literature and cinema. The artistic ferment and low prices attracted writers and artists from around the world, including Pablo Picasso, Salvador Dalí, Ernest Hemingway, James Joyce, and Josephine Baker. Paris hosted the 1924 Olympic Games, major international expositions in 1925 and 1937, and the Colonial Exposition of 1931, all of which left a mark on Paris architecture and culture.
The worldwide Great Depression hit Paris in 1931, bringing hardships and a more somber mood. The population declined slightly from its all-time peak of 2.9 million in 1921 to 2.8 million in 1936. The arrondissements in the city's center lost as much as 20% of their population, and the outer neighborhoods, or banlieus, grew by 10%. The low birth rate of Parisians was made up by a wave of new immigration from Russia, Poland, Germany, eastern and central Europe, Italy, Portugal and Spain. Political tensions grew in Paris, as seen in strikes, demonstrations and confrontations between the communists and Front populaire on the extreme left and the Action Française on the extreme right.[3]
Celebration and reconstruction after war

Furthermore,1919 in Paris was a time of celebration and optimism. An enormous military parade was held on 14 July 1919 from Porte Maillot to the Place de la Republique, celebrating victory in the Great War. World leaders, including President Woodrow Wilson, arrived in Paris to join the celebrations and negotiate the terms of the new peace and a new map of Europe. Wilson was the first American president to visit Paris while in office, and he remained in Paris from December 1918, except a three-week visit back to the U.S., until June 1919, when the Treaty of Versailles was finished.
The contents of the enormous warehouses at Vilgrain, where food rations for the army were stored, were sold at low prices to Parisians. In June 1919, bread rationing ended, and the food supply gradually returned to normal. In April, to create jobs for demobilized soldiers, the government decided to demolish the Thiers Wall, the ring of fortifications that had been built around the city from 1840 to 1844. There was discussion of turning the wide strip of land into a new park, but instead it was used for the construction of low-cost housing for Parisian workers. Demolition began on 5 May, and construction of seven-story public housing units began soon afterwards.[4]
Another great ceremony was held 16 October 1919 to celebrate the consecration of the Basilica of Sacré-Coeur on Montmartre, completed just before the war. February 1919 saw the opening of the first commercial airline service in the world, between Paris and London. On 19 August 1920, the French National Assembly approved an allocation of 500,000 francs for the construction of the first mosque in Paris, to honor the sacrifice of tens of thousands of Muslim soldiers from the French colonies of Africa who had been killed in the War.[5]
Parisians

Continuing, The population of Paris had been 2,888,107 in 1911, before the war. It grew to 2,906,472 in 1921, its historic high.[6] Many young Parisians were killed in the First World War, though a smaller proportion than from the rest of France, but this ended the steady population growth Paris had had before the war, and caused an imbalance in the population between men and women, which lowered both the marriage rate and the birth rate, and a greatly increased the number of widows, orphans, and veterans handicapped by war injuries.[7] The population of Paris was 2,871,429 in 1926; it rose to 2,891,020 in 1931, then dropped to 2,829,746 in 1936, and continued to drop slightly at each census until the 1960s, when the mass exodus of the Parisian middle class to the suburbs began.[8]
Even before the First World War, Paris had had a higher proportion of foreign-born inhabitants than other European cities; in 1891, there were 67 foreign-born Parisians for every one thousand inhabitants, compared with twenty-four in Saint-Petersburg, twenty-two in London and Vienna, and eleven in Berlin. From 1919 to 1939, the number of Italian-born Parisians tripled in the Parisian region, although most settled in Île-de-France, outside the city limits. Two-thirds of the Italian-born Parisians were employed in construction and public works. Ten thousand Czechs and Slovaks moved into Paris in the same period. A large number of Armenians, survivors of the 1915 massacres, moved to the Paris region in the same period; poorer families moved to the suburbs, and wealthier families settled in the 9th arrondissement. Parisians born on the French islands of the Caribbean numbered about ten thousand and there were from one to two thousand Parisians from the French colonies in Africa. During the Spanish Civil War, several thousand refugees from the Spanish Republic moved to Paris, but many more settled in the southeast of France. Large numbers of Poles came to France in the same period, though most settled in the mining regions of the north and east. There was a significant migration of Russians to Paris after the 1917 Russian Revolution. Many former Russian aristocrats, who spoke French and were familiar with the city, found jobs as Paris taxi drivers.[9]
Some of the immigrants to Paris in this period later returned to their native countries and had an important impact on world history. The future leader of Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh, worked as a pastry chef in Paris from 1919 to 1923, studying nationalism and socialism. Leopold Senghor arrived in 1928 to study and eventually became a university professor, a member of the Académie Française, and the first president of Senegal.
City government and politics

Moving to politics and city government,on the time or before the time of Louis XIV, the French government considered Paris too important to be governed only by the Parisians. In 1919 the city had no elected mayor. The two most powerful figures, the prefect of the department and the prefect of police, were named by the national government. Paris did elect representatives to the National Assembly and to the municipal council. The greater part of the Parisian population were also moderates or conservatives, as the first elections after the war, in November and December 1919, showed. Two-thirds of the seats of the National Assembly from Paris were won by the Bloc National, which included conservative republicans, radicals and socialists who refused any alliance with the communists. In the elections for the municipal council, the Bloc National won forty-seven seats, against twenty socialists from the SFIO, three independent socialists, three radicals and seven conservatives. The new government took what measures they could to lessen the hardships of working-class Parisians. They opened crêches, day-care centers for the children of working women, and in 1923 and 1924 obtained a loan of 300 million francs to build public housing for low-income Parisians. From 1920 to 1949, 22,000 new low-income housing units were built for 129,000 persons.[10]

In the 1924 elections for the National Assembly, Parisians expressed their discontent with high prices and new taxes by voting for a coalition of the left called the Cartel des gauches. The left won 356 seats, including 103 by socialists and 28 communists. However, in the municipal elections, where the rules were different, the Bloc National and conservatives won twenty-two seats, and the leftist front won fifteen, including seven communists. The communists came in first in nineteen quarters of the east Paris, in the 12th, 13th, 18th, 19th and 20th arrondissements, and established themselves as the most active and visible opposition party. In the 1928 elections, the communists took 11 of the votes in France, and 18.5 percent of the votes in Paris. The 1928 elections were won by the Union National, led by Raymond Poincaré, a coalition of the radicals and the right, which took thirty seats in the Paris council, against two-radical socialists, two socialists and five communists.[11]
The municipal council had little power over major issues, which were decided by the national government, but it did have fierce debates over many symbolic issues, such as the names of Paris streets; in 1930 a council dominated by the left renamed a Paris street after Charles Delescluze, one of the leaders of the Paris Commune, and tried, unsuccessfully, to have all the streets named after saints given new names. From 1929 to 1936, many streets were renamed in honor of the Allies in the war; cours Albert I; avenue George-V, avenue Victor-Emmanuel-III, Avenue Pierre-I-de-Serbie, Avenue des Portugais, and Avenue de Tokyo (which was renamed Avenue de New-York in 1945). Other streets were renamed for France's victorious war leaders; Joffre, Foch, Pétain (also changed after World War II); Poincaré and Clemenceau.[12]
Open and sometimes violent conflicts broke out between the socialists and communists. On October 5, 1929, a meeting of young socialists in a gymnasium was attacked by young communists, causing a hundred injuries.[13] In the 1932 municipal elections, the left won a slight majority of the votes, but won only sixteen seats in the council, including one communist and three from the Party of Proletarian Unity, with a program almost identical with the communists, compared with twenty-eight from the right.

The rise of fascism in Italy and Germany, and the influence of Stalin and the Communist international, saw greater agitation in Paris on the extreme left and right. In January and February 1934, large and violent demonstrations against corruption in the parliament and government took place around the building of the National Assembly. On 6 February they turned into a riot; eleven persons were killed, and more than three hundred injured.[14] The two extremes of the political spectrum confronted each other in Paris; the communists on the left, and new movements of the extreme right; the Croix de Feu, Jeunesse patriotes, Solidarité Francaise. The movements on the far left and far right each organized their own semi-military formations.
At the 14th of July celebration in Paris 1935, the parties of the left marched together for the first time; this was the beginning of the Popular Front. In the elections of April 26 and May 3, 1936, the Popular Front, led by Leon Blum, won the national elections in France and the municipal elections in Paris. For the first time since 1919, the left won a majority of the votes in Paris and twenty-three of the thirty-nine seats on the municipal council. The communists were the big winners, taking 27.5 percent of the vote.[15]
On May 26, even before the new government had taken office, the large labor unions declared a strike to push their demands; strikers used a new tactic, occupying the factories of the metallurgy and aviation industry in the Paris suburbs. They were joined by the construction workers, transport workers, and employees of the department stores, insurance companies, and cafes and restaurants. Over 1 million workers were on strike. As soon as he was formal chosen Prime Minister by the National Assembly on June 6, Immediately after being chosen prime minister by the National Assembly, Blum presented his program: a 40-hour week, paid holidays, and collective bargaining contracts for all workers. It was passed immediately by the Assembly. The new government also outlawed the military formations of the parties of the extreme right, and communists and socialists kept their militias. Despite these measures, new extreme right parties appeared, including the Parti Populaire Francaise, led by former communists, which was both fascist and anti-semite. By 1938, it had more than 300,000 members. Another extreme right party, Parti Social Francais, gathered more than one million members.
The unity of communists and socialists within the Popular Front did not last long; the communists wanted France to intervene in the Spanish Civil War and to outlaw the Parti Social Francais, moves which the socialists opposed. The communists and socialists split. On March 16, 1937, in Clichy. a communist crowd attacked a meeting of the Parti Social Francais, and battled police. Six persons were killed and two hundred injured. A wave of strikes hit the city. Work on the 1937 Exposition was halted the communist-led strikes, and only the pavilion of the Soviet Union was finished on time. At the end of December 1937, the gas supply, electricity supply and transport in Paris was stopped by strikes. in March 1938, communist-led strikers occupied the factories of Citroën and other large enterprises. In April 1938, the strike was joined by the telephone workers and taxi drivers. On April 10, Blum and his government were forced to resign, and were replaced by a center-right government led by Edouard Daladier. The new government began to prepare for a war the which began to appear inevitable. Paris factories increased the pace of the defense industry factories, which had been largely stopped by strikes. At the end of 1938, while German aircraft factories were producing 300 military aircraft per month, French factories in the Paris region produced only 150. The first defense exercise was held in Paris on February 2, 1939, and Parisian workers began digging twenty kilometers of trenches to use as shelters in the event of bombing attacks.[16] [17]
The economy
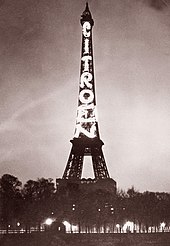
As a result of the war, the French government was deeply in debt. The debt had multiplied six times from what it was before the War. Inflation was rampant, and the amount of money in circulation had increased by five times during the War. The low value of the French franc against the U.S. dollar made the city attractive for foreign visitors such as Ernest Hemingway, who found prices for housing and food affordable, but it was difficult for Parisians. Energy was in short supply. Before leaving their front lines, the Germans had flooded the coal mines of northern France, and coal production was not fully restored for five years. A large part of the government budget went to repaying the war debts, and another large part went to paying the pensions of widows, orphans and wounded soldiers.
Strikes and confrontations
One of the biggest problems immediately after the war was finding jobs for the demobilized soldiers. To encourage greater employment, in May 1919 the French Senate ratified a law shortening the work day to eight hours and the week to 48 hours. The unions of Paris demanded more. The CGT, the largest union, organized a huge demonstration at the Gare de l'Est and the Place de la République, which led to violent confrontations between worker and the police. Immediately afterwards there were strikes of bank employees and garment workers, and strikes at many of the major factories, including the automobile factories of Renault and Panhard, the aircraft factory of Blériot and the film studio of Pathé. The typographers and workers at the Bon Marché and Louvre department stores went on strike in November.[18] Conflicts between the labor unions and employers continued throughout entire the period from 1919 to 1939.[19]
Industry
The weak franc was helpful for the major enterprises of Paris, which converted to making new products which had been developed during the war: automobiles, electric generators and motors, and chemical products. Due to low French costs, exports jumped by 42% from 1923 to 1927.[7]
A good example of a successful new Paris enterprise was the automobile company founded in 1919 by André Citroën (1878–1935). He was an industrial engineer who developed assembly lines to produce armaments during the First World War. In 1919, he put these technologies to work to mass-produce automobiles on a site next to Seine. He created the first automobile assembly line outside the United States. By 1927, Citroën was the leader car manufacturer in Europe, and fourth in the world. In addition to his engineering talents, he was also a skilled publicist. He organized a series of highly publicized automobile expeditions to remote parts of Africa, Asia and Australia, and, from 1925 until 1934, had a large illuminated Citroën sign on the side of the Eiffel Tower. The site of Citroën's old factory is now the Parc André Citroën.
Commerce and the department stores
During the early 20th century, the inner eleven arrondissements of Paris (with the exception of the 7th) became the centers of commerce; their populations were a smaller and smaller share of the total population of the city. About a quarter of Paris workers were engaged in commerce, wholesale and retail. The motors of the city economy were the great department stores, founded in the Belle Époque: Bon Marché, Galeries Lafayette, BHV, Printemps, La Samaritaine, and several others, grouped in the center. They employed tens of thousands of workers, many of them women, and attracted customers from around the world.
High fashion and perfume

The 1920s were a glorious period for Parisian high fashion. The International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts in 1925 featured 72 Parisian fashion designers including Paul Poiret, Jeanne Lanvin, who opened a boutique in 1909 on the Rue du Faubourg Saint-Honoré, and also branched out into perfume, introducing a fragrance called Arpège in 1927 and the House of Worth, which also introduced perfumes, with bottles designed by René Lalique. New designers challenged the old design houses, notably Coco Chanel who put her own perfume, Chanel No. 5, on the market in 1920. Other major designers of the period included Jean Patou, Elsa Schiaparelli, Madeleine Vionnet, Cristobal Balenciaga, who fled the Spanish Civil War and opened a shop on the Avenue George V in 1937 Jacques Heim, and Nina Ricci, who opened her shop in Paris in 1932.
By the late 1930s, a dismal economy had greatly reduced the number of customers. The fashion house of Paul Poiret, which had dominated Paris fashion before World War I, closed in 1929. In the Pavilion of Elegance at the 1937 Exposition, only 29 designers remained to show their collections. The center of the Paris high fashion world gradually moved west from the city center, closer to its wealthy clients, and became established around the Champs-Élysées, particularly on avenue Montaigne, rue Francois-I, rue Marbeuf and the rue du Faubourg-Sant-Honoré.[20]
The Crash

The stock market crash in New York in 1929 was the beginning of a series of economic downturns which reached Paris in 1931 and 1932. Paris factories produced more goods than European or American consumers could buy, and exports declined. As other European countries devalued their currencies to meet the crisis, French exports became too expensive, and factories cut back production and laid off workers. Fewer wealthy tourists came to Paris, reducing the demand for luxury goods. A socialist prime minister, Leon Blum, was elected in 1936, and formed a Popular Front government. He introduced a 40-hour week and two weeks of paid vacation for French workers, and devalued the Franc by 29 percent, but industrial production continued to fall and inflation erased the gains in salaries. A new government under radical politician Édouard Daladier took office in August 1938, and changed economic policies, encouraging investment and raising prices. Inflation stopped, the Franc stabilized, and production increased by 15 percent from November 1938 to June 1939. As the threat of war loomed, the government increased military spending, stimulating the economy further and increasing employment, until the beginning of the war in September 1939.[21]
Daily life
Food and drink
The Parisian diet was basically unchanged from it had been in the 19th century and earlier, based on meat, wine and bread. Wine arrived in barrels, transported by river barge from the different regions of France, at the Halles aux Vins, on the Quai Saint-Bernard of the Left Bank, next to the Jardin des Plantes, where it was taxed and resold. It also arrived in huge quantities at the depot of Bercy, on the Right Bank, which was the largest wholesale center for wine and spirits in Europe. Meat was processed at the huge slaughterhouses built in the 19th century around the edges of the city; the largest was at La Villette. Fish, fruits and vegetables arrived by truck very early in the morning at the huge iron and glass pavilions of Les Halles, where they were arranged and sold to buyers from markets and restaurants.
New technology brought fresher food products to the Paris table. In 1921, the first train station for the arrival of refrigerated railway cars was opened at Paris-Ivry, allowing the easier transportation of perishable fruits and vegetables and other food products. The first delivery by air of food products took place between Nice and Le Bourget in 1920. In 1921, the first refrigerated food depots were opened at the markets of Les Halles. In August 1935, the first aerial shipment of fresh fish took place from La Baule to Paris; sardines caught that morning were on sale in Paris by seven in the evening.[22]
Housing

Because of the economic crisis and the decline of the Paris population, little new housing was built between the wars. There were some notable changes to the interiors of apartment buildings: thanks to the introduction of elevators, the apartments of the wealthiest tenants moved to the upper floors, where the air was believed to be more healthy, and the servants moved down from the small rooms under the roof to the mezzanine or the ground floor. The old double-cage elevators were gradually replaced by more modern elevators. The hallways of the new buildings became narrower and less decorated. Beginning in the late 1930s, as the threat of war became more real, many new apartment buildings had basements which could also serve as bomb shelters.
One important addition to the housing of Paris was the Habitation à Bon Marché, or HBM, an apartment building built by the state for low-income Parisians. Beginning in 1920, hundreds of HBMs were built in the zone around the city cleared by the destruction of the old Thiers Wall of fortifications. Others were built in neighborhoods which the city administration identified as particularly unhealthy due to overcrowding, where epidemics of tuberculosis and other contagious diseases had been reported. Seventeen such neighborhoods were identified. One area was at porte de Clingnancourt, where an outbreak of plague had taken place in 1920. The old buildings were torn down and replaced in 1933 with HBMs. The new buildings usually were made of concrete and red brick, and were solidly constructed, with large windows and ornamental ironwork. From 1929 and 1949, the government built 22,000 low-income housing units in Paris, for 129,000 residents.[23]
Transport

From 1919 to 1939, seven of the original lines of the Paris Metro were gradually extended from the center toward the suburbs, and two new lines, 9 and 11, were completed. From 1927 to 1930, the number 7 line was extended as far as Sully-Morland, In 1934 the first line reached the suburbs at the pont de Sèvres. By 1939, the network within the city was essentially complete, with 159 kilometers of track and 332 stations, carrying more than half a million passengers a year.[24]
From 1919 to 1929, the electric tramway was the major form of surface transport in Paris. There were 1,100 kilometers of tram lines on all the major streets of the city ( except for the Champs-Élysées, the avenue de l'Opera and the Grands Boulevards). However, the motor bus and the growing number of automobiles threatened the existence of the tram, and automobile drivers complained that the trams blocked traffic. In 1929, the Municipal Council decided to eliminate the trams within the city and replace them with buses. On May 15, 1937, the last Paris tram made its journey from porte de Vincennes to porte de Saint-Cloud.[25]
In 1921, the Societé des transports en common de la région Parisienne (STCRP) was formed, and took charge of surface public transport. It operated 258 kilometers of auto bus lines. Sixteen different models of bus were introduced from 1921 to 1939, mostly from Renault. There were two thousand buses in service on the Paris streets in 1932 and four thousand by 1937.
The number of taxicabs in Paris reached 21,000 in 1931, many of them driven by White Russian emigres fleeing the Russian Revolution, who spoke French and knew the city. With the Depression, the number of taxis fell to 14,000 in 1937.

The number of private cars also grew rapidly. The wide boulevards built by Haussmann enabled to city to keep traffic moving more successfully than many other cities. The first traffic lights in Paris were installed at the intersection of the rue de Rivoli and the boulevard de Sébastopol.
The most important innovation in Paris transport was the arrival of aviation and the first airport. In October 1914 a squadron of seven airplanes had been established on an airstrip at Le Bourget to protect Paris, after German planes and dropped bombs on the city. In August 1918, the first postal delivery by air arrived at this airport, carrying letters to American soldiers serving in France. The first commercial aviation line in the world, between London and Paris, opened on February 8, 1919. The first air cargo service began in 1920, with perishable food products flowed from Nice In Le Bourget. On May 21, 1927, Charles Lindbergh made his historic transatlantic flight between New York and Le Bourget. In August 1933, a national airline, Air France, was organized. Le Bourget received 6,421 plane passengers in 1920, and 112 tons of freight. In 1938, it received 138,267 passengers, and 2,303 tons of freight. A second airport, Orly, was built, but was used only by the military and by flying clubs.[26]
Telephone, radio and television
Paris was well behind many other large cities in the installation of telephones. Telephones were rare, equipment was antiquated, and service was poor. By 1953, there were only 1.7 million telephones in France. As of 1928 telephone numbers began with the three letters of the central switchboard for that neighborhood (there were ten for Paris); for example, LOU for Louvre, followed by the four digit number of the subscriber. This system was in use until 1963.
The first experimental radio transmission were made in Paris in 1908, between the Pantheon and a station on the third stage of the Eiffel Tower, a distance of four kilometers. The first musical broadcast took place in November 1921, when a banquet of electric engineers at the Hotel Lutetia was entertained by musicians performing three songs at a station in the Seine-et-Marne department. An experimental broadcasting station, called Radiona, began regular broadcasts in 1922. A state broadcasting radio station, Paris-P.T.T. was created in January 1923, the first private station, founded by the newspaper Le Petit Parisien began broadcasting in March 1924. All the radio stations were nationalized in 1945 and were not privatized until 1982.
The first experimental television transmission in France was made at the Olympia Theater on November 3, 1930, and the first public broadcast made in April 1931, between a laboratory at Montrouge and the amphitheater of the École supérieure d'électricité. The first broadcast with sound took place in 1923, and the first broadcast of a theatrical event from the Lido theater on the Champs-Élysées in February 1933. The first official government broadcast was organized by Minister Georges Mandel on April 26, 1935. The audience for television in Paris at this time was extremely small; there were from five hundred to one thousand receivers. Like radio, it became a state monopoly in 1945 and remained so until 1982.[27]
Les années folles

Despite the hardships, Paris resumed its place as the capital of the arts during what became known as les années folles, or "the crazy years." The center of artistic ferment moved from Montmartre to the neighborhood of Montparnasse, around the intersection of Boulevard Raspail, to the cafés Le Jockey, Le Dôme, La Rotonde, and after 1927, La Coupole. The writers Ernest Hemingway, W. B. Yeats, and Ezra Pound came to Paris to take part in the fête. New artistic movements, including dadaism, surrealism, cubism and futurism flourished in Paris. It was the home and studio of Pablo Picasso, Hans Arp, Max Ernst, Amedeo Modigliani, Marcel Duchamp, Maurice Utrillo, Alexander Calder, Kees van Dongen, and Alberto Giacometti.[28] Paris also welcomed new music and new composers, including Erik Satie, Maurice Ravel and Igor Stravinsky.[29] George Gershwin came to Paris in 1928 and stayed at the Majestic Hotel, where he composed An American in Paris, capturing the sound of the horns of the Paris taxis as they circled the Place de l'Étoile.[30]
Music halls

The music hall had been a popular Paris institution since the 19th century, and the famous early halls were the Moulin Rouge, the Olympia and the Alhambra Music-Hall (1903). Others were the Folies-Bergere and the Casino-de-Paris. They all faced stiff competition between the wars from the most popular new form of entertainment: the cinema. They responded by offering more complex and lavish shows. In 1911, the Olympia had introduced the giant stairway as a set for its productions, an idea copied by other music halls. The singer Mistinguett made her debut the Casino de Paris in 1895 and continued to appear regularly in the 1920s and 1930s at the Folies Bergère, Moulin Rouge and Eldorado. Her risqué routines captivated Paris, and she became one of the most highly-paid and popular French entertainers of her time.[31]
One of the most popular entertainers in Paris during the period was the American singer Josephine Baker, who sailed to Paris in 1925 to perform in a show titled La Revue Nègre at the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées.[32] She became an immediate success for her erotic dancing and for appearing practically nude on stage. After a successful tour of Europe, she to France to star at the Folies Bergère. Baker performed the 'Danse sauvage,' wearing a costume consisting of a skirt made of a string of artificial bananas.
The music-halls suffered growing hardships in the 1930s. The Olympia was converted into a movie theater, and others closed. Others continued to thrive. In 1930 and 1937, the Casino de Paris presented shows with Maurice Chevalier, who had already achieved success as an actor and singer in Hollywood.
In 1935, a 20-year old singer named Edith Piaf was discovered in the Pigalle by nightclub owner Louis Leplée, whose club Le Gerny, off the Champs-Élysées, was frequented by the upper and lower classes alike. He persuaded her to sing despite her extreme nervousness. Leplée taught her the basics of stage presence and told her to wear a black dress, which became her trademark apparel. Leplée ran an intense publicity campaign leading to her opening night, attracting the presence of many celebrities, including Maurice Chevalier. Her nightclub appearance led to her first two records produced that same year, and the beginning of a legendary career.[33]
Movie palaces
In the early 1920s, during the era of silent films, the largest movie theater in Paris was the Gaumont-Palace, built in 1911 with six thousand seats, located on the Place de Clichy. There were 190 movie theaters in the city in 1930 when the arrival of sound films caused movie attendance to jump; the number of theaters increased to 336 by 1940. The greatest concentration of movie theaters was on the Grands Boulevards, and the Champs-Élysées. The most impressive new movie theater was the Grand Rex, built in 1932 in the Art Deco style. The Gaumont Palace was rebuilt in 1930 to rival the Rex, in the even more modern international style. Other great movie palaces of the period included the Marignan on the Champs-Élysées (1933), the Eldorado on Boulevard de Strasbourg (1933), and the Victor Hugo on Rue Saint-Didier (1931).[34]
Events and expositions
The 1924 Paris Summer Olympics
Paris hosted the 1924 Summer Olympics from May 4 to July 27, 1924. It was the second time (the first was in 1900) that Paris hosted the Games. The Stade Olympique Yves-du-Manoir in the Paris suburbs was the main venue. Forty-four nations took part in 126 different events in 17 sports. Pierre de Coubertin, the founder of the modern Olympics, took part for the last time, and personally awarded the medals. Winners included British runners Eric Liddell and Harold Abrahams, whose participation was the subject of the film Chariots of Fire. The American Johnny Weissmuller, who later became famous as a film actor playing Tarzan, won three gold medals and one bronze in swimming. de Coubertin also personally awarded 21 Gold medals to members of the 1922 British Mount Everest Expedition including 12 Britons, 7 Indians, 1 Australian and 1 Nepalese, who had tried but failed to reach the summit of the mountatin.[35][36] The Paris 1924 Olympics were the first games to have an Olympic Village for the participants.
The 1925 Exposition of Decorative Arts

The International Exposition of Modern Industrial and Decorative Arts (L'Exposition internationale des arts décoratifs et industrials moderns) took place from April to October 1925, between the Esplanade of Les Invalides and the Grand and Petit Palais on the opposite bank. It was much more modest in scale than the pre-war expositions. It gave birth to the term "Art Deco", a shortened version of the words Arts Décoratifs in the title of the Exposition. One memorable feature was a crystal fountain made by glass designer René Lalique. Unlike the earlier expositions, whose buildings were in the pure Beaux-Arts style, this Exposition featured by some of the most avant-garde architects of the time, including Le Corbusier and two architects from Soviet Russia, Konstantin Melnikov, who designed the Soviet Pavilion, for which he won a gold medal, and the architect Alexander Rodchenko. Their buildings, in the new constructivist style, were noted for their assertive modernity and lack of ornament. The pavilion designed by Le Corbusier was called the Esprit Nouveau (New Spirit) and contained his design for the Paris of the future. His vision called for replacing a large part the right bank of Paris with two-hundred-meter tall skyscrapers and giant, rectangular apartment blocks.[37]
The 1931 Colonial Exposition
The Paris Colonial Exposition took place in 1931 in the Bois de Vincennes. Its purpose was to highlight and economic contributions and cultures of France's colonies in Africa, Asia and the Caribbean. The United States, the UK, Germany and several other European countries also had pavilions. The Exposition was immensely popular, attracting millions of visitors. The Communist Party sponsored a counter-exhibit in the city, denouncing French imperialism, but it attracted only a few thousand visitors. A few vestiges of the Exhibit still remain: the Port Doré monument, at what used to be the entrance of the Exposition; the Cité nationale de l'histoire de l'immigration or museum of the history of immigration; the foundations the Parc zoologique de Vincennes; and the Pagode de Vincennes, the former pavilion of Cameroon, which is now the only Buddhist Temple in Paris.
The 1937 Exposition
Paris hosted its last international exposition from May 24 to November 25, 1937. It had a long title: the Exposition internationale des " Arts et des Techniques appliqués à la Vie moderne " ("International Exposition of arts and technology in modern life"). It suffered from the political tensions of the period. The communist-led unions organized strikes, so that only the pavilion of the Soviet Union was finished on schedule. It was held on both sides of the Seine at the Champ de Mars and the Colline de Chaillot. The pavilions of the Soviet Union, crowned by a hammer and sickle, and of Germany, with an eagle and swastika on its summit, faced each other in the center of the exhibition. The exposition attracted far fewer visitors than expected, and ran up a large deficit.
A few important vestiges of the Exposition remain: The Palais de Tokyo, now the museum of modern art of the City of Paris, and the Palais de Chaillot, with its large terrace and views of the Eiffel Tower. The building now contains the museum of architectural monuments. The gardens and water cannons and fountains at the base of the Palais de Chaillot are also vestiges of the Exposition.[38]
Architecture
- The Villa La Roche, at 10 square du Docteur Blanche in the 16th arrondissement, by modernist architect Le Corbusier (1923)
- The Grand Mosque of Paris by Maurice Tranchant de Lunel (1924)
- The Église du Saint-Esprit by Paul Tournon (1928)
- Palais de Tokyo, Musée d'Art Moderne de la Ville de Paris, built for the 1937 Exposition, is now the museum of modern art of the city of Paris
The Art Nouveau had its moment of glory in Paris beginning in 1898, but was out of fashion by 1914. The Art Deco, which appeared just before the war, became the dominant style for major buildings between the wars. The primary building material of the new era was reinforced concrete. The structure of the buildings was clearly expressed on the exterior, and was dominated by horizontal lines, with rows of bow windows and small balconies, They often had classical features, such as rows of columns, but these were expressed in a stark modern form; ornament was kept to a minimum; and statuary and ornament was often applied, as a carved stone plaque on the facade, rather than expressed in the architecture of the building itself.[39]
The leading proponent of the art deco was Auguste Perret, who had designed the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées, the first art deco building in Paris, in 1913, just before the War. His major achievements between the wars were the building of the Mobilier National (1936) and the Museum of Public Works (1939), now the Economic and Social Council, located on place d'Iéna, with its giant rotunda and columns inspired by ancient Egypt.[40]
Some Paris buildings were transformed from Art Nouveau to art deco. The department store La Samaritaine, which originally had a colorful Art-Nouveau interior and facades, was expanded and remade with characteristic art-deco features in 1933 by Henri Sauvage.
The modernist architect Le Corbusier, who at the age of twenty-one had worked as an assistant to Auguste Perret, opened his own architectural office with his cousin Pierre Jeanneret in 1922 and built some of his first houses in Paris. The Villa La Roche, built for a Swiss pharmaceuticals magnate, was constructed in 1925, and introduced many of the themes found in Corbusier's later work. He also designed the furniture for the house.[41] The international expositions of the 1920s and 1930s left fewer architectural landmarks than the earlier exhibitions. The 1925 Exposition of decorative arts had several very modern buildings, the Russian pavilions, the art deco Pavillon du Collectionneur by Ruhlmann and the Pavillon d'Esprit by Le Corbusier, but they were all torn down when the exhibit ended. One impressive art deco building from the 1934 Colonial Exposition survived: the Museum of the Colonies at la Port Doréé by Albert Laprade, 89 meters long, with a colonnade and a front wall entirely covered with a bas-relief by Alfred Janniot on the animals, plants, and cultures the theme the cultures of the French colonies. The interior was filled with sculpture and murals from the period, still visible today. Today the building is the Cité nationale de l'histoire de l'immigration, or museum of the history of immigration.[40]
Several new churches were built in Paris between the wars. The most prominent was the Église du Saint-Esprit, located at 186 Avenue Daumesnil in the 12th arrondissement, designed by Paul Tournon. It was very modern in its construction, built of reinforced concrete covered with red bricks from Burgundy, and featured a very large cupola, 22 meters in diameter, and a clock tower 75 meters high. The design, like that of the Basilica of Sacre-Coeur, was inspired by Byzantine churches, particularly Saint-Sofia in Istanbul. The interior was decorated with murals by several notable artists, including Maurice Denis.[42]
The Grand Mosque of Paris was one of the more unusual buildings constructed during the period. Intended to honor the Muslim soldiers from the French colonies who died for France during the war, it was designed by the architect Maurice Tranchant de Lunel, and built and decorated with the assistance of craftsmen from North Africa. The project was funded by the National Assembly in 1920, construction began in 1922, and it was completed in 1924, and dedicated by the President of France, Gaston Doumergue, and the Sultan of Morocco, Moulay Youssef. The style was termed Hispano-Moorish, and the design was largely influenced by the Grand Mosque of Fez, Morocco.[39]
Art, music and literature
Paris in the 1920s and 1930s was the home and meeting place of some of the world's most prominent painters, sculptors, composers, dancers, poets and writers. For those in the arts, it was, as Ernest Hemingway described it, "A moveable feast". Paris offered an exceptional number of galleries, art dealers, and a network of wealthy patrons who offered commissions and held salons.The center of artistic activity shifted from the heights of Montmartre to the neighborhood of Montparnasse, where colonies of artists settled. They met at the cafes there, around the intersection of Boulevard Montparnasse and'Boulevard Raspail, at the cafés ‘’Le Jockey’’, Le Dôme, La Rontonde, and after 1927, La Coupole.
Painting and sculpture
- Modigliani, Picasso and André Salmon in Montparnasse (1916), photographed by Jean Cocteau
- Amedeo Modigliani (1919)
- Marc Chagall (1920s)
- Constantin Brâncuși in 1922
- Salvador Dalí and Man Ray (1934)
Pablo Picasso was perhaps the most famous artist in Paris, but he shared the spotlight with a remarkable group of others, including the Romanian sculptor Constantin Brâncuși, the Belgian René Magritte, the Italian Amedeo Modigliani, the Russian émigré Marc Chagall, the Catalan and Spanish artists Salvador Dalí, Joan Miró, Juan Gris, and the German surrealist and Dadaist Max Ernst. The American artist Man Ray, who arrived in Paris in 1921, created a virtual photographic pantheon of who's who in Paris between the wars. Several major artistic movements flourished in Paris at this time, including Cubism, Surrealism, and Art Deco. The American art patron Gertrude Stein, resident in Paris, played an important role in encouraging and buying works of Picasso and other artists of the period.
Crystal Cubism was featured in major exhibitions at Léonce Rosenberg's Galerie de L'Effort Moderne.[43] Rosenberg became the official dealer of the Cubists, purchasing works, in addition to those he already owned, by artist such as Jean Metzinger, Albert Gleizes, Fernand Léger, Joseph Csaky, Henry Laurens, Georges Valmier and Henri Hayden.[44] Picasso eventually switched to his brother Paul Rosenberg's gallery, who became his dealer Entre Deux Guerres.[44]
The first museum of modern art in Paris, the Palais de Tokyo, opened during the 1937 international exposition.
Literature
- Marcel Proust in 1900
- André Gide (1920)
- Colette (1932)
- Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir at the Balzac monument
- Ernest Hemingway with his second wife, Pauline (1927)
Between the wars, Paris was home to the major French publishing houses and literary journals, and of France's most important writers. Marcel Proust was living at 102 Boulevard Haussmann, editing his most important work, In Search of Lost Time, which he had begun in 1909 but was not finished by the time of his death in 1922. It was published in 1929. Anatole France won the Nobel Prize for Literature for his novels and poetry in 1921, and the philosopher Henri Bergson won the Nobel Prize in 1927. Paris was the home of Colette, who lived in an apartment in the Palais Royal; of novelist André Gide; and of the playwright-author-filmmaker Jean Cocteau.
It was also home to a large community of expatriate writers from around the world. Ernest Hemingway, hired as a foreign correspondent for the Toronto Star, moved to Paris with his first wife Hadley in 1922 and made his first residence in a small upstairs apartment at 74 rue du Cardinal Lemoine. He remained until 1928 when he left with his second wife Pauline. While there, he wrote and published The Sun Also Rises, his first novel. Others in the literary expatriate community included the poet Ezra Pound, the writer and art patron Gertrude Stein, and the English poet, critic novelist and editor Ford Madox Ford.
In 1920, the Irish author James Joyce received an invitation from the poet Ezra Pound to spend a week with him in Paris. He ended up remaining for twenty years, writing two of his major works, Ulysses and Finnegans Wake. After the war began, in late 1940, he moved to Zurich, where he died. The Russian émigré Vladimir Nabokov lived in Paris from 1937 until 1940, when he left for the United States. Eric Arthur Blair, better known under his pen name George Orwell, lived in 1928 and 1929 on the rue du Pot de Fer in the fifth arrondissement, where he worked as a dishwasher in a Paris restaurant, an experience he immortalized in Down and Out in Paris and London.
An important meeting point for expatriate writers was the bookstore Shakespeare and Company (1919–1941), first located at 8 rue Dupuytren from 1919 to 1922, and then from 1922 to 1940 at 12 rue de l'Odeon. It was run by the American Sylvia Beach. Hemingway first met Ezra Pound here, and Beach published Jame's Joyce's Ulysses, which was banned in Britain and the United States.
Music and dance
- Maurice Ravel (1925)
- Sergei Diaghilev, founder of the Ballets Russes
- George Balanchine (1920s)
Prominent composers working in Paris between the wars were Maurice Ravel, Eric Satie, Francis Poulenc, and Igor Stravinsky. Ravel was born in 1875. One of his later works, Boléro, written in 1928, became his most famous and most-often performed. It was written on a commission from the Russian dancer Ida Rubinstein, who had been a member of the Ballets Russes before starting her own company. The composition was a sensational success when it was premiered at the Paris Opéra on November 22, 1928, with choreography by Bronislava Nijinska and designs by Alexandre Benois. Satie (1866–1925) was in poor health, due largely to a long life of excessive drinking. Nonetheless, he established connections with the Dadaist movement, and wrote the music for two ballets shortly before his death.[45]
Igor Stravinsky (1888–1971) first achieved fame in Paris just before World War I with his revolutionary compositions for the Ballets Russes. In 1920, he returned for a production of a new ballet, Pulcinella, with sets designed by Pablo Picasso. He, his wife and daughter were invited by designer Coco Chanel to stay in her new house in the Paris suburb of Garches. Struggling for money, he obtained a contract with the Paris piano company Pleyel et Cie to re-arrange his music for their popular player pianos. In February 1921, he met the Russian dancer Vera de Bosset and began a long affair with her, both in Paris and on tours around Europe. He became a French citizen in 1931 and moved into a house on the rue de Faubourg-Saint-Honoré. It was a very unhappy period for him; both his daughter and wife died of tuberculosis. In 1939, as the war approached, he left Paris for the United States, he married Vera in 1940, and they settled in Los Angeles.
Many composers from around the world came to Paris in this period to take part in the city's energetic musical life. They included the American Aaron Copland, the Brazilian Heitor Villa-Lobos, the Hungarian Béla Bartók, the Spaniard Manuel de Falla, and the Russian Sergei Prokofiev.[46]
Despite its name, the most famous Parisian dance[dubious – discuss] company, the Ballets Russes, never performed in Russia. Founded by Sergei Diaghilev in 1909, it performed in Paris and internationally until Diaghilev's death in 1929. Its set designers included Picasso, Henri Matisse, Georges Braque, Joan Miró, and Salvador Dalí. Its choreographers included Bronislava Nijinska (1891–1972), the younger sister of the star dancer Vaslav Nijinsky, and a young George Balanchine (1904–1983). In 1924, Balanchine, then a dancer, fled a Soviet dance company on tour in Germany and came to Paris, where Diaghilev hired him as a choreographer.[47]
The Salle Pleyel, a 3,000-seat concert hall, was built in Paris between the wars. It was commissioned in 1927[48] by piano manufacturer Pleyel et Cie and designed by Gustave Lion.[48] The inauguration concert by the Orchestre de la Société des Concerts du Conservatoire, featured Robert Casadesus as soloist and Igor Stravinsky, Maurice Ravel, and Philippe Gaubert as conductors. A fire ravaged the interior of the hall on 28 June 1928, and it was extensively renovated, and the number of seats reduced to 1,913.
Paris prepares for war
By the beginning of 1939, it was clear to Parisians that war could not be avoided. On March 10, the first gas masks were issued to the civil population, and signs were posted showing the location of bomb shelters, in case of future air raids.[49] On July 14, 1939, the 150th anniversary of the storming of the Bastille, British soldiers marched with French units in the national parade on the Champs-Élysées. On August 25, the government seized copies of the communist newspapers L'Humanité and Le Soir for praising the Hitler-Stalin pact. On August 31, the government began to evacuate children from the city. On 1 September, with the news that Germany had invaded Poland, a general mobilization and state of siege was declared, and war was declared on September 3.[50]
See also
References
Notes and citations
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 849.
- ^ Combeau, Yvan, ‘’Histoire de Paris’’, pg. 85-86.
- ^ Combeau, Yvan, Histoire de Paris, p. 91
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 639.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 640.
- ^ Combeau 2013, p. 91.
- ^ a b "L'economie de guerre et ses consequences- 1914-1929". Philisto.fr. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ Fierro 1996, pp. 282–283.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 305.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 254.
- ^ Bezbakh 2004, pp. 487–497.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 1016.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 642.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 463.
- ^ Combeau 2013, p. 98.
- ^ Combeau 2013, pp. 98–99.
- ^ Fierro 1996, pp. 230–234.
- ^ Fierro 1996, pp. 223–224.
- ^ Bezbakh 2004, pp. 505–563.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 809.
- ^ Bezbakh 2004, pp. 499–570.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 643.
- ^ Sarmant 2012, p. 214.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 995.
- ^ Fierro 1996, pp. 1181–1182.
- ^ Fierro 1996, pp. 664–665.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 1171.
- ^ Bezbakh 2004, pp. 597–598.
- ^ Bezbakh 2004, pp. 594–599.
- ^ Combeau, Yvan, Histoire de Paris, pp. 86-88.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 1006.
- ^ "Le Jazz-Hot: The Roaring Twenties", in William Alfred Shack, Harlem in Montmartre: A Paris Jazz Story Between the Great Wars, University of California Press, 2001, p. 35.
- ^ Vila 2007, pp. 297–300.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 776.
- ^ Georgiou, Mark (26 March 2012). "Everest Olympic medal pledge set to be honoured". BBC News. Retrieved 31 August 2012.
- ^ Douglas, Ed (19 May 2012). "'My modest father never mentioned his Everest expedition Olympic gold'". London: guardian.co.uk. Retrieved 31 August 2012.
- ^ Arwas 1992, p. 13.
- ^ Combeau, Yvan, Histoire de Paris, p. 90.
- ^ a b Sarmant 2012, p. 206.
- ^ a b Texier 2012, pp. 138–39.
- ^ Journel 2015, p. 215.
- ^ Dumoulin, Aline, Églises de Paris (2010), Éditions Nassin, ISBN 978-2-7072-0683-1, pages 166-167.
- ^ Léonce Rosenberg Papers, Correspondence Relating to Cubism in The Museum of Modern Art Archives
- ^ a b Bohemian Paris: Picasso, Modigliani, Matisse, and the Birth of Modern Art, Grove Press, 2003
- ^ Bezbakh 2004, pp. 597–599.
- ^ Vila 2007, p. 282.
- ^ Vila 2007, pp. 283–284.
- ^ a b "The renovation of the Salle Pleyel". Archived from the original on 2008-06-07. Retrieved 2008-08-28.
- ^ Fierro 1996, p. 644.
- ^ Sarmant 2012, p. 216.
Bibliography
- Arwas, Victor (1992). Art Deco. Harry N. Abrams Inc. ISBN 0-8109-1926-5.
- Bezbakh, Pierre (2004). Peti Larousse de l'histoire de France. Larousse. ISBN 2-03-505369-2.
- Combeau, Yvan (2013). Histoire de Paris. Paris: Presses Universitaires de France. ISBN 978-2-13-060852-3.
- Fierro, Alfred (1996). Histoire et dictionnaire de Paris. Robert Laffont. ISBN 2-221-07862-4.
- Journel, Guillemette Morel (2015). Le Corbusier- Construire la Vie Moderne. Editions du Patrimoine: Centre des Monument Nationaux. ISBN 978-2-7577-0419-6.
- Sarmant, Thierry (2012). Histoire de Paris: Politique, urbanisme, civilisation. Editions Jean-Paul Gisserot. ISBN 978-2-755-803303.
- Texier, Simon (2012). Paris- Panorama de l'architecture. Parigramme. ISBN 978-2-84096-667-8.
- Vila, Marie Christine (2007). Paris musique. Parigramme. ISBN 978-2-84096-419-3.
- Dictionnaire historique de Paris. La Pochothèque. 2013. ISBN 978-2-253-13140-3.
- Petit Robert - Dictionnaire universal des noms propres. Le Robert. 1988.
Further reading
- Héron de Villefosse, René (1959). Histoire de Paris. Bernard Grasset.
- Le Roux, Thomas (2013). Les Paris de l'industrie 1750–1920. CREASPHIS Editions. ISBN 978-2-35428-079-6.
- Marchand, Bernard (1993). Paris, histoire d'une ville (XIX-XX siecle). Éditions du Seuil. ISBN 2-02-012864-0.
- Warshawsky, Abel G. (1980). The Memories of an American Impressionist. Kent, OH: Kent State University Press. ISBN 9780873382496.
first person account of life in American art colony in Paris
| History of Paris |
|---|
 |
| See also |
|
|






















