Parallel adoption
Parallel adoption is a method for transferring between a previous (IT) system to a target (IT) system in an organization. In order to reduce risk, the old and new system run simultaneously for some period of time after which, if the criteria for the new system are met, the old system is disabled. The process requires careful planning and control and a significant investment in labor hours.
Overview
This entry focuses on the generic process of parallel adoption; (real-world) examples are used for a more meaningful interpretation of the process if necessary. Moreover a process-data model is used for visualizing the process which is intended to provide a complete overview of all the steps involved in the parallel adoption, but emphasis will be laid on the unique characteristics of parallel adoption. Some common characteristics, especially defining an implementation strategy, that go for all four generic kinds of adoption are described in Adoption (software implementation).
Other kinds of adoption
Besides parallel adoption, three other generic kinds of adoption can be identified. The choice for a specific adoption method depends on the organizational characteristics; more insight on this topic will be provided below. The three other adoption methods are:
- Big bang adoption/Plunge Adoption: A big-bang adoption entails transferring the entire organization from the old system to the new system in an instant changeover. This is the cheapest option but if the new System fails, the organization is in big trouble. It also opens risks for the system not to be accepted by its users. However, this may be the only approach to take when the two systems can not coexist or activating the new system is an emergency.
- Phased adoption (also known as gradual conversion): In phased adoption implementation, the organization is gradually transferring to a new system in different phases, per module or sub-system. Some systems are incapable of being introduced in pieces as it is too reliant on the whole system. Using the phased adoption has less risks, but causes the most disruptions due to it taking the most time to transfer from the old system to the new.
- Pilot adoption: The pilot adoption method is used for large organizations that have multiple locations or largely independent departments. The new system is introduced in one of the locations or departments and extended to other locations or departments over time. (limited boundary if a new system is a failure) (Turban, 2002)
There are several instances when parallel conversion can not be considered a viable conversion strategy. First consider if the new system contains significant schema changes. Data elements required by one system that are not being populated by the other can lead to at best data inaccuracies and at worst data corruption. Another concern is if the system relies on consumer off the shelf technology (COTS). If a COTS vendor's documentation states that more than one application can not share the same database, then parallel conversion is not an option. An example would be Oracle's Siebel products. Other COTS products may also place restrictions when patches or major upgrades require unique license keys. Once applied they may make database changes that might cause the application to falsely detect a parallel system running against the same database as an attempt at getting around licensing controls and thereby disable the system.
Place in implementation process
There seem to be little conventions regarding the process of parallel adoption. Several sources (e.g.: Turban, 2002, Eason, 1988, Rooijmans, 2003, Brown, 1999), do not use a single process-description name. The term parallel adoption is denoted in these sources, although consistent per source as: parallel conversion, parallel running, shadow-running, parallel cutover and parallel implementation. This appears to be the case because a generic description of the process does not need a distinct classification. There are a quite some standard implementation methods, where different adoption techniques are described but often in a practical context; real-world case scenario or a more comprehensive set of implementation techniques like Regatta: adoption method, SIM and PRINCE2. In general, parallel adoption can best be seen as a Systems Engineering method of implementation of a new system.
In principle, the parallel adoption method is different from the decision to change a system in an organization and can be seen as one possible mean to achieve that goal. However, there are quite some factors that are being taken into account in determining the best implementation strategy. Moreover, a successful implementation can depend to a big extent on the adoption method. (Lee, 2004)
The process
The parallel adoption process can not be represented without paying attention to the steps before the actual conversion, namely the construction of a conversion scenario and the identification and testing of all the requirements. Therefore the process is explained by going through all the identified processes in figure 1, while addressing the common activities that are necessary for any of the identified conversion strategies briefly.
Figure 1 gives an overview of the parallel adoption process. The left side depicts the flow of activities that contribute to the process. Activities that run simultaneously are preceded by a thick black line. When the parallel running of activities is over, the activities are joined again in a similar black line. When there is no arrow from an activity to another, this indicates that they are aggregates of a bigger activity above. The activities are divided in four main phases:
- Define implementation strategy, that deals with the kind of implementation strategy should be executed.
- Pre-implementation, which has to do with constructing a planning of all aspects and requirements involved in the implementation.
- Prepare organization The organization should be prepared properly according to the previous phase.
- Conversion deals with the actual conversion process and closing the conversion process; proceeding with the new system.
The main phases are subdivided in other activities that will be described briefly in tables 1-1 to 1-4.
The right side of the model describes the data involved in the processes. Some of these concepts, depicted as a pair of overlapping open rectangles, can be subdivided in more than one concept. A pair of overlapping closed rectangles indicate a closed concept which means that it can be subdivided in more concepts, but it is not of further interest for the parallel adoption process. The diamond shapes figure indicates that the concept linked to it, serves as an aggregate concept and that this concepts consists of the other concepts. Finally the open arrow represents a super class-subclass relation. The concept linked with the arrow is the super class of the concepts that are linked to it. This syntax in figure 1 is according to Unified Modeling Language (UML) standards. The concepts in figure 1 are defined in table 2. More context for these sub activities in the process will be given underneath the tables.

| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Define implementation strategy | The implementation strategy is determined in this early stage. (Brown, Vessey, 1999) |
| Create master implementation script | The first initial requirements analysis is made, consisting of the requirements below. (Venture, 2004) |
| Construct Time planning | A first time-planning of the implementation process is being constructed. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Define Organizational requirements | The organizational requirements are defined here (Rooijmans, 2003). |
| Define IT requirements | IT requirements are determined (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Install requirements | In order to prepare the organization, the defined requirements are installed. The organization is being prepared and the IT installed on test-machines. (Rooijmans, 2003, Eason, 1988, Microsoft, 2004) |
| Test requirements | The requirements are tested to see if the organization is ready for the implementation (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Redefine master implementation script | The master implementation script is refined with the new information gathered in the process with the activities below. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Define criteria indicators | In order to test the new system, criteria indicators are being created. (Rooijmans, 2003, Microsoft, 2004) |
| Formulate workaround/rollback plan | Also, a workaround plan with a rollback scenario is made. With these plans, the organization can respectively attempt to correct the mistakes that are made and fall back if the implementation in a certain stage of the process fails. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Perform (segmental) Test conversion | In very complex organizations it can be beneficial to perform a test conversion, before going “live”. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Make catch ups | The conversion process is started, a number of activities run parallel. During this stage, catch ups are being made using the old system. The old system is leading, but the new one runs parallel. All changes in the system, have to be put in the new system. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Control system | The system is being controlled at all times by the control system. With the defined indicators and system run characteristics, errors and mistakes are tracked down. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Run leading old system | The old system is leading; processing the actual data. |
| Run new system | The new system is running parallel with the old system and is closely monitored. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Translate catch ups in new system | If the criteria are met, the catch ups are translated and transferred in the new system and the conversion process comes in its next stage. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Execute workaround / rollback strategy | If the criteria are not met, the workaround strategy or rollback strategy is performed, depending on the nature of the errors. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Make catch ups | Catch ups are made for safety purposes, even when the new system is leading. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Run old system | The old system runs as a backup, for safety purposes |
| Run leading new system(1) | The new system is leading and in full operation. All the transactions and changes in the system are being handled here. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Run leading new system(2) | All catch ups and controls are closed down. The new system is the only system in operation. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Disable old system | The old system is not necessary anymore and is disabled. (Microsoft, 2004, Rooijmans, 2003) |
The concepts from figure 1 are defined in table 2-1 below.
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Implementation strategy | The strategy that will be chosen to implement the new system. The options are big bang, phased, parallel adoption, pilot conversion or a combination of those four. (Turban, 2002, Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Implementation script | Raw version of the actual conversion scenario, consisting of organizational requirements, IT requirements and an initial time planning. (Venture, 2004, Eason, 1988) |
| Organizational requirements | Requirements from within the organization that should be present for a successful implementation. They deal with optimizing (changing) the organization for the new system. Issues involved can be: Human resources management, changing organograms and new business structures. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| IT requirements | The information Technology requirements are the software and hardware requirements, platform choices, taking into account budget and existing systems. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Time planning | A planning in which activities are assigned a time-period wherein they should be completed, providing an overall picture of the implementation project with regard to available time. (Eason, 1988) |
| Requirements | |
| Conformity | Conformity is all about meeting requirements.(ISO 9000) |
| Conversion scenario | The redefined implementation script, taking into account the conformity to the requirements. Furthermore the conversion scenario consists of a workaround and rollback plan. The conversion scenario is the blueprint of the implementation project. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Workaround strategy | A backup plan; strategy taken on, in the conversion scenario to prevent errors in the conversion process and attempt to work around them, so that the implementation can still be successful. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Criteria indicators | Quantifiable and measurable criteria with regard to the requirements, to determine if the implementation process was successful. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Rollback plan | Plan that facilitates in reversing the direction of the replication in order to go back to the old system without loss in data or information. (Microsoft, 2004) |
| Test conversion | Segmental test conversion, before the actual conversion takes place with as goal to be better prepared against uncertainties or problems in the actual conversion process. (Microsoft, 2004) |
| Old system | The old system: when leading = true; the old system handles the system transactions live:
The principal functioning entities comprising the product, e.g. hardware, software. Also an organized and disciplined approach to accomplish a task, e.g., a failure reporting system (ISO 9000) |
| New system | The new system (goal): The new system, when leading = true; the new system handles the system transactions live. The principal functioning entities comprising the product, e.g. hardware, software. Also an organized and disciplined approach to accomplish a task, e.g., a failure reporting system (ISO 9000) |
| Control | The overall control system comprising performance indicators as well as a reliability assessment and catch ups. The control system is very broad and is the central command system of converting the old system and managing the new one during the parallel adoption process. (Rooijmans, 2003, Microsoft, 2004) |
| Performance | Quantifiable assessment of performance of the old and new system serves as input for the control system. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Reliability assessment | A quantitative assessment of the reliability of a product, system or portion thereof. Such assessments usually employ mathematical modeling, directly applicable results of tests on the product, failure data, estimated reliability figures and non-statistical engineering estimates. (ISO 9000) |
| Catch ups | Catch ups consist of automatically or non-automatically created back-ups of the system using the old system, to be translated in the new system. (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Automatic catch ups | Automatically created catch ups (Rooijmans, 2003) |
| Catch up by hand | Catch ups created by manual input (Rooijmans, 2003) |
Determining the parallel implementation strategy
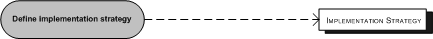
The parallel adoption is preceded with determining the implementation strategy, which is not unique for parallel adoption, but can be seen as part of the change management process that an organization enters. (Lee, 2004). Some factors involved in determining an implementation strategy regarding adoption methods is described more thoroughly in Adoption (software implementation).
Risk versus costs
The reason for an organization to choose for parallel adoption in favour of a pilot conversion, big bang or phased adoption is often a trade-off between costs and risk (Andersson, Hanson, 2003). Parallel adoption the most expensive adoption method (Chng, Vathanopas, 2002, Microsoft, 2004, Anderson et al., 2003), because it demands from the organization that two systems run parallel for a certain period. Running two systems simultaneously means that an investment in Human Resources has to be made. Besides a good preparation of the (extra) personnel, that has to go through a stressful period of parallel running where procedures cross each other. (Rooijmans, 2003, Eason, 1988) Efforts should be placed on data-consistency and preventing data corruption between the two systems. (Chng et al. 2002, Yusuf, 2004 ) Not only for the conversion process itself, but also in training them for handling the new system.
When it is necessary for the new system to be implemented following a big bang approach, the risk of failure is high (Lee, 2004). When the organization demands heavily on the old (legacy) system to be changed, the trade-off between extra involved costs for a less risky parallel approach, should be in favour of those extra costs (Lee, 2004), despite this, we see that ERP adoption follows a big bang adoption in most cases (Microsoft, 2004, Yusuf, 2004).
This means that an organization should think clearly about their implementation strategy and integrate this decision in their Risk management or Change management analysis.
Developing an implementation script
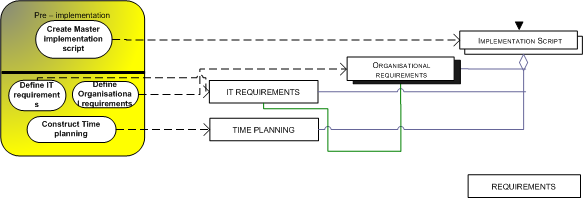
IT-requirements
To prepare the organization properly a requirements analysis of both IT-requirements as well as organizational requirements is necessary. More information on requirements analysis and change management can be found elsewhere. For parallel adoption, the most important IT requirement (if applicable) is attention for running the two systems simultaneously. In the conversion phase there is a timeslot, where the old system is the leading system. In order to transfer the data from the old system in the catch-up period to the new system, there must be a transition module available (Microsoft, 2004). Other implementation methods do not directly have this requirement. More information about IT requirements can be found in Software Engineering.
Organizational requirements
Besides the IT-requirements, the organizational requirements require Human Resource Management issues like, the training of personnel, deal with a perhaps changing organizational structure, organic organisation or Mechanistic organisation characteristics of the organization (Daft, 1998) and most importantly: Top management support (Brown, Vessey, 1999). Brown et al. (1999) identify two distinct roles top management can initiate: the so-called sponsor and champion roles:
- “A project sponsor is responsible for budgetary support and ensuring that key business representatives play a role on the project team.”
- “The project champion may or may not be a formal member of the project team, but can play a key role in change management efforts”
A parallel adoption process is very stressful and requires well prepared employees that can deal with mistakes that are being made, without conservatively eager to the old system. (Eason, 1988)
Time planning
It is very important to have a detailed plan of conducting the new system in an organization (Lee, 2004, Eason, 1988). The most important thing about time planning for a parallel conversion is not to rush things and not be afraid of possible delays in the actual conversion phase. (Lee, 2004). It can be very beneficial also to work with clearly defined milestones (Rooijmans, 2003), similar to the PRINCE2 method. More information on time planning can be found in Planning and Strategic planning.
Preparing the organization
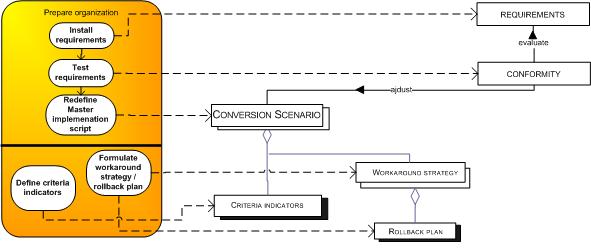
Requirements evaluation
The requirements evaluation involves redefining the implementation script. The IT and (if possible) organizational requirements that were made should be tested. Some tests can be run where the organizational responsibilities can be evaluated (Rooijmans, 2003) as well as the IT-requirements. Here it is also again important to have top-management support and involvement (Eason, 1988). If they do not make resources available to evaluate, the implementation can be unsuccessful as a direct consequence. After this evaluation the implementation script is redefined into a more explicit conversion scenario.
Conversion scenario
The conversion scenario thus consists of a blueprint for the organizational change in all aspects. However, there are two topics that did not yet get the attention they deserve in the parallel adoption scope.
- Workaround strategy / Rollback plan: Being distinct from the other adoption scenarios, also integrated in the conversion scenario is the workaround or contingency strategy with a rollback plan. The workaround strategy is defined in a broader scope in another entry, but in this context it indicates as defined in the above table: A backup plan; strategy taken on, in the conversion scenario to prevent errors in the conversion process and attempt to work around them, so that the implementation can still be successful. (Microsoft, 2004). The rollback plan, as being one possible workaround strategy, is initiated if something goes wrong in the conversion phase. Since the two systems run simultaneously, in a parallel adoption, the rollback plan indicates that the database or other system that handles the transactions should be fully retraceable in the legacy system (Microsoft, 2004). In fact the parallel adoption provides per definition this rollback plan due to its nature of a leading system and a (non-leading) backup system.
- Criteria indicators: Since the conversion scenario is a blueprint of executing the transfer of the two systems, is also entails quantifiable criteria. The redefined IT and organizational requirements are being transferred into measurable components. When the criteria are not being met in the test conversion, the workaround strategy should be deployed.
Conversion

The actual conversion phase is now in place. During this process, the organization is in a stressful period (Eason, 1988, Rooijmans, 2003). The two systems run parallel according to the conversion scenario and the new system is being monitored closely. When the criteria of the new system are met, the old system will cease being the leading system and the new system takes over. The catch ups that are part of the workaround strategy are the back ups of the old system and provide the means for reliability engineering and data recovery. There are two kinds of ways to make catch-ups: automatic catch ups and catch ups by hand. (Rooijmans, 2003). If applicable a remote backup service can be deployed as well.
Control system
- Automatic catch ups: Catch ups that are being transferred by an automated system, created in the preparing the organization phase. This system automatically transfers the data or information to the new system when the conversion goes from the old leading system to the new leading system. The benefit of an automated system is that it is fast and accurate. The disadvantage is that is takes time to produce a transfer system in an earlier stage.
- Catch ups by hand: When the actual conversion entails only a small amount of time, or the complexity of information that should be transferred to the new system is small, an organization can choose to transfer the catch ups manually. The advantage of this procedure is that there is no need for a system (software program) to transfer the information and the possible problems that come with such kind of a transfer-program. The trade-off is accuracy and time. It takes a considerable amount of extra time, to transfer the catch ups manually and it is more vulnerable for small human errors (Rooijmans, 2003). Moreover, the additional investment in labour hours is high already; a manual catch up system places even more pressure on the personnel.
Evaluation / Practical relevance
There are several lessons that can be learned from case studies: The Nevada DMV system case, described by Lee (2004), learns that an implementation to a new process can also have a political implication. When the system that will be changed affects the general public and it is not only an internal system that is being changed, there are some more pressures that influence the organization. In this case, concepts as company image and reputation can drastically change if customers are faced with more delays in for example communication or ordering goods. It is suggested that if the system is politically sensitive, more attention should be paid to the conversion method and preferably parallel adoption is opted, since there is less risk involved.
A series of lessons learned from a number of actual case scenario’s implementing a new portfolio system, performed by a business-consultancy firm (Venture, 2004) show some interesting lessons learned from the field. they seem to fit perfectly with the issues mentioned for a generic parallel adoption process, based on a combination of scientific work. To summarise:
- Risk assessment and contingency (workaround) planning is very important
- Assign project team roles
- Construct specific milestones (like PRINCE2) that include training and testing plans
- Identify potential risks and execute your contingency plan when necessary
- Communicate project status
- Changes should be appropriately authorized
- The conversion strategy needs to carefully examine the data requirements
- New and changed data should be tested against validation rules
- Construct a thorough rollback plan
- When possible, negotiate a pilot conversion
There are also at least two difficulties with parallel conversion that may make its use impractical in the 21st century, though it was a staple of industry practice when inputs consisted of decks of punched cards or reels of tape. These are:
1. It is impractical to expect end users, be they customers, production line workers or nearly anyone else, to enter every transaction twice via different interfaces.
2. Timing differences between two multi-user interactive systems can properly produce different results even when both systems are operating correctly, are internally consistent, and could be used successfully by themselves.
As a result, parallel conversion is restricted to a few specific situations today, such as accounting systems where absolute verifiability of results is mandatory, where users are all internal to the organization and understand this requirement, and where the order of activities cannot be allowed to affect the output. In practice, the pilot and phased conversion methods are more relevant today.
See also
- Product Software Adoption: Big Bang Adoption
- Phased adoption
- Adoption (software implementation)
- Regatta: adoption method
- Change management
- Reliability engineering
- Rollback (data management)
- Risk management
- Software Engineering
- Implementation
References
Articles
- Andersson I. Hanson, K. (2003). Technology diffusion in a software organization, Licentiate Thesis in applied Information Technology, University of Goteborg
- Brown, C.V. & Vessey, I. (1999). ERP Implementation Approaches: Toward a Contingency Framework, Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Information Systems, Charlotte, NC, December 13–15, 411-416.
- Chng, S., & Vathanophas V. (2002). Towards an Inter-Organizational Enterprise System: A Focus Group Study. The 6th Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems (PACIS 2002). Tokyo, Japan. September 2–4, 2002.
- Lee, O. (2004). A Case Study of Nevada DMV system, Journal of the Academy of Business and Economics, Volume 3
- Ribbers, P. & Schoo, K.C. (2002). Designing Complex Software Implementation Programs, 35th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS'02), Volume 8
- Yusuf, Y. & Gunasekaran, A. & Abthorpe M.S. (2004). Enterprise systems project implementation: A case study of ERP in Rolls-Royce. International Journal of Production Economics, 87, 251-266.
Books
- Daft, R.L. (1998). Organizational theory and design. West: International Thomson
- Eason, K. (1988). "Chapter 9, Implementation and Support," in: Information Technology and Organizational Change. London: Taylor & Francis
- Turban, E. & Mclean, E. & Wetherbe J. (2002) “Chapter 14, Building information systems”, in: Information Technology for management. New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc
- Rooimans, R., Theye, M. de, & Koop, R. (2003). Regatta: ICT-implementaties als uitdaging voor een vier-met-stuurman. The Hague: Ten Hagen en Stam Uitgevers.
